Image display apparatus and method
An image display device and image technology, which are applied in image communication, static indicators, televisions, etc., can solve the problems of dynamic image pseudo-contour color level confusion, dynamic image blurring, and damage to display quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
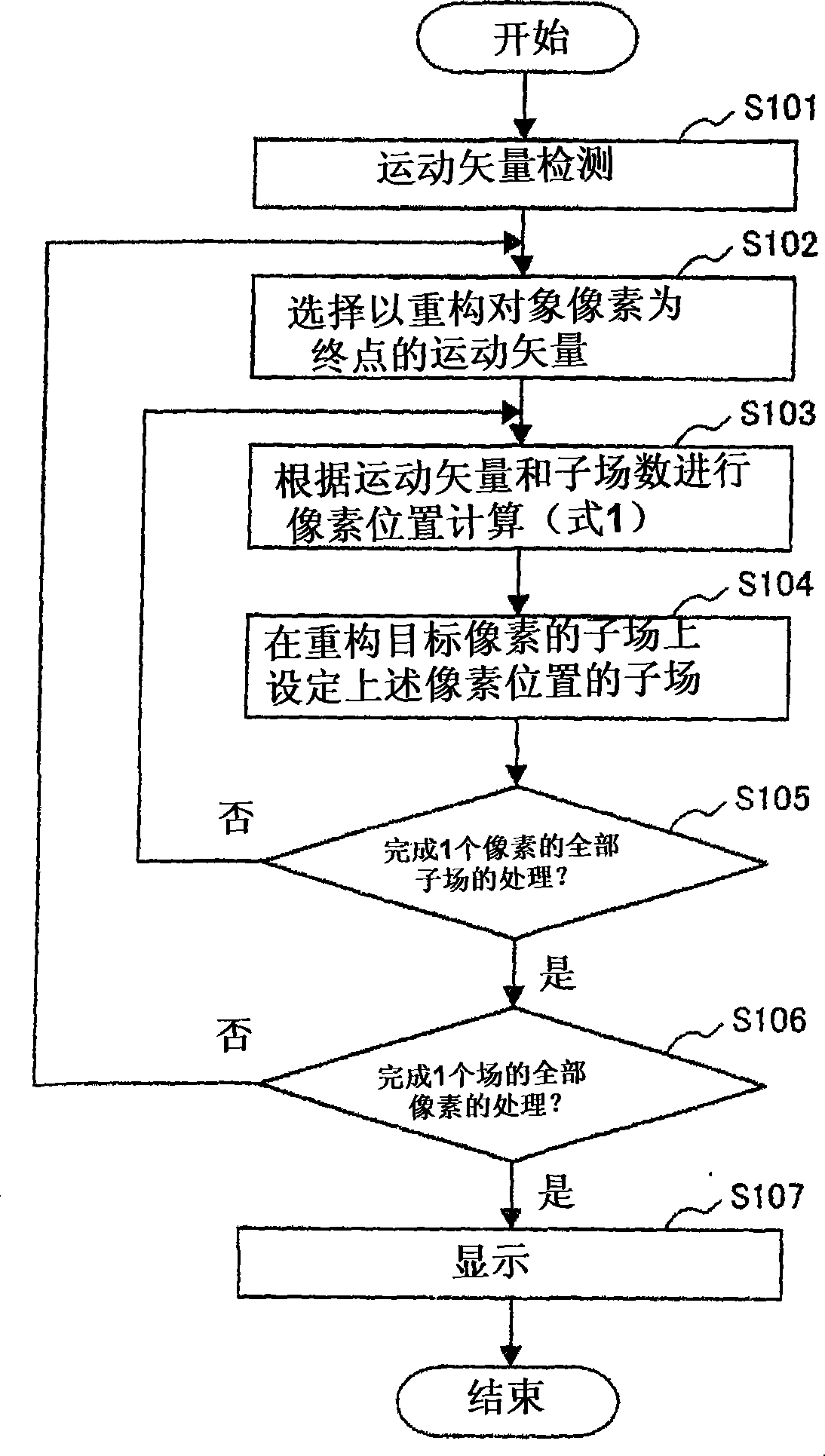
[0078] The first embodiment of the present invention is as Figure 9 The image display in the case where the intervals of light emission start times between subfields shown in (a) are equal intervals. In the figure, the horizontal axis represents the image horizontal position and the vertical axis represents time, showing display data when the number N of subfields is six. Furthermore, the interval between the light emission start times between the subfields is constant T0 regardless of the light emission periods E1 , E2 , E3 , E4 , and E5 of the subfields.
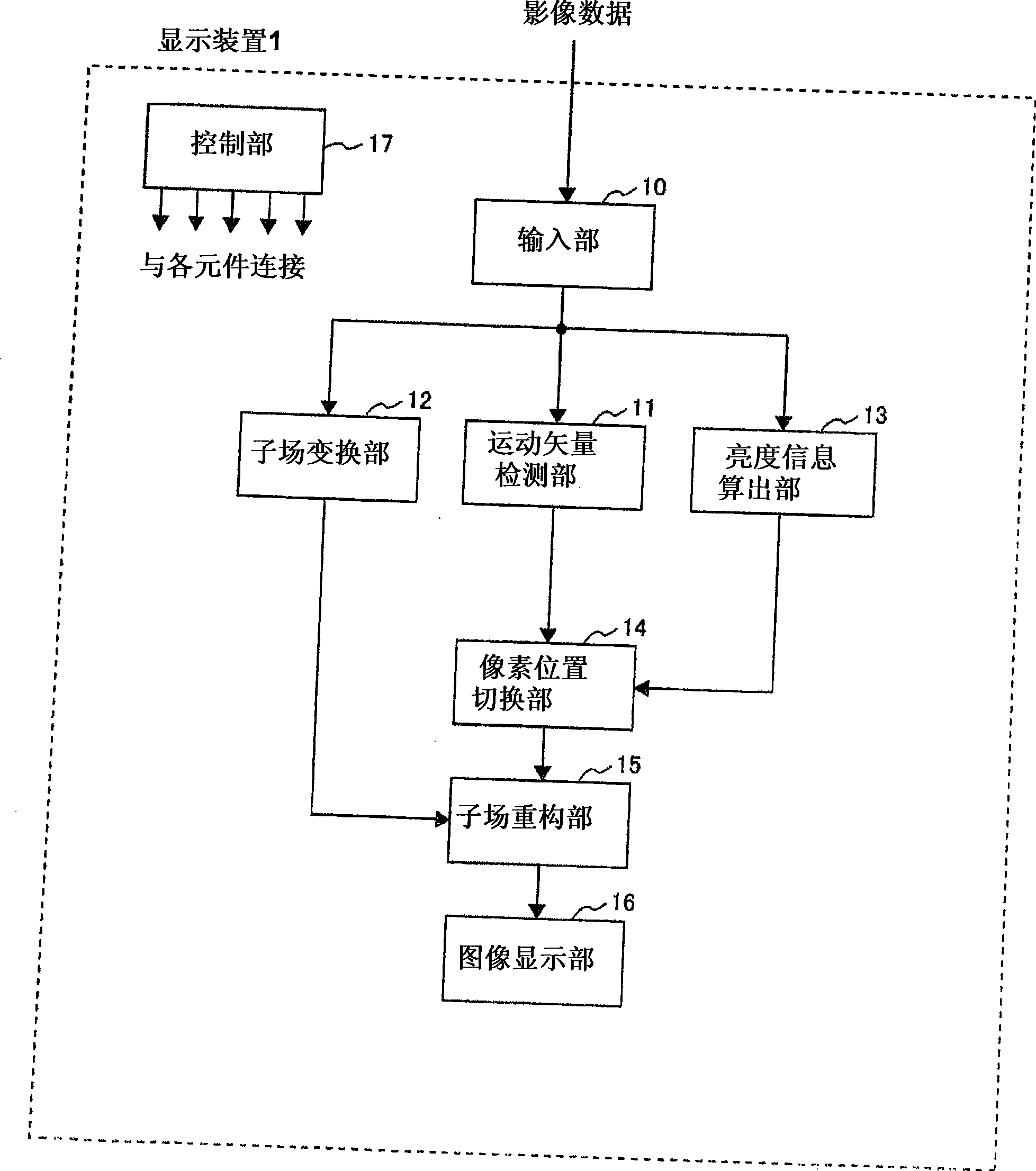
[0079] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing an example of the image display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The structure of the image display device 1 includes an input unit 10, a motion vector detection unit 11, a subfield conversion unit 12, a brightness information calculation unit 13, a pixel position switching unit 14, a subfield reconstruction unit 15, an image display unit 1...
Embodiment 2
[0143] The second embodiment of the present invention is as Figure 9 The display method shown in (b) considers the light emission period of the subfield and makes the interval of the light emission start time variable.
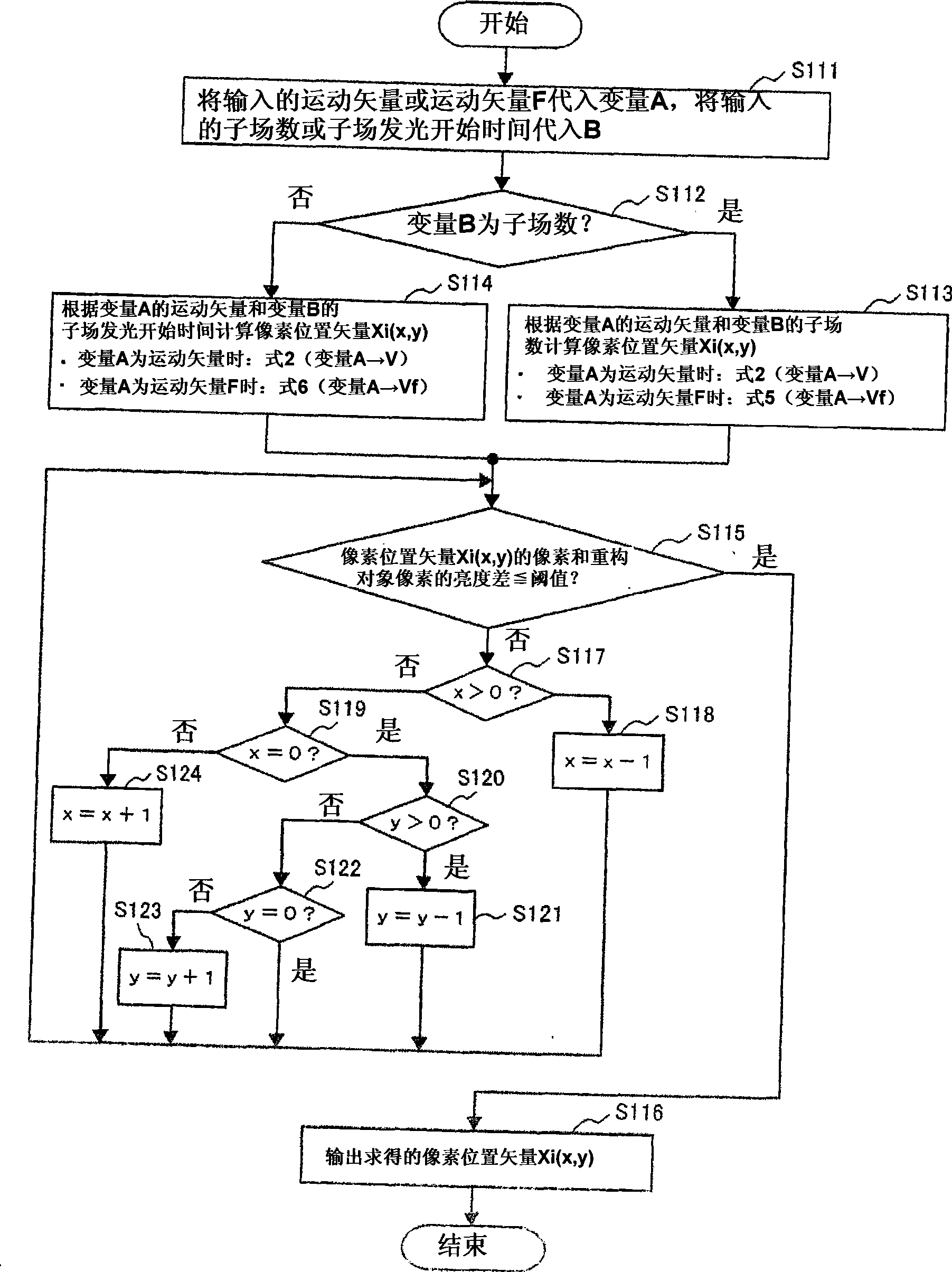
[0144] Figure 9 In (b), the time intervals T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 of the light-emitting start times between the subfields correspond to the light-emitting periods E1', E2', E3', E4', and E5' of each subfield, respectively. variable. Here, variable corresponding to the light-emitting periods E1', E2', E3', E4', E5' means, for example, that the time intervals T1, T2, T3, T4, T5 are determined by the light-emitting periods E1', E2 ', E3', E4', and E5' are determined for the value of the function of each variable. Therefore, unlike the first embodiment, the intervals T1 , T2 , T3 , T4 , and T5 between the light emission start times used in the present embodiment are not the same time length.
[0145] Here, the meaning that the interval of the light emission ...
Embodiment 3
[0193] In the third embodiment of the present invention, an intermediate field between the current field and the previous field is generated, and the sub-field data is reconstructed from the motion vector F whose end point is the pixel of the intermediate field and the starting point is the pixel of the previous field. In addition, as in the above-mentioned first embodiment, the intervals of the light emission start times between the subfields are fixed at equal intervals.
[0194] Figure 14 It is a diagram for explaining the intermediate field and the motion vector F used in this embodiment. The motion vector F is a vector indicating from which pixel of the previous field A the pixels of the middle field B located between the current field C and the previous field A moved. which is, Figure 14 where is a motion vector that ends at pixel b in the middle field and starts at pixel a in the previous field A.
[0195] Here, for the method of generating the intermediate field f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com