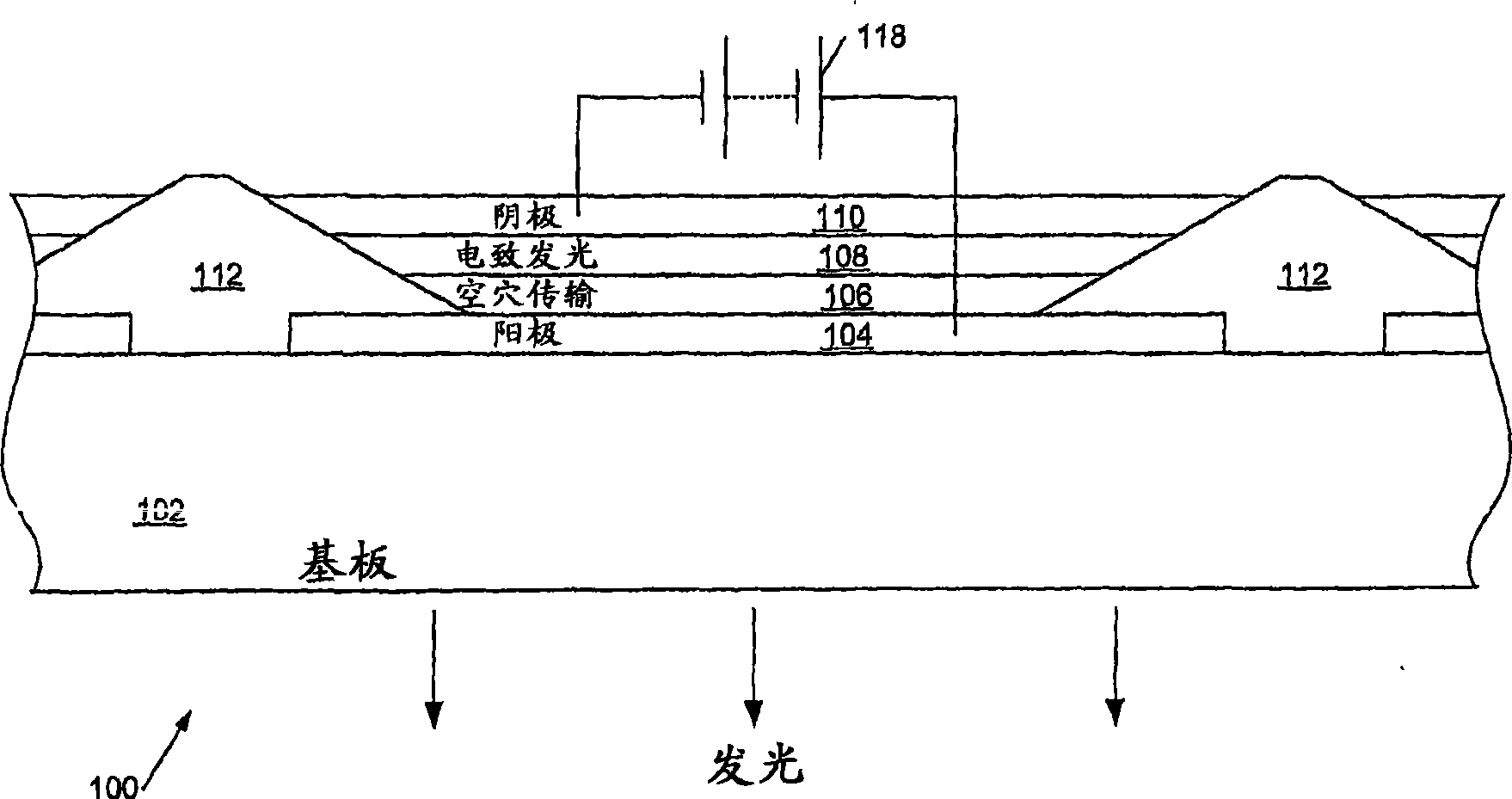
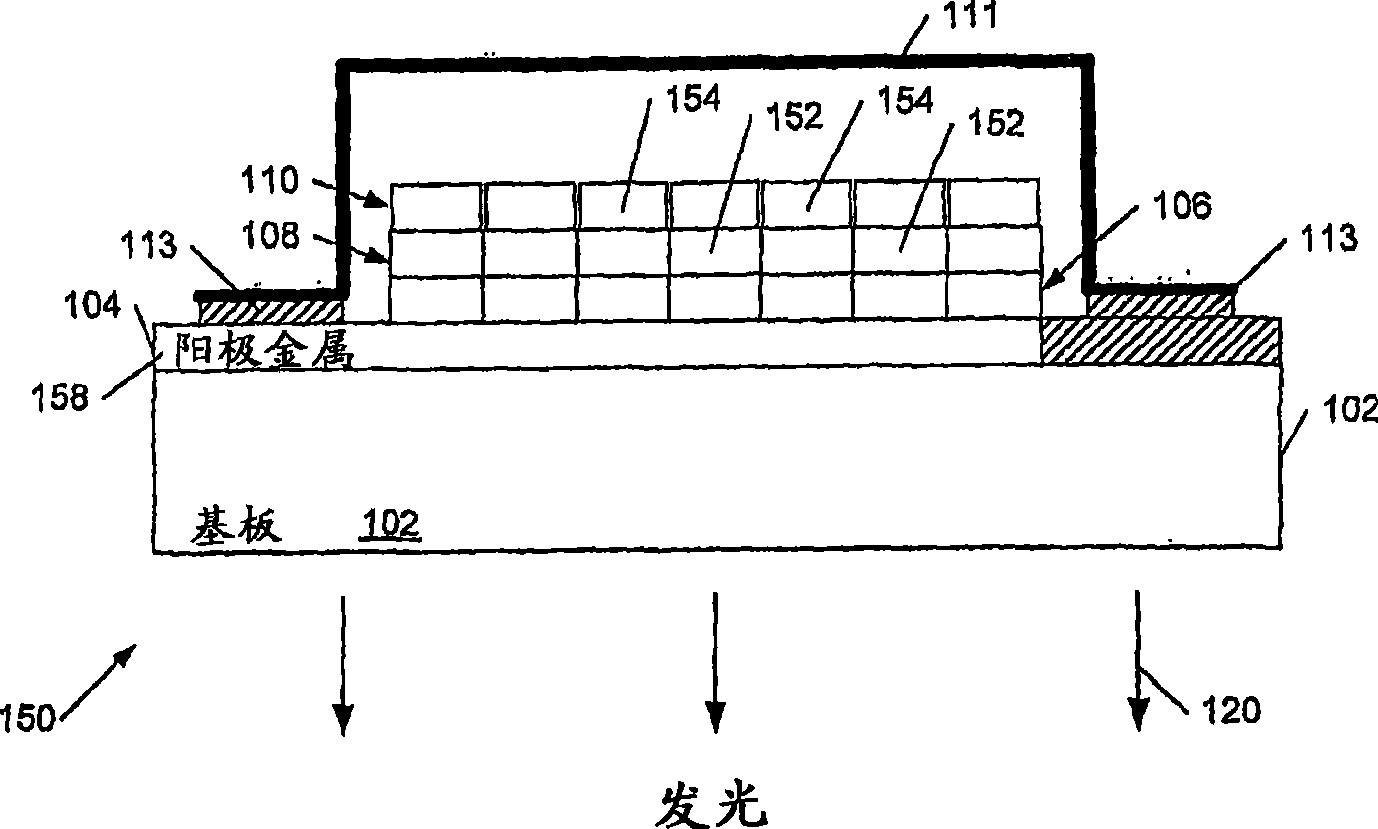
Display drive system
一种显示器、显示器件的技术,应用在补偿烧屏领域,能够解决显示器总体老化、驱动电压增大、变化等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] refer to Figure 4a and Figure 4b , which respectively show the curves of OLED efficiency (unit: candela / ampere) versus driving time (unit: hour) and OLED driving voltage (unit: volt) versus driving time (unit: hour). These two curves have been fitted by the same extended exponential function:
[0048] exp - ( t τ ) n or 1 - exp - ( t τ ) n
[0049] It can be seen that there is a strong correlation between the drop in OLED device efficiency and the increased drive voltage required for the same drive / light output. The driving voltage V can be expressed as follows:
[0050] V = V 0 = 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com