Faraday polarization apparatus
A technology of Faraday rotator and magneto-optical rotation, which is applied in instruments, optics, nonlinear optics, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult consistency of combined magnetic field, high absorption coefficient, and difficult consistency control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
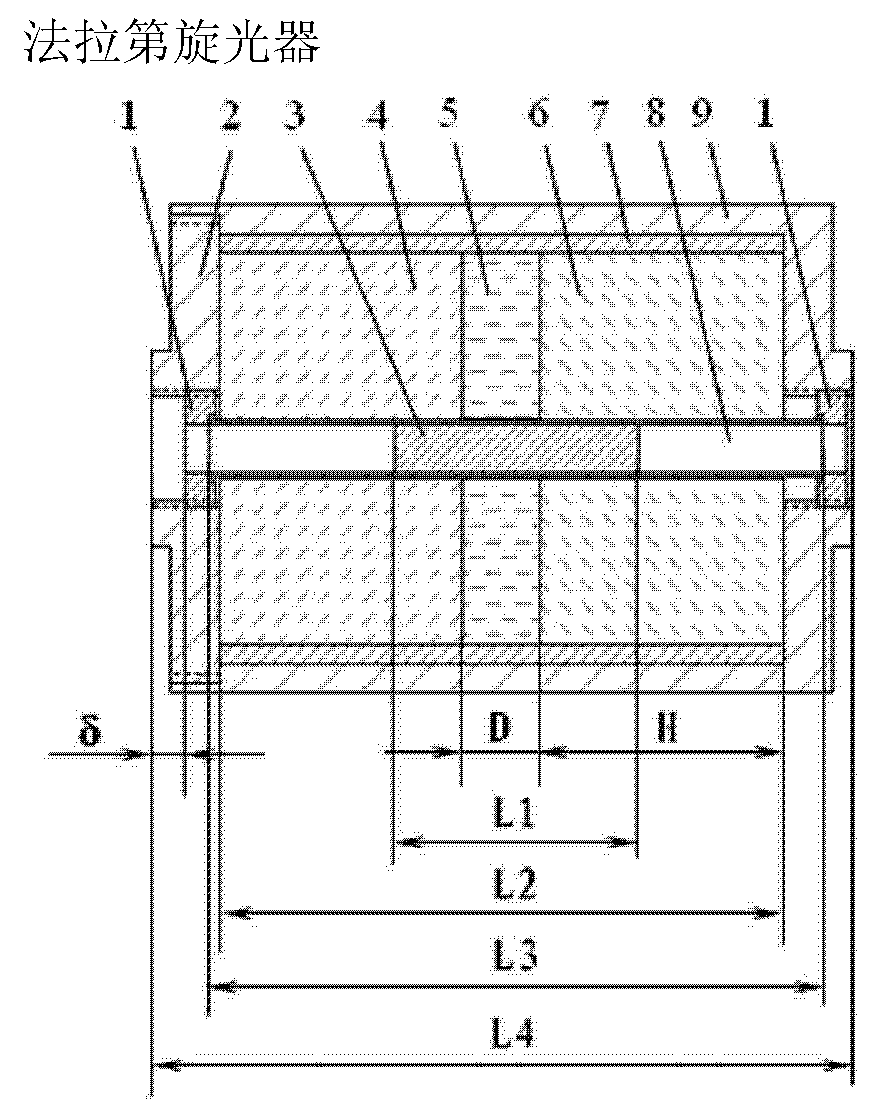
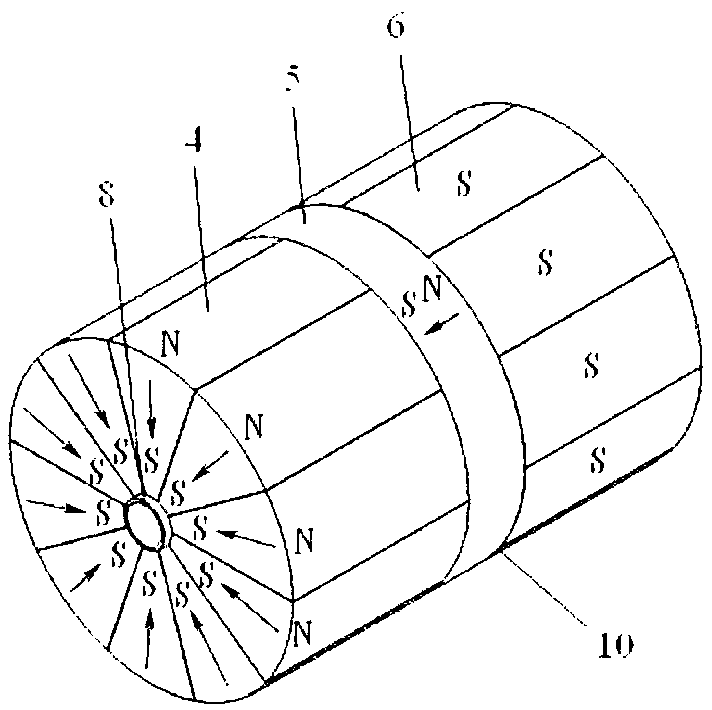
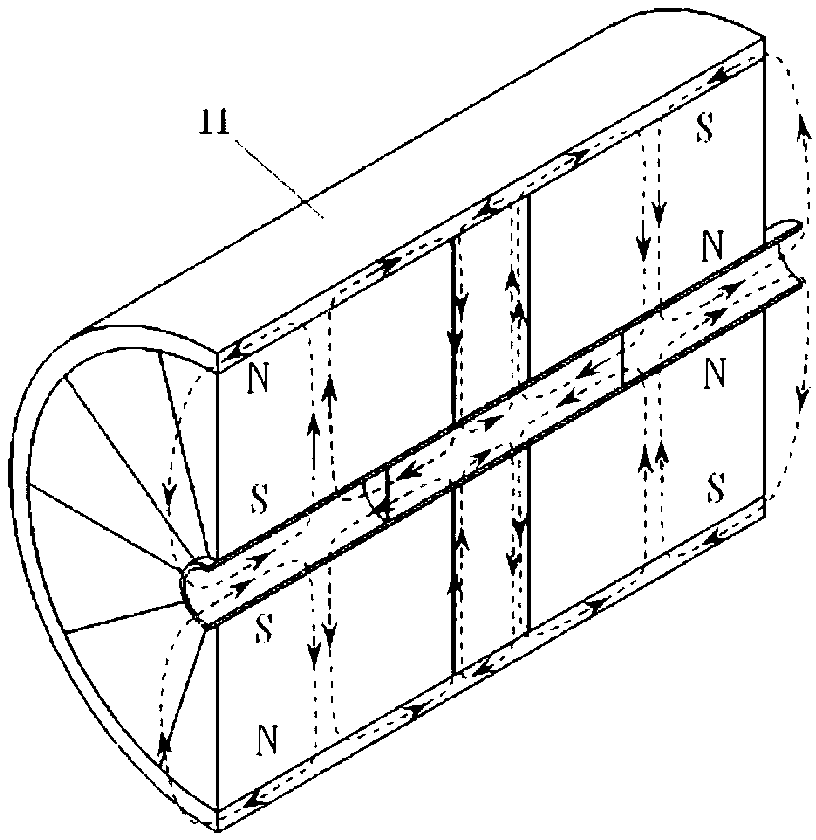
[0019] see Figures 1 to 3 , the Faraday rotator provided by the present invention consists of an adjusting plate 1, an end cap 2, a magnetic rotator 3, a first fan-shaped magnetic block 4, an intermediate magnetic block 5, a second fan-shaped magnetic block 6, a magnetic shielding sleeve 7, and a magnetic rotator The sleeve 8 and the shell 9 are composed of a composite magnet 11 composed of the first fan-shaped magnetic block 4, the second fan-shaped magnetic block 6, the middle magnetic block 5 and the magnetic shielding sleeve 7, and the adjusting piece 1, the end cover 2, and the magnetic rotation rod The sleeve 8 and the shell 9 complete the adjustment and fixation of the relative position between the compound magnet 11 and the magnetic rotation rod 3 . After the composite magnet 11 is placed in the shell 9, it is compressed with the end cover 2. There is a screw hole at the position coaxial with the inner hole of the composite magnet 11 on the shell 9 and the end cover 2...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The magnetic rotation rod sleeve 8 can be divided into 2 sections or 3 sections according to needs, so as to facilitate the fixing of the magnetic rotation rod 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com