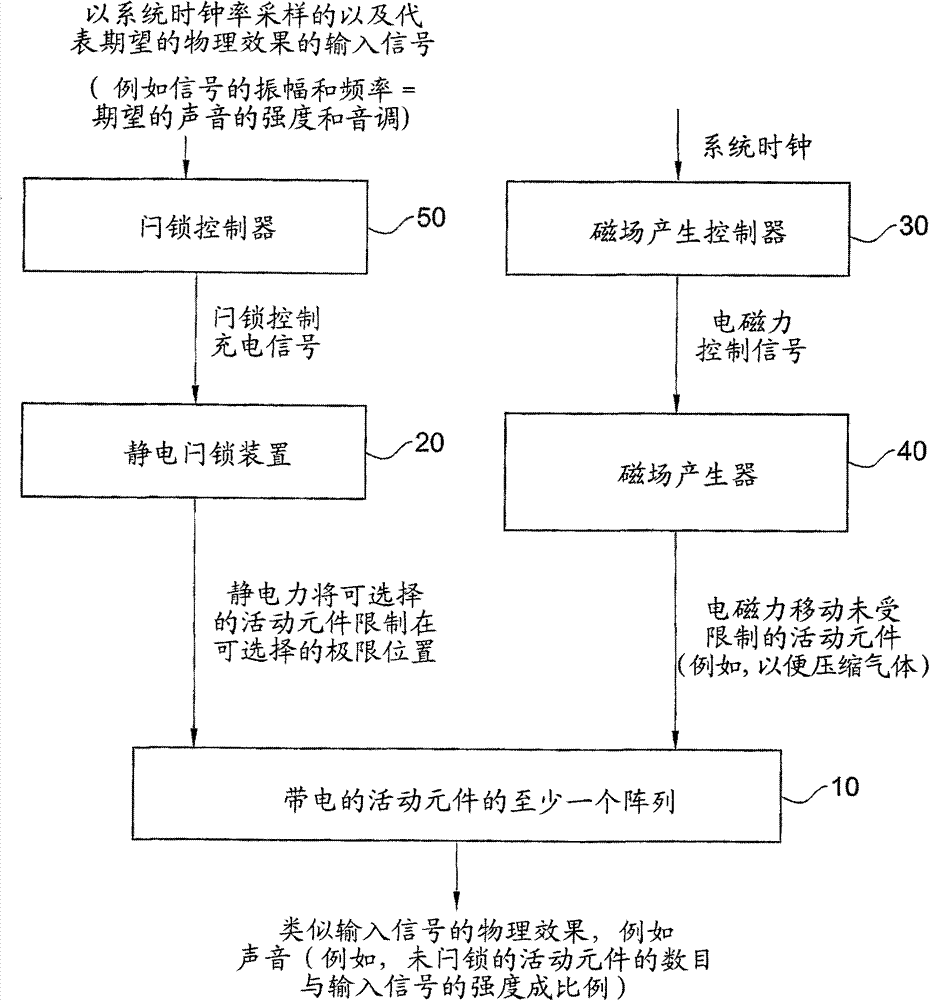
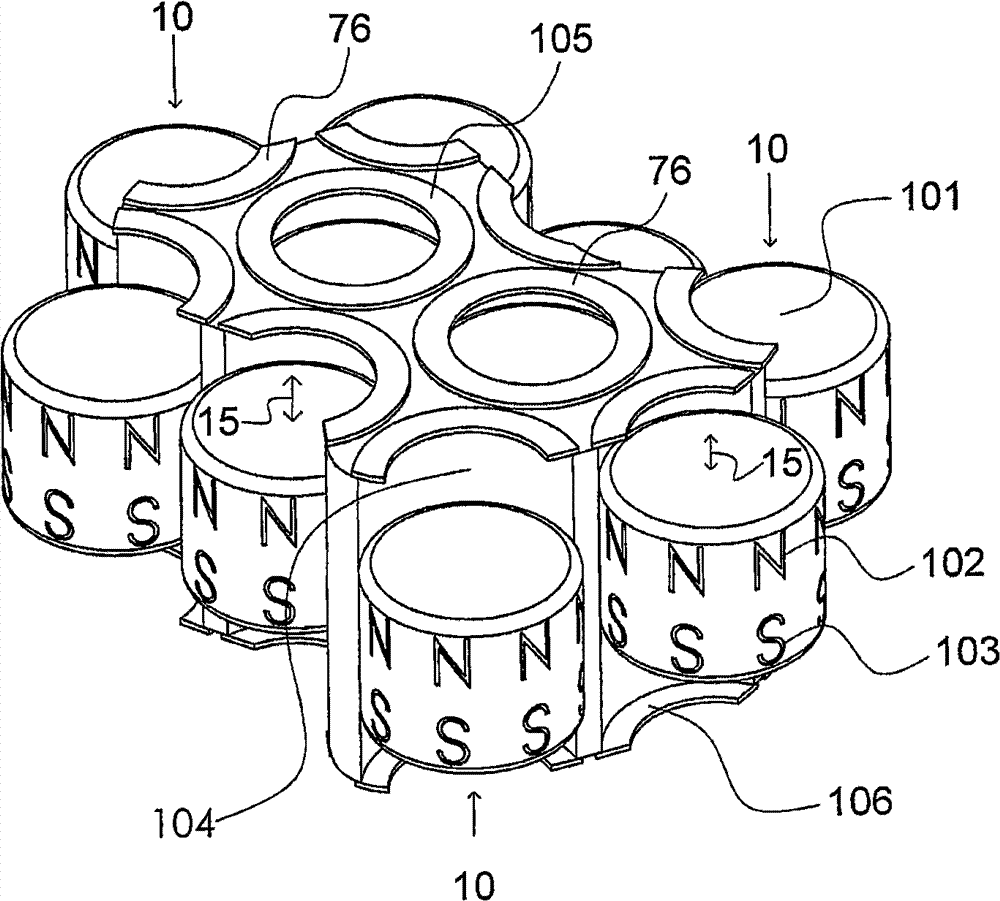
Volume and tone control in direct digital speakers
A digital loudspeaker and volume control technology, applied in frequency/direction characteristic devices, frequency response correction, etc., can solve problems such as peak-to-peak amplitude reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0352] Example 1: It would be desirable to make a cell phone speaker that is very small, low cost, and loud enough to hear a ringing sound in the next room, but of mediocre sound quality. The desired small size and low cost require loudspeakers to have a relatively small area, e.g. a maximum of 300mm 2 . This requires a large displacement if a relatively high target maximum loudness is desired, eg 90 dB SPL. Acceptable levels of distortion (10%) and dynamic range (60 dB) in a cell phone speaker require a minimum array size of 1000 elements (using M=10 (60 / 20) calculate). Thus, a suitable loudspeaker may include 1023 moving elements divided into 10 binary groups, each element occupying approximately 0.3mm 2 area. The cell size will therefore be about 550 μm x 550 μm.
[0353] For practical reasons, the largest moving element that fits into this space may have a diameter of 450 μm. A reasonable displacement of such a moving element may be around 150 μm PTP (peak-to-peak), ...
example 2
[0354] Example 2: It is desirable to make high fidelity headphones that have very high sound quality (the highest possible) and very low noise, yet are small enough to be comfortable to wear, and finally, are as cost-effective as possible benefit.
[0355] For high sound quality, wide dynamic range (at least 96dB), wide frequency range (20Hz-20KHz) and very low distortion (2 unit, so that 65535 components fit into a 2621mm 2 , for example in an area of 52mm×52mm. The sampling rate is generally at least twice the highest frequency you want the speaker to produce, or 40KHz. The closest standard sampling rate is 44.1KHz.
example 3
[0356] Example 3: It may be desirable to make public address loudspeakers, for example for dance halls, which are very loud, have a wide frequency range, extending to very low frequencies, and have low distortion. Therefore, PA (Public Address) loudspeakers typically have many large moving elements. A 600 μm movable element can be used, which is capable of a displacement of 200 μm PTP. Such a component occupies 750μm x 750μm or 0.5625mm 2 unit. Due to low frequency requirements a minimum of 262143 active elements divided into 18 binary groups can be used. The dimensions of the loudspeaker may be approximately 40cm x 40cm. This loudspeaker typically reaches a maximum loudness level of 120dB SPL and extends down to 15Hz.
[0357] Reference is now generally made to FIGS. 20-23, which depict preferred systems for use with direct digital loudspeakers, such as here at Figure 1A-19 any of the loudspeakers shown in , or such as a conventional direct digital loudspeaker as may be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com