Declaration and consumption of a causality model for probable cause analysis
A technique of causality, modeling, applied in the field of computer systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009] overview
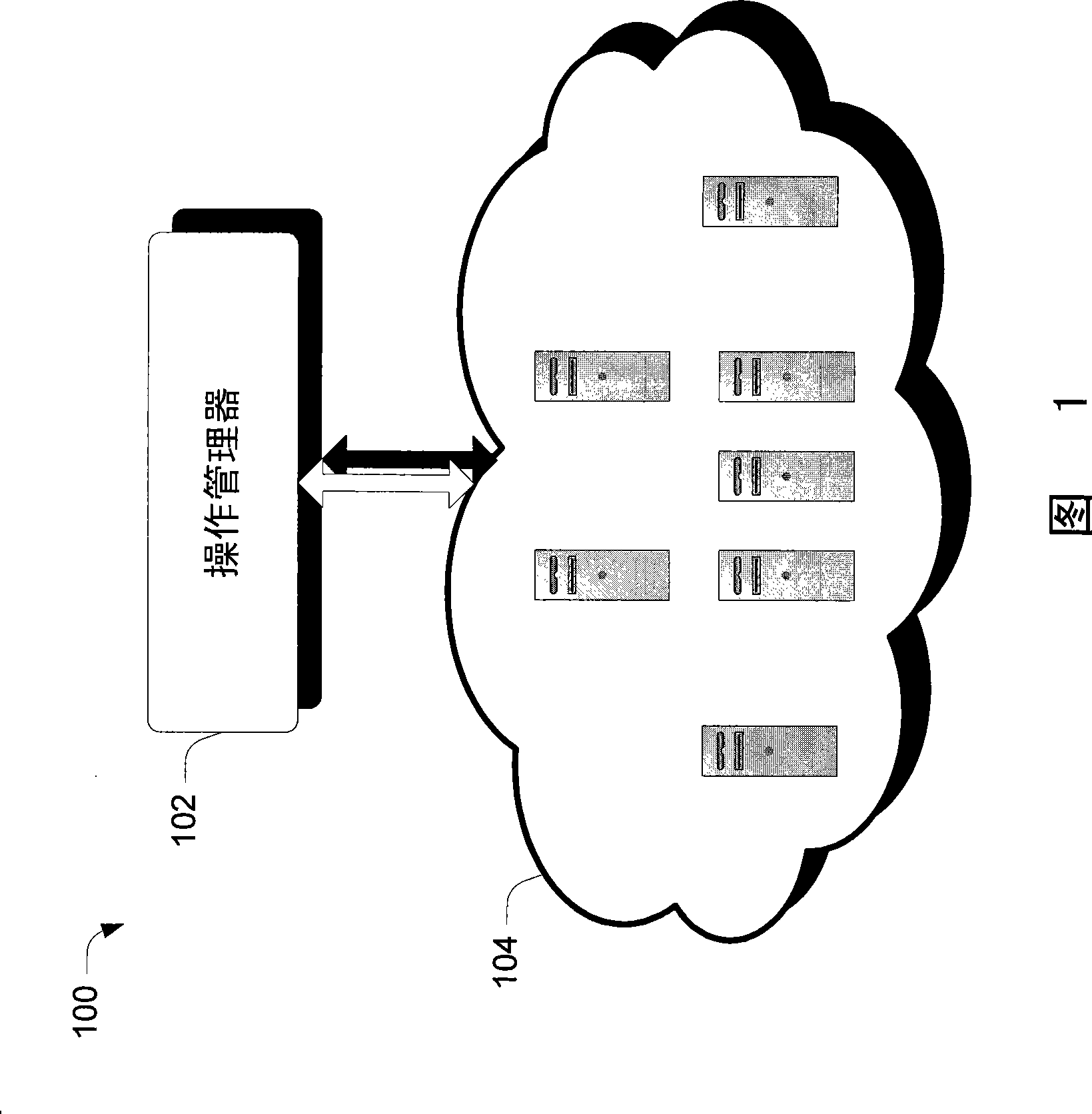
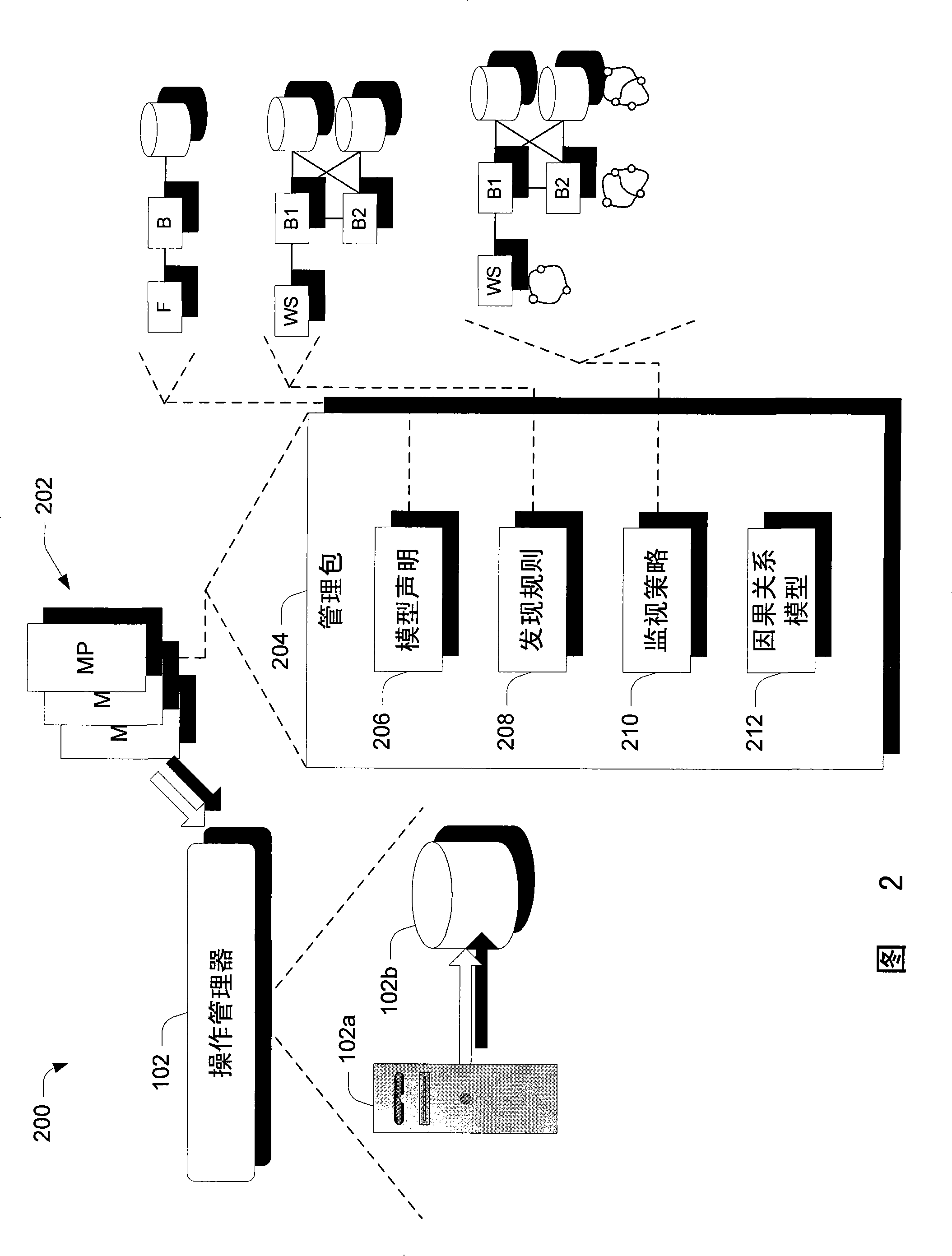
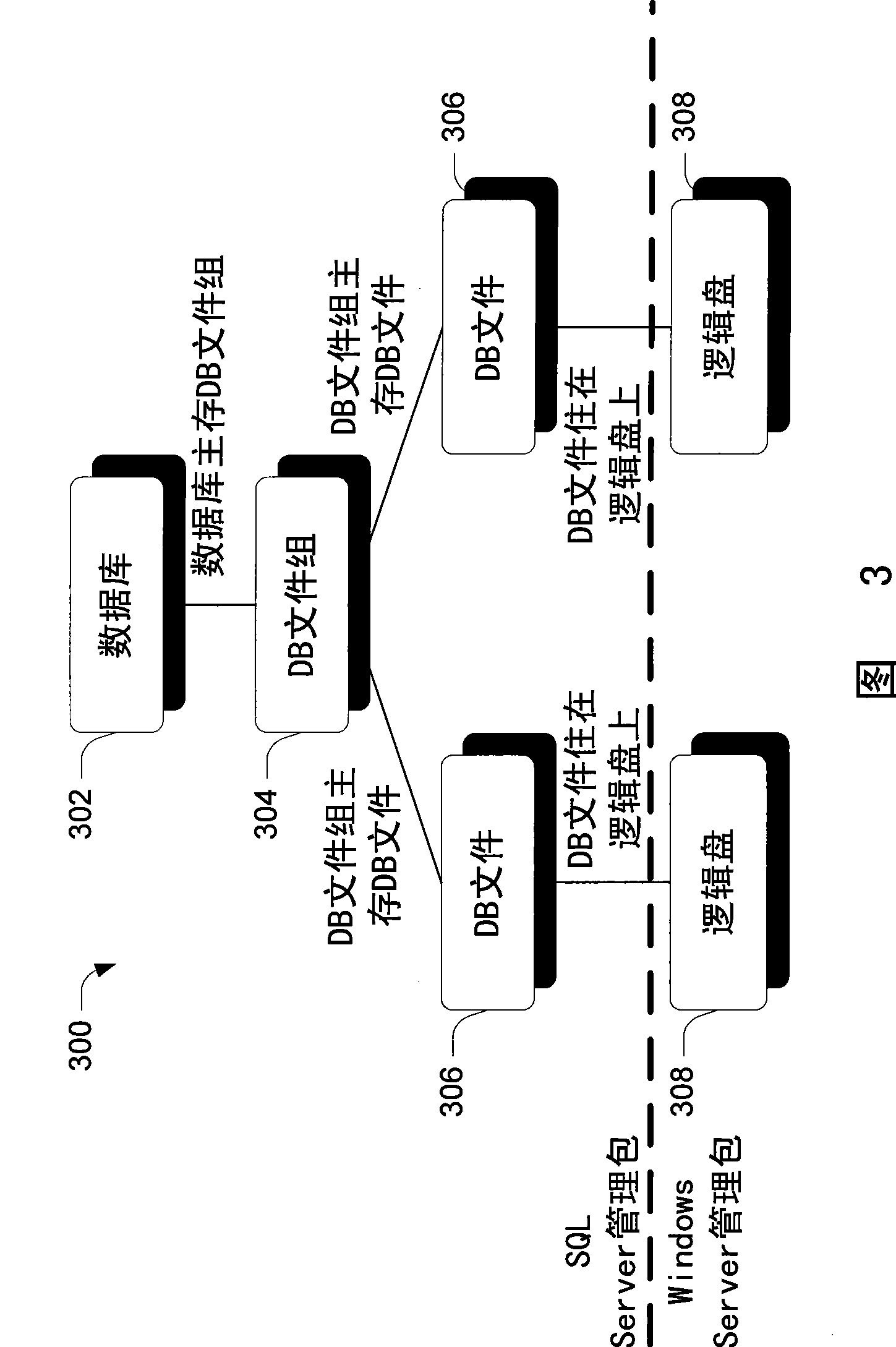
[0010] Embodiments are employed in the context of a model-based management system. In at least some embodiments, a causality model is used to express the causality of system entities without necessarily requiring knowledge of the overall composition of the particular system of which the system entities are a part. The causality model can allow causality to be expressed in terms of the relationships a particular system entity has with other system entities. These other system entities may be entities that share a direct relationship, or more generally, an indirect relationship, with the entity to which the causal relationship is expressed.
[0011] Furthermore, in at least some embodiments, the causality representation is in some sense separate from the root cause analysis algorithms that may be used to analyze the causality data. Thus, those who know and construct these causality expressions for a particular system do not have to know the analysis algorithm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com