Delay management for distributed communications networks
A technology of communication network and network, applied in the field of delay management of distributed communication network, which can solve the problems of increased complexity and cost, increased complexity and/or cost of distributed antenna system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
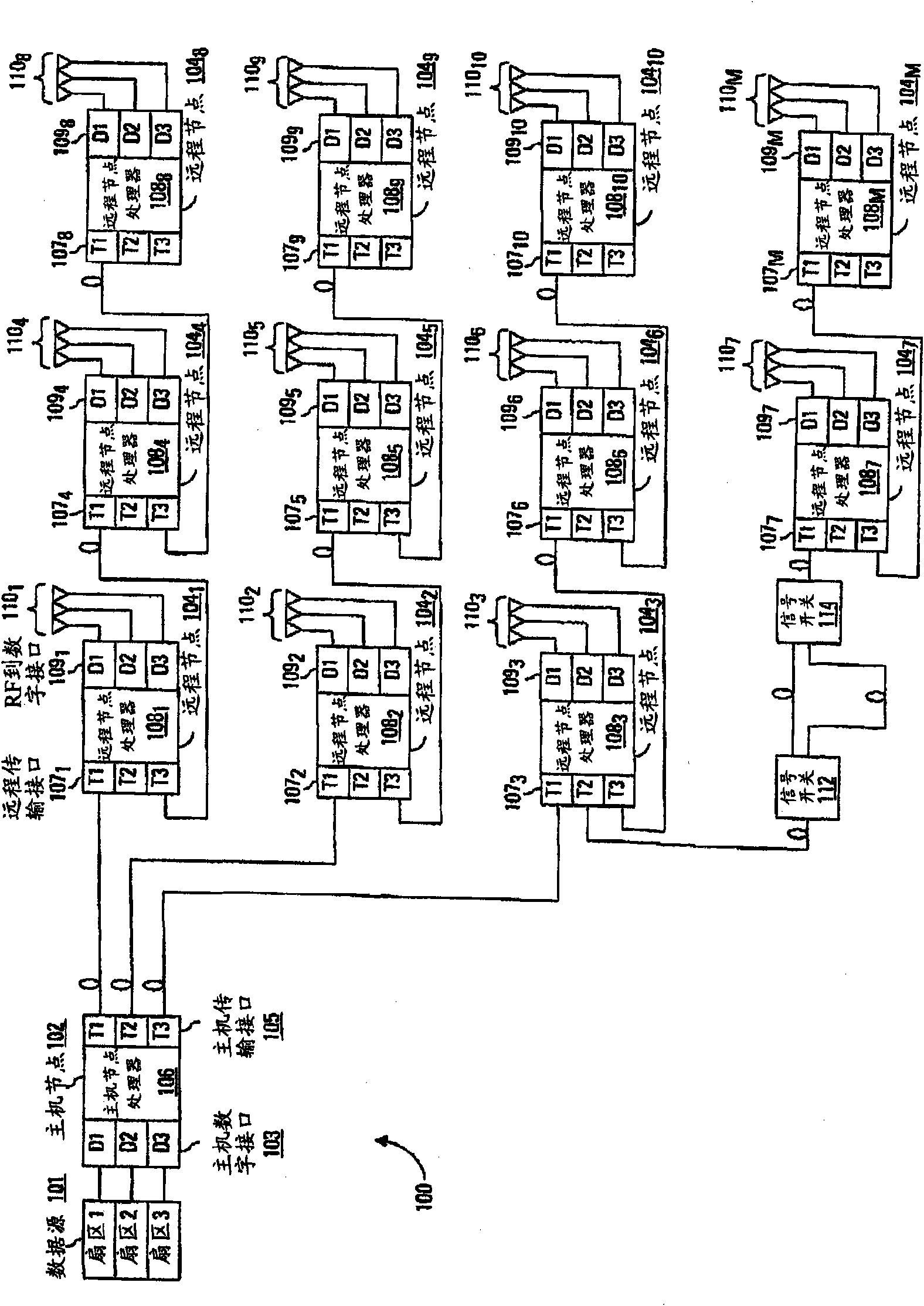
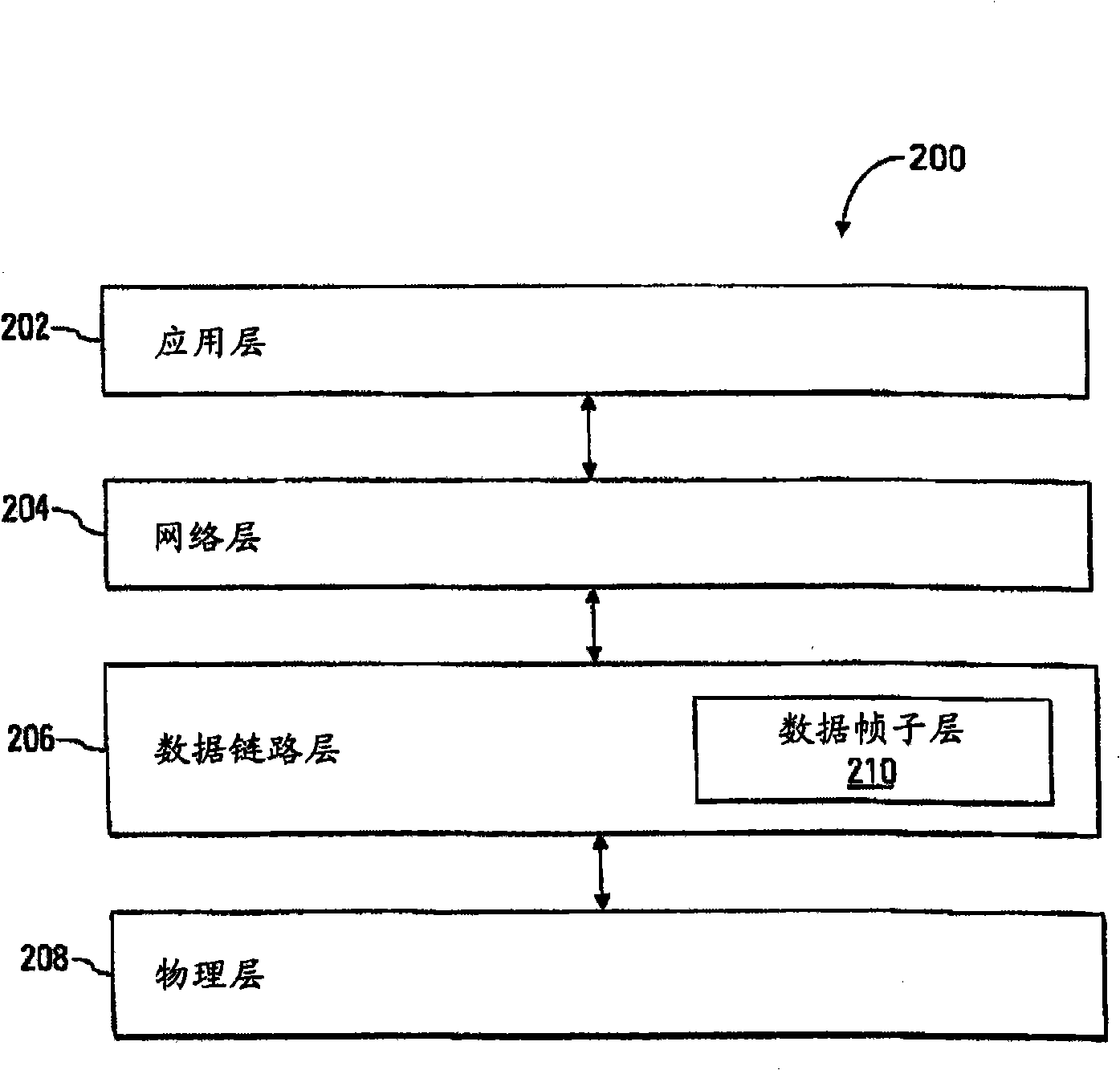
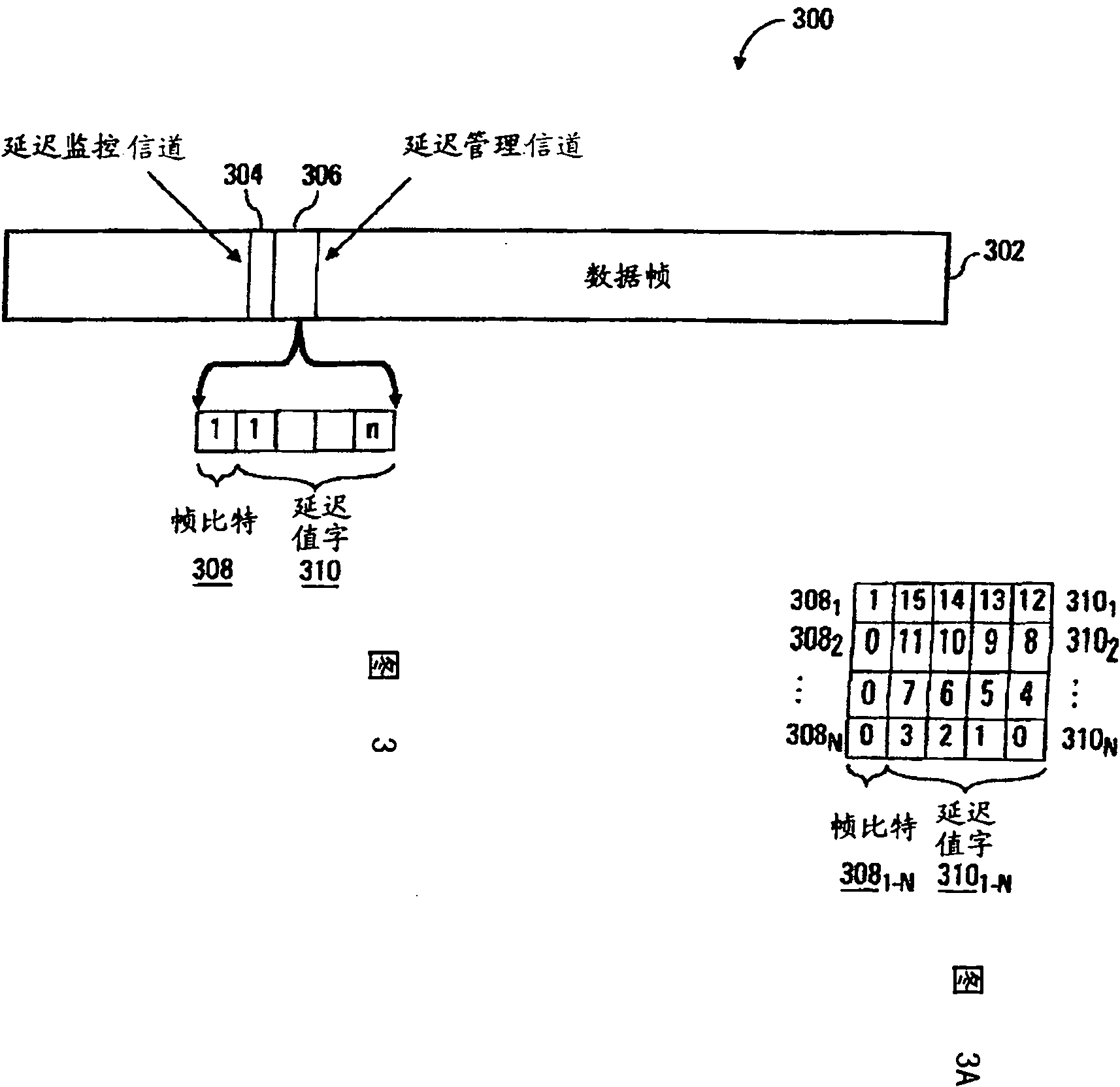
[0010] The detailed description that follows relates to delay management of a distributed communication network, such as a distributed antenna system. The delay management discussed here enables network administrators to establish desired delays at multiple nodes in a point-to-multipoint communication network with a suitably high degree of repeatability and control. The desired delay may be per node collectively or per individual node. Advantageously, the communication networks discussed herein use a distributed approach to determining signal path delays from the host to each node in the system. This is done at each node by discovering transmission delays (eg, propagation times) on the links between the node and its neighboring (eg, consecutive) nodes in the network. For example, each node learns the distance between itself and any downstream neighbors. Based on these transmission delays between nodes, the nodes in the system cooperate to determine the signal path delay of e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com