Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and method for manufacturing the same
A non-aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery technology, which is applied in the field of safety technology, can solve the problems of increasing the thermistor material layer, the danger of lithium-ion secondary batteries, and the inability to guarantee the safety of lithium-ion secondary batteries. safety effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0070] In Embodiment 1, a lithium ion secondary battery is taken as an example of a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery, and its structure is shown.
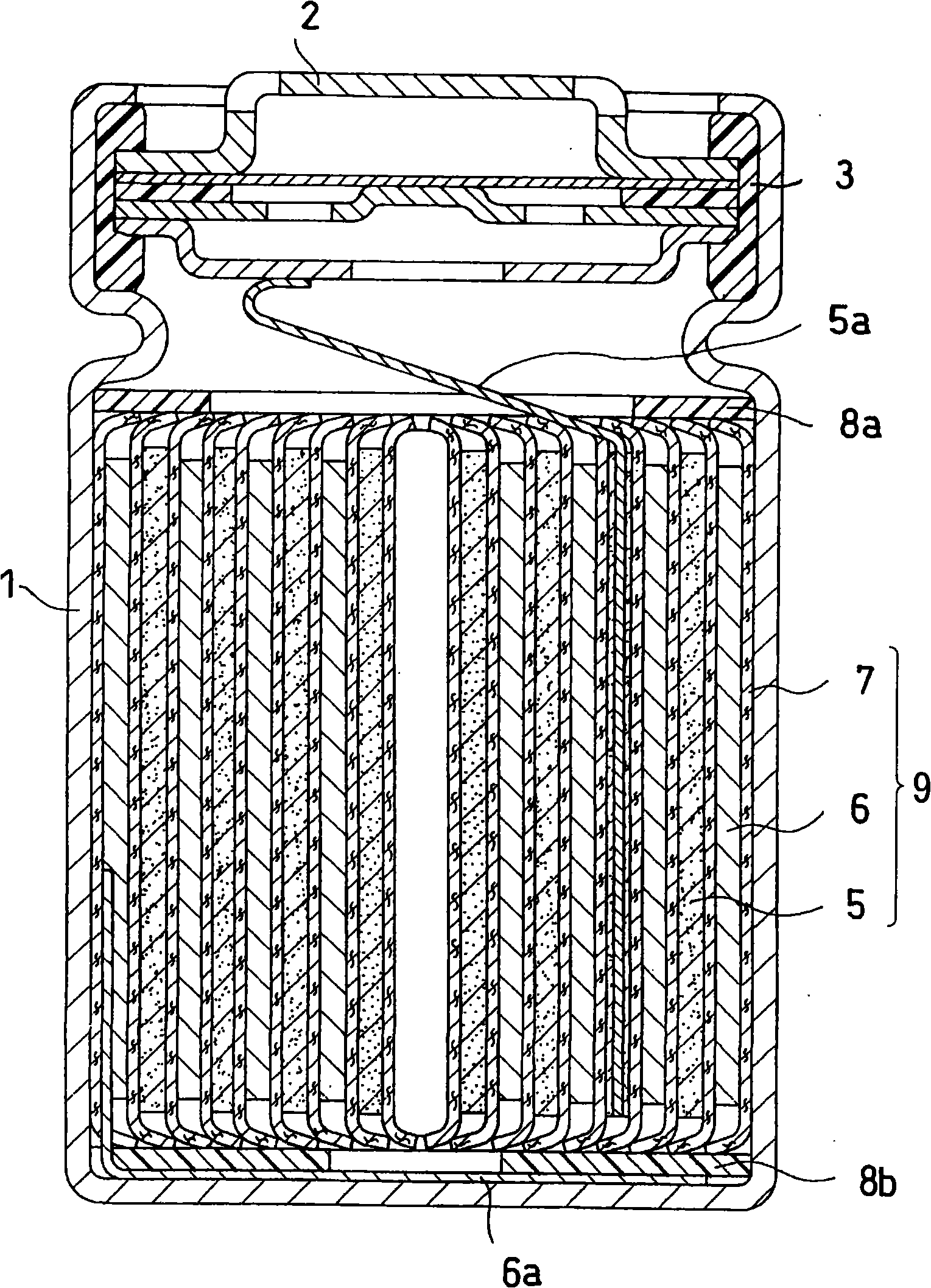
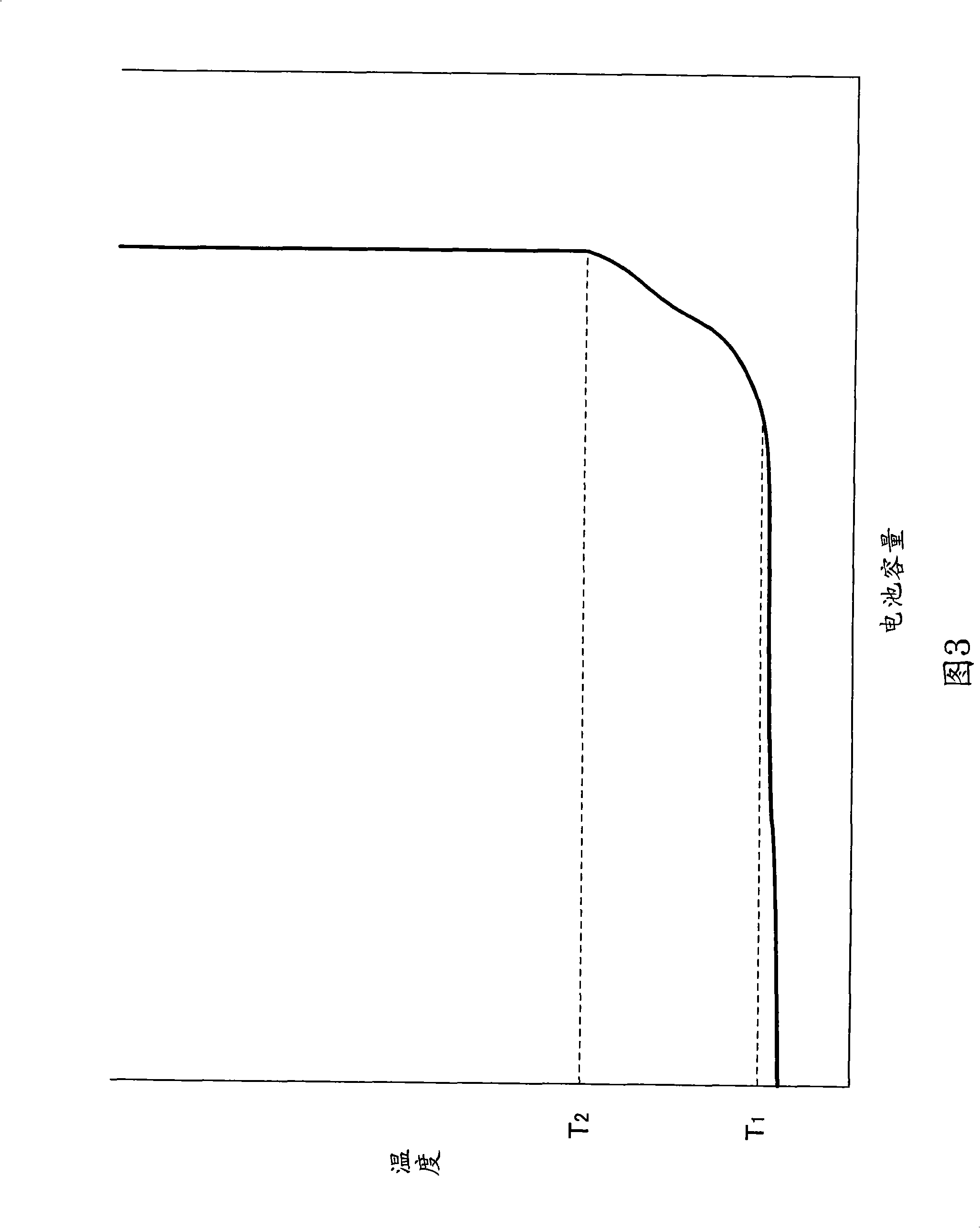
[0071] figure 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing the structure of the lithium ion secondary battery according to the present embodiment. figure 2 It is a sectional view showing the structure of the electrode group 9 included in the lithium ion secondary battery according to the present embodiment. FIG. 3 is a graph showing general temperature characteristics of a positive electrode active material.
[0072] Such as figure 1 As shown, the lithium ion secondary battery according to this embodiment includes, for example, a battery case 1 made of stainless steel, and an electrode group 9 accommodated in the battery case 1 .
[0073] An opening 1 a is formed on the upper surface of the battery case 1 . The sealing plate 2 is crimped on the opening 1a via the gasket 3, and the opening 1a is sealed by caulking the sea...
Embodiment approach 2
[0141] In Embodiment 2, the material of the porous insulating layer is different from the material of the porous insulating layer in Embodiment 1 described above. Hereinafter, the differences between the present embodiment and the above-mentioned first embodiment will be mainly described.
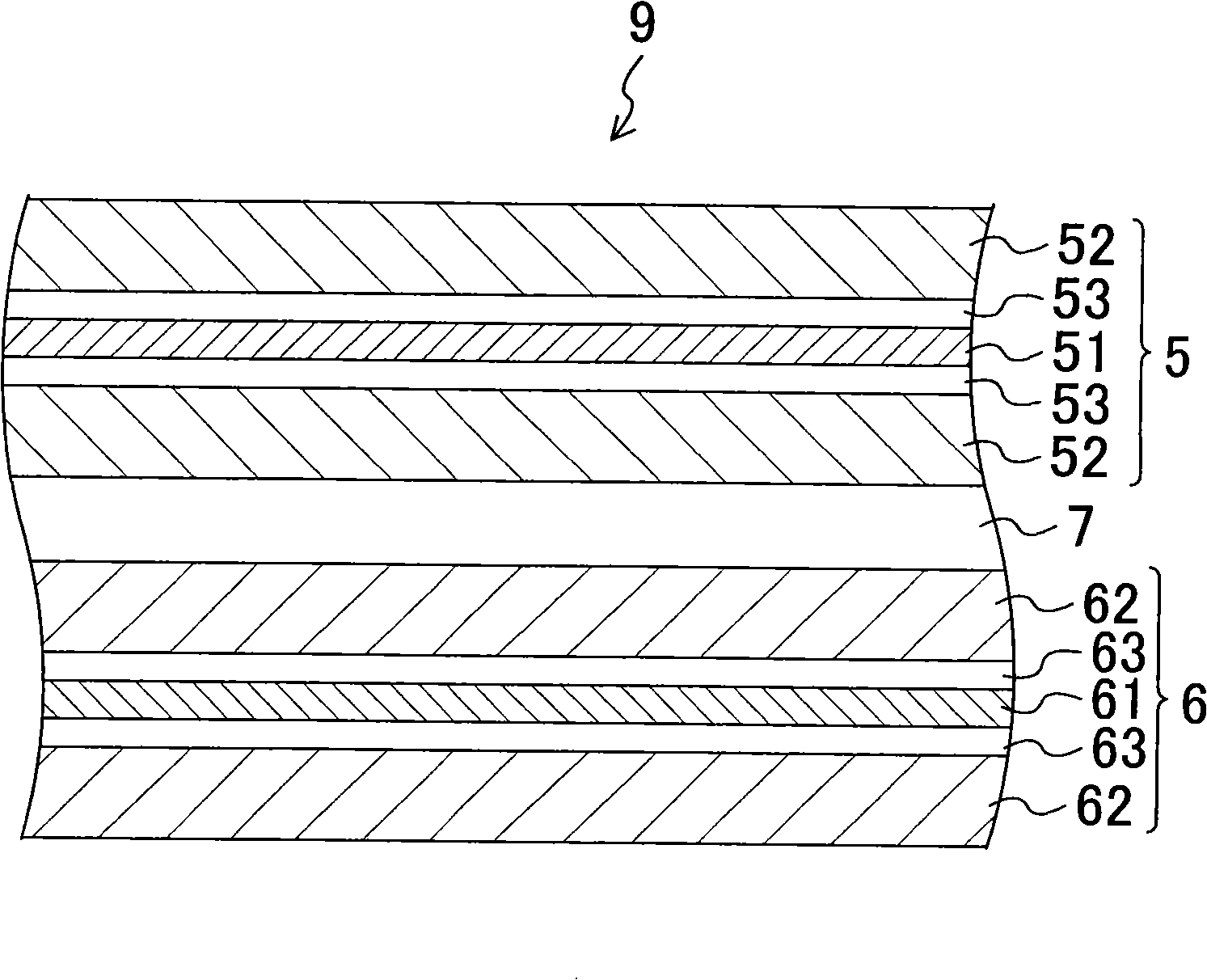
[0142] Figure 5 It is a sectional view showing the structure of the electrode group 19 in this embodiment.
[0143] As in Embodiment 1, the electrode group 19 in this embodiment includes the positive electrode 5 , the negative electrode 6 , and the porous insulating layer 17 . The positive electrode 5 includes a PTC layer 53 , the negative electrode 6 includes a PTC layer 63 , and the porous insulating layer 17 includes a material (not shown) that has no shutdown characteristics.
[0144] In the present embodiment, the material having no shutdown characteristic is a material which has no shutdown characteristic at a temperature lower than 130°C but has a shutdown characteristic at a temp...
Embodiment approach 3
[0149] In Embodiment 3, the structure of the electrode group and the fabrication method of the electrode group are different from those in Embodiment 1. Hereinafter, the differences between the present embodiment and the first embodiment will be mainly described.
[0150] Figure 6 It is a sectional view showing the structure of the electrode group 29 in this embodiment. Figure 7 It is a cross-sectional view showing a part of the electrode group in the comparative example.
[0151] The electrode group 29 in this embodiment includes a positive electrode 25 , a negative electrode 26 and a porous insulating layer 7 , the positive electrode 25 includes a PTC layer 53 , and the negative electrode 26 includes a PTC layer 63 .
[0152] As in the first embodiment, the PTC layers 53 , 63 each contain a material having a positive temperature coefficient of resistance. However, unlike Embodiment 1, the PTC layer 53 is provided in the positive electrode mixture layer 52 , and the PTC ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com