Spread spectrum communication method based on multi-level quasi-orthogonal spread spectrum code sequence
A technology of spread spectrum code sequence and spread spectrum communication, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, multiplexing code generation, transmission system, etc., and can solve the cycle limitation of spread spectrum communication transmission rate, large correlation coefficient of pseudo-random code, system multiple access interference, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
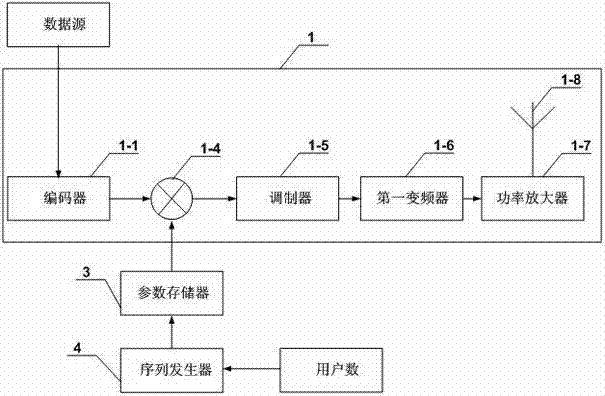
[0034] Specific implementation mode one, combine figure 1 , figure 2 and Figure 27 Description of this embodiment, a spread spectrum communication method based on a multi-level quasi-orthogonal spread spectrum code sequence, which is completed based on a synchronous spread spectrum communication system. The synchronous spread spectrum communication system includes a transmitting end system 1, a receiving end System 2, parameter memory 3 and sequence generator 4;
[0035] The signal output end of the sequence generator 4 is connected to the pseudo-random code sequence input end of the parameter memory 3, and the two pseudo-random code sequence output ends of the parameter memory 3 are respectively connected to the pseudo-random code sequences of the sending end system 1 and the receiving end system 2 input terminal;
[0036] The process that described sequence generator 4 generates one group of pseudo-random code sequence is:
[0037] Step 1, the orthogonal code group i...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific implementation mode two, combine figure 2 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the transmitting end system 1 is composed of an encoder 1-1, a first multiplier 1-4, a modulator 1-5, and a first frequency converter 1 -6, power amplifier 1-7 and radio frequency antenna 1-8 are formed, and a data input end of the first multiplier 1-4 is the pseudo-random code sequence input end of sending end system 1, and described first multiplier 1-4 The other data input end of the first multiplier is connected with the data output end of the encoder 1-1, the data output end of the first multiplier 1-4 is connected with the data input end of the modulator 1-5, and the signal output end of the modulator 1-5 It is connected with the signal input end of the first frequency converter 1-6, and the signal output end of the first frequency converter 1-6 is connected with the signal input end of the power amplifier 1-7,...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific implementation mode three, combine Figure 27 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the receiving end system 2 is composed of a receiving antenna 2-1, a low noise amplifier 2-2, a second frequency converter 2-3, a filter 2- 4, the demodulator 2-5, the second multiplier 2-6 and the decision device 2-9 are formed, the signal output end of the receiving antenna 2-1 is connected with the signal input end of the low noise amplifier 2-2, the low noise amplifier 2 The signal output terminal of -2 is connected with the signal input terminal of the second frequency converter 2-3, the signal output terminal of the second frequency converter 2-3 is connected with the signal input terminal of the filter 2-4, and the signal of the filter 2-4 The output end is connected with the signal input end of the demodulator 2-5, and the data output end of the demodulator 2-5 is connected with a data input end of the sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com