Patents
Literature
337 results about "Spread spectrum communication systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spread Spectrum refers to a system originally developed for military applications, to provide secure communications by spreading the signal over a large frequency band.
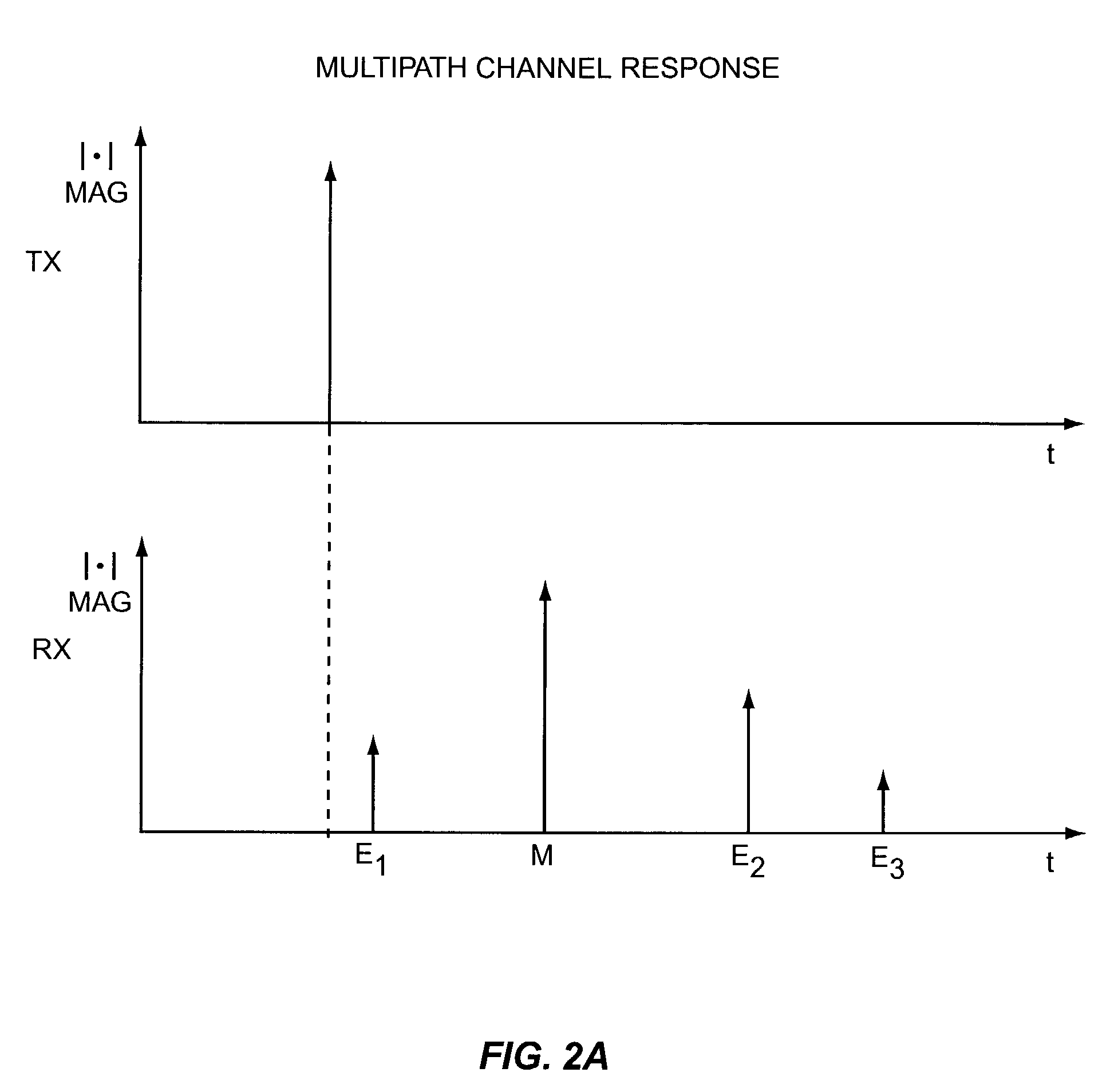
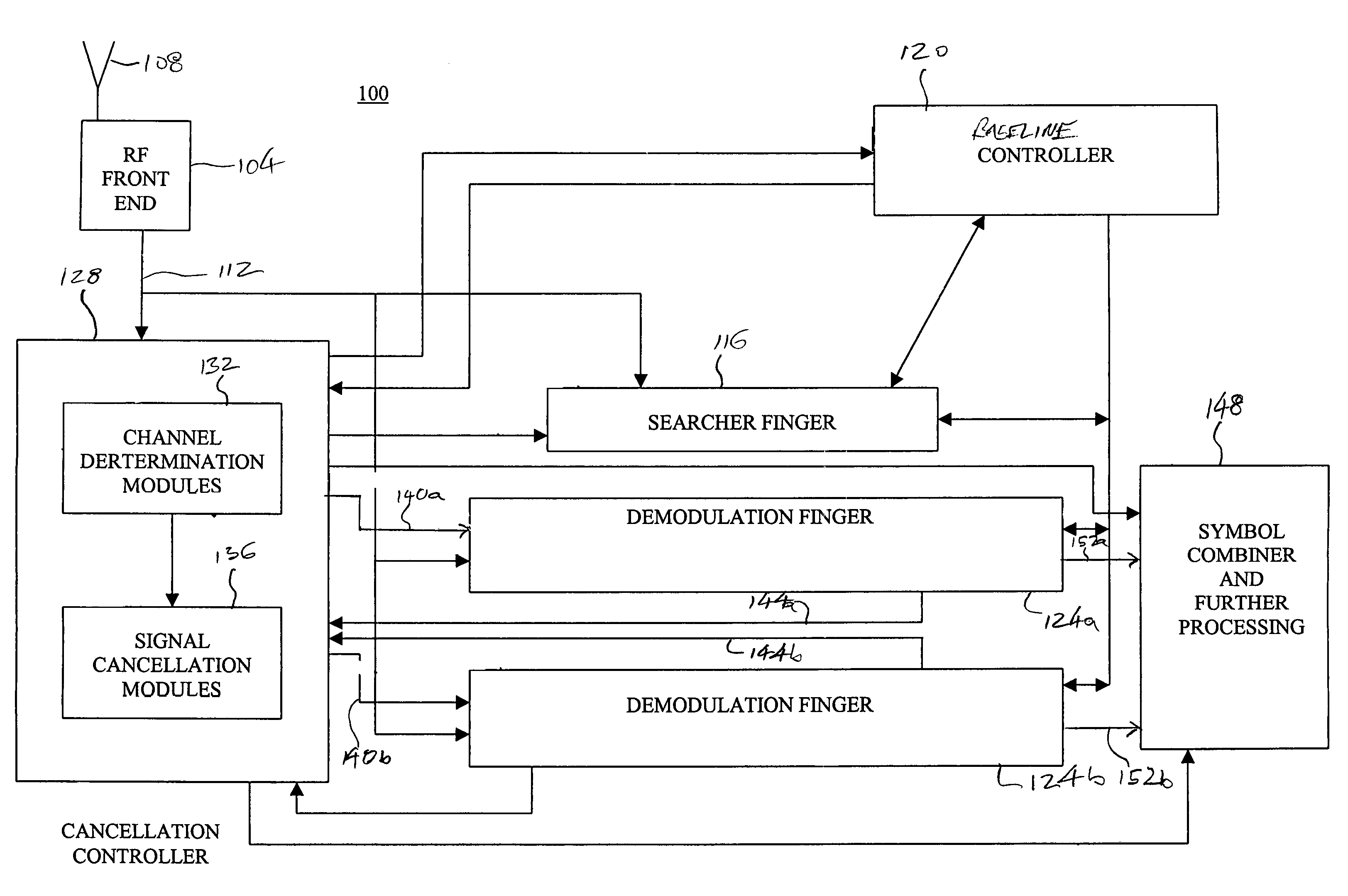
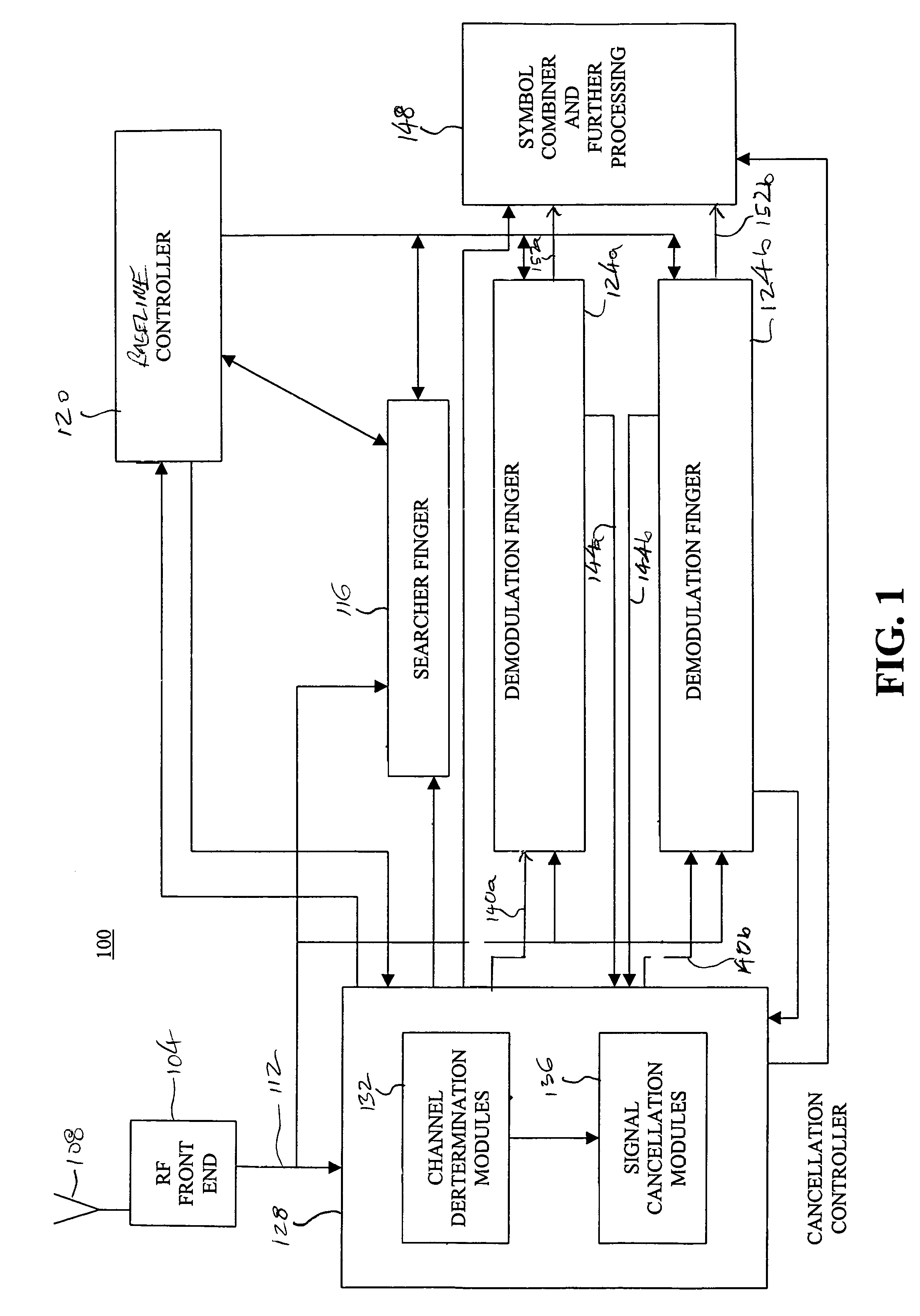
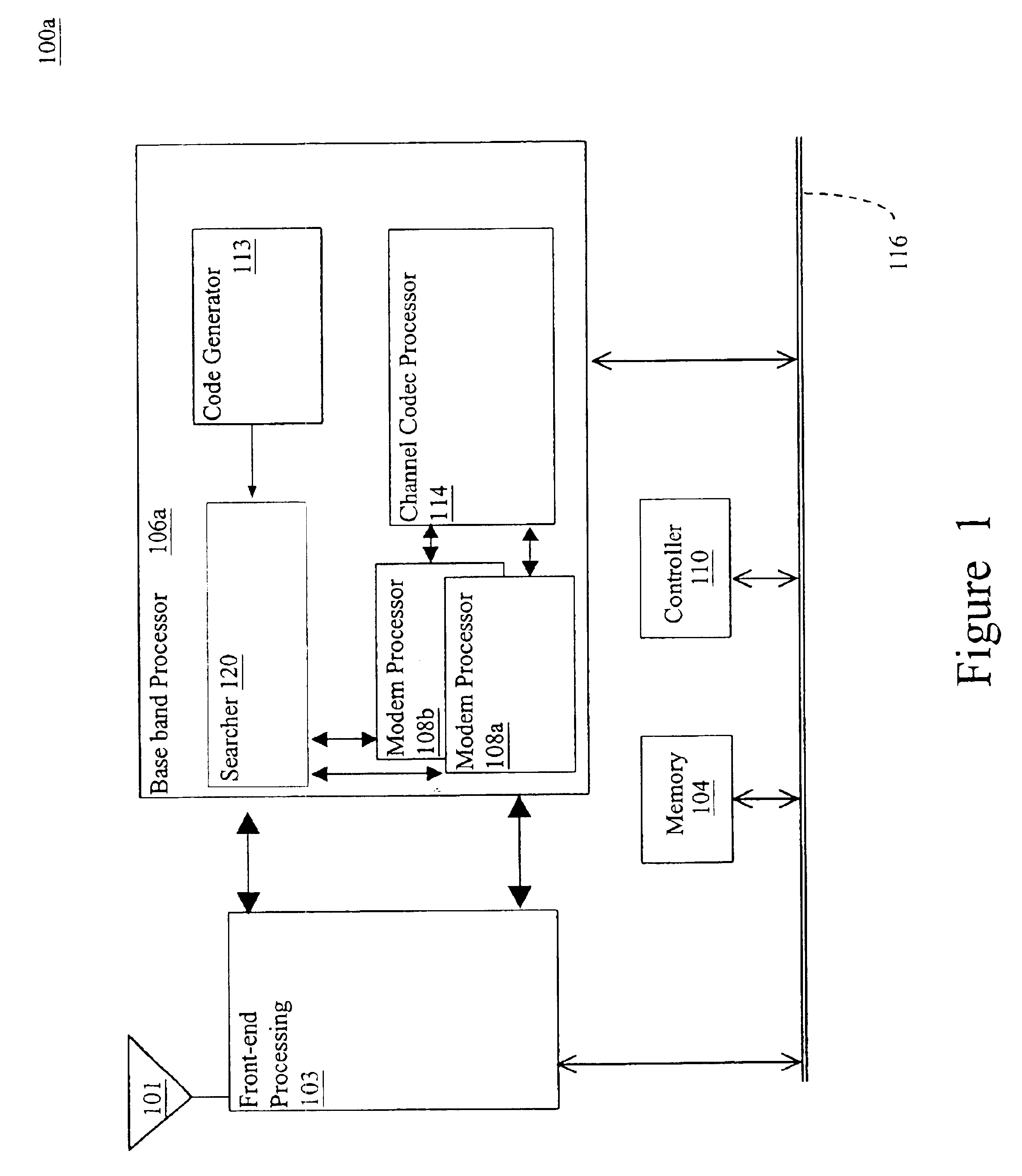
Method and apparatus for multipath signal compensation in spread-spectrum communications systems
ActiveUS7054396B2Effective multipath signal compensationChange effective lengthMultiple-port networksError preventionCommunications systemImage resolution
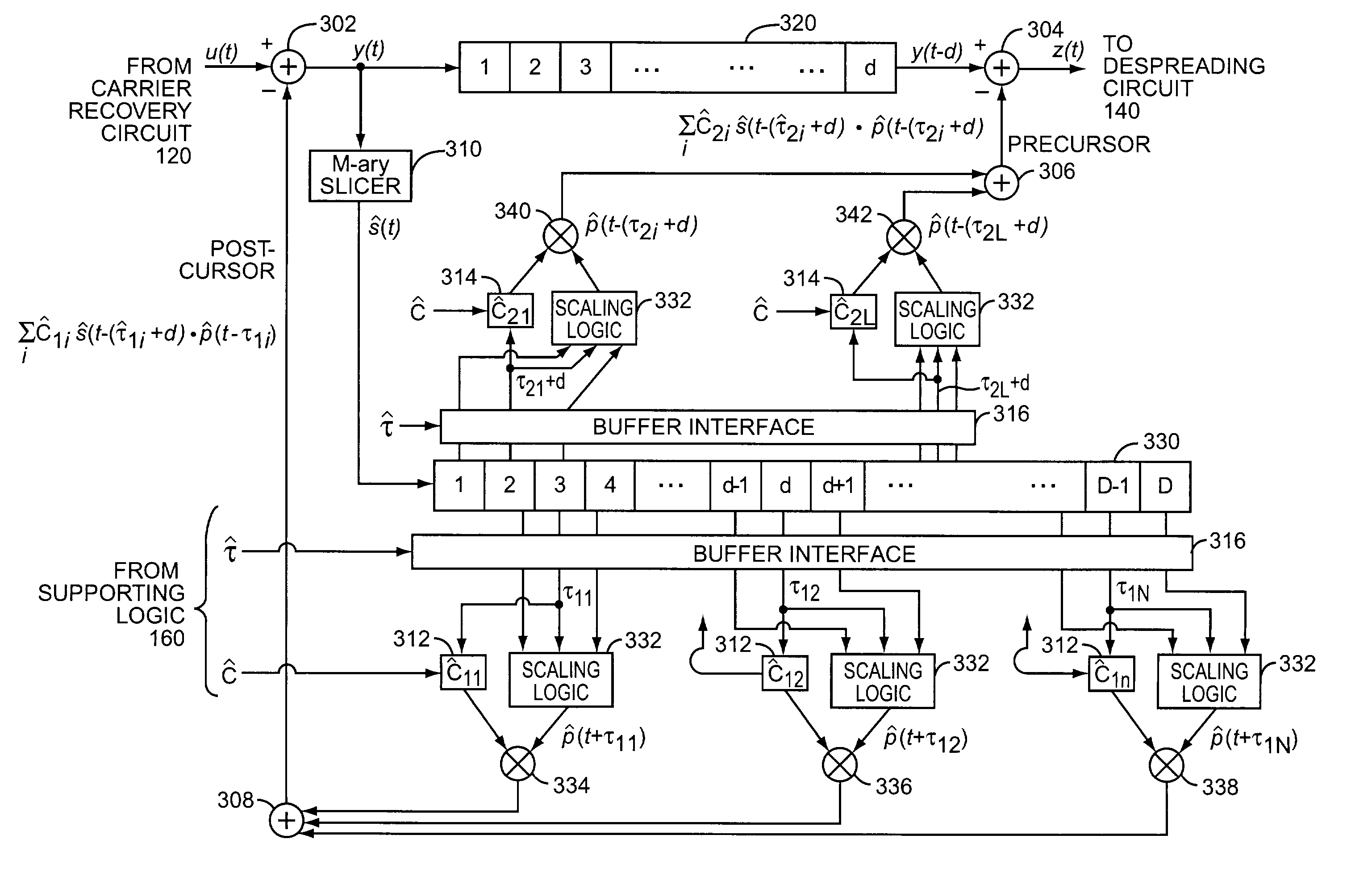
The equalizer of the present invention operates on input multipath signal samples, preferably at chip or sub-chip resolution, to remove or substantially cancel the effects of one or more secondary signals from the main path signal. Using predetermined path information for one or more of the secondary path signals, including magnitude, phase, and time offset relative to the main path signal, the equalizer compensates input multipath signal samples by subtracting estimated secondary signal values from the input samples. For each input sample, the equalizer forms a sliced sample, where the sliced sample represents a nominal phase value defined by the modulation scheme used in the original chip or symbol transmission that is closest in value to the actual phase of the input sample. These sliced samples are held in a running buffer and used, in combination with the predetermined path information and scaling logic, to form the estimated secondary signal values for compensating the input samples.
Owner:QORVO US INC
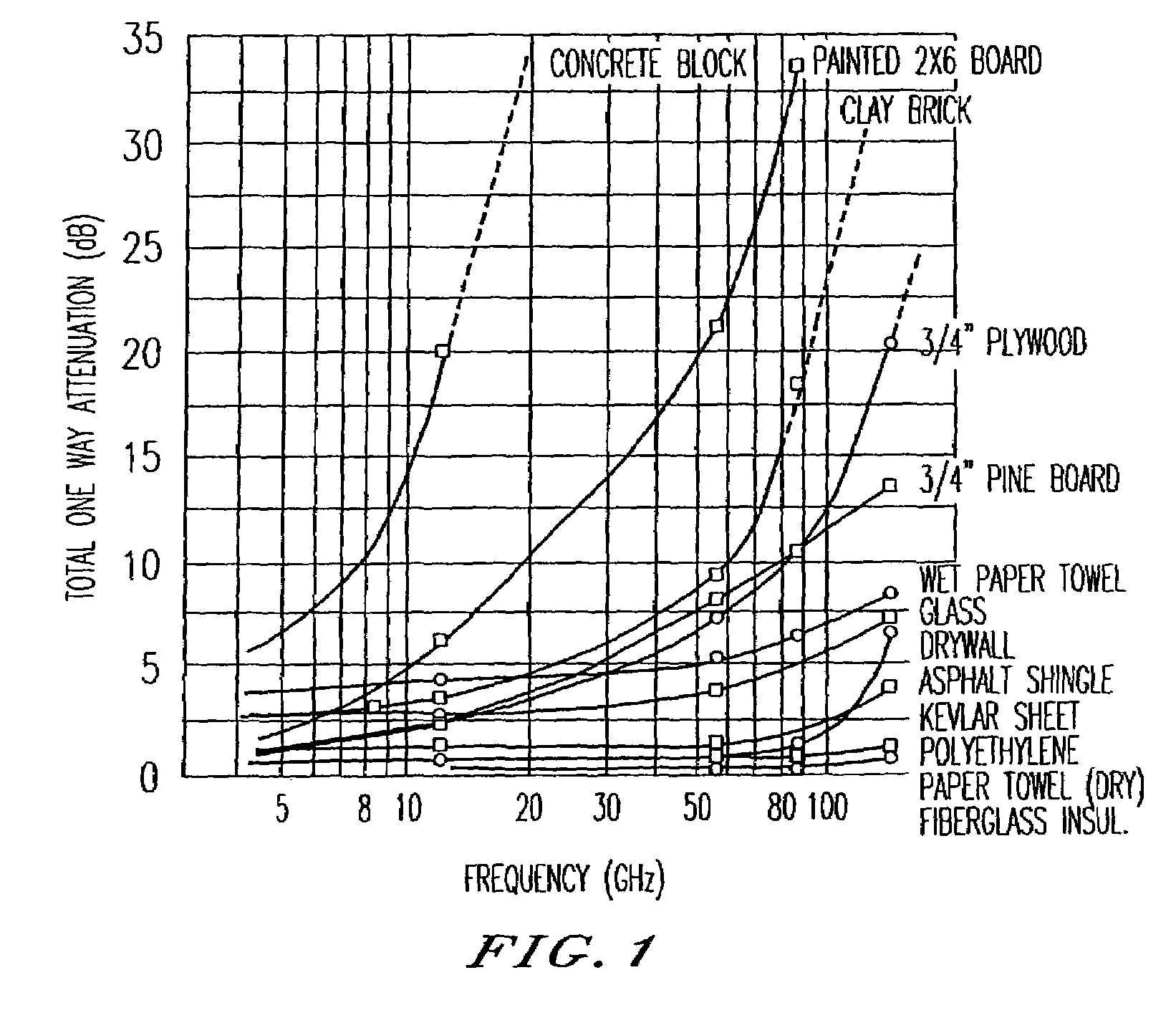
Ultra wide bandwidth spread-spectrum communications system
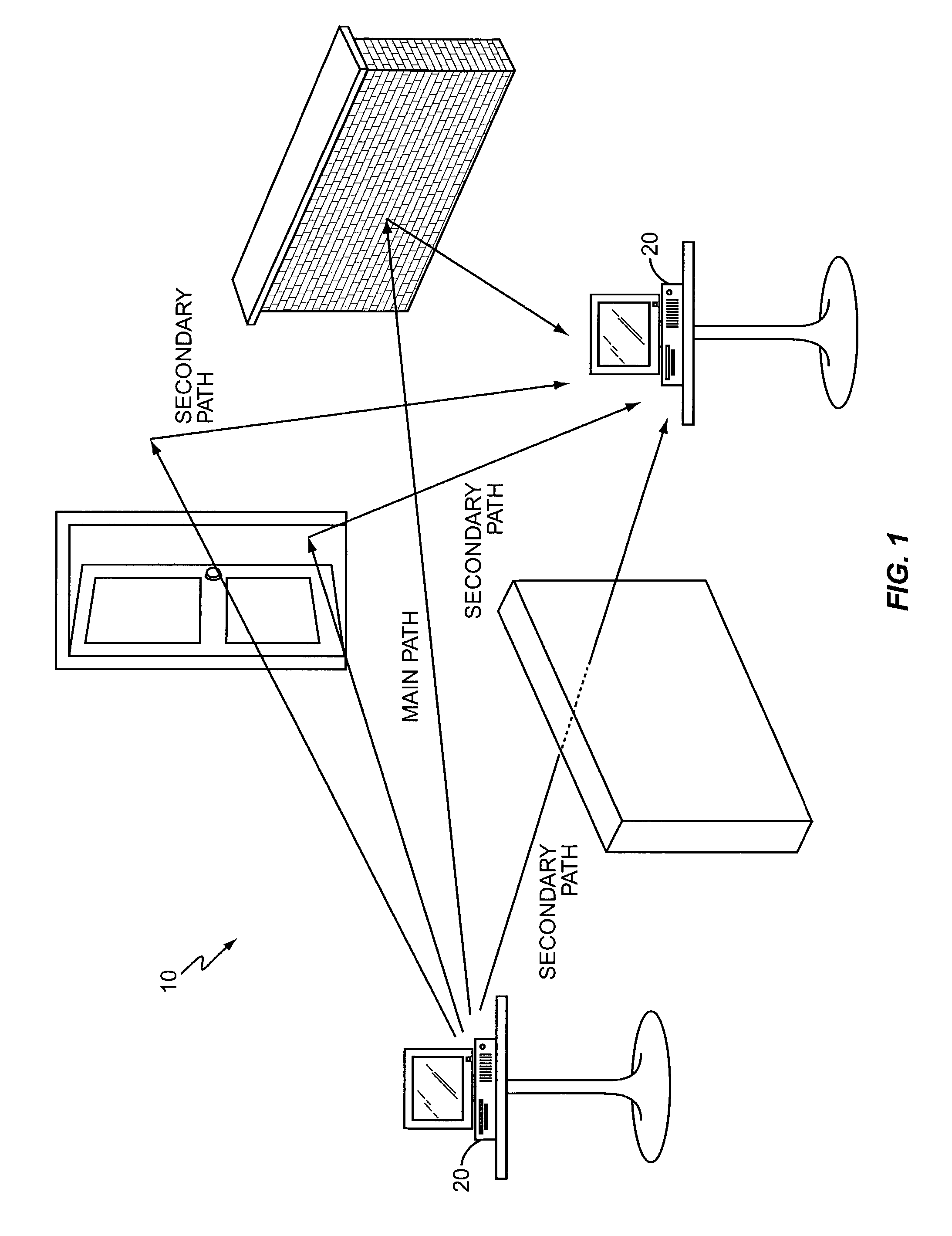
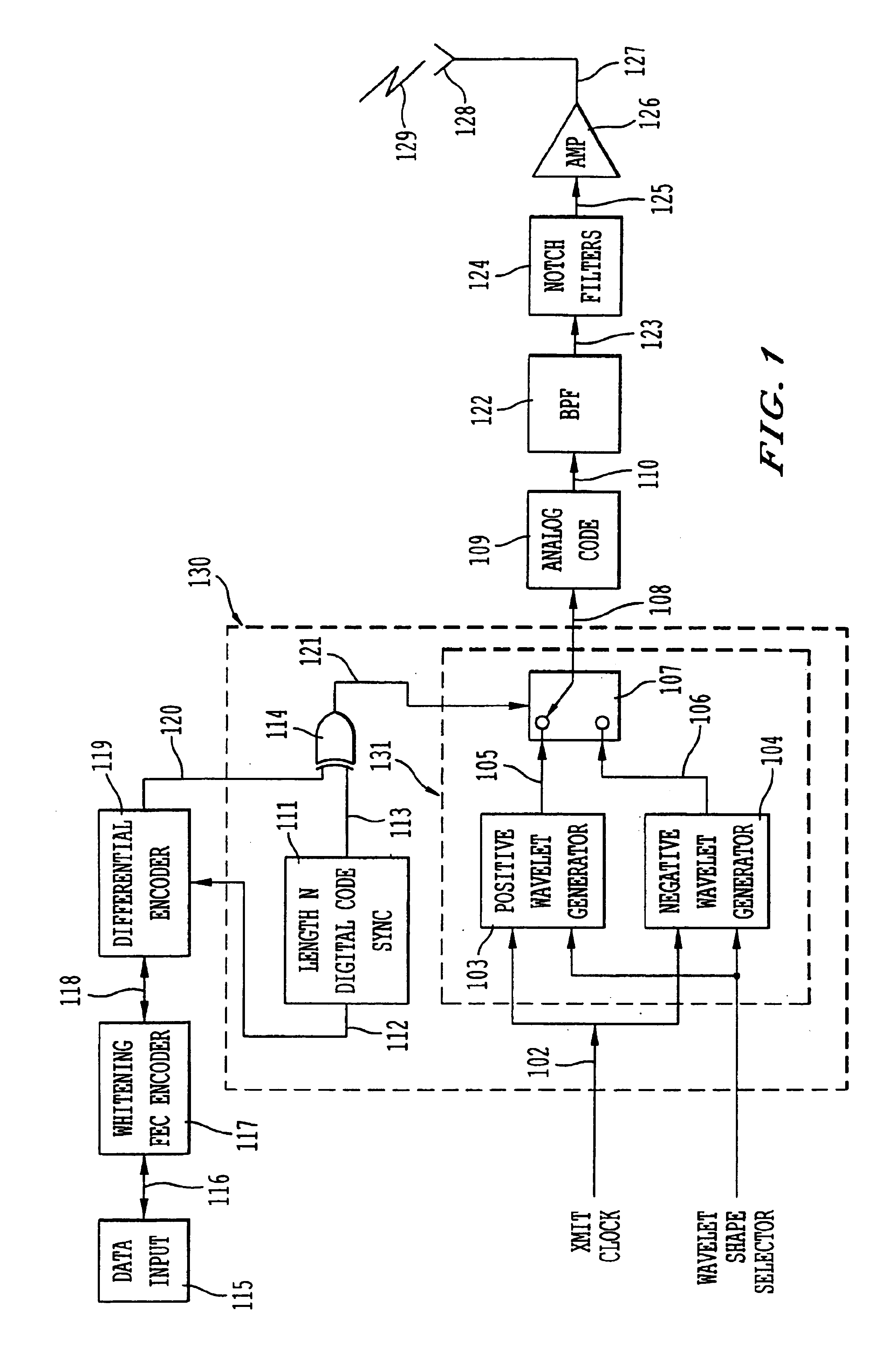
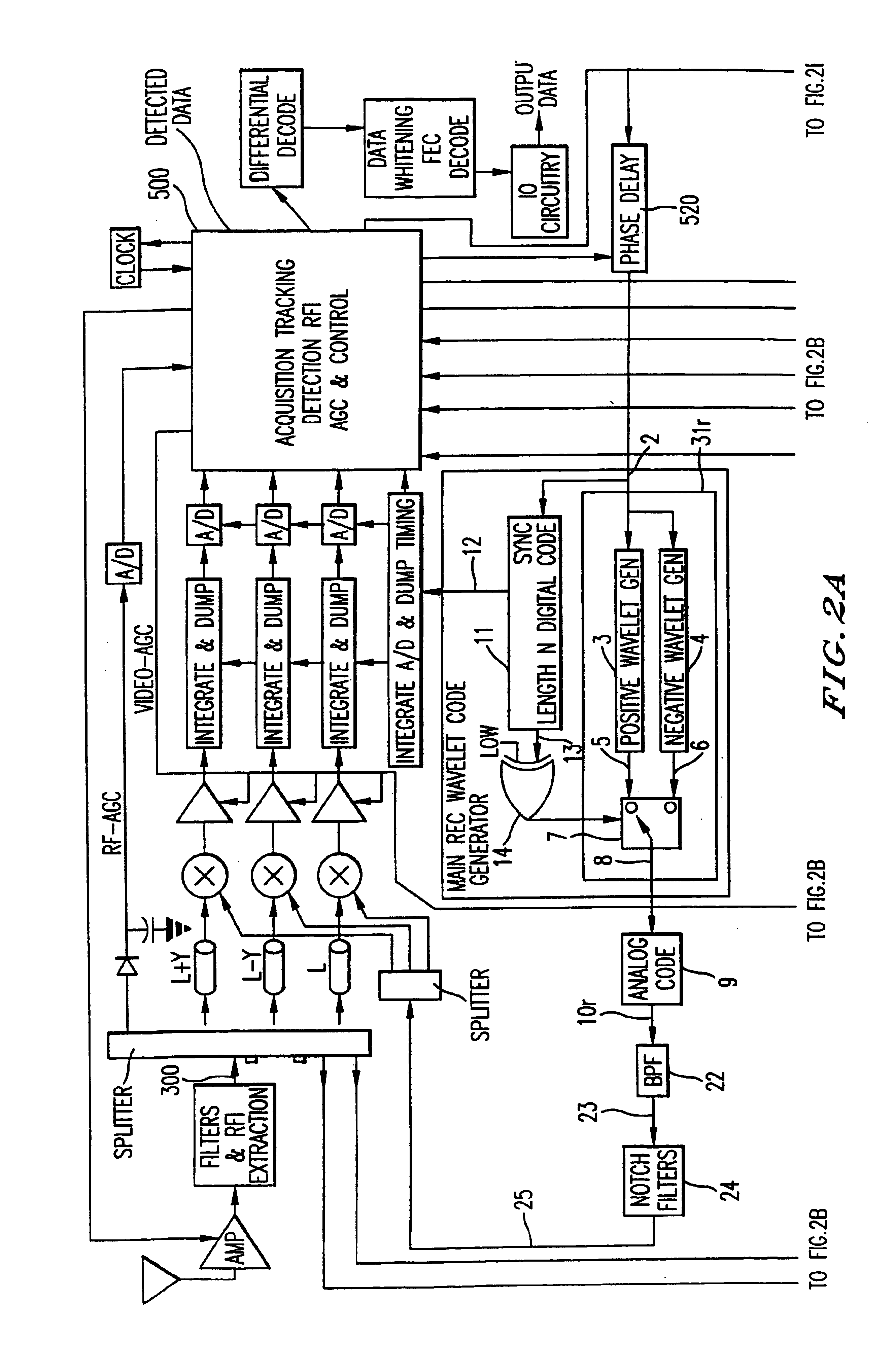
InactiveUS6901112B2Modulated carrier system with waveletsMultiplex communicationMultipath interferenceEngineering
An ultra wide bandwidth, high speed, spread spectrum communications system uses short wavelets of electromagnetic energy to transmit information through objects such as walls or earth. The communication system uses baseband codes formed from time shifted and inverted wavelets to encode data on a RF signal. Typical wavelet pulse durations are on the order of 100 to 1000 picoseconds with a bandwidth of approximately 8 GHz to 1 GHz, respectively. The combination of short duration wavelets and encoding techniques are used to spread the signal energy over an ultra wide frequency band such that the energy is not concentrated in any particular narrow band (e.g. VHF: 30-300 MHz or UHF: 300-1000 MHz) and is not detected by conventional narrow band receivers so it does not interfere with those communication systems. The use of pulse codes composed of time shifted and inverted wavelets gives the system according to the present invention has a spatial resolution on the order of 1 foot which is sufficient to minimize the negative effects of multipath interference and permit time domain rake processing.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
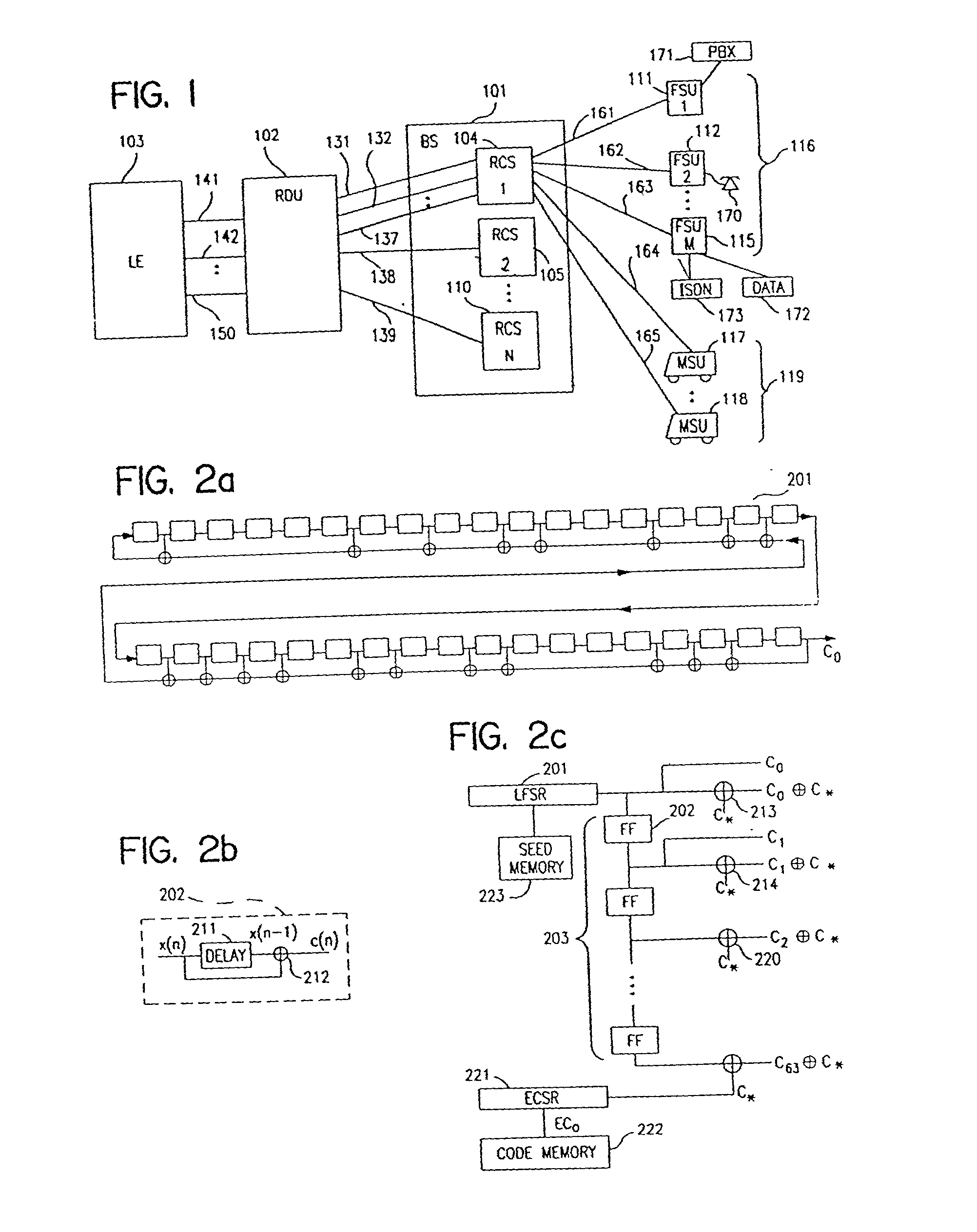
Method for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020051434A1Easy to liftReduce capacityRadio transmission for post communicationSystem capacityModem device
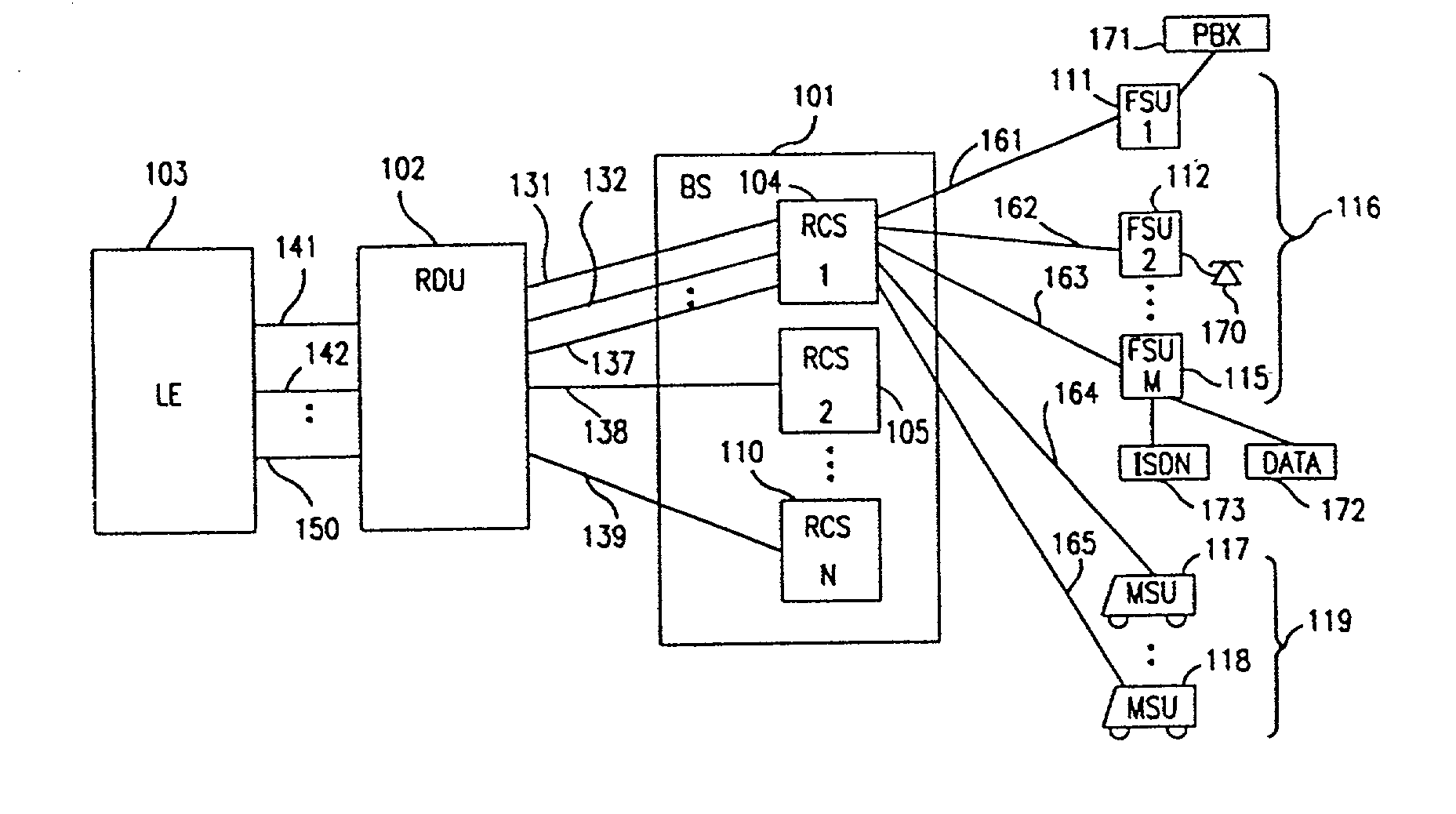
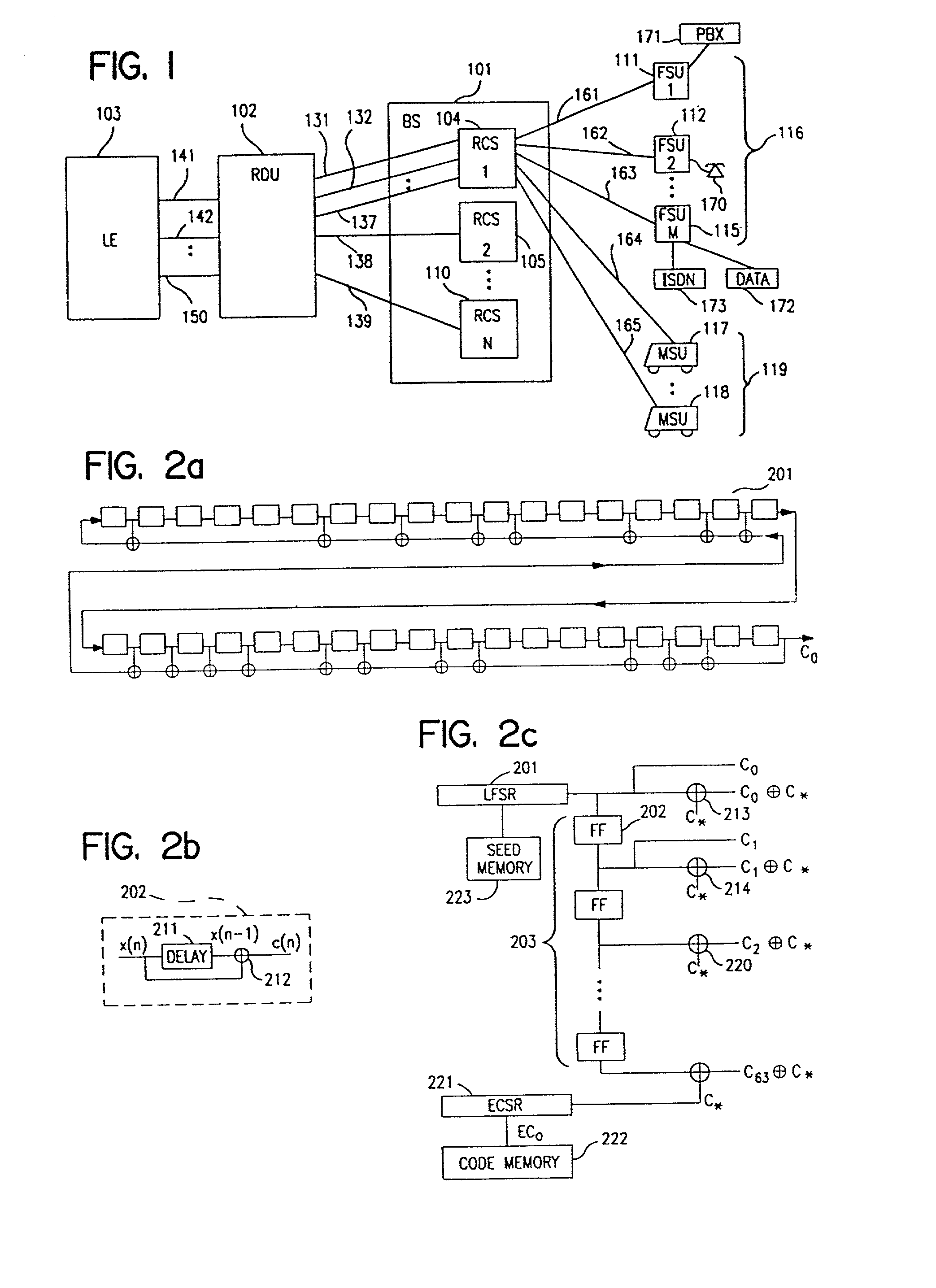
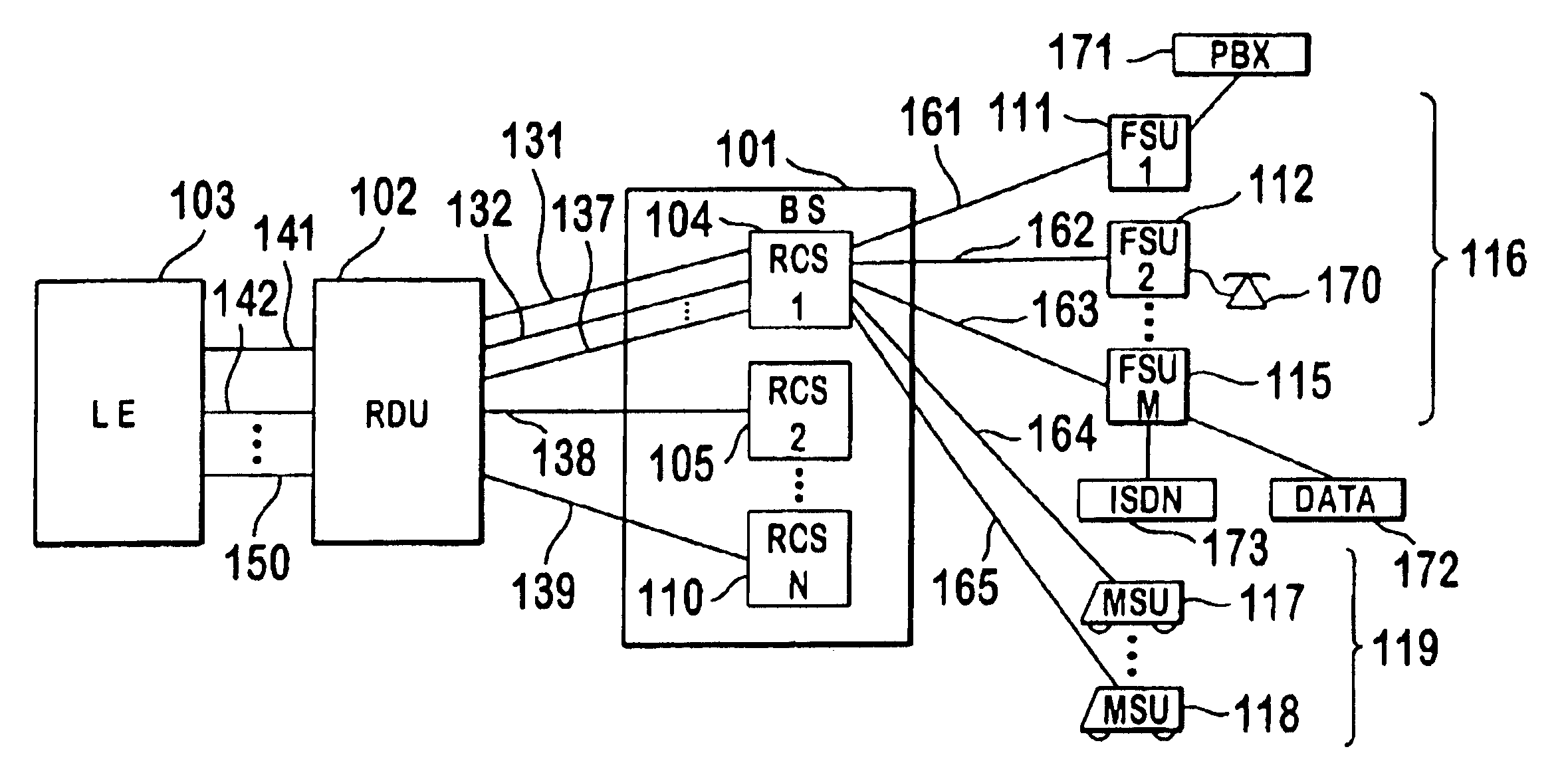
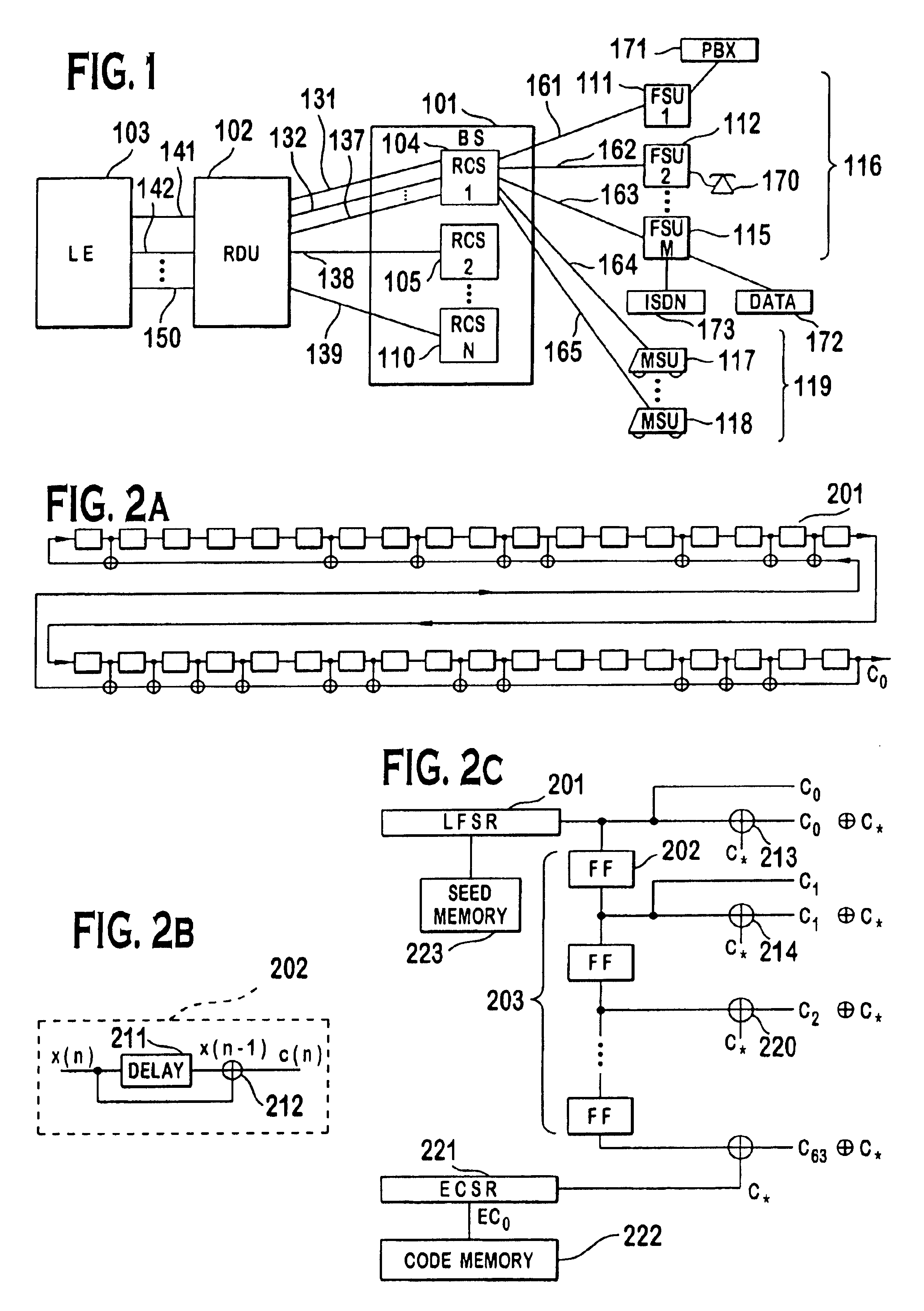
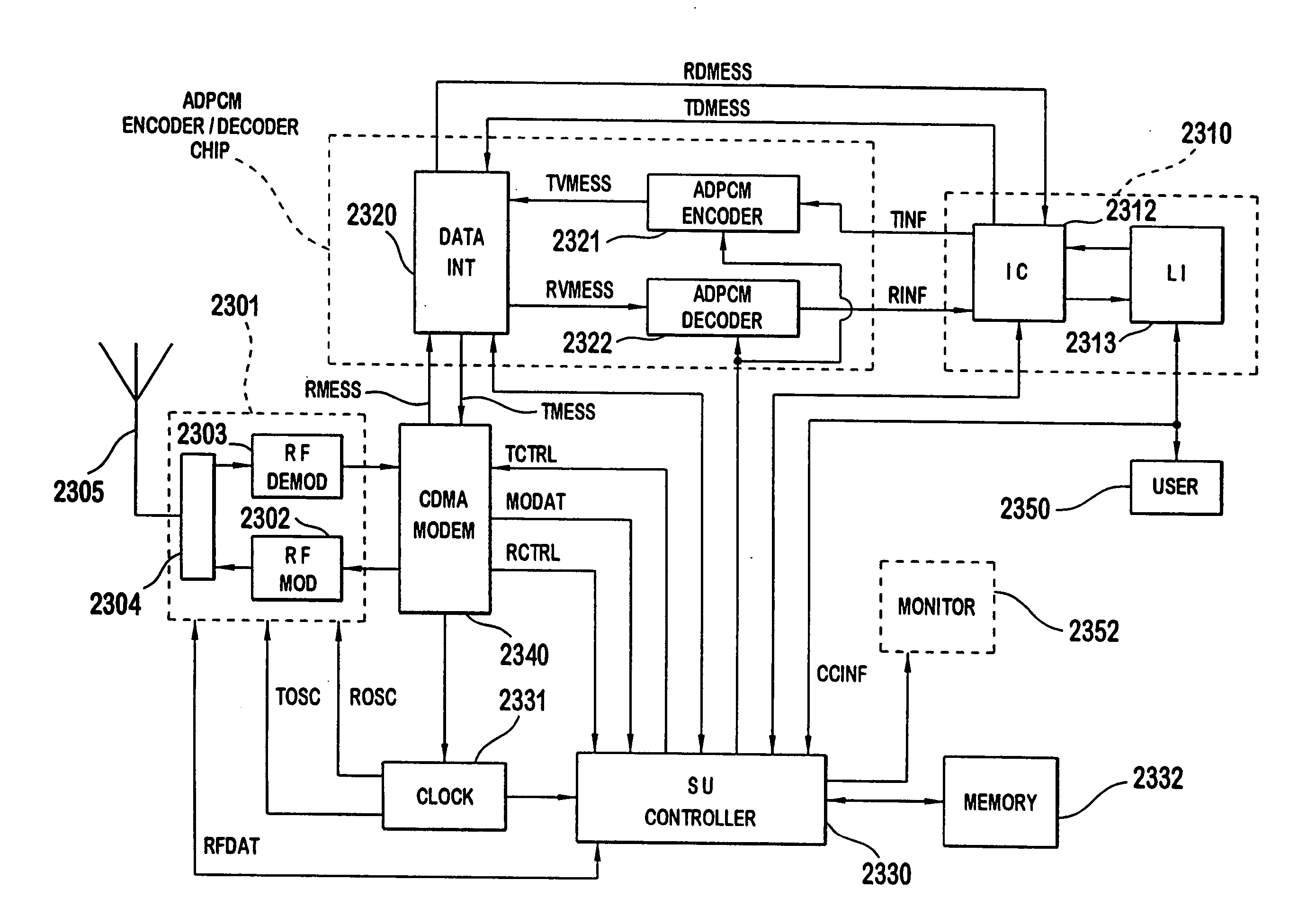
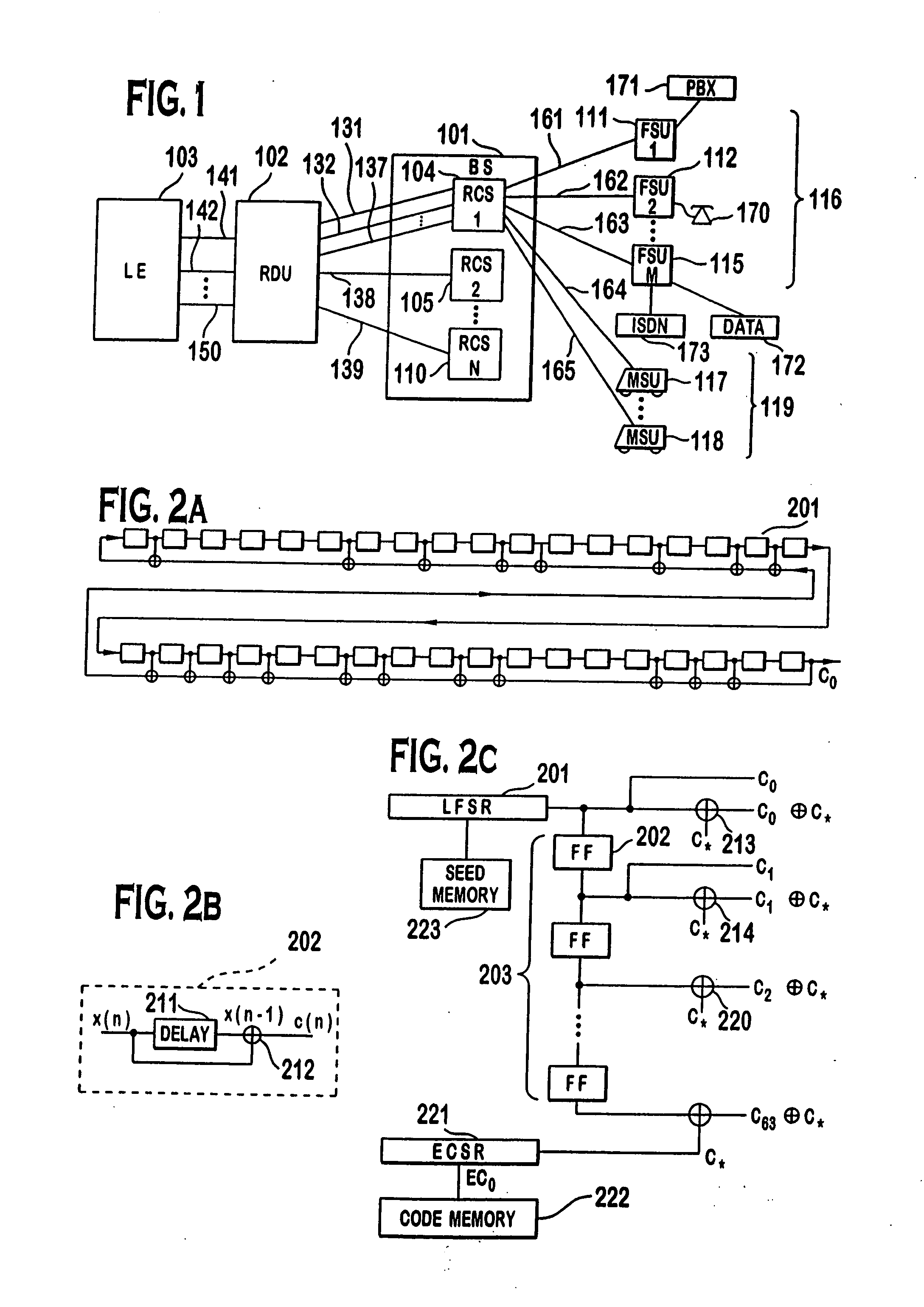
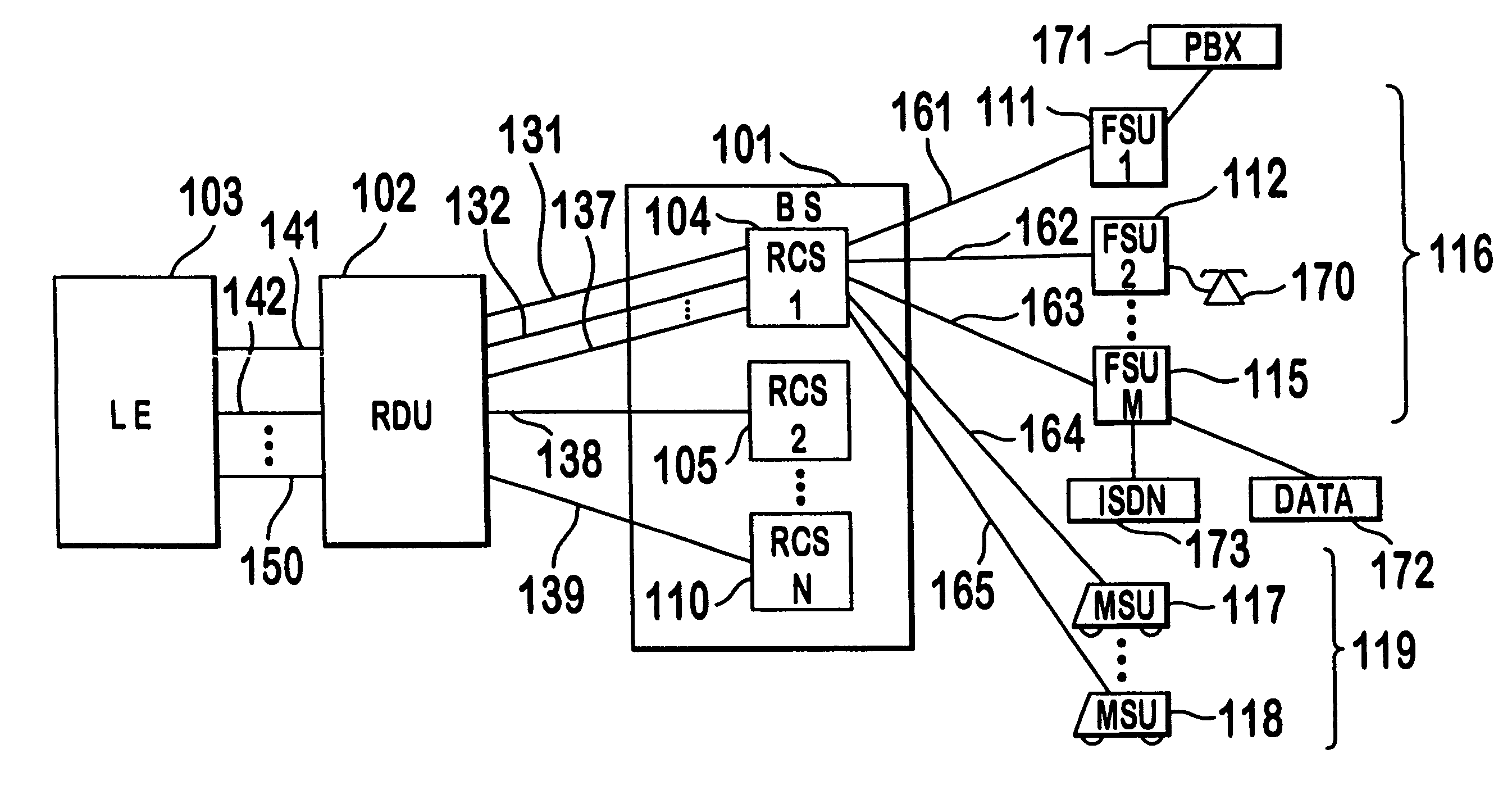
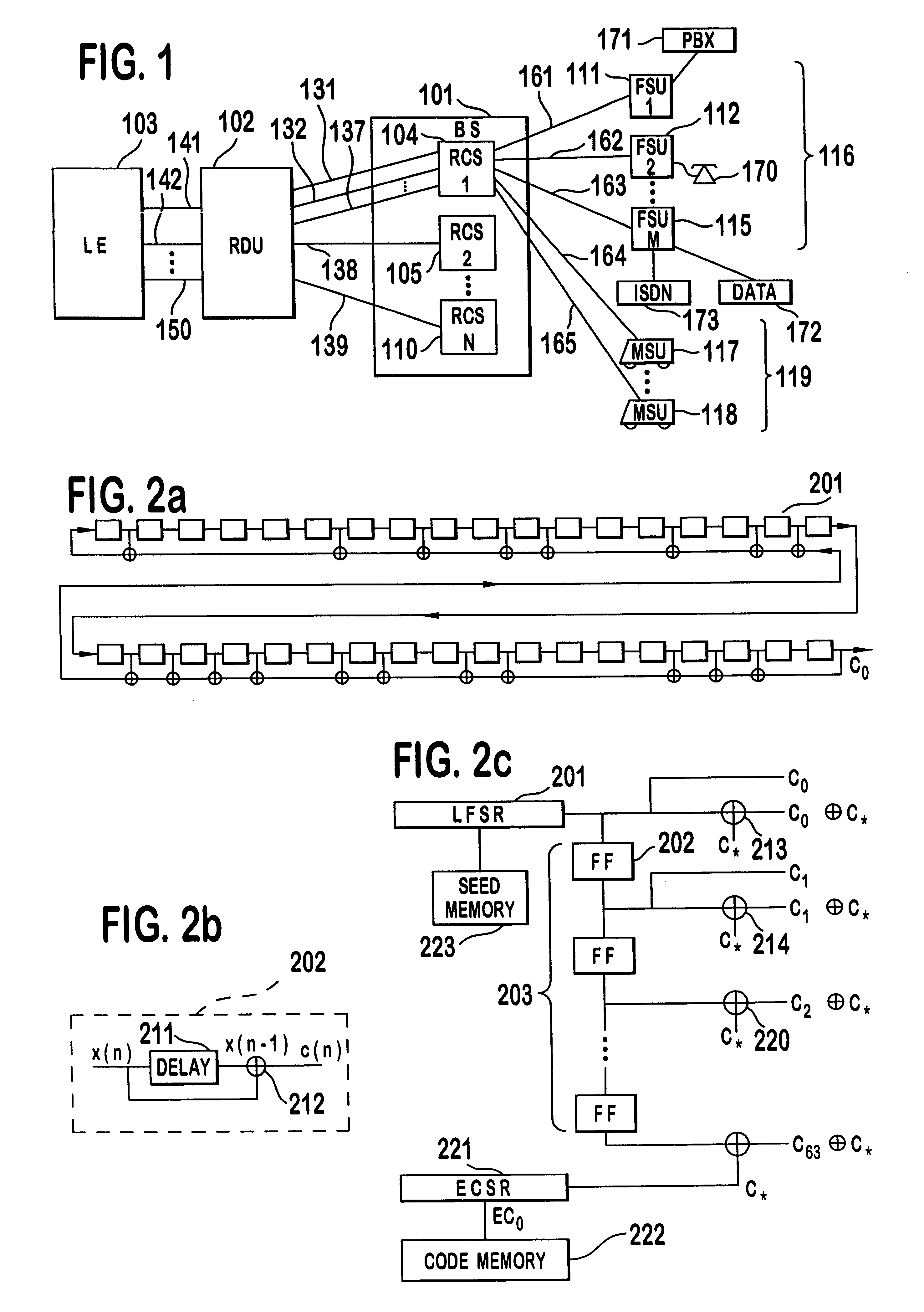
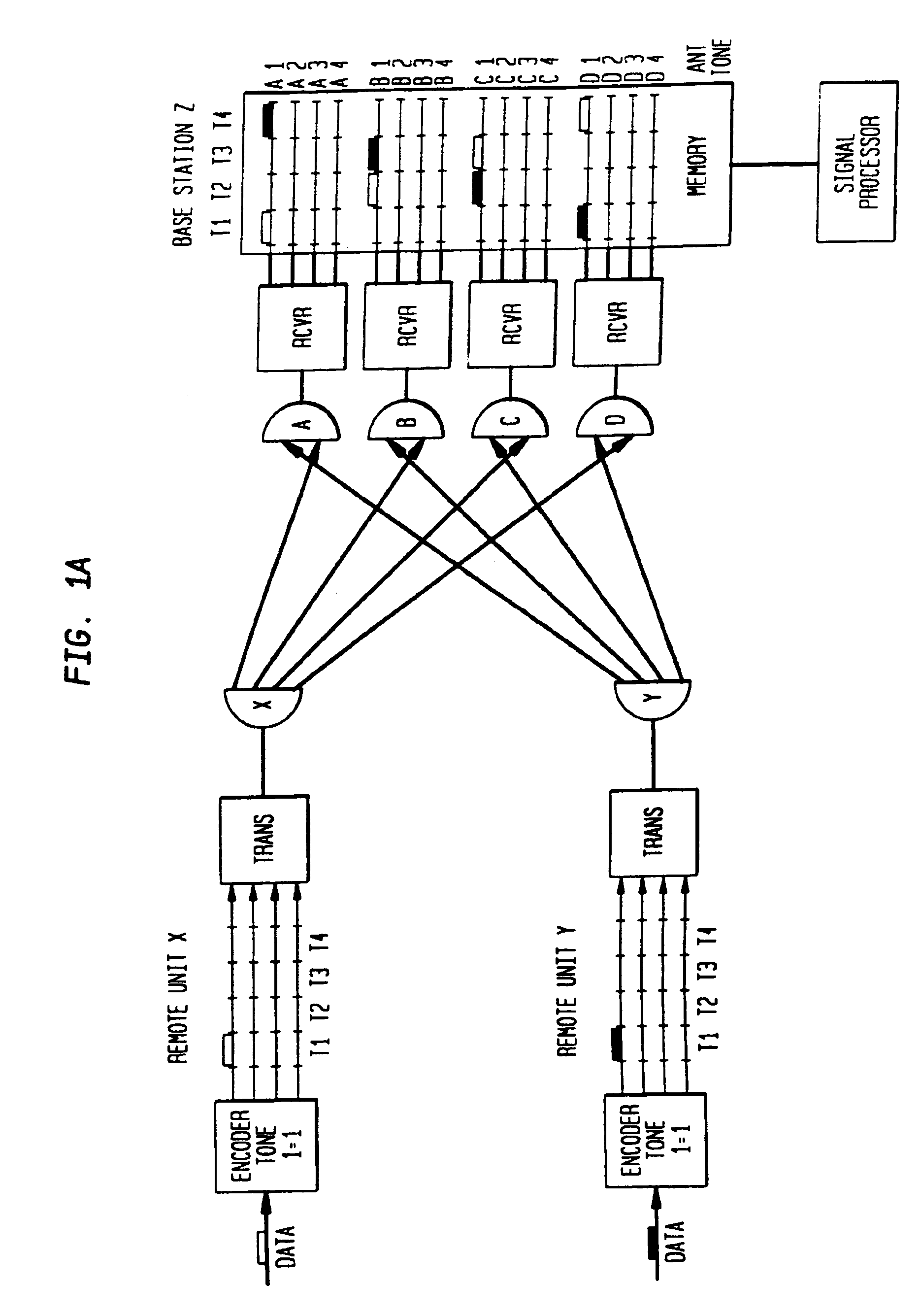
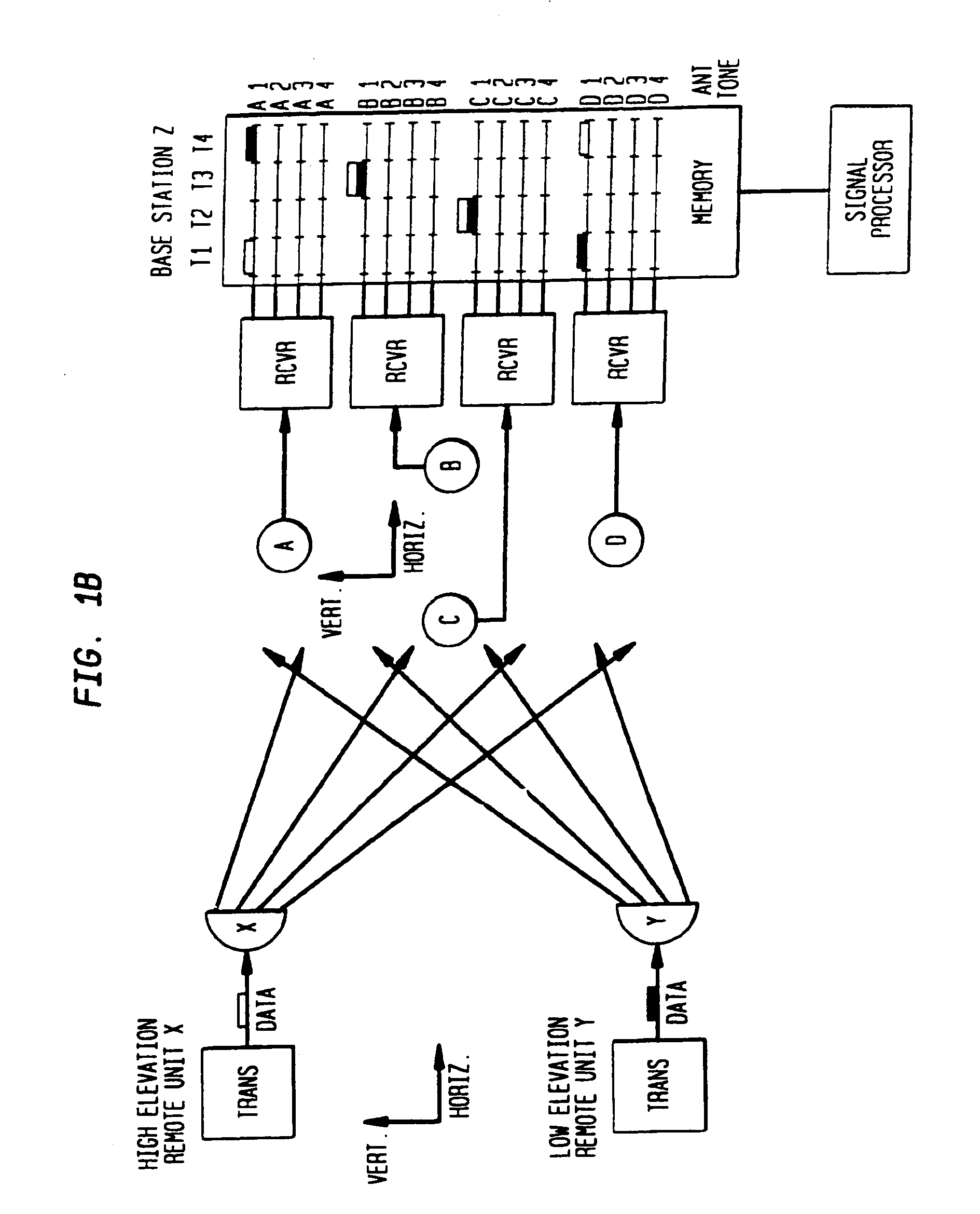
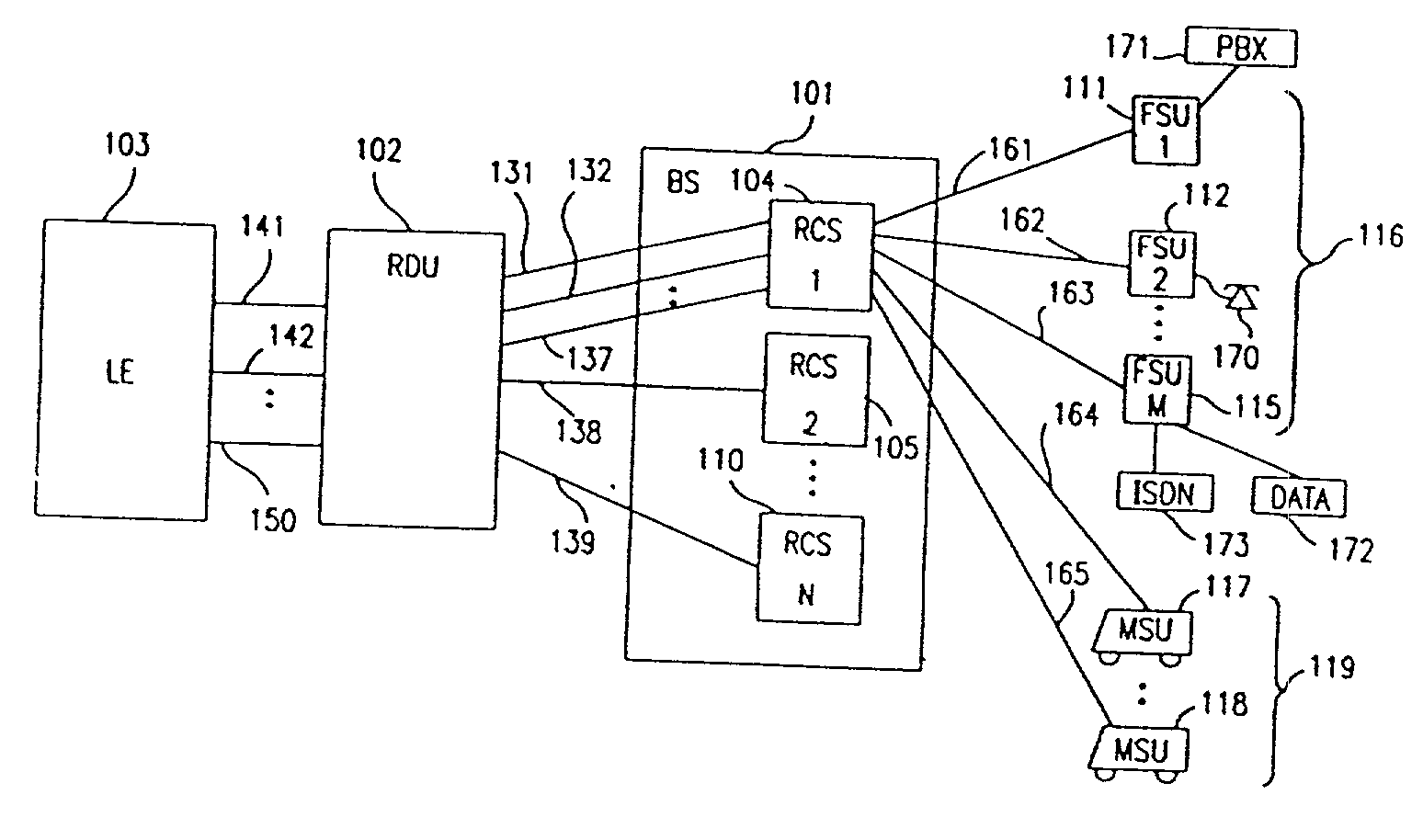
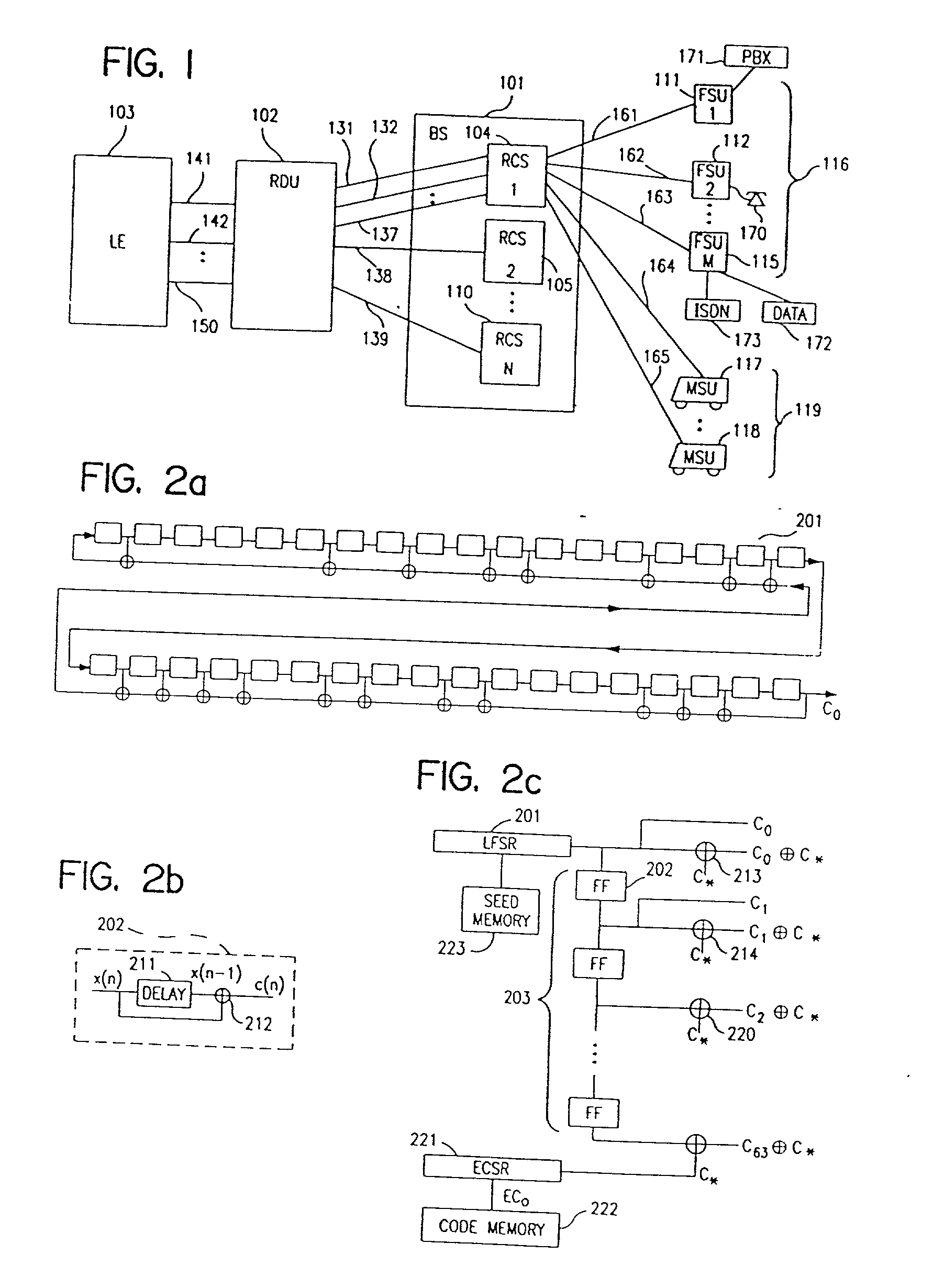
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS6885652B1Increase profitPower managementBaseband system detailsModem deviceSystem capacity
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Frequency hopping spread spectrum system with high sensitivity tracking and synchronization for frequency unstable signals
InactiveUS6934316B2Improve dynamic rangeReduce sensitivityData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFrequency-hopping spread spectrumFast Fourier transform
A wireless spread spectrum communication system for transmitting data includes a plurality of end point transmitters and at least one receiver. The end point transmitters transmit data via a frequency hopped spread spectrum signal where the transmitting signal is sent without the benefit of frequency stabilization. The receiver is responsive to the frequency hopping spread spectrum signals and includes a correlator and a signal processor. The correlator samples at least a first portion of a preamble of the signal and correlates the portion of the preamble with a known preamble pattern to determine a probability of correlation. The signal processor applies a Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to the signal in response to the probability of correlation to track a narrowband frequency of the signal based on at least a second portion of the preamble and to decode data encoded within the signal subsequent to the preamble.
Owner:ITRON
Method of performing antenna diversity in spread spectrum in wireless local area network
InactiveUS6563858B1Good diversity selection metricGood energySpatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsHigh rate
A method of performing antenna diversity in a wireless spread spectrum communication system is disclosed. A spread spectrum phase shift keyed (PSK) packet signal having data symbols formed from high rate mode chips is received in each of two respective spaced antenna of a spread spectrum receiver. The bit sync peak sample is determined within the packet signal for each antenna. Predetermined bit sync samples are subtracted a predetermined number of chips on either side of the bit sync peak sample from the peak for each antenna. The antenna having the higher value obtained in the subtracting step accomplished for each antenna is selected.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC +1
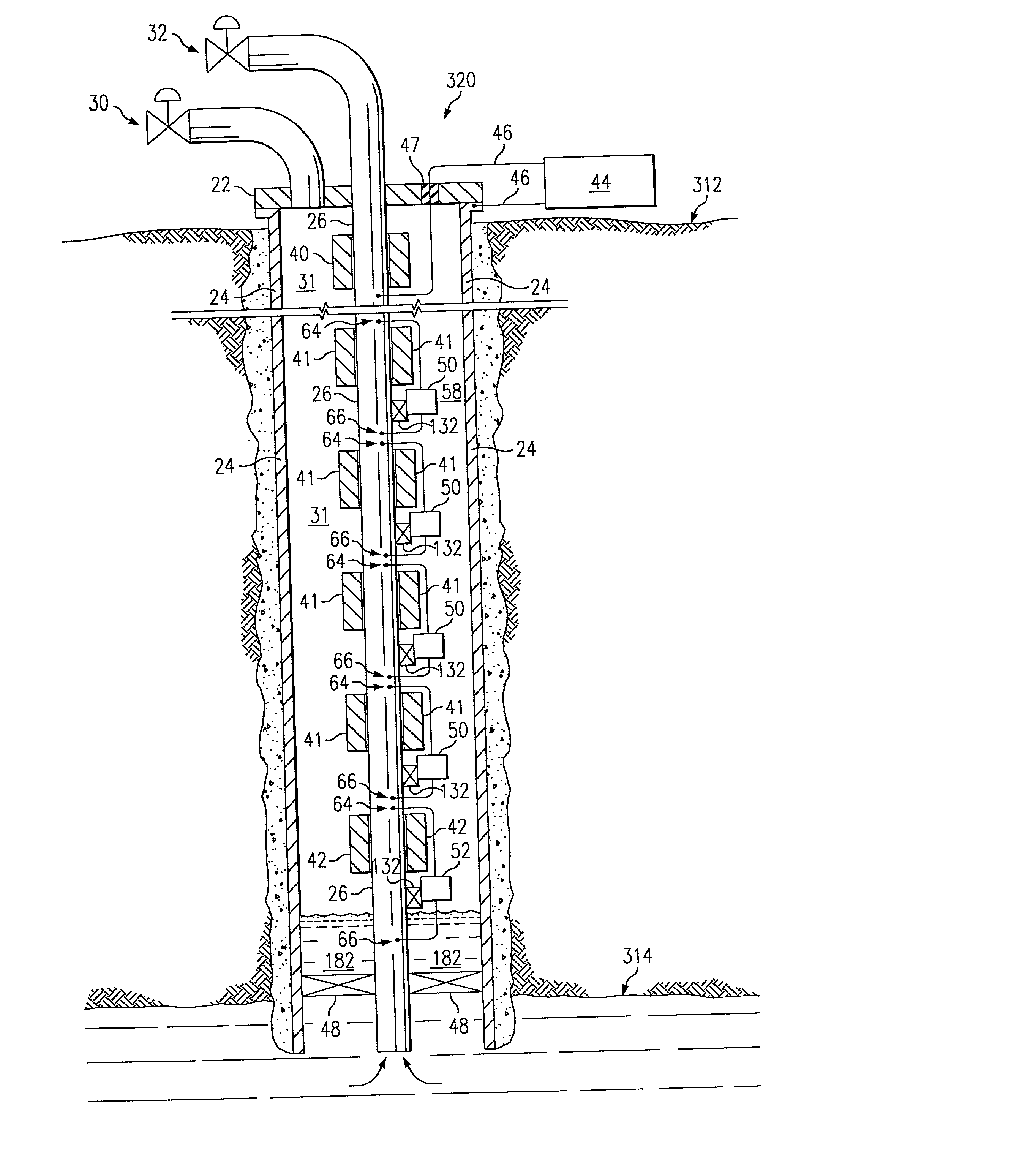
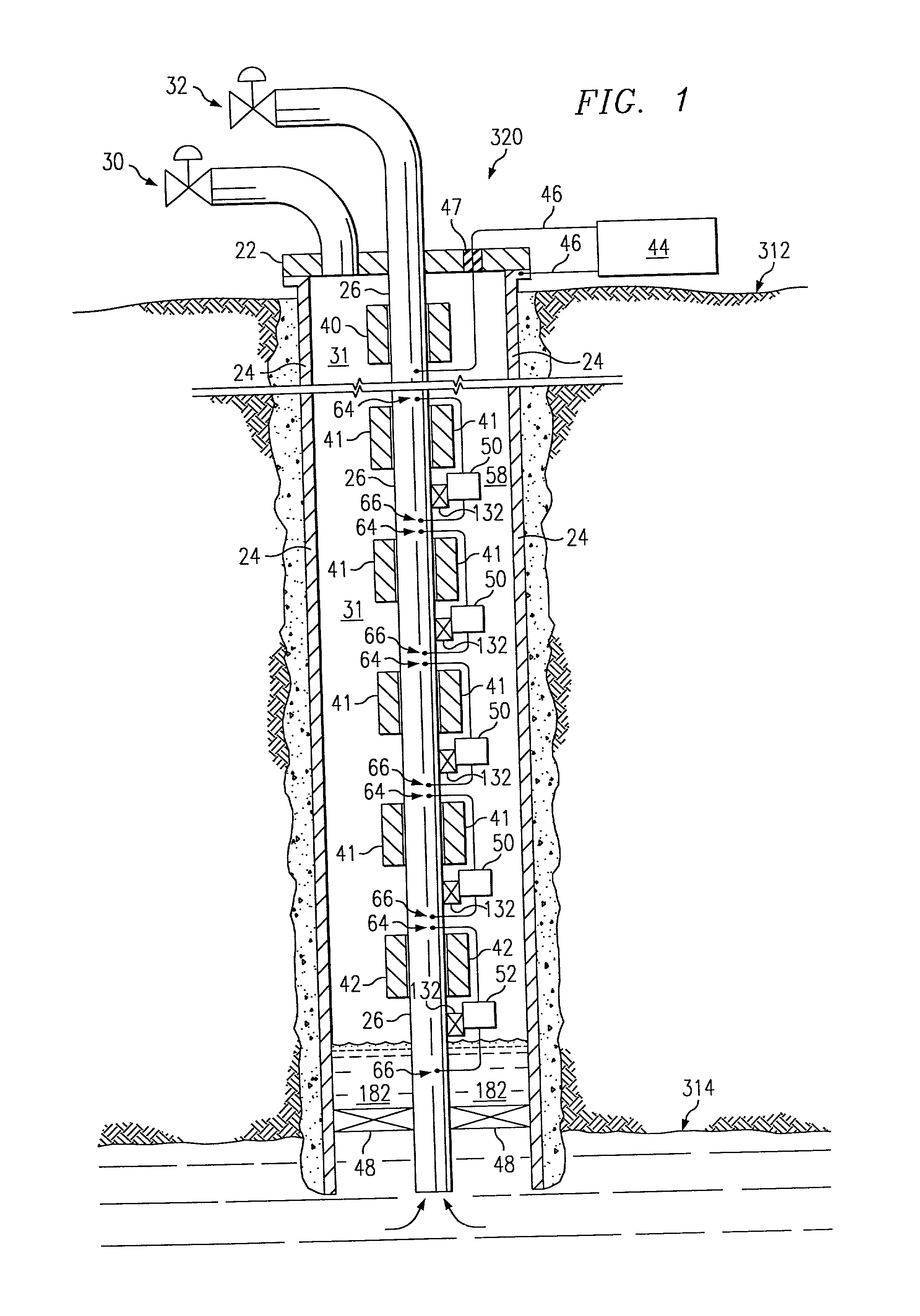
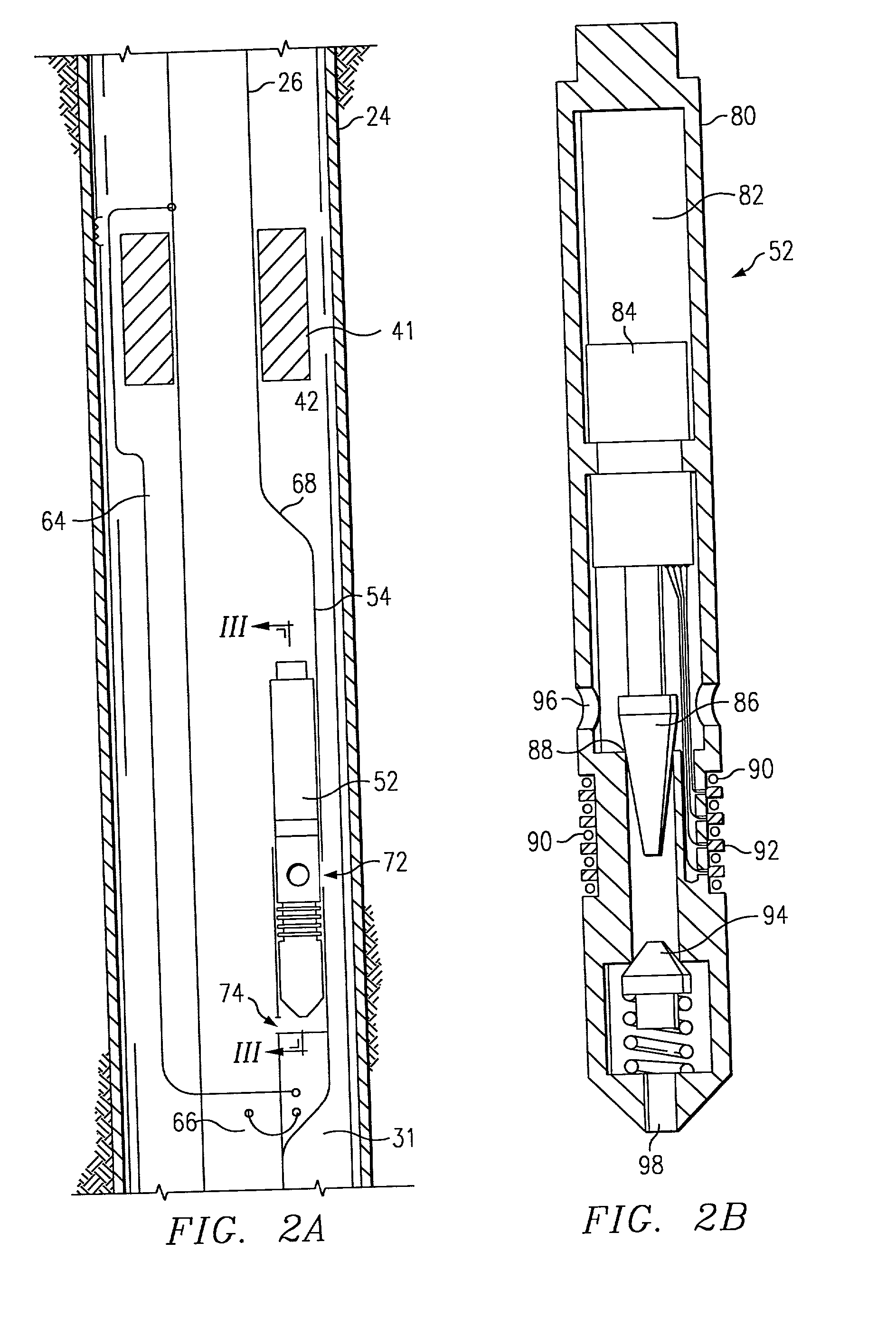
Petroleum well having downhole sensors, communication and power
A petroleum well has an electronic module and a number of sensors which communicate with the surface using the tubing string and casing as conductors. Induction chokes at the surface and downhole electrically impede AC flow through the (tubing or casing if so configured) with the resulting voltage potential useful for power and communication. A high bandwidth, adaptable spread spectrum communications system is used to communicate between the downhole electronics module and a surface master spread spectrum modem. Downhole sensors, such as pressure, temperature, acoustic and seismic sensors accurately assess downhole physical conditions. In a preferred form, the electronics module and sensors are wireline insertable and retrievable into a side pocket mandrel in the tubing string. Permanent downhole sensors that can communicate with the surface allow such diverse applications as optimizing well and field performances, monitoring and assessing the geophysics of the fomrations around the well, assessing well and reservoir reserves, assessing reservoir conditions.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS20040252668A1Easy to liftMaximize signal to noisePower managementBaseband system detailsSystem capacityCode division multiple access
A subscriber unit for use in a multiple access spread-spectrum communication system includes a spread spectrum radio interface, responsive to a rate function signal from a base station, and first and second despreaders. The base station assigns the rate function spread-spectrum message channels and the first despreader recovers and modifies an information signal one of the spread spectrum message channels. The information channel mode is then modified for processing by the second despreader, with the second despreader supporting a different information signal rate. The subscriber unit has a capability of communicating with a dynamically changing a transmission rate of an information signal which includes multiple spread spectrum message channels. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for a radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
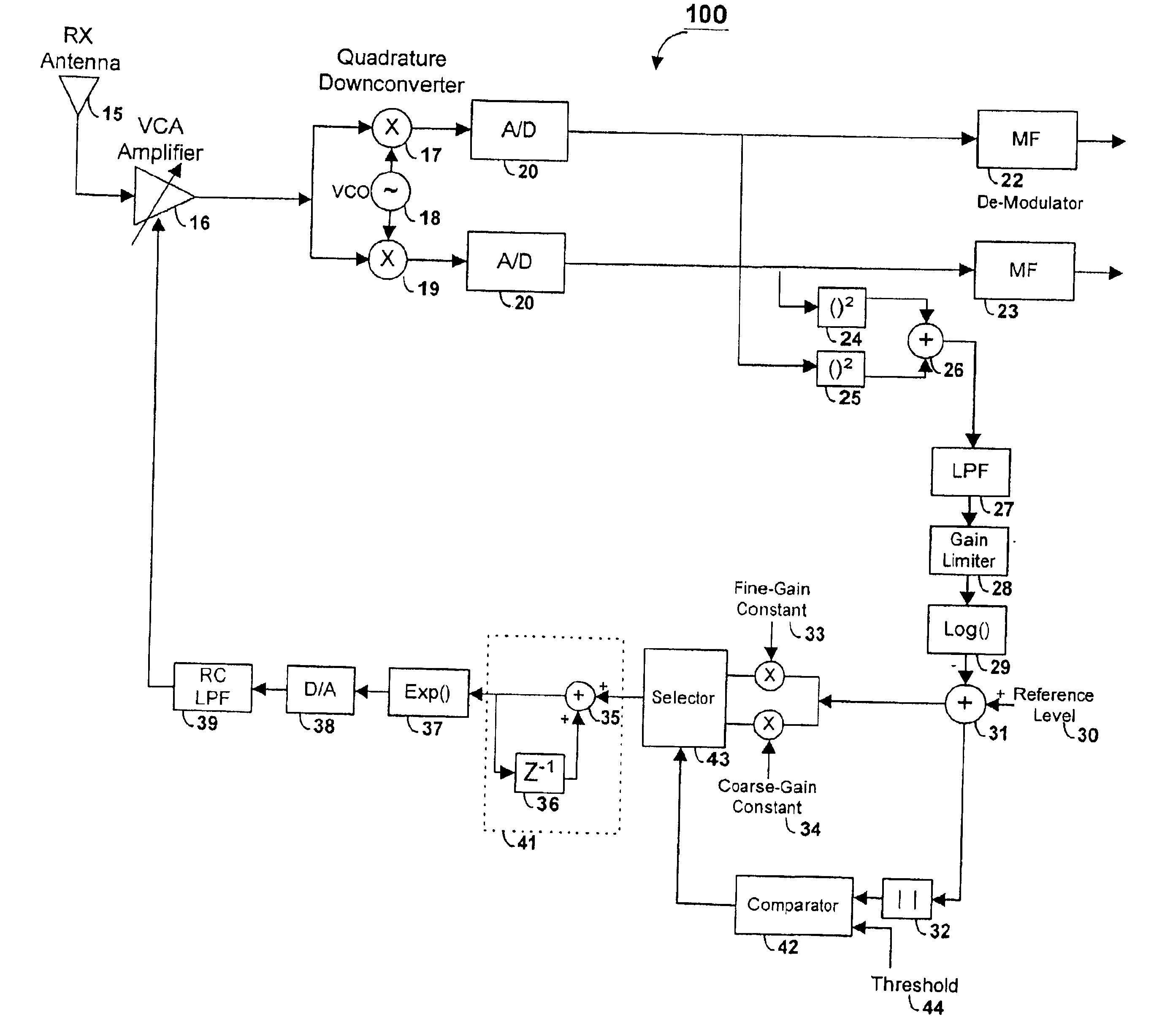
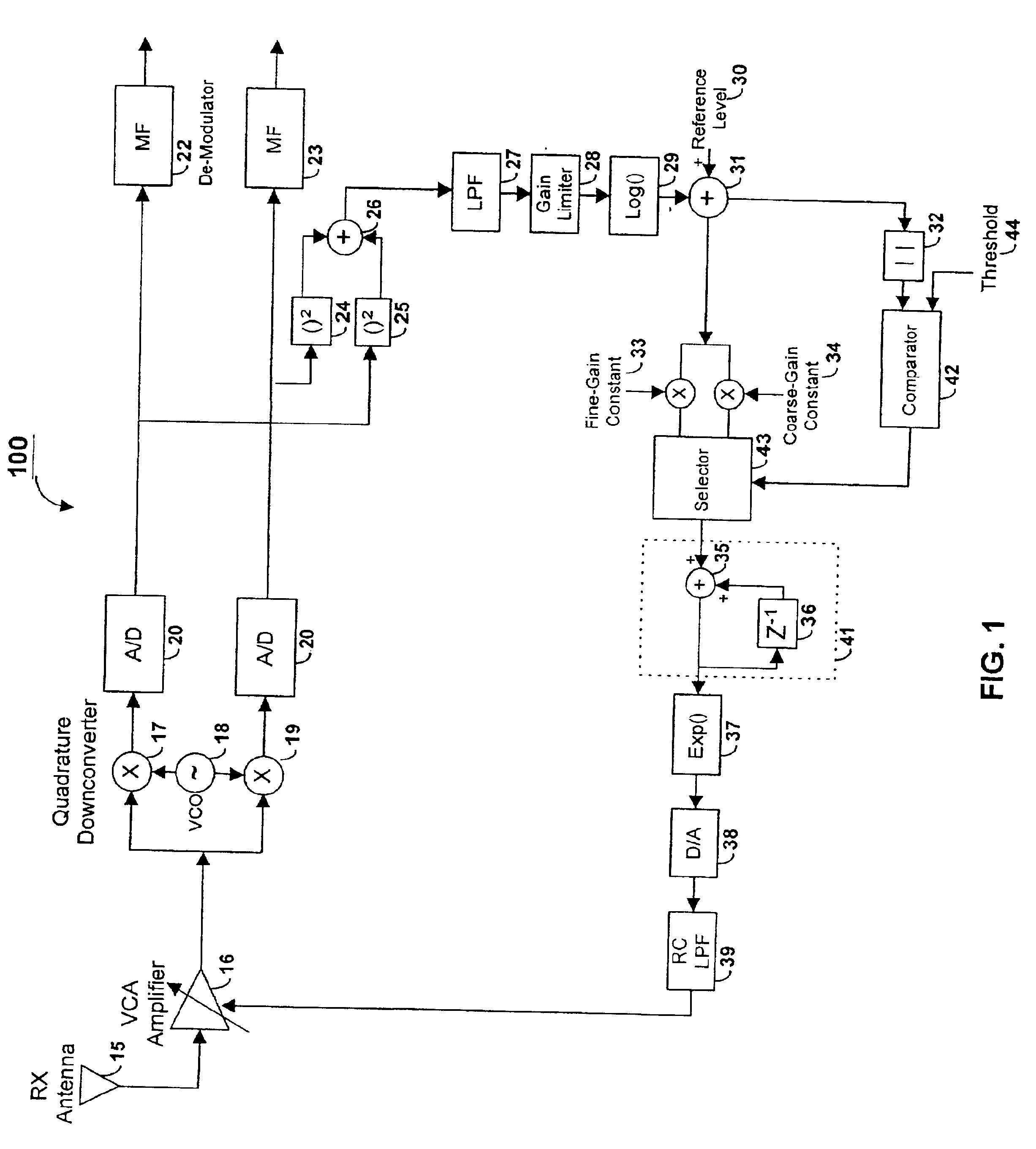
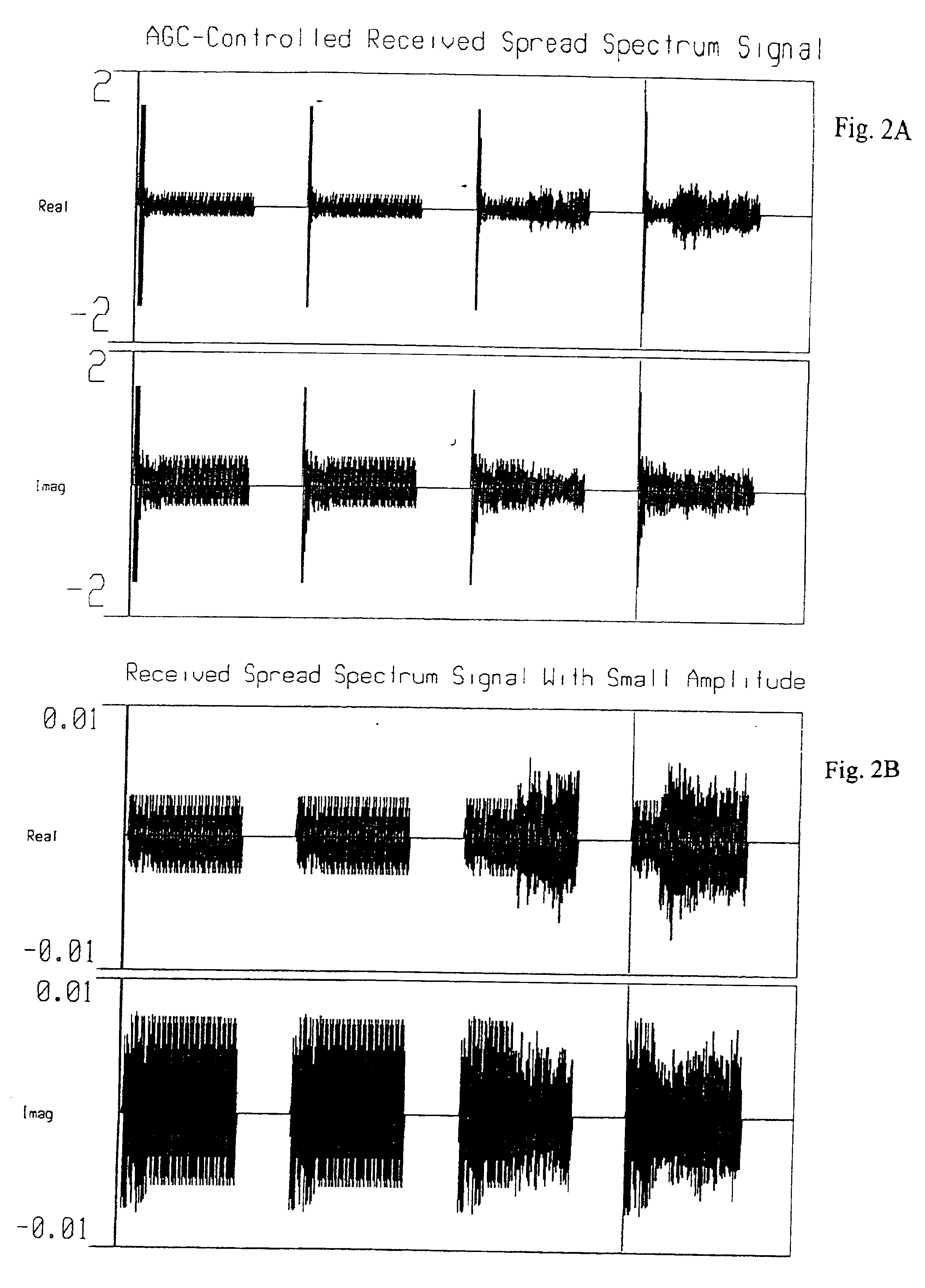
Method and apparatus of a fast two-loop automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6843597B1Small sizeLow costGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
In a burst-mode, high-speed spread-spectrum communications system, faster convergence of a receiver's automatic gain control (AGC) circuit reduces the time required to bring a received signal within the operating range of an operation amplifier and other radio-frequency and digital sections of the receiving system. A gain control circuit includes a coarse-gain feedback loop and a fine-gain feedback loop to improve convergence speed and at the same time maintain the stability of the AGC circuit. The coarse-gain feedback loop quickly brings the received signal, using a large gain signal, to the desired operating range. The fine-gain feedback loop uses a smaller gain signal to gradually smooth the received signal to avoid saturation on the A / D converters.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
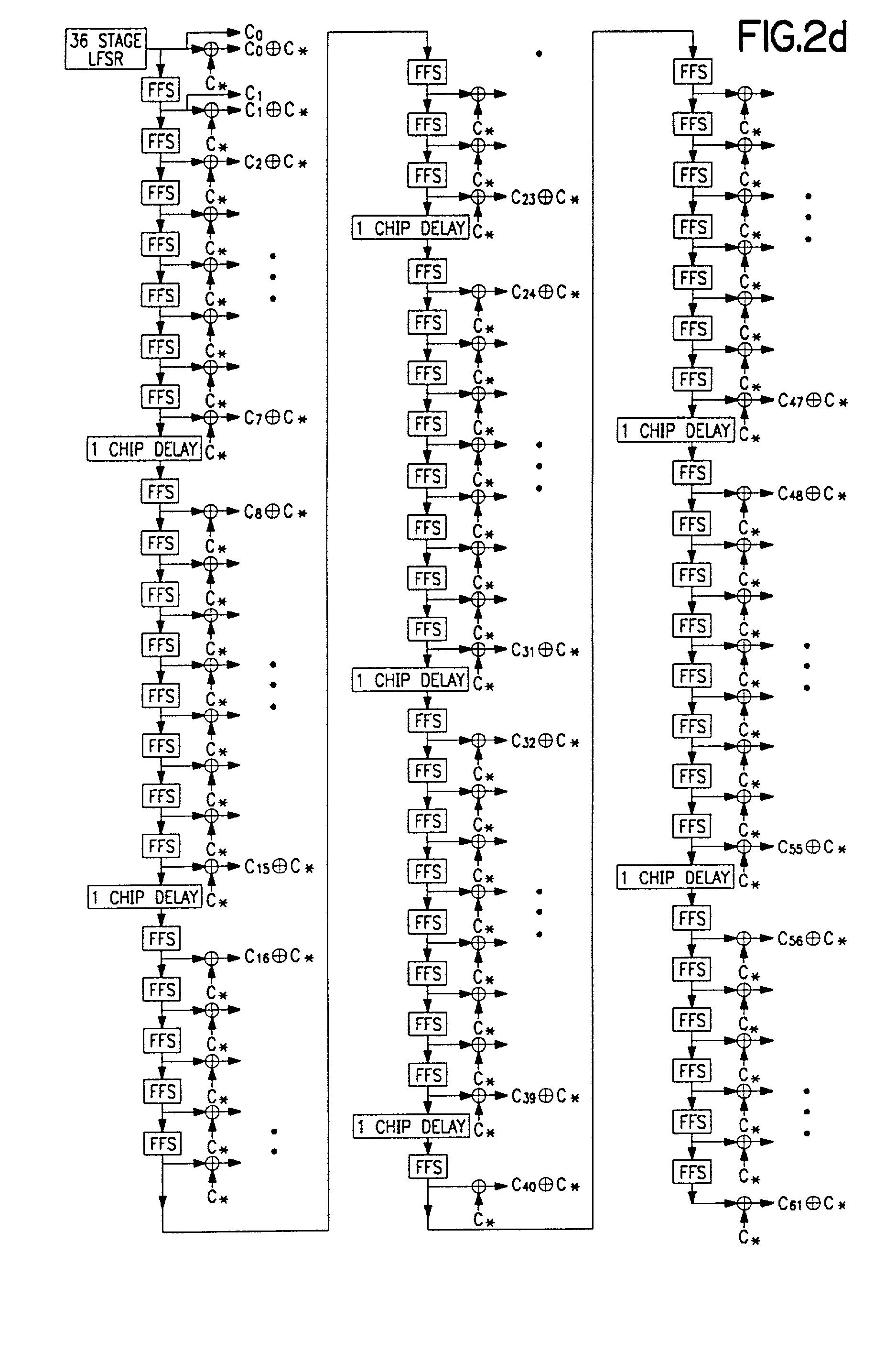
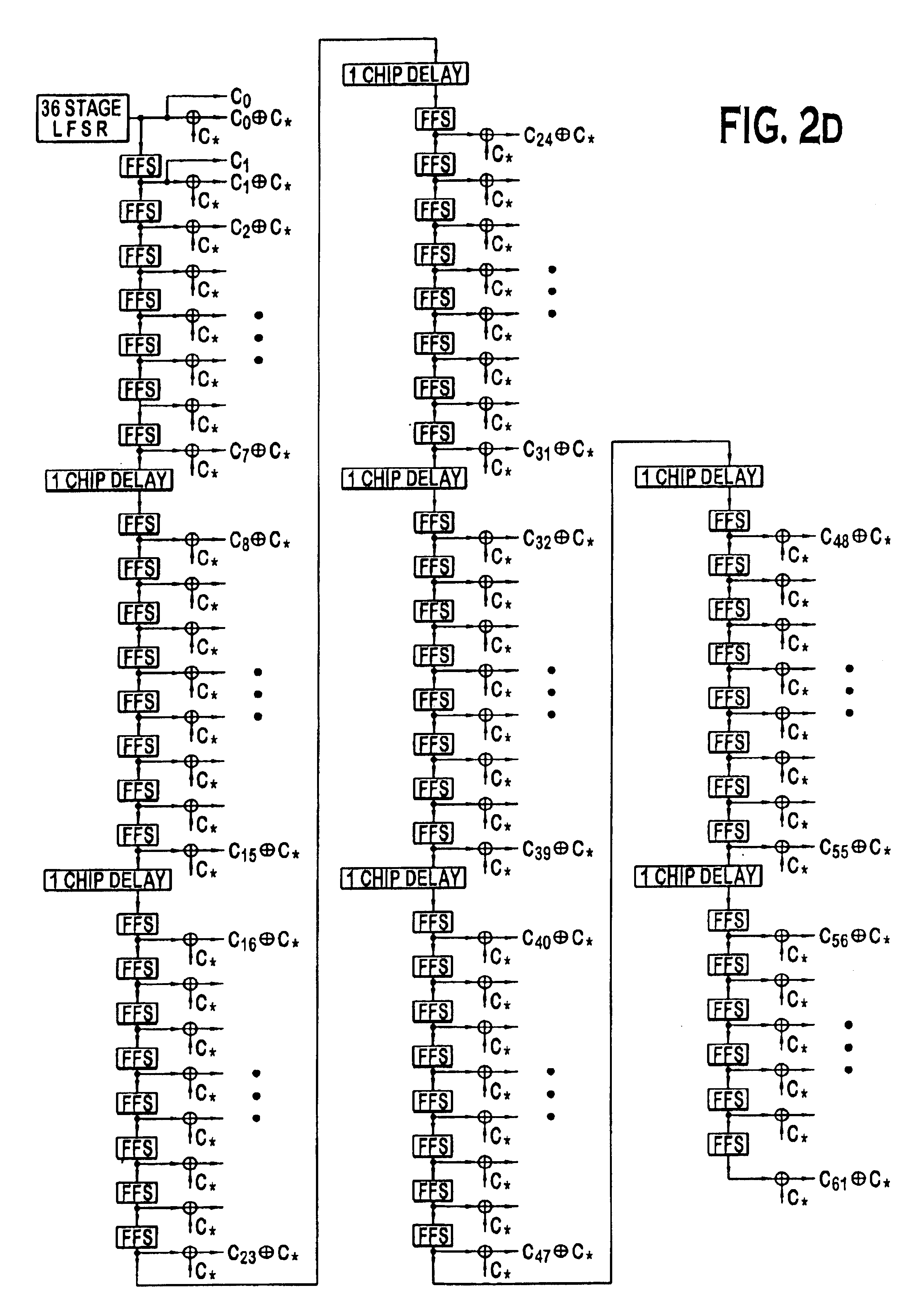
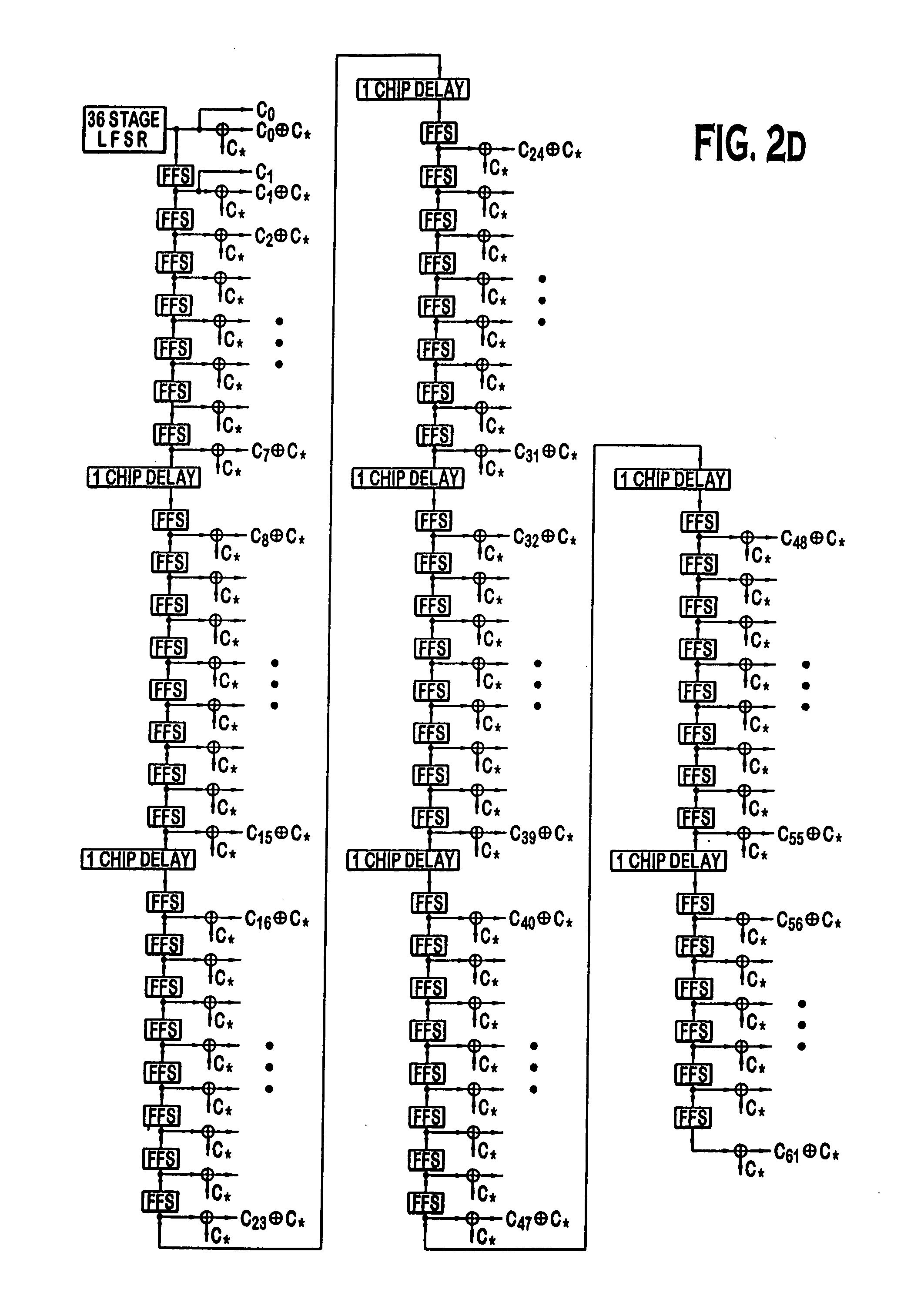
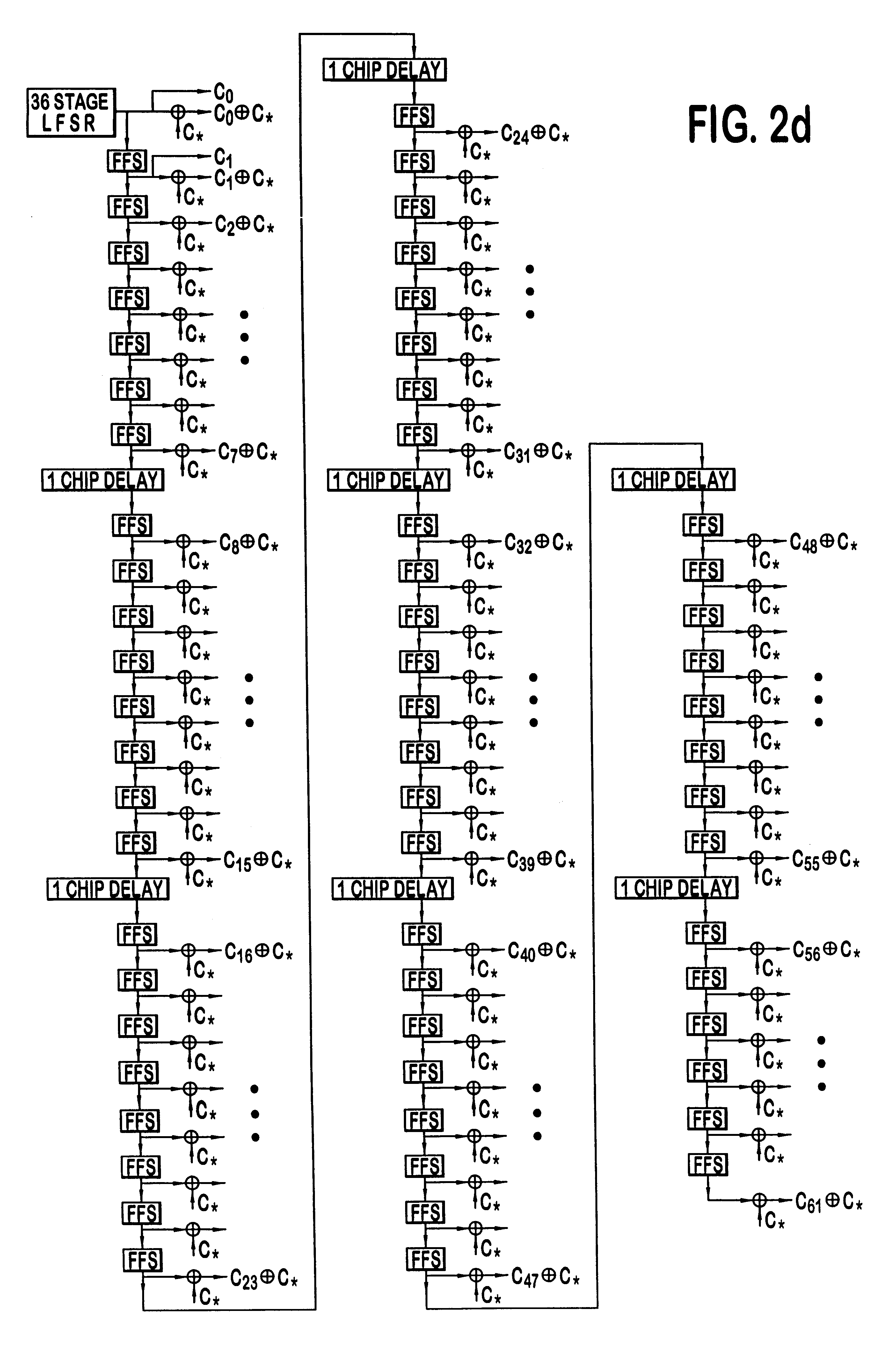
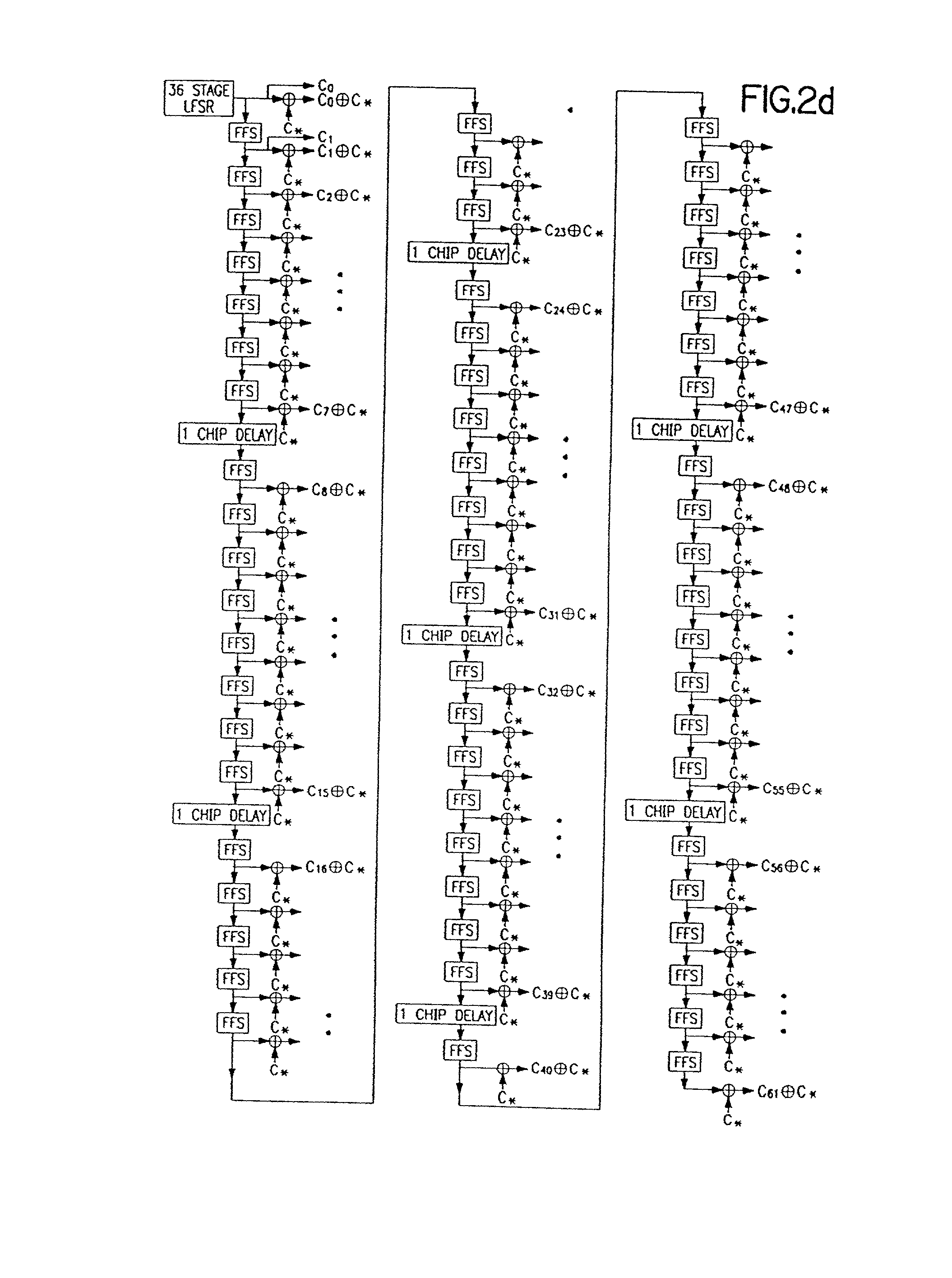
PN generators for spread spectrum communications systems
InactiveUS6661833B1Random number generatorsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemMobile station
Techniques to improve the acquisition process in a spread spectrum environment. The signals from different CDMA systems are spread with different sets of PN sequences, with the PN sequences in each set being uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the other sets. By using uncorrelated PN sequences, the likelihood of detecting a pilot signal from an undesired system is reduced or minimized, and the mean time to acquisition of the pilot signal from the desired system is improved. The mobile station can attempt to acquire the pilot signal by processing the received signal with a first set of PN sequences corresponding to a first hypothesis of the particular signal being acquired. If acquisition of the pilot signal fails, a second set of PN sequences corresponding to a second hypothesis is selected and used to process the received signal. The PN sequences in the second set are uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the first set. The PN sequences for the first set can be generated based on the characteristic polynomials defined by IS-95-A, and the PN sequences for the second set can be the reverse of the PN sequences for the first set.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
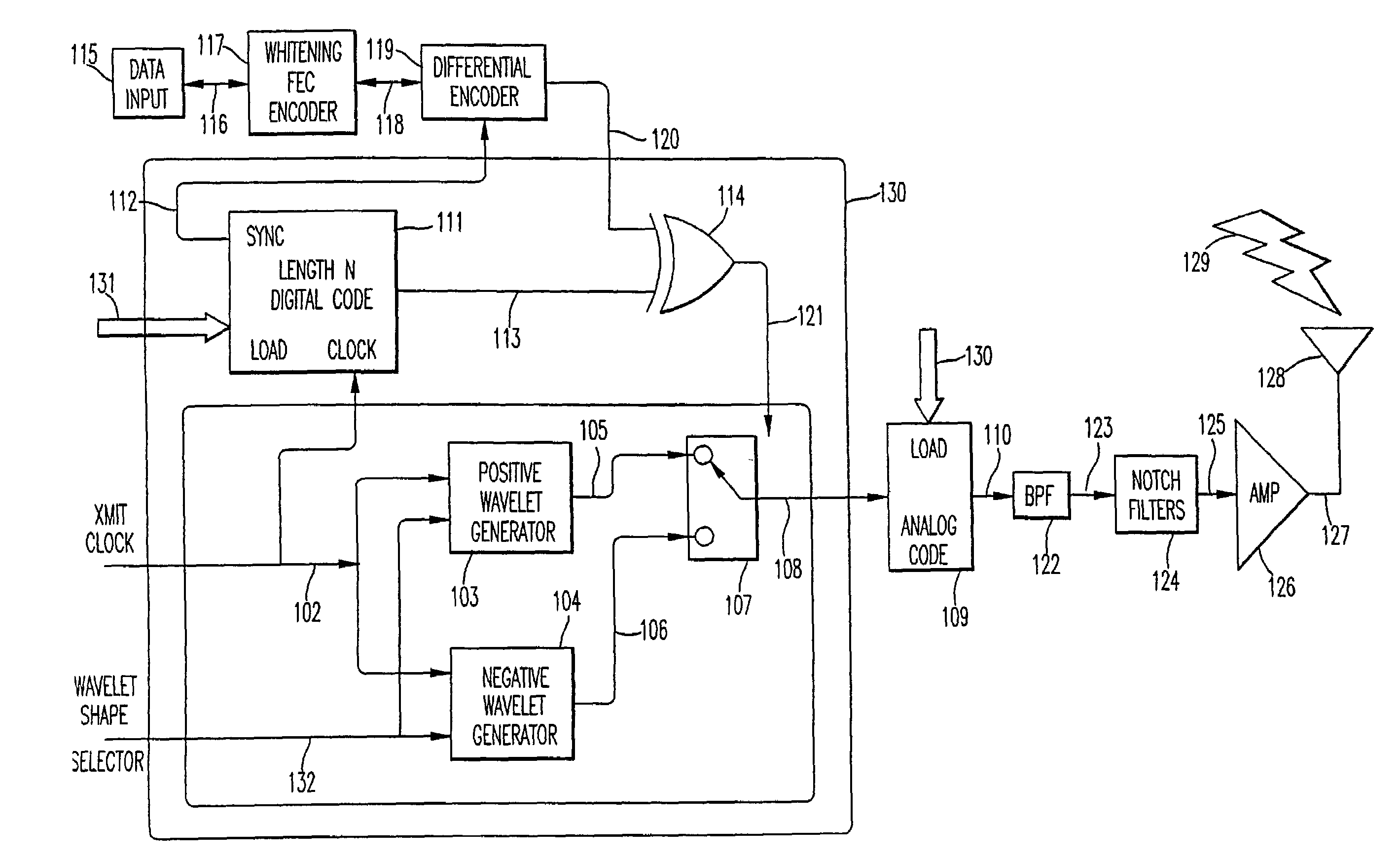
Ultra wide bandwidth communications method and system
InactiveUS7280607B2For signal receptionImprove communication efficiencyModulated carrier system with waveletsCode conversionMultipath interferencePicosecond
An ultra wide bandwidth, high speed, spread spectrum communications system uses short wavelets of electromagnetic energy to transmit information through objects such as walls or earth. The communication system uses baseband codes formed from time shifted and inverted wavelets to encode data on a RF signal. Typical wavelet pulse durations are on the order of 100 to 1000 picoseconds with a bandwidth of approximately 8 GHz to 1 GHz, respectively. The combination of short duration wavelets and encoding techniques are used to spread the signal energy over a an ultra wide frequency band such that the energy is not concentrated in any particular narrow band (e.g. VHF: 30-300 MHz or UHF: 300-1000 MHz) and is not detected by conventional narrow band receivers so it does not interfere with those communication systems. The use of pulse codes composed of time shifted and inverted wavelets gives the system according to the present invention has a spatial resolution on the order of 1 foot which is sufficient to minimize the negative effects of multipath interference and permit time domain rake processing.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
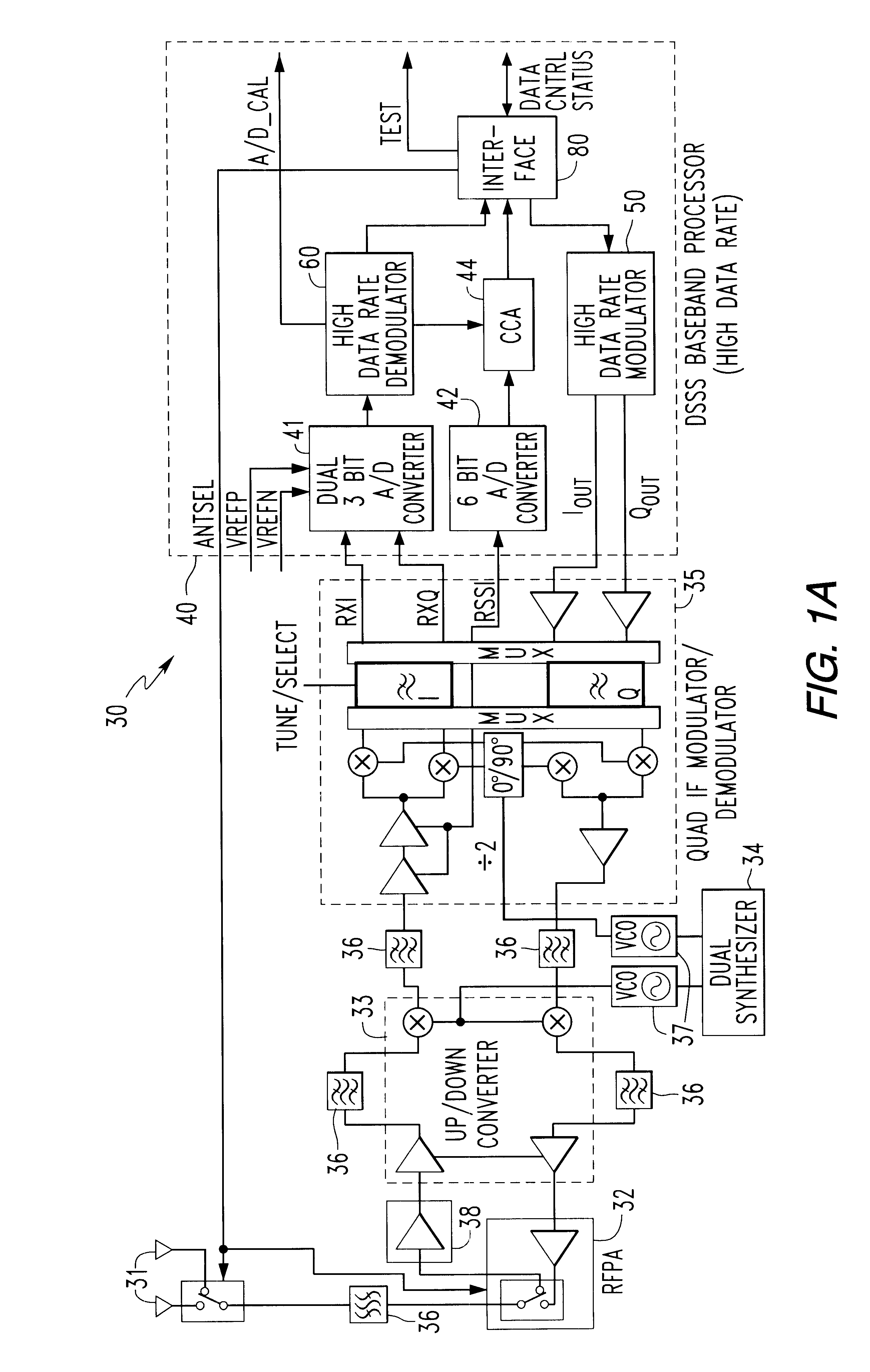
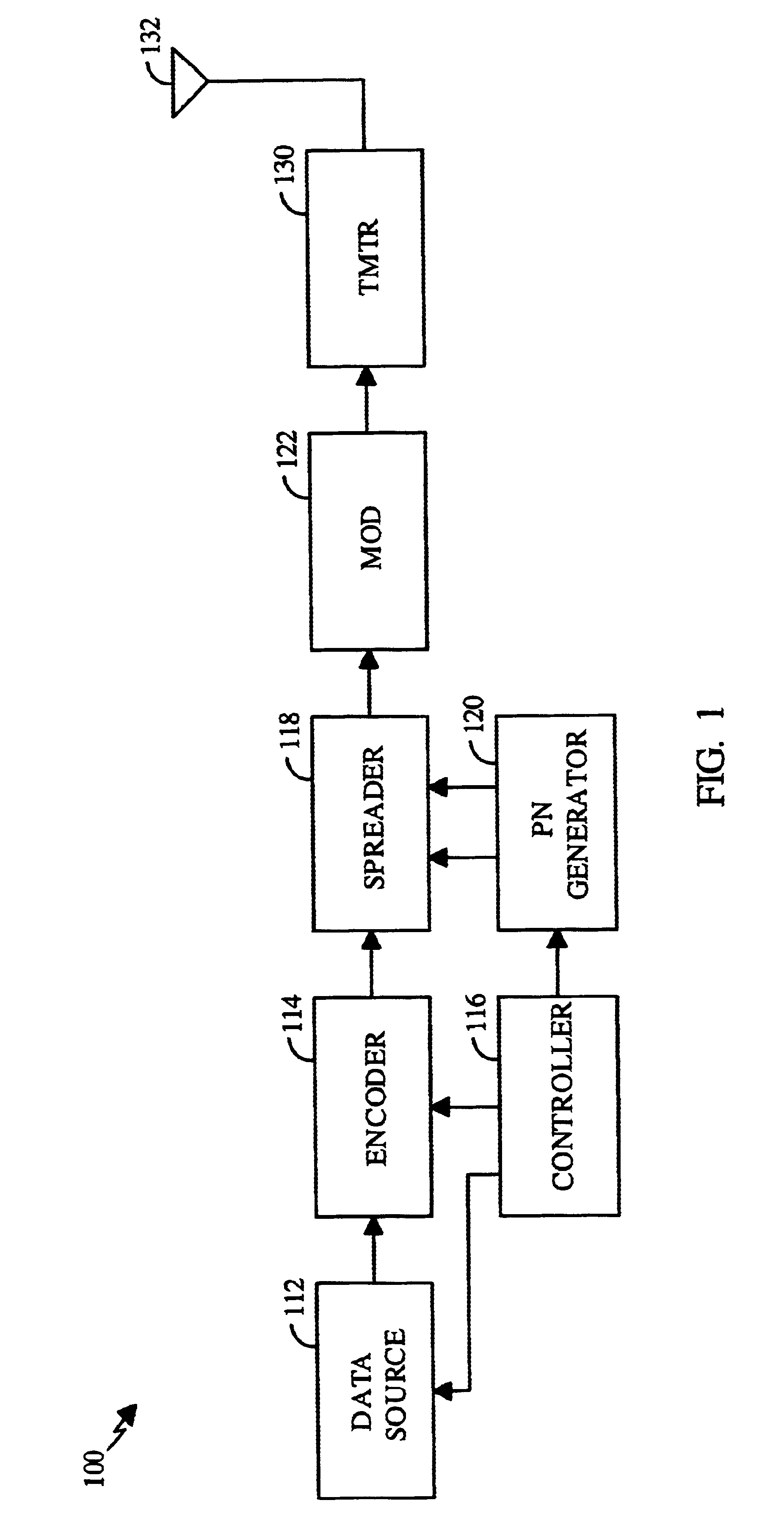
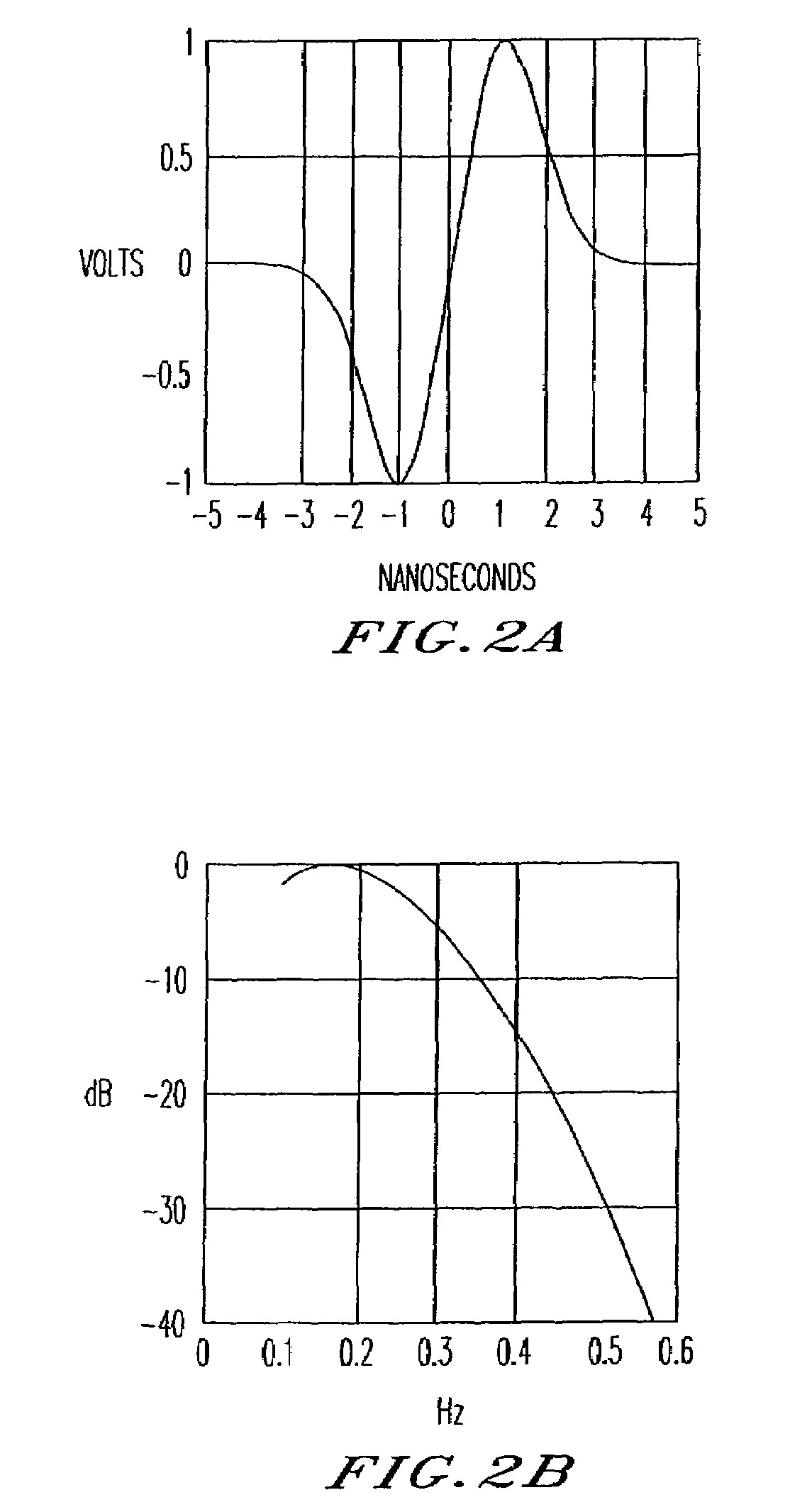
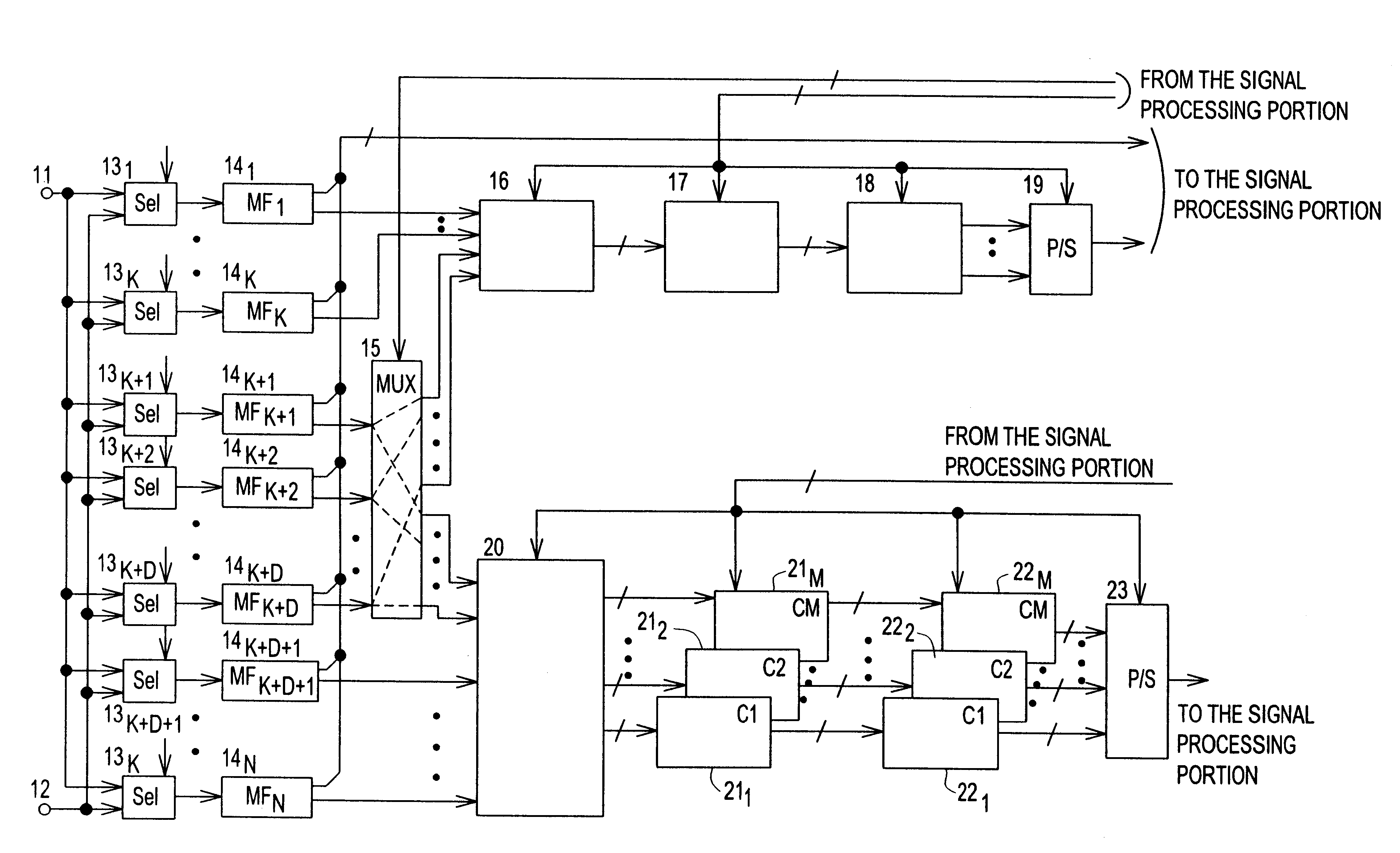
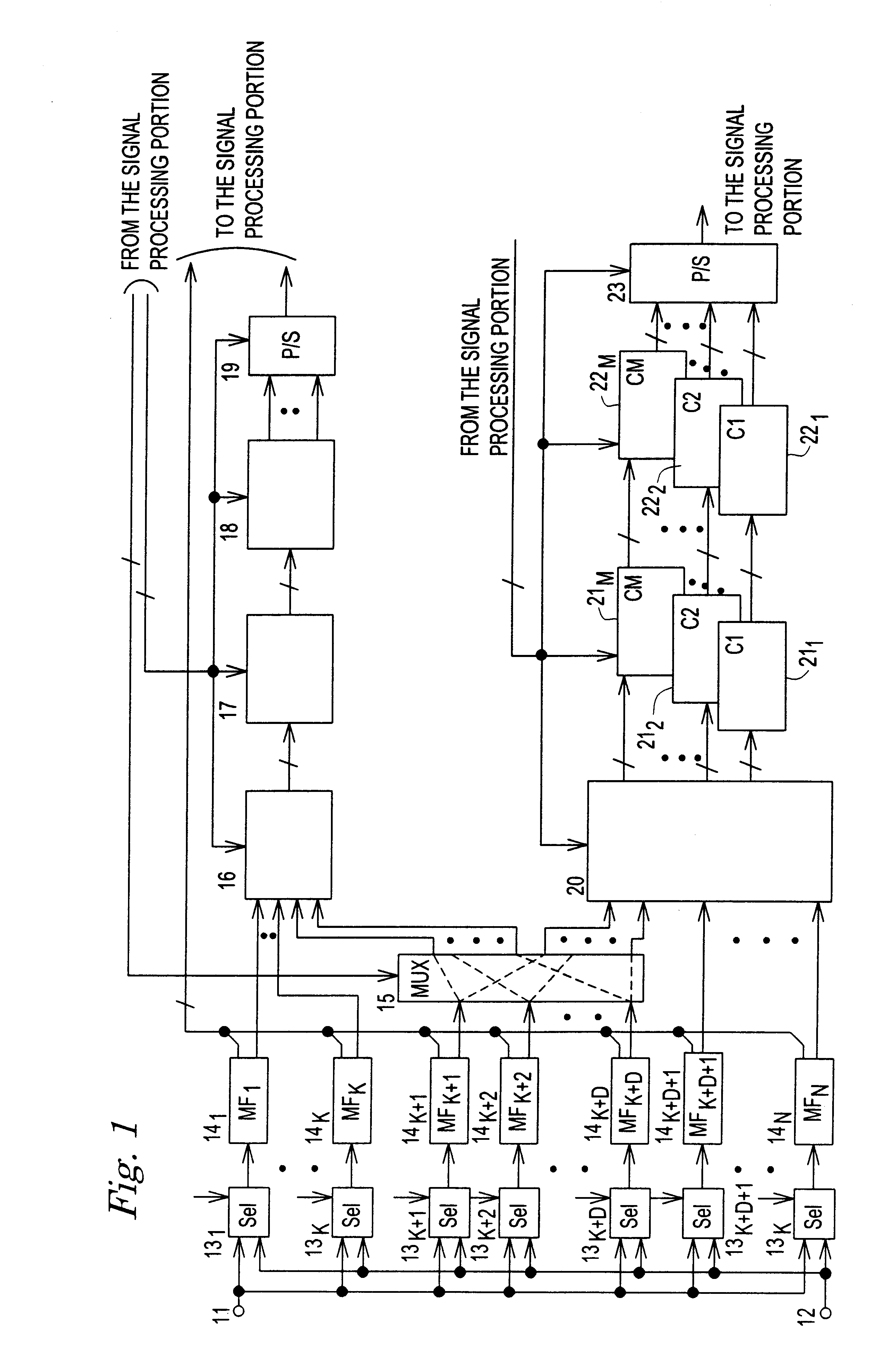
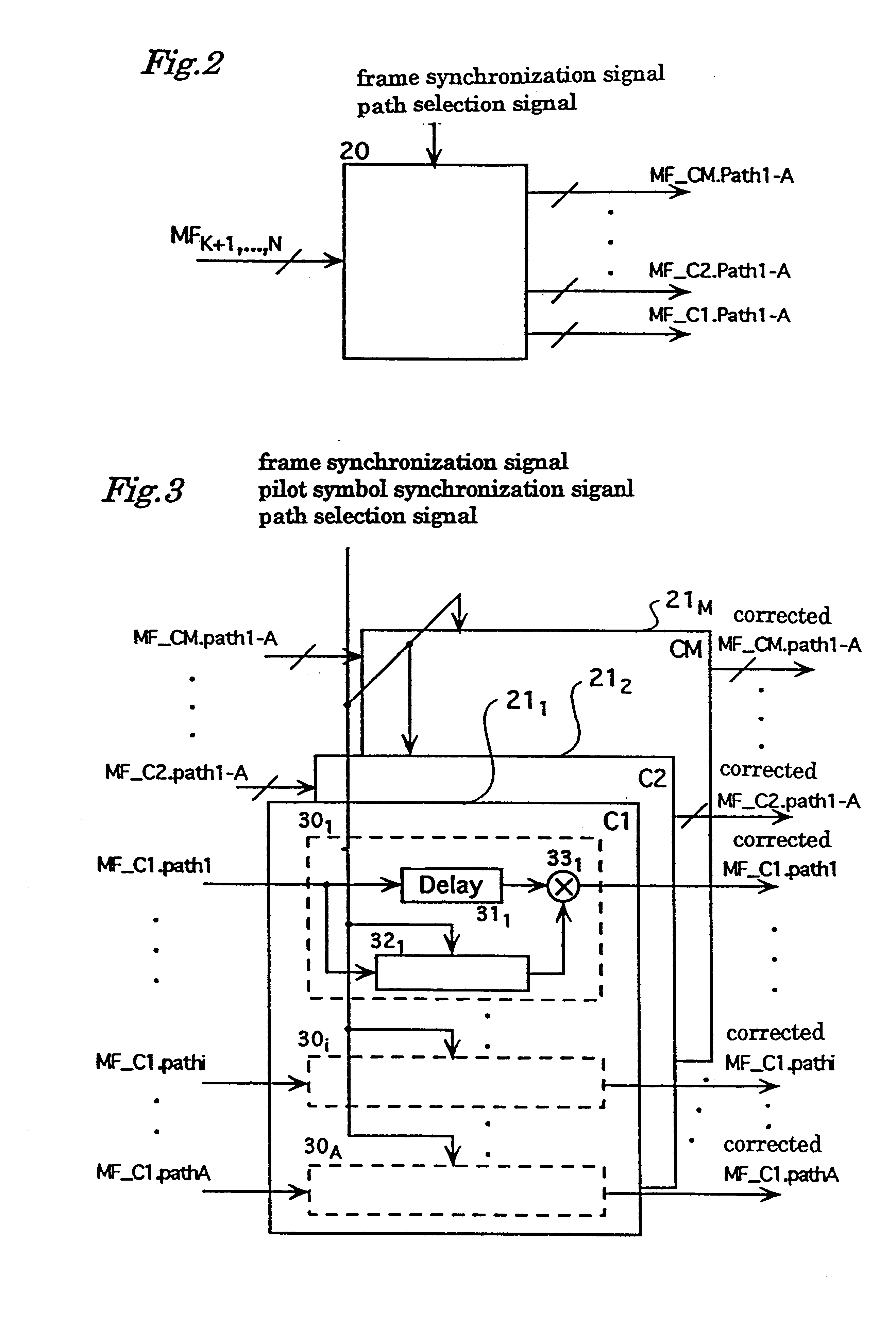
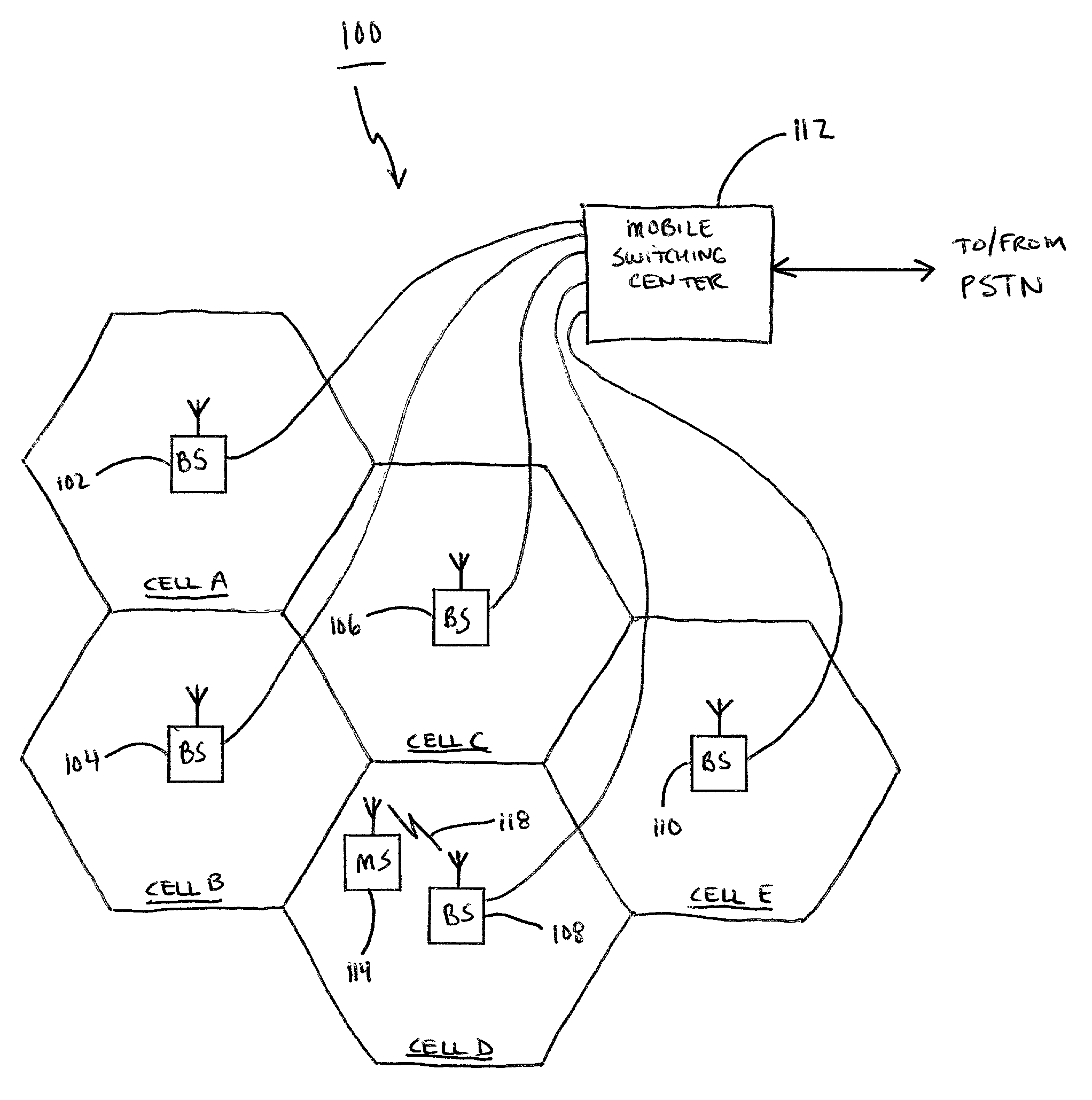
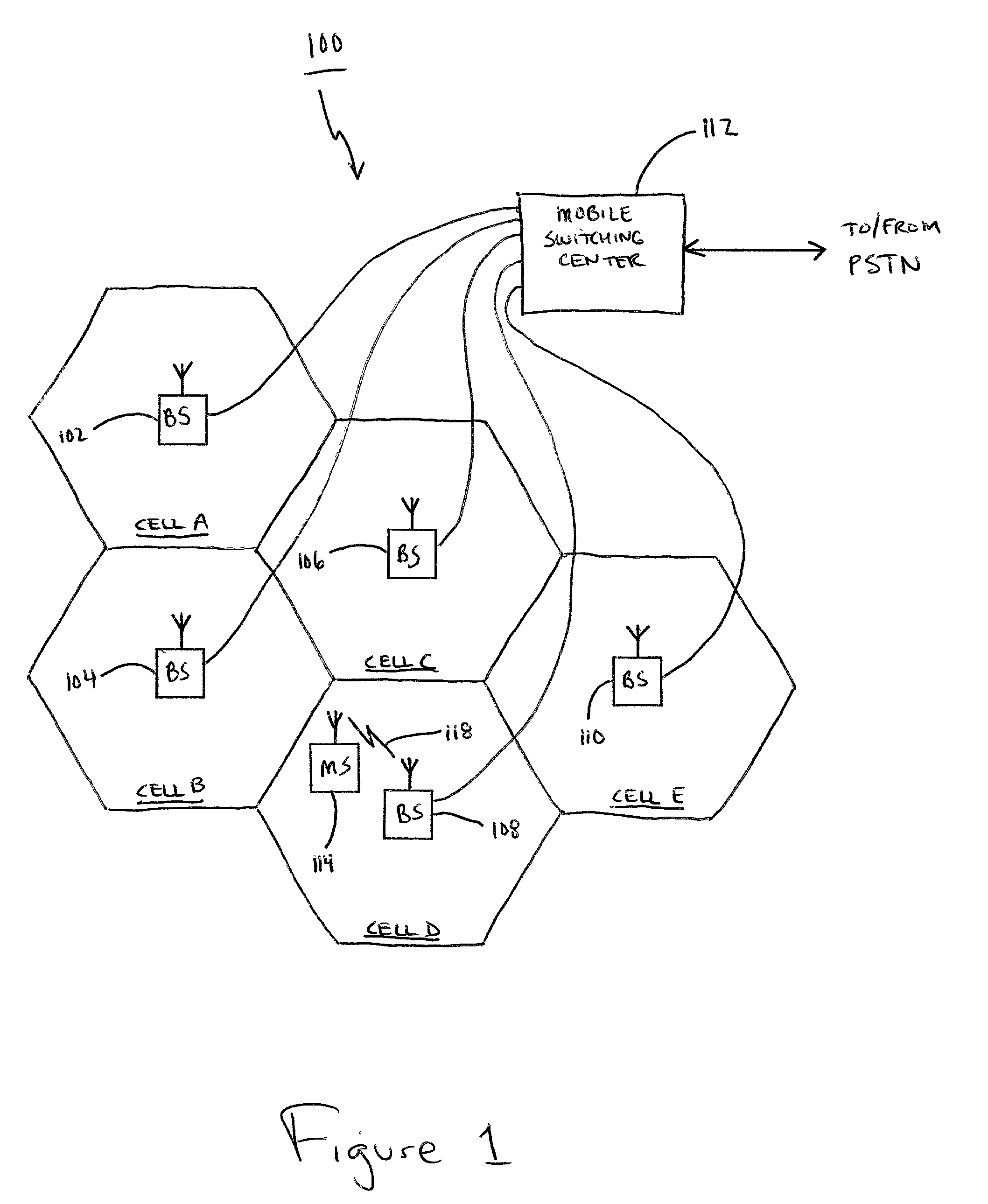
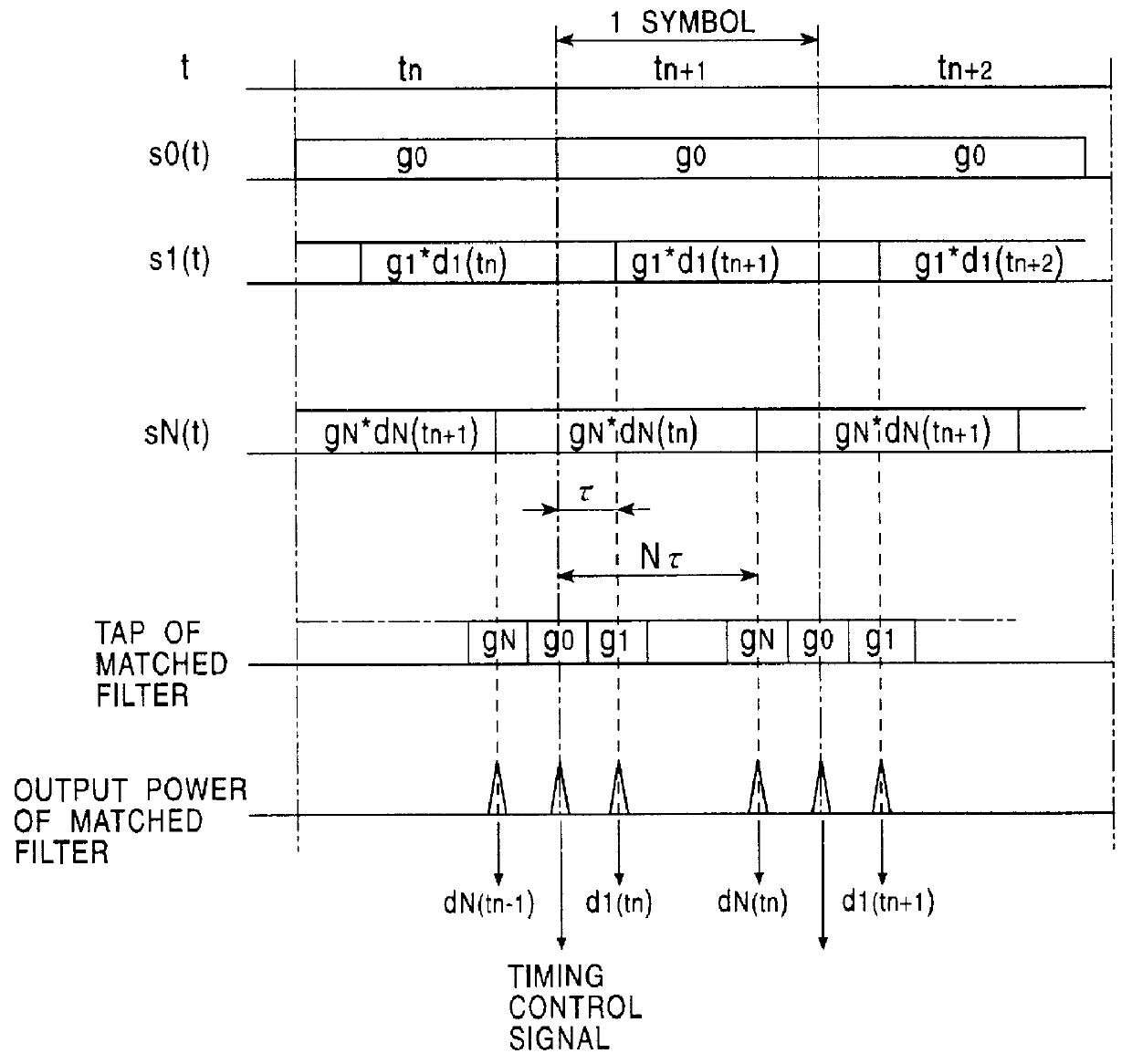
Spread spectrum communication system
A receiver for spread spectrum communication system receives a traffic channel and common control channel by a plurality of matched filters at least one of which is selectively available for the traffic or the common control channel. At the initial acquisition, a plurality of matched filters are used for receiving the common control channel. At the hand-over, a plurality of matched filters are used to receive traffic channels of the current base station and the base stations in the adjacent cells.
Owner:DAITA FRONTIER FUND +1
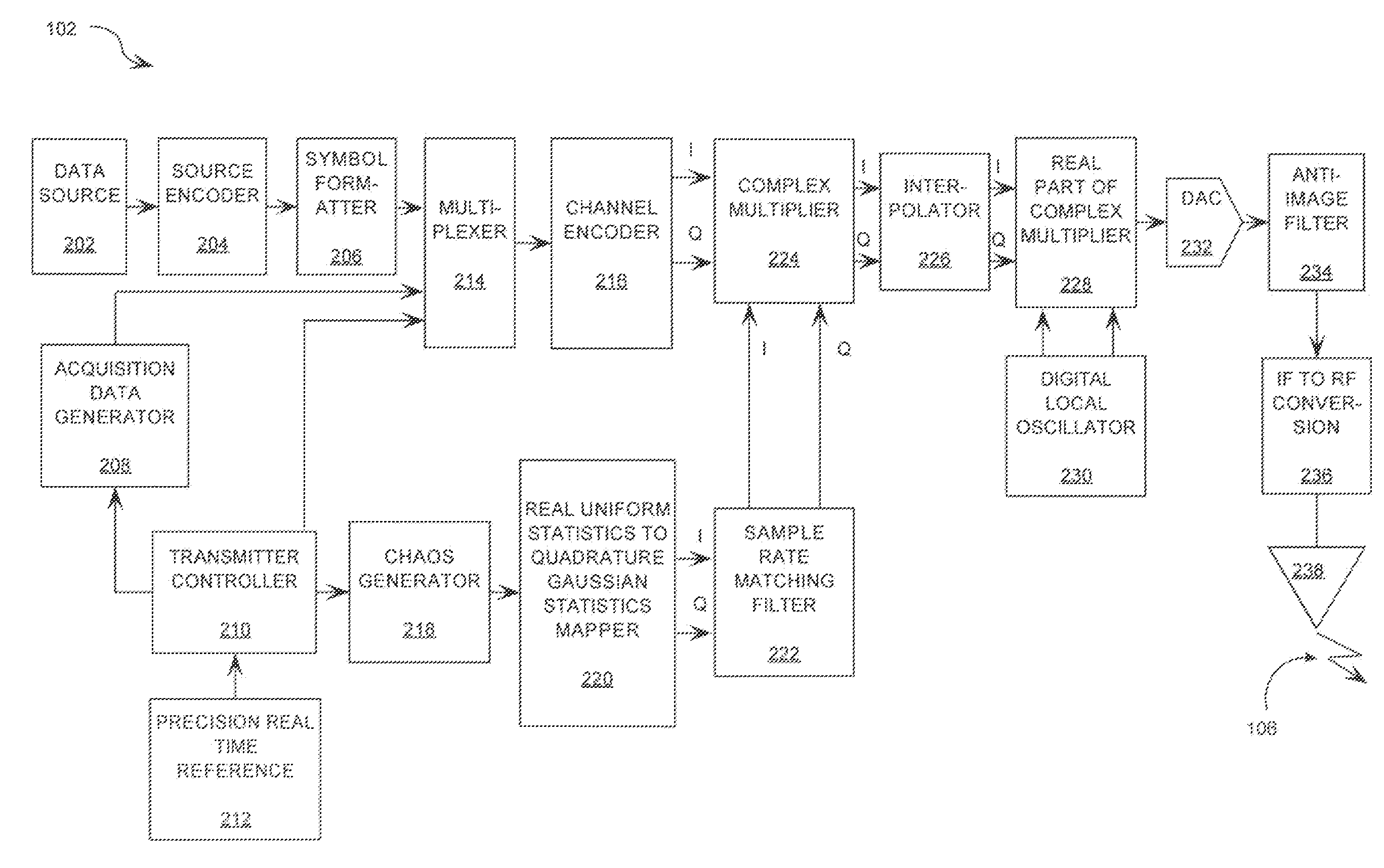
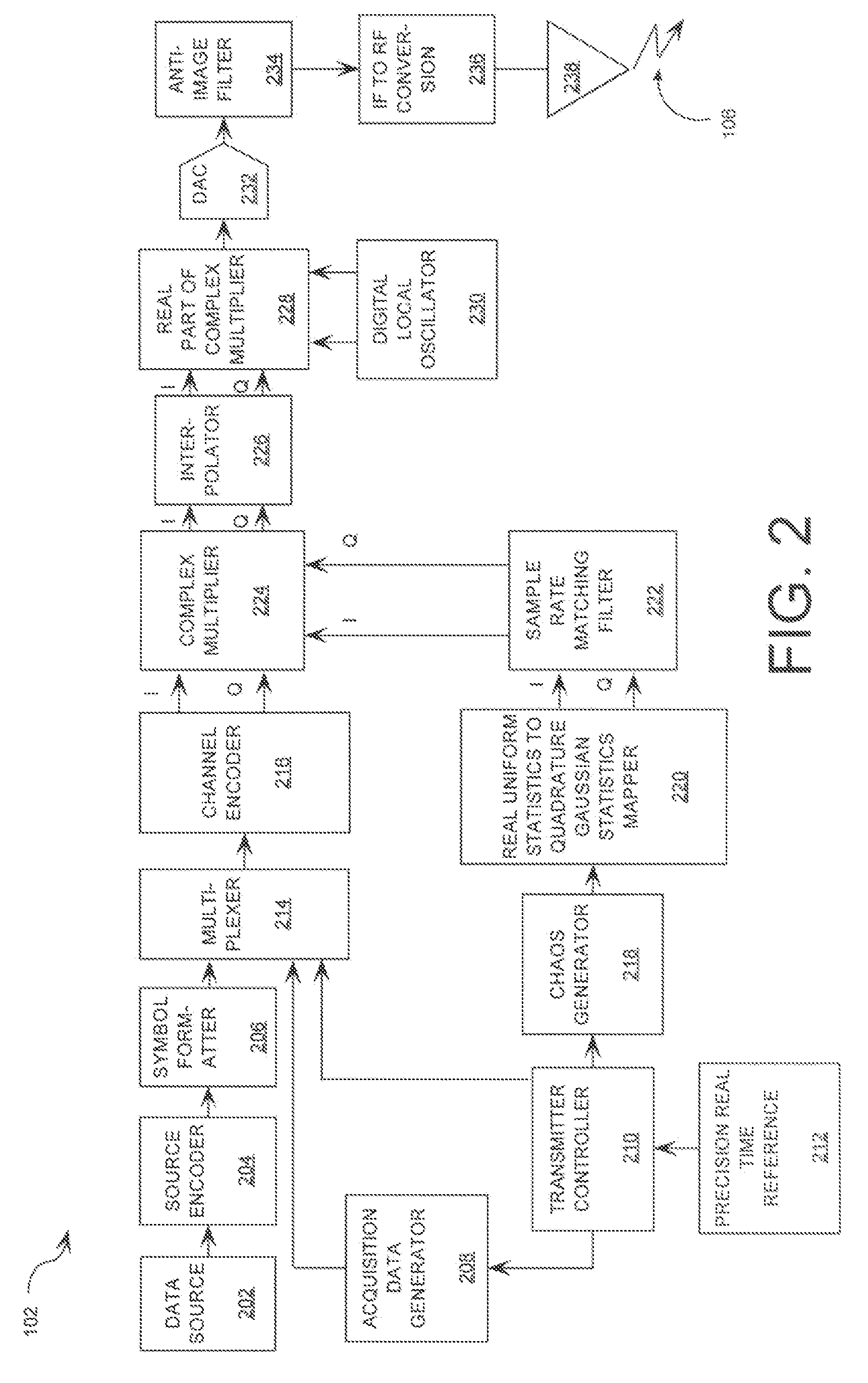
Spread Spectrum Communications System and Method Utilizing Chaotic Sequence
ActiveUS20080304666A1Minimize timing difference uncertaintyMinimize the differenceMultiplex code generationSecuring communicationCommunications systemNumbering system
A method is provided for generating a coherent chaotic sequence spread spectrum communications system. The method includes phase modulating a carrier with information symbols. The method also includes generating a string of discrete time chaotic samples. The method further includes modulating the carrier in a chaotic manner using the string of discrete time chaotic samples. Each of the discrete time chaotic samples has a shorter sample time interval than the duration of the information symbols. The generating step includes selecting a plurality of polynomial equations. The generating step also includes using residue number system (RNS) arithmetic operations to respectively determine solutions for the polynomial equations. The solutions are iteratively computed and expressed as RNS residue values. The generating step further includes determining a series of digits in the weighted number system based on the RNS residue values. The method further includes synchronizing the chaos generated at the receiver with that generated at the transmitter without periodic transfer of state update information.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
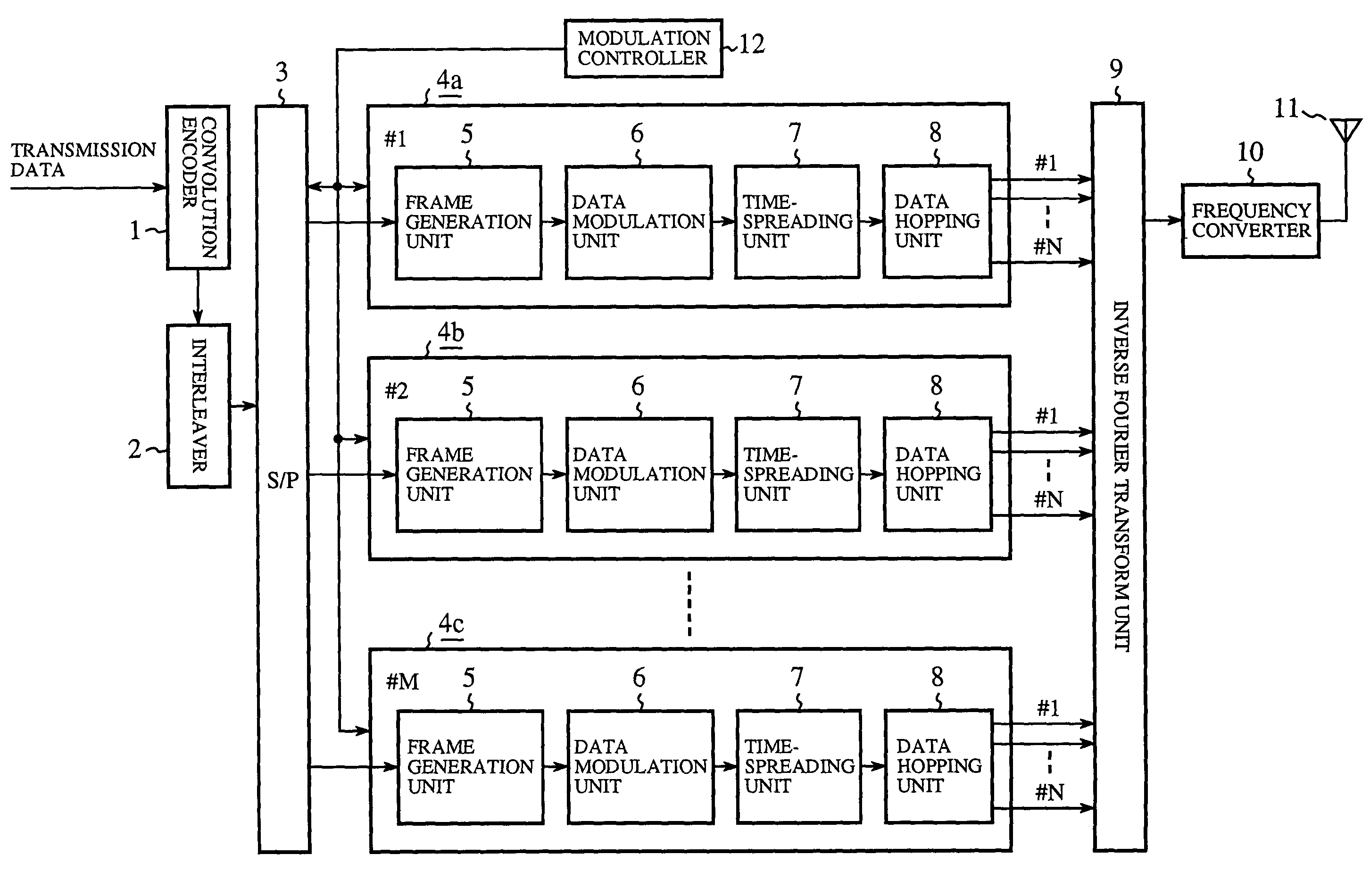
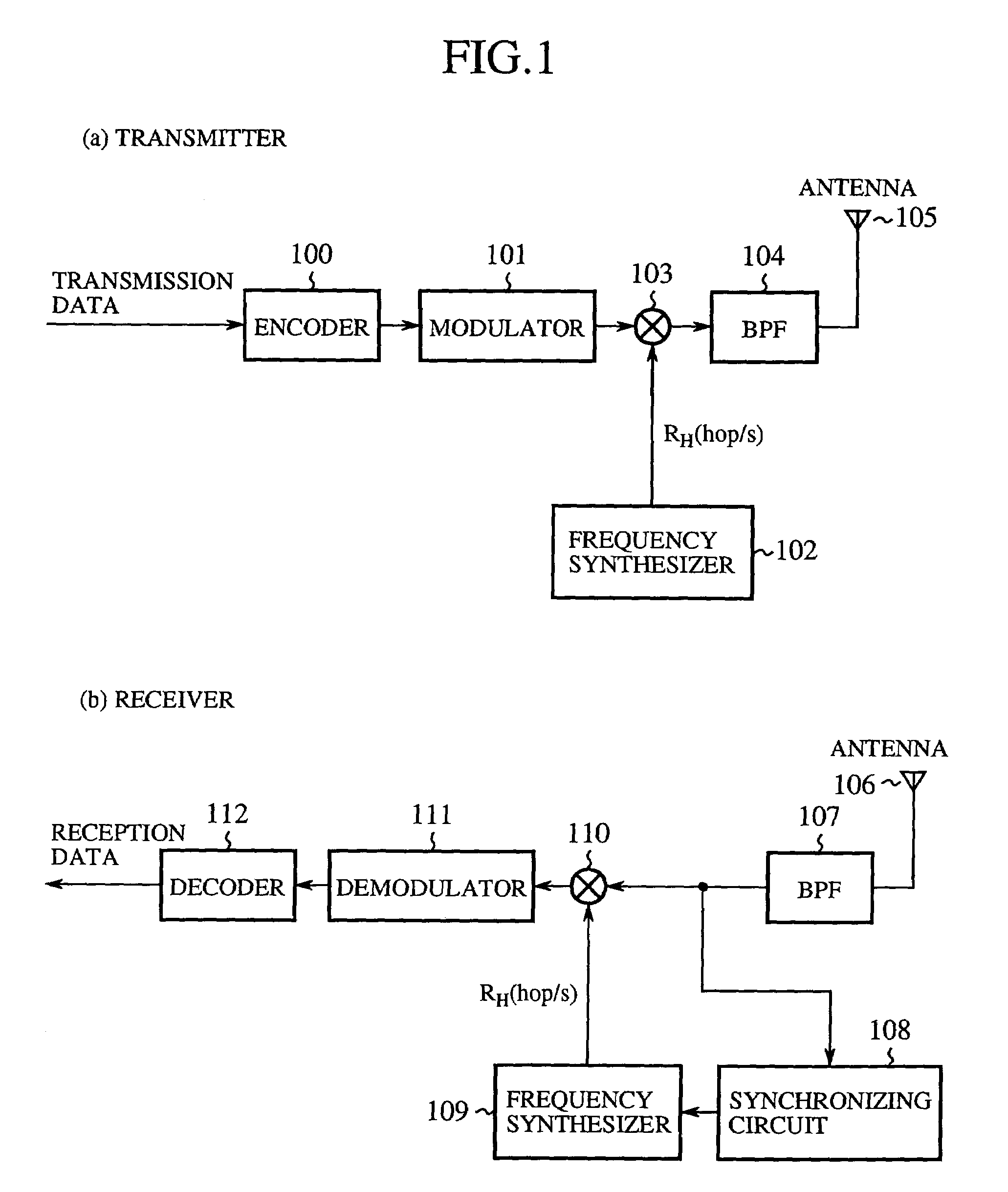
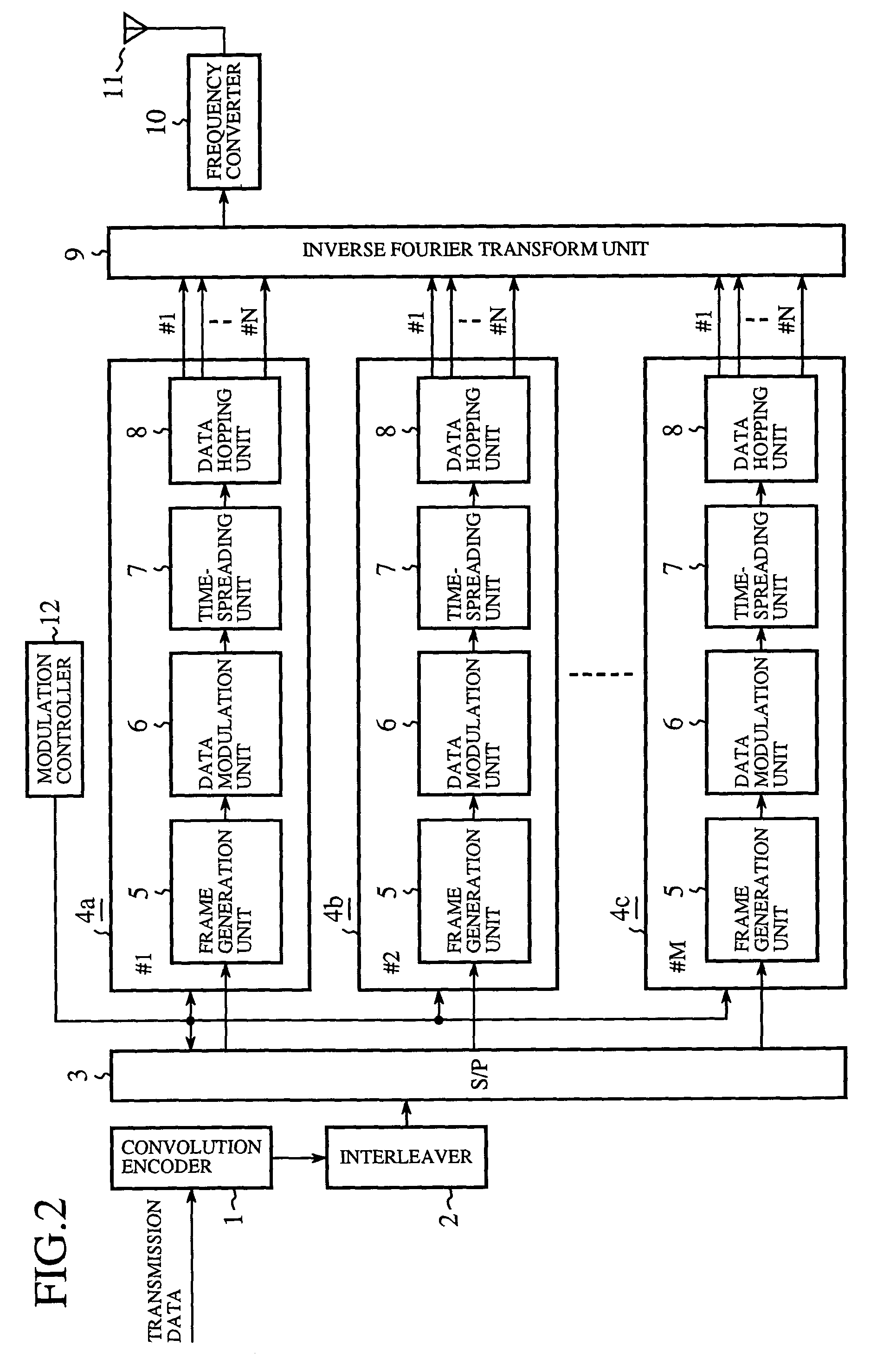
Transmitter and receiver for spread-spectrum communication system, and modulation and demodulation methods thereof
InactiveUS7272162B2Reduce data transfer rateImprove communication qualityError preventionRadio transmissionFrequency-hopping spread spectrumData selection
A data hopping device is provided with a hopping generation unit and a data selection unit, the hopping pattern generation unit generating a predetermined hopping pattern, and the data selection unit outputs a plurality of subcarrier transmission signals corresponding to respective subcarriers, by receiving transmission data and outputting only the data carried in the subcarrier designated by the hopping pattern as the subcarrier transmission signal, while maintaining the other subcarrier transmission signals at a zero output level. An inverse Fourier transform device subjects the entirety of subcarrier reception signals output from the data selection unit to inverse Fourier transform and outputs frequency-hopped spread-spectrum transmission signals.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Capacity management method for a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Apparatus for initial power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020141478A1Save capacityInterference minimizationEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationModem deviceSystem capacity
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
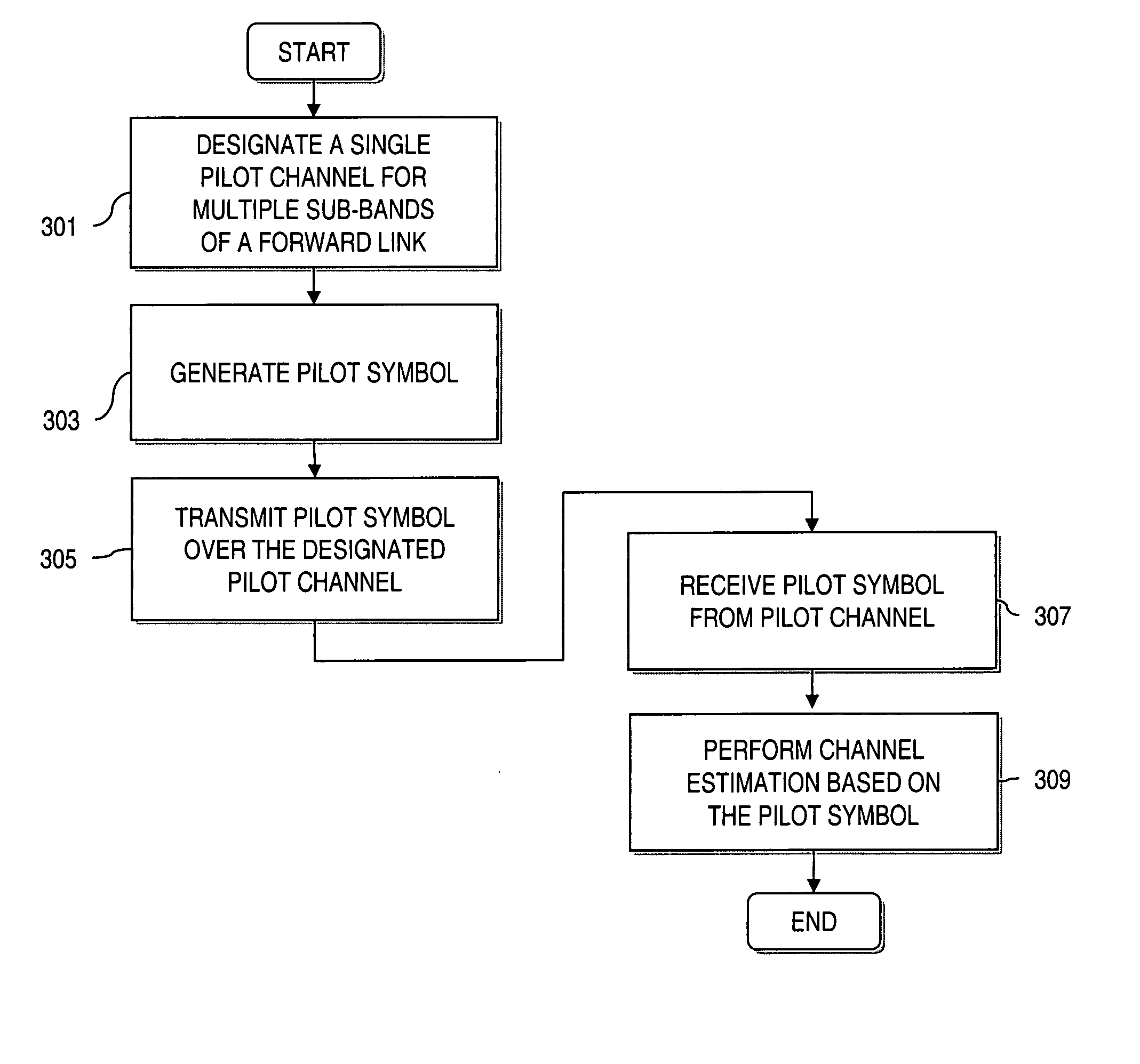
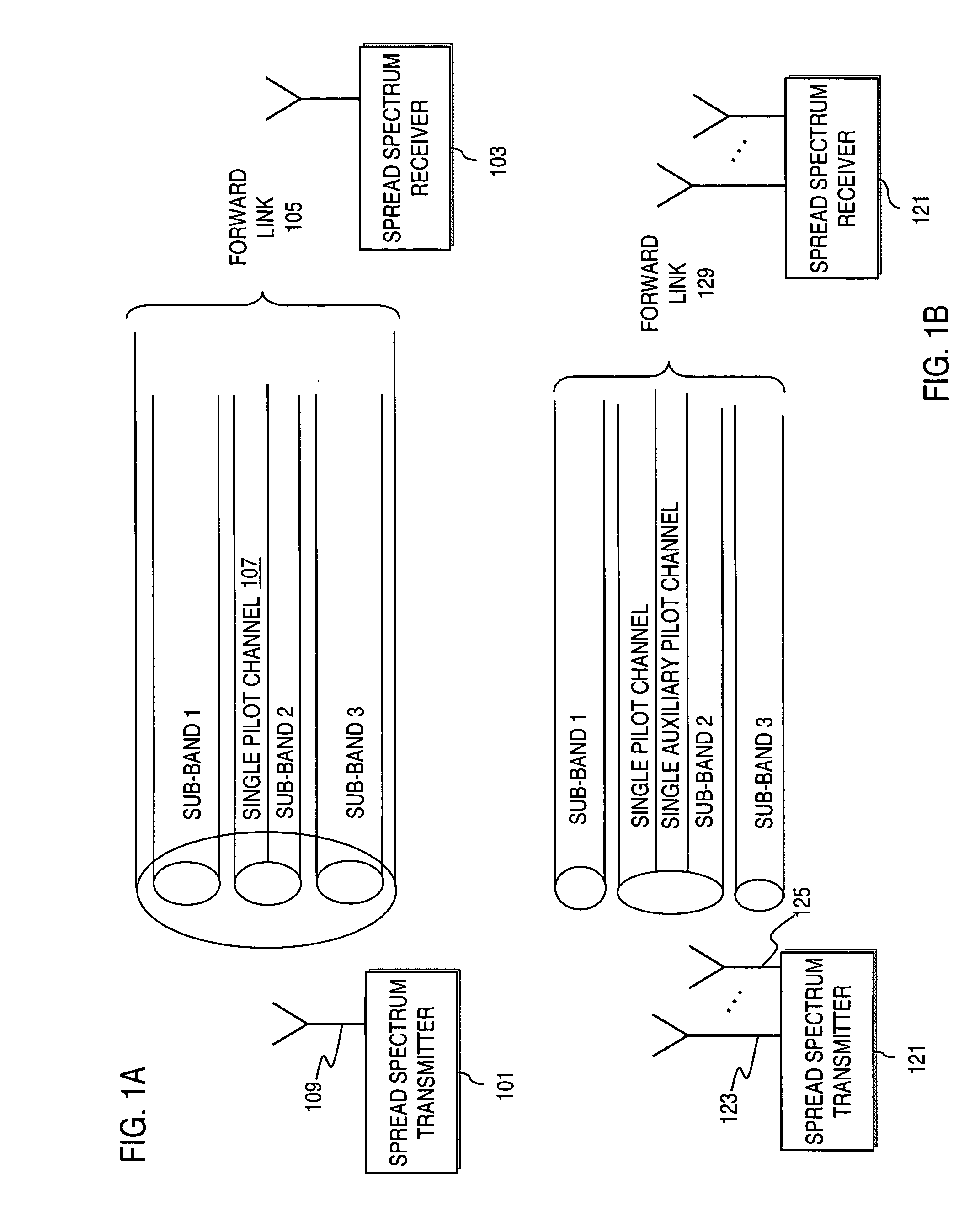
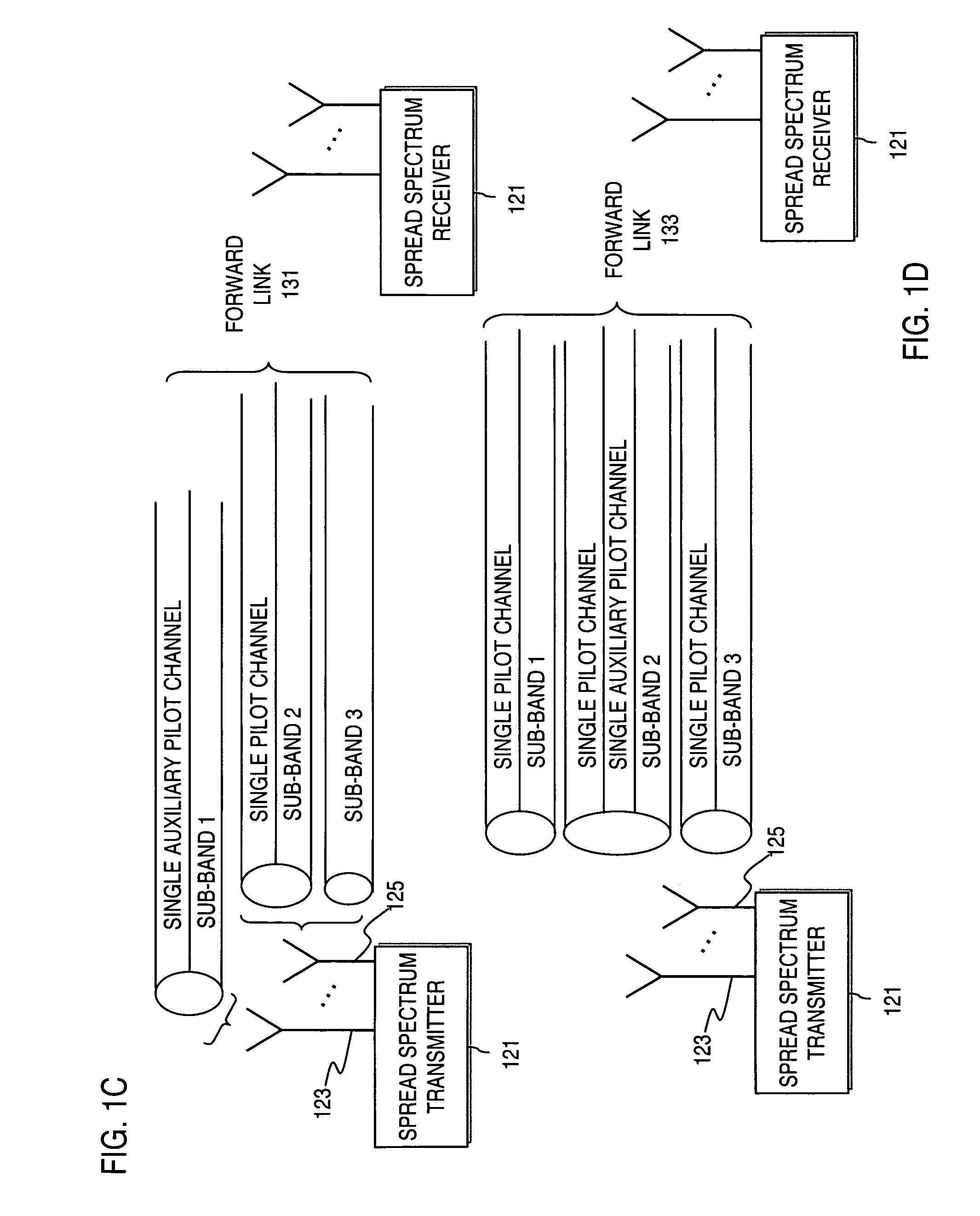
Method and apparatus for providing an efficient pilot scheme for channel estimation
InactiveUS20060140289A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTelecommunicationsCommunication link
An approach for utilizing a pilot scheme in a spread spectrum communication system (e.g., Multi Carrier Code Division Multiple Access (MC-CDMA)) is provided. A communications link includes a sub-bands and a single pilot channel that is designated for the sub-bands for channel estimation. Pilot symbols transmitted over the single pilot channel are used to determine a first channel estimate associated with a first one of the sub-bands, and a second channel estimate corresponding to a second one of the sub-bands is derived from the first channel estimate.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System and method for performing code and frequency channel selection for combined CDMA/FDMA spread spectrum communication systems
ActiveUS7106707B1Effective distributionMaximizing channel utilizationNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemInterference factor
A system and method for maximizing channel utilization by efficiently allocating codes and frequencies based on estimated relative interference between subscriber units in a wireless communications network, such as an ad-hoc wireless communications network, in such a way as to minimize multiple access interference. The system and method perform the operations of collecting existing and proposed transmission information between nodes in the network, and calculating a respective interference factor for each existing transmission between certain nodes and each proposed transmission by a transmitting node. The interference factors can be calculated based on, for example, respective distances between certain nodes. The system and method then assign the communications channel configuration, including a frequency channel and code channel, to the transmitting node for communications to other nodes as designated by a minimum of the calculated respective interference factors.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
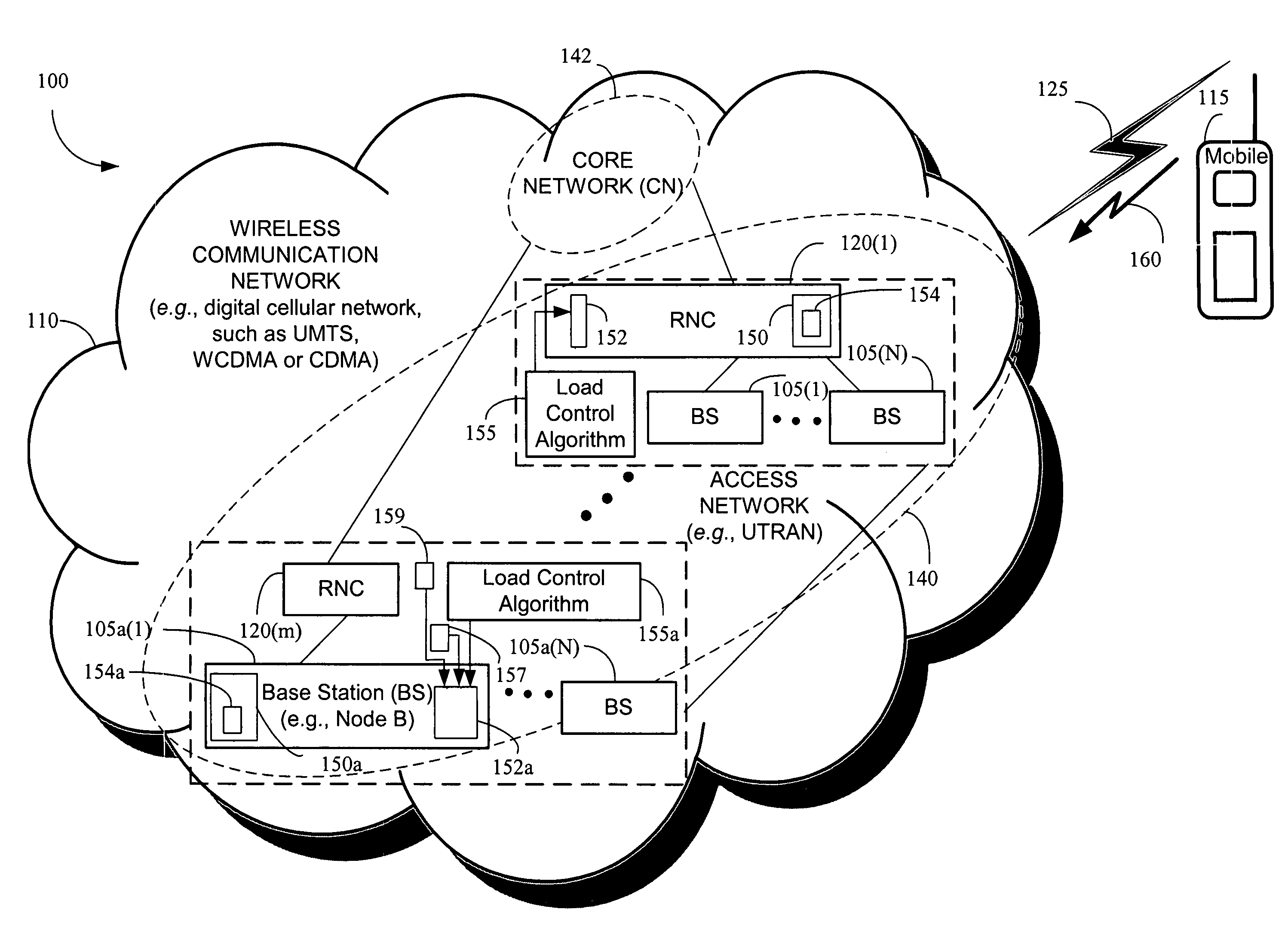
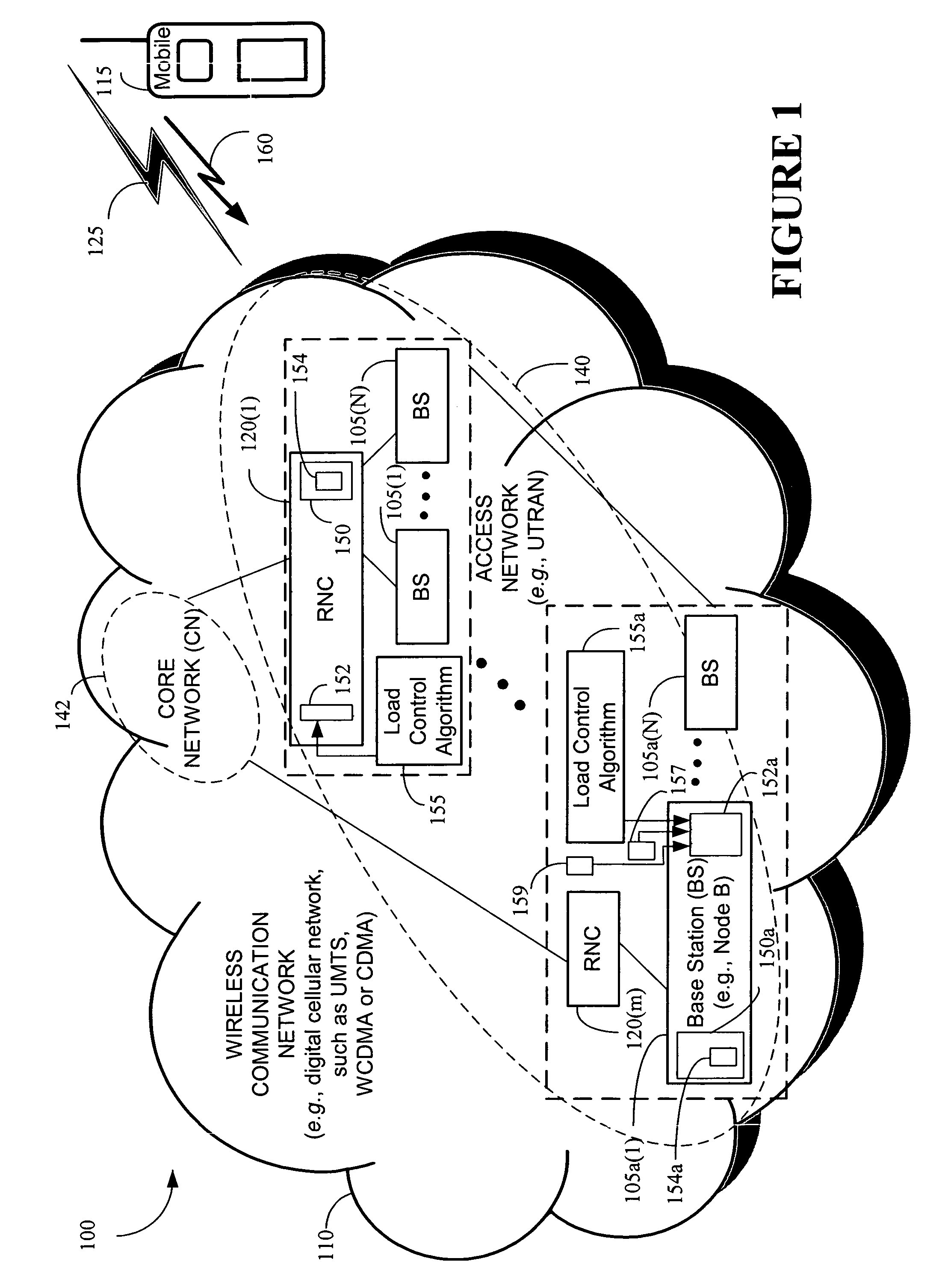
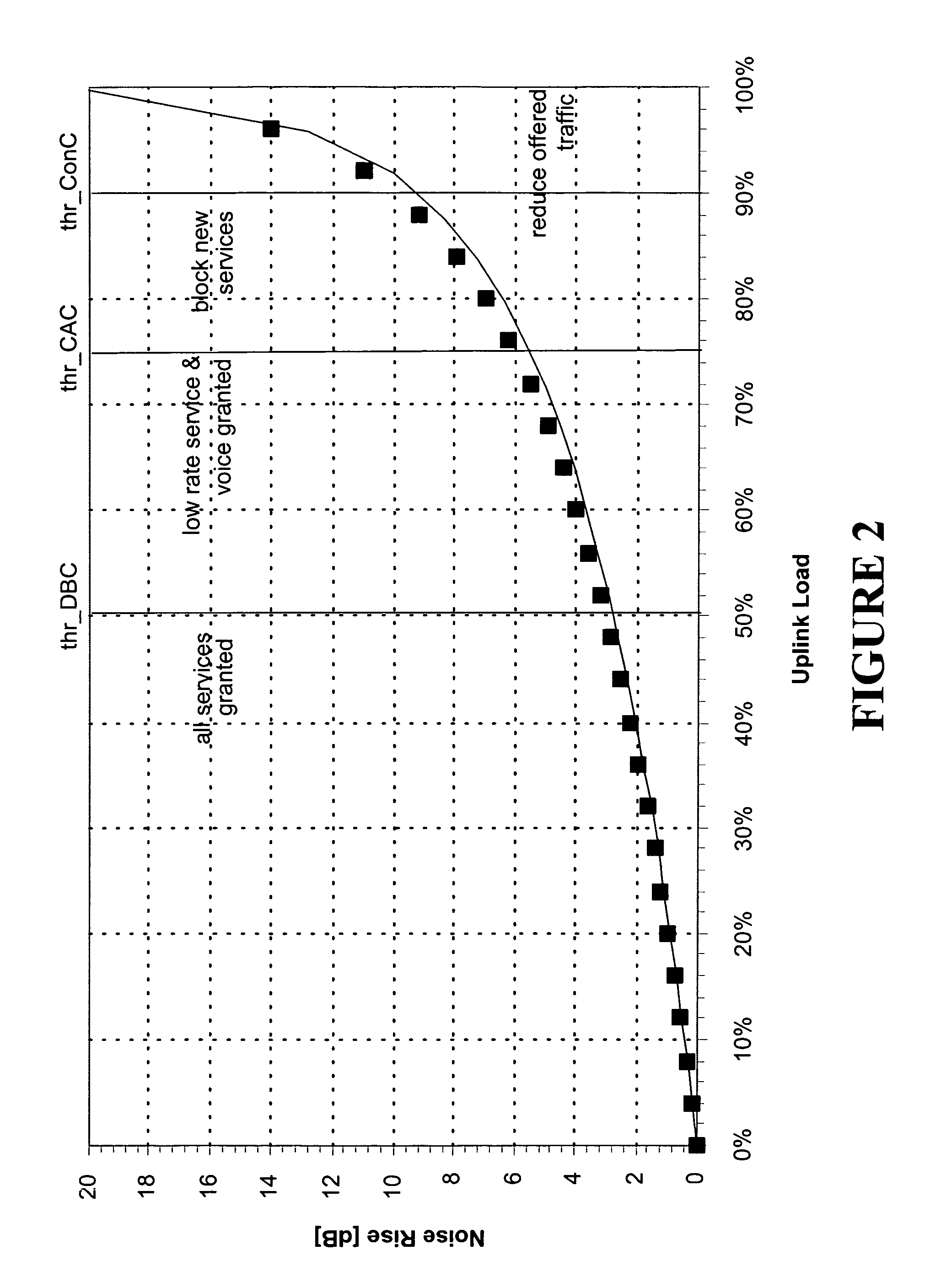
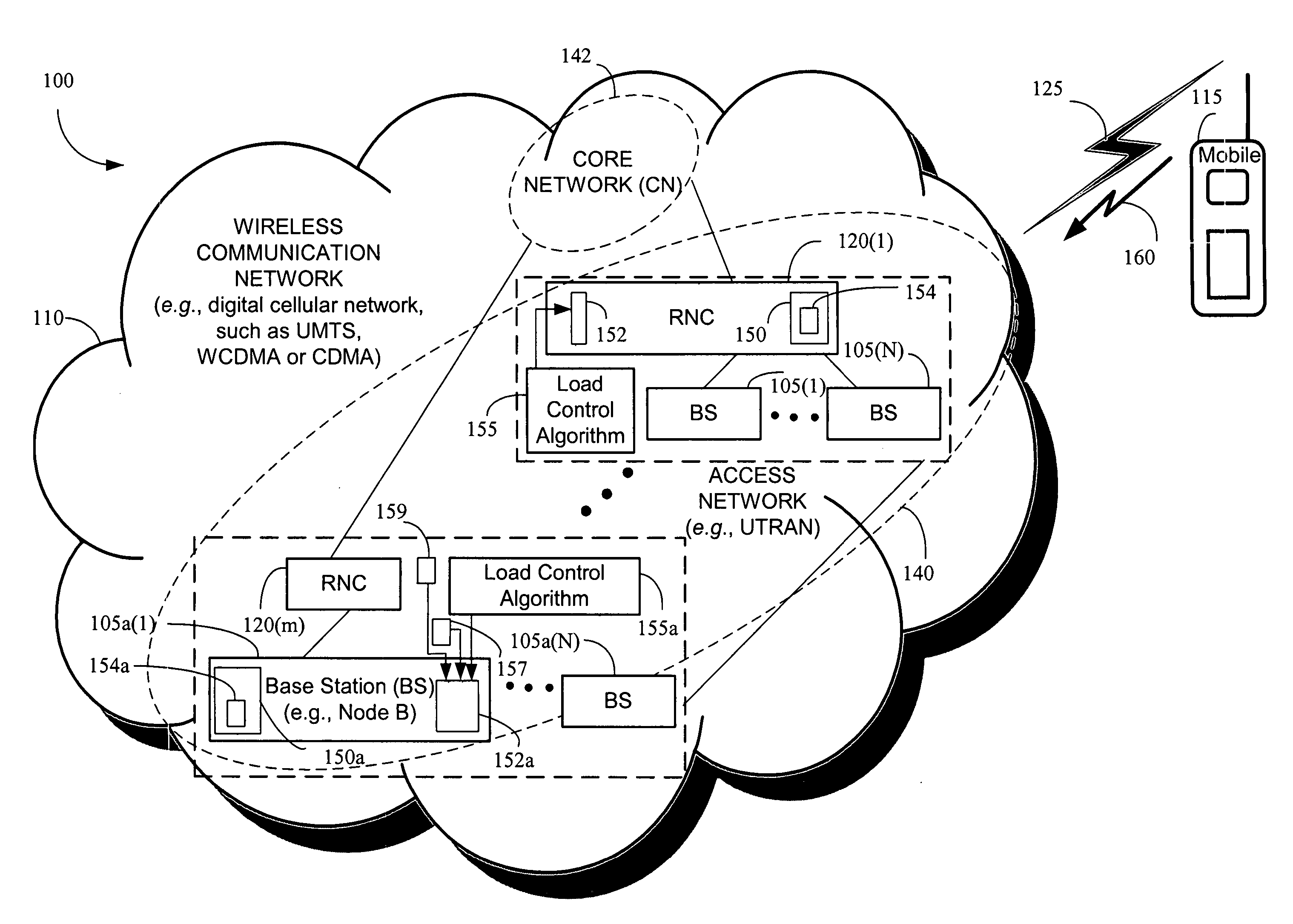
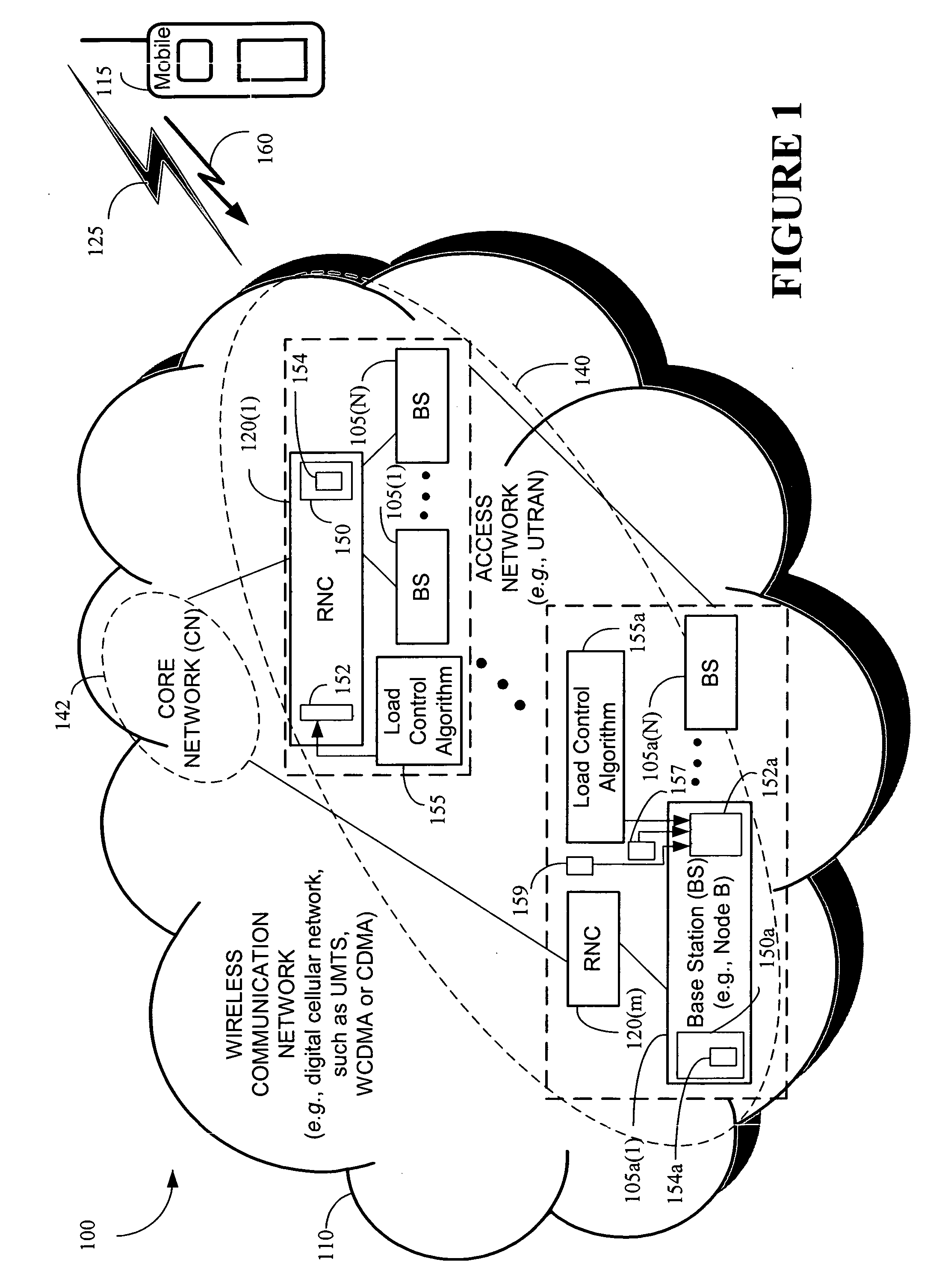
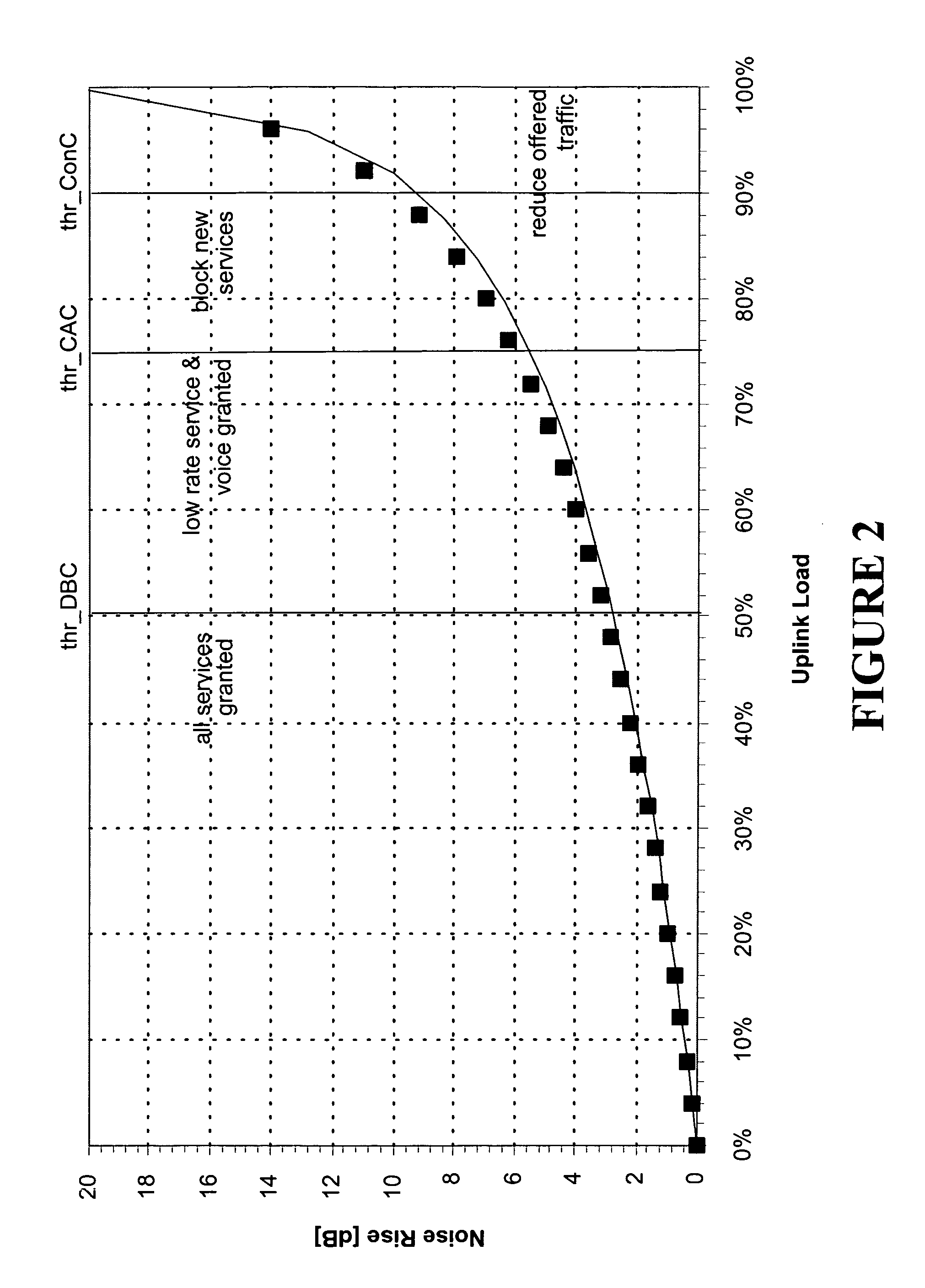
Responding to changes in measurement of system load in spread spectrum communication systems
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
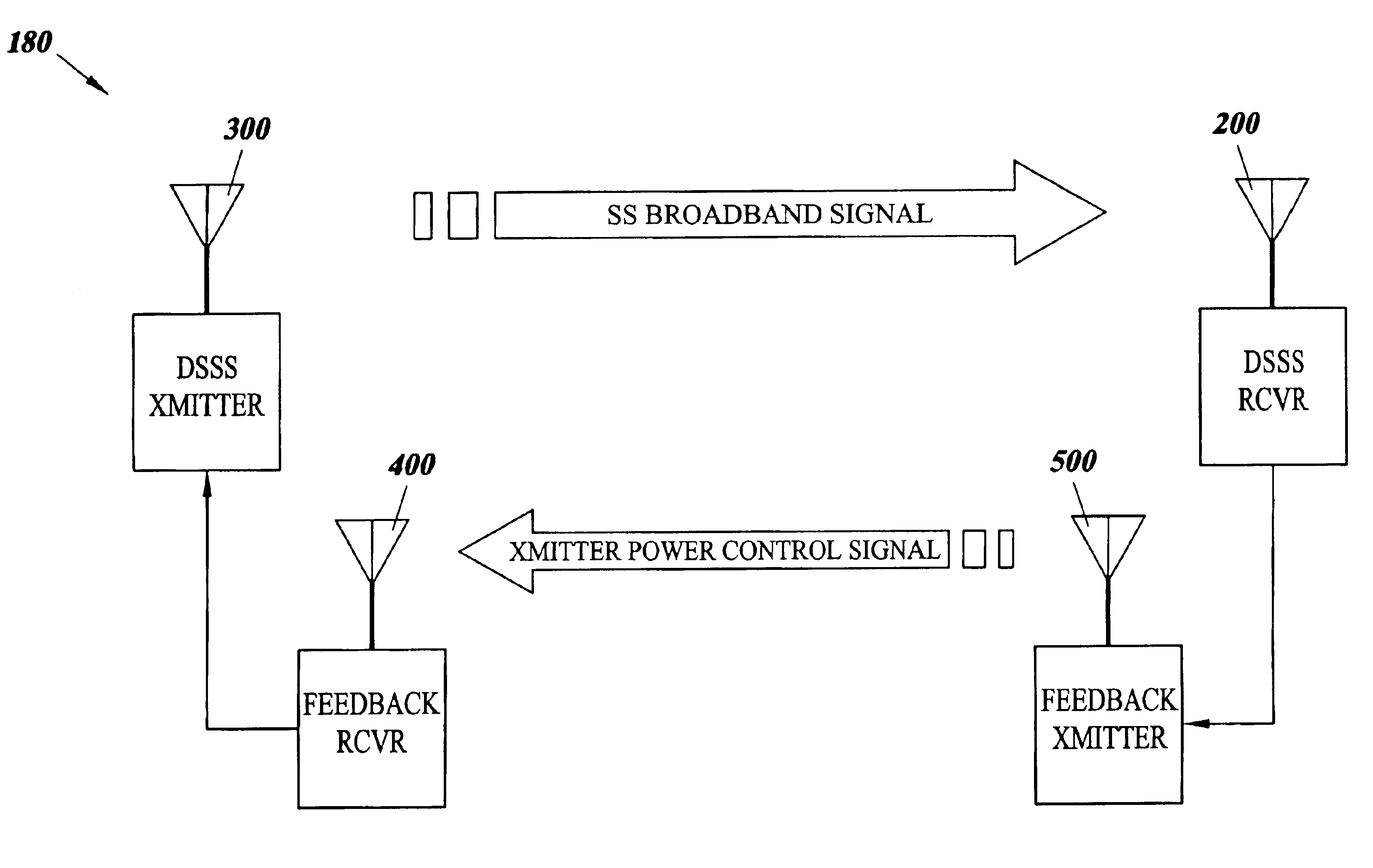
Methods and systems for optimizing signal transmission power levels in a spread spectrum communication system
Owner:UMBRELLA CAPITAL
Technique for improving open loop power control in spread spectrum telecommunications systems
InactiveUS20020183086A1Easy to controlPower managementTransmission control/equalisingMobile stationChannel sounding
A technique for improving open loop power control in spread spectrum telecommunications systems is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the technique is realized by transmitting at least one first access channel probe for a first message from a mobile station to a base station, wherein the transmission power level of each access channel probe in the at least one first access channel probe is increased until a base station acknowledgment is received for a specific access channel probe of the at least one first access channel probe at a first transmission power level. The first transmission power level is then stored at the mobile station. At least one second access channel probe for a second message is then transmitted from the mobile station to the base station, wherein the transmission power level of an initial access channel probe of the at least one second access channel probe for the second message is based upon the first transmission power level.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
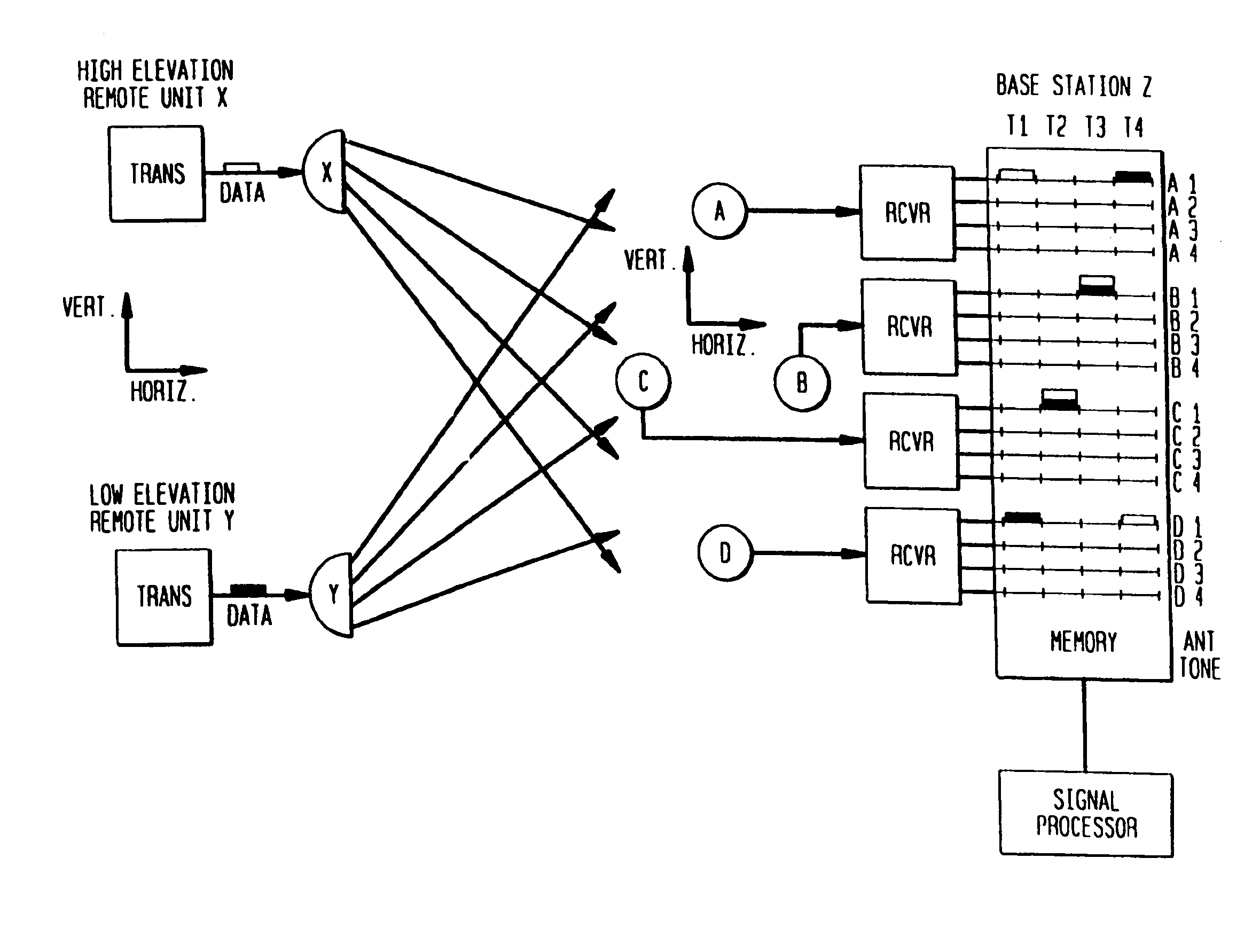
Vertical adaptive antenna array for a discrete multitone spread spectrum communication system
InactiveUS7061969B2Maximized the overall signal-to-interference level of a base station's coverage areaImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex code allocationCommunications systemAntenna element
Two or more antenna elements are arranged in the vertical direction to give vertical spatial adaptivity to a wireless discrete multitone spread spectrum communications system. The system is based on a combination of Discrete Multitone Spread Spectrum (DMT-SS) and multi-element adaptive antenna array technologies. This enables the automatic positioning of a beam in the vertical direction to position nulls where interferers are located on the same azimuth but are separated in elevation.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Adaptive vector correlator for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020036998A1Easy to liftReduce capacityEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationModem deviceSystem capacity
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
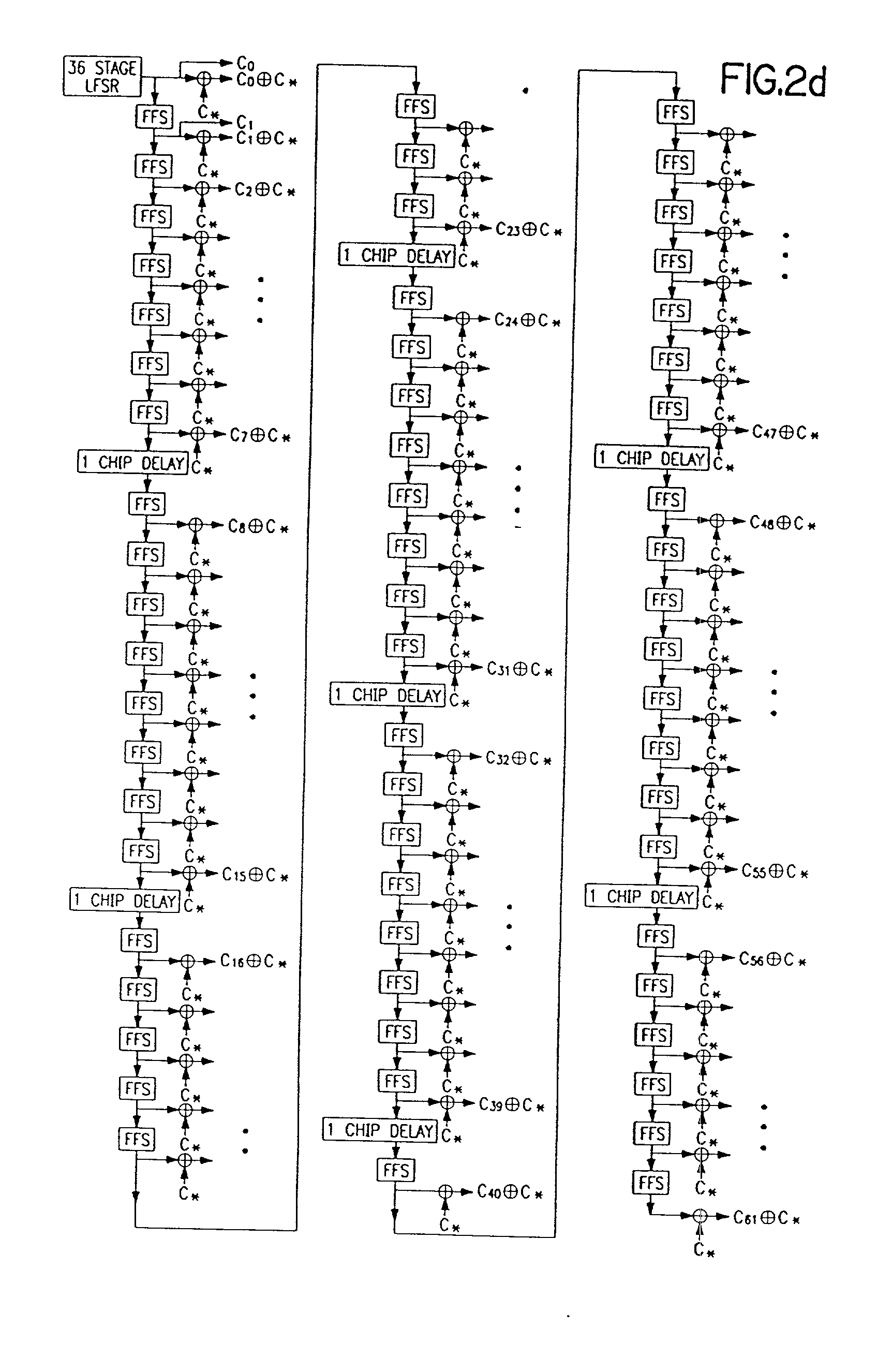
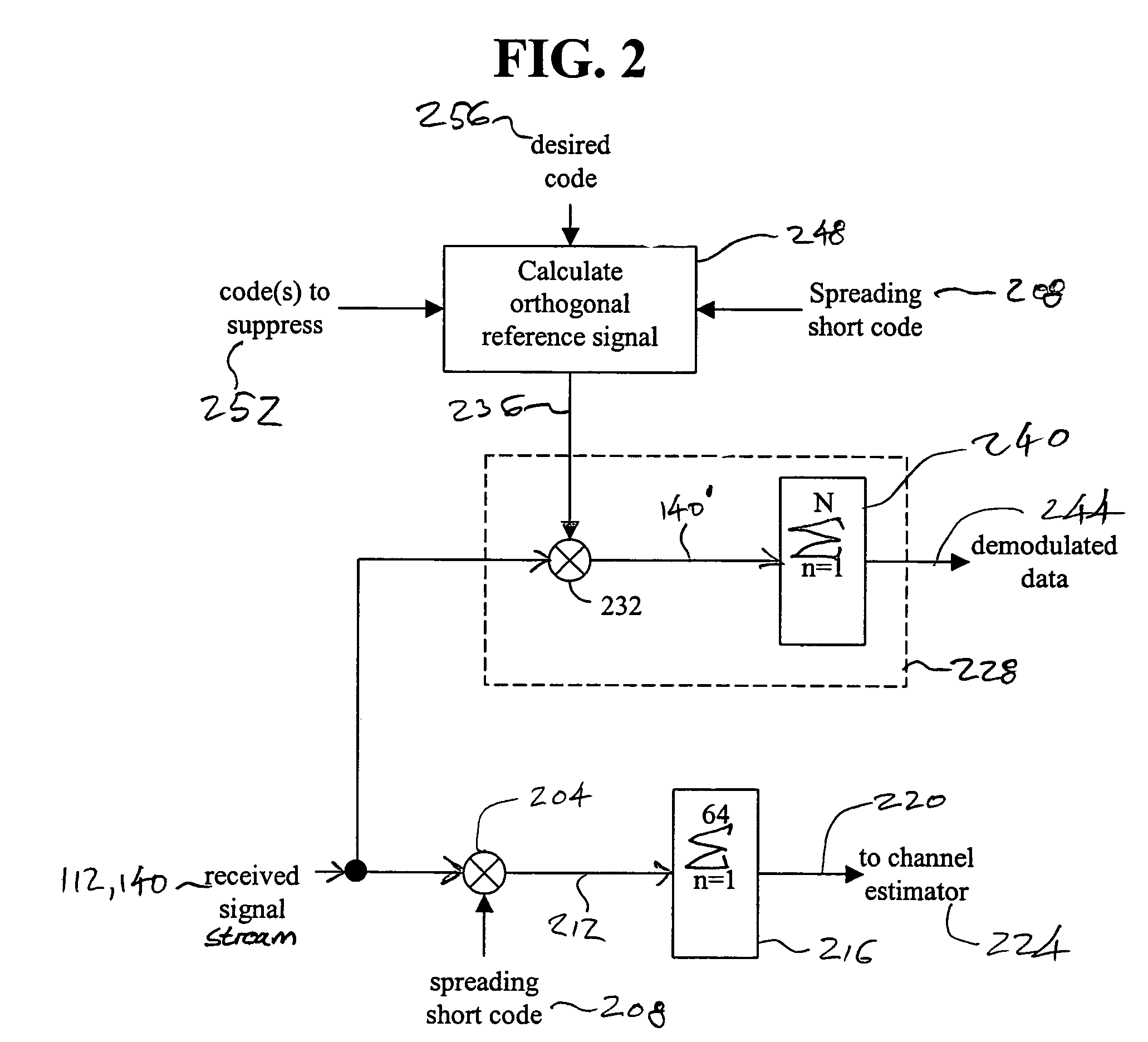
Method and apparatus for interference suppression with efficient matrix inversion in a DS-CDMA system
ActiveUS7430253B2Efficiently invertingTrivial matrix inversion and computationError preventionModulated-carrier systemsInterference eliminationCommunications system
The present invention is directed to signal cancellation in spread spectrum communication systems. In particular, the present invention provides method and apparatus for selectively canceling interfering signals, even where symbols to be canceled do not align with symbols associated with a desired signal path. Furthermore, the interference cancellation provided by embodiments of the present invention is capable of functioning to remove interference associated with channels utilizing a symbol length that is different than the symbol length of a desired signal path. In accordance with a further embodiment of the present invention, method and apparatus for efficiently calculating projections to enable signal cancellation are provided.
Owner:III HLDG 1
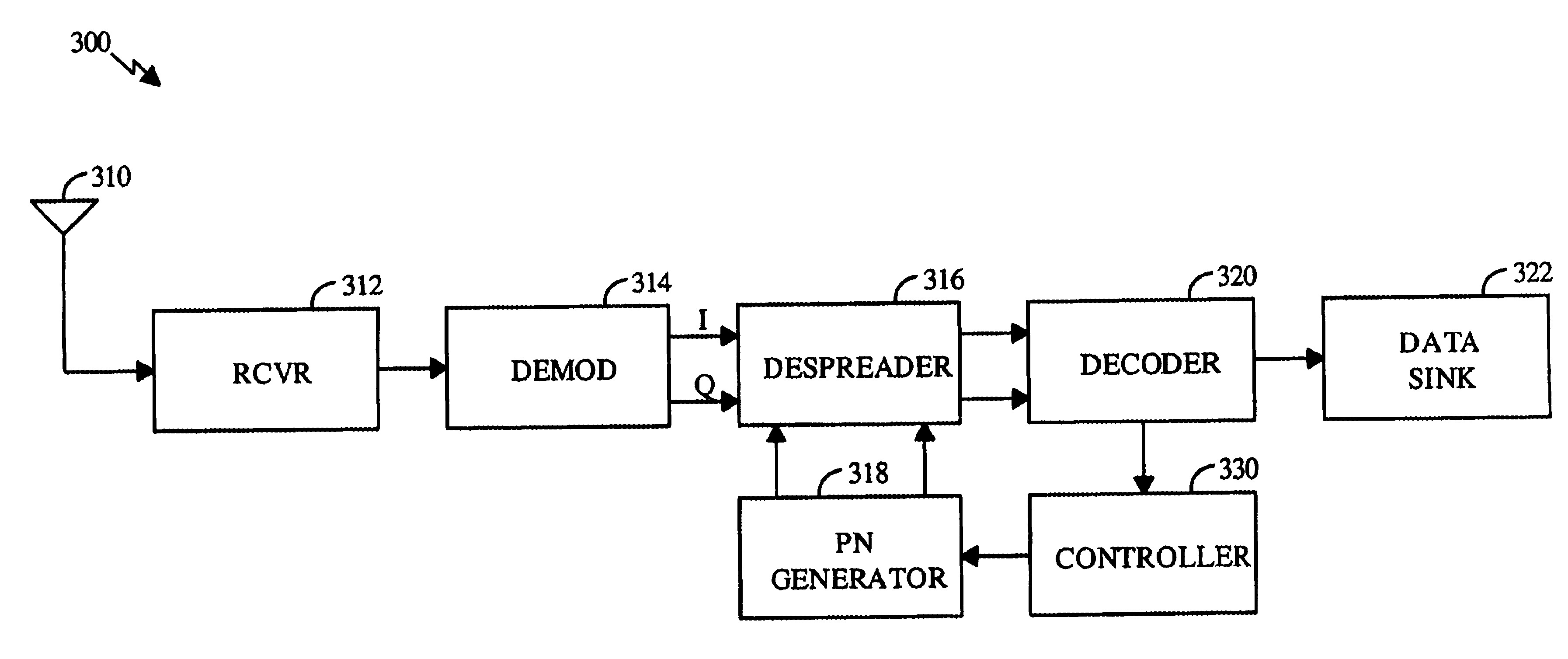
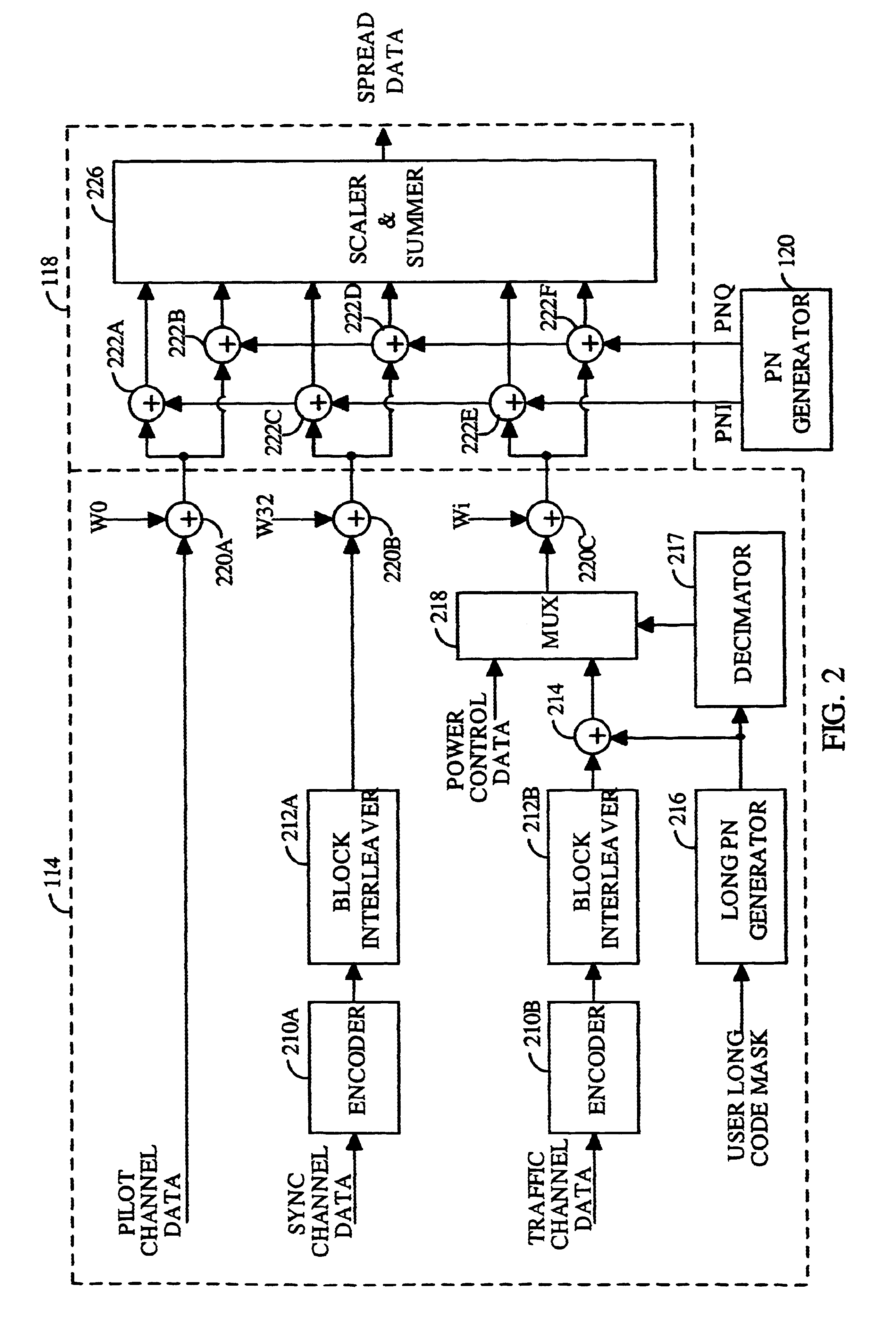
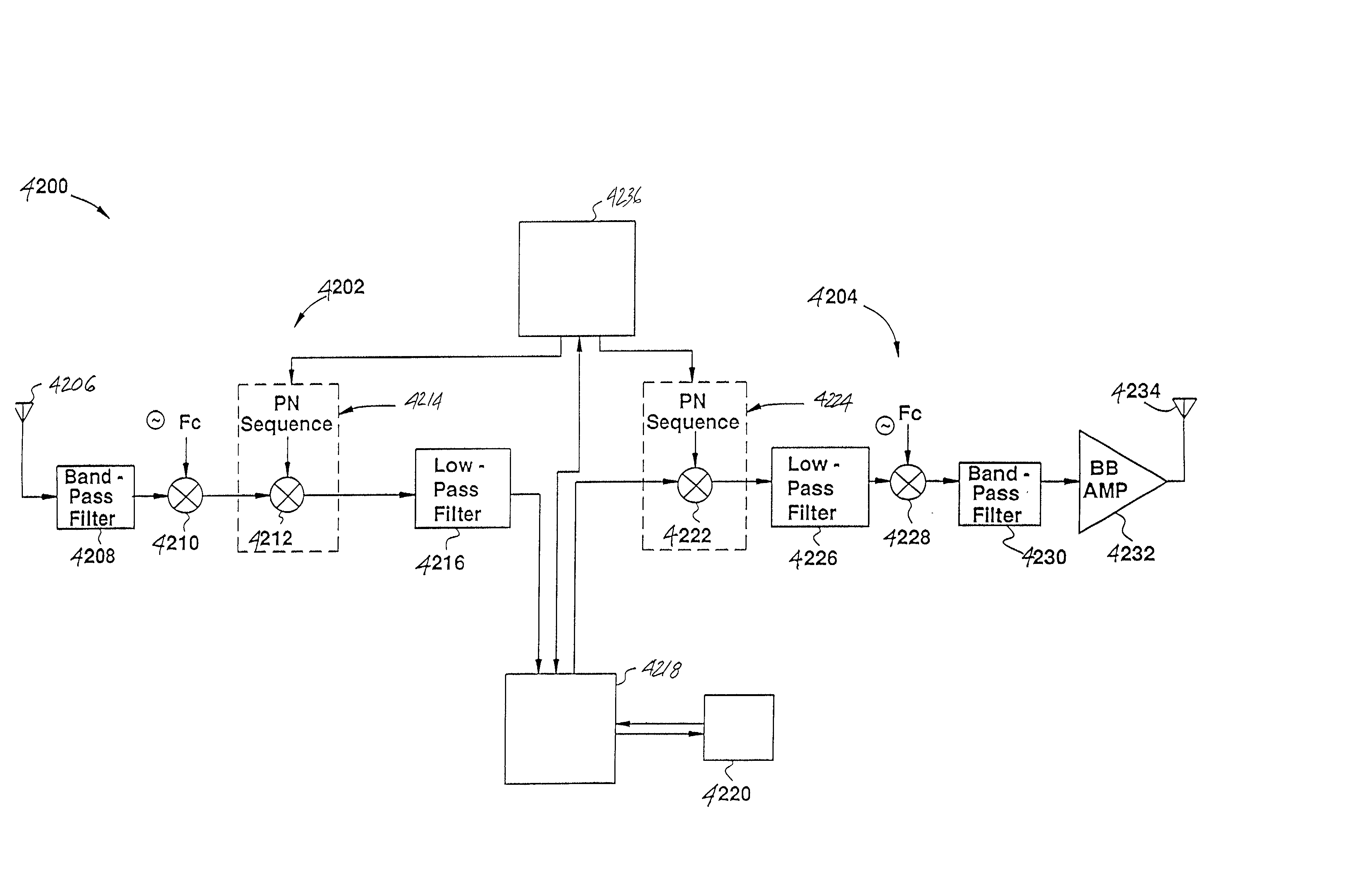
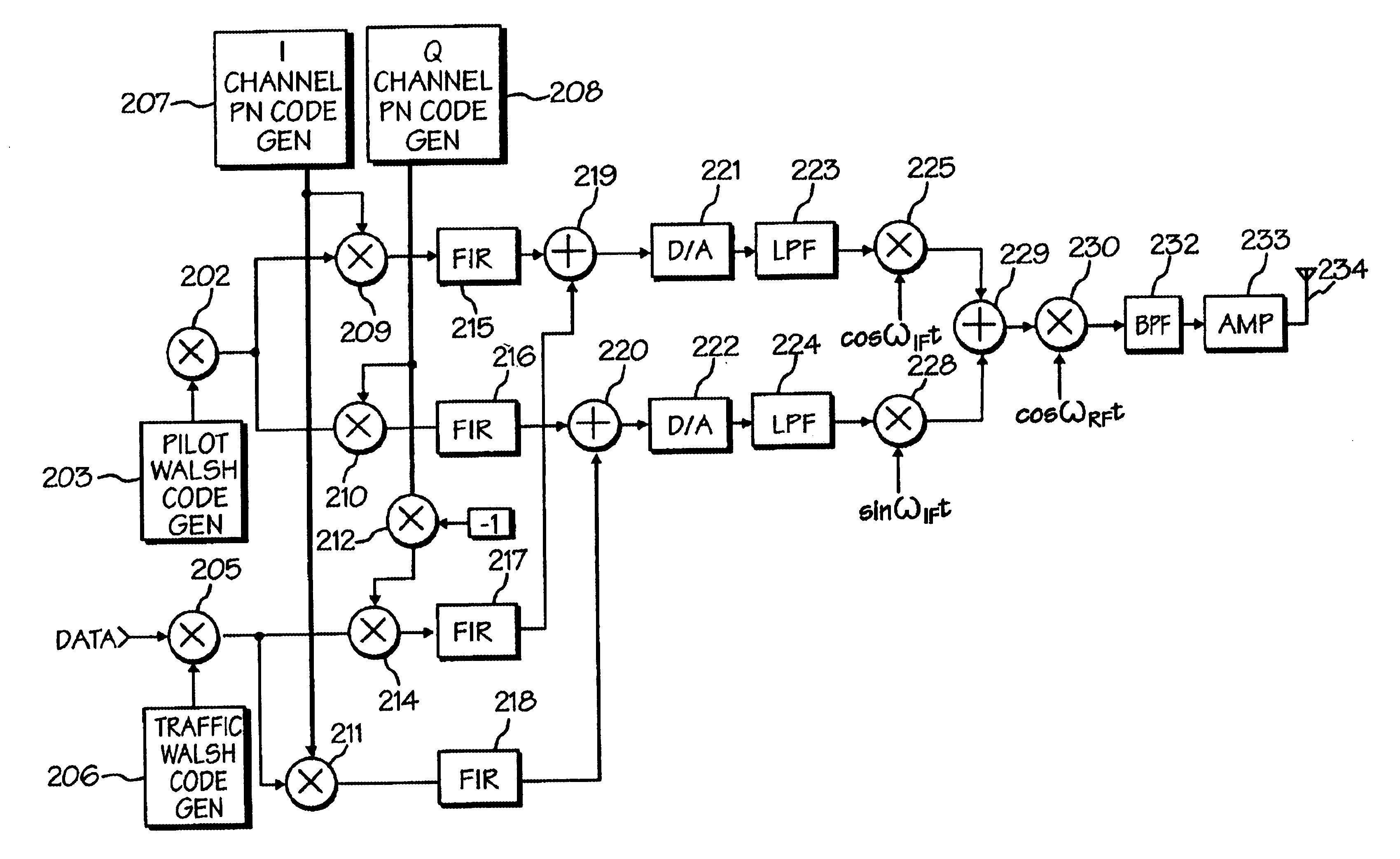
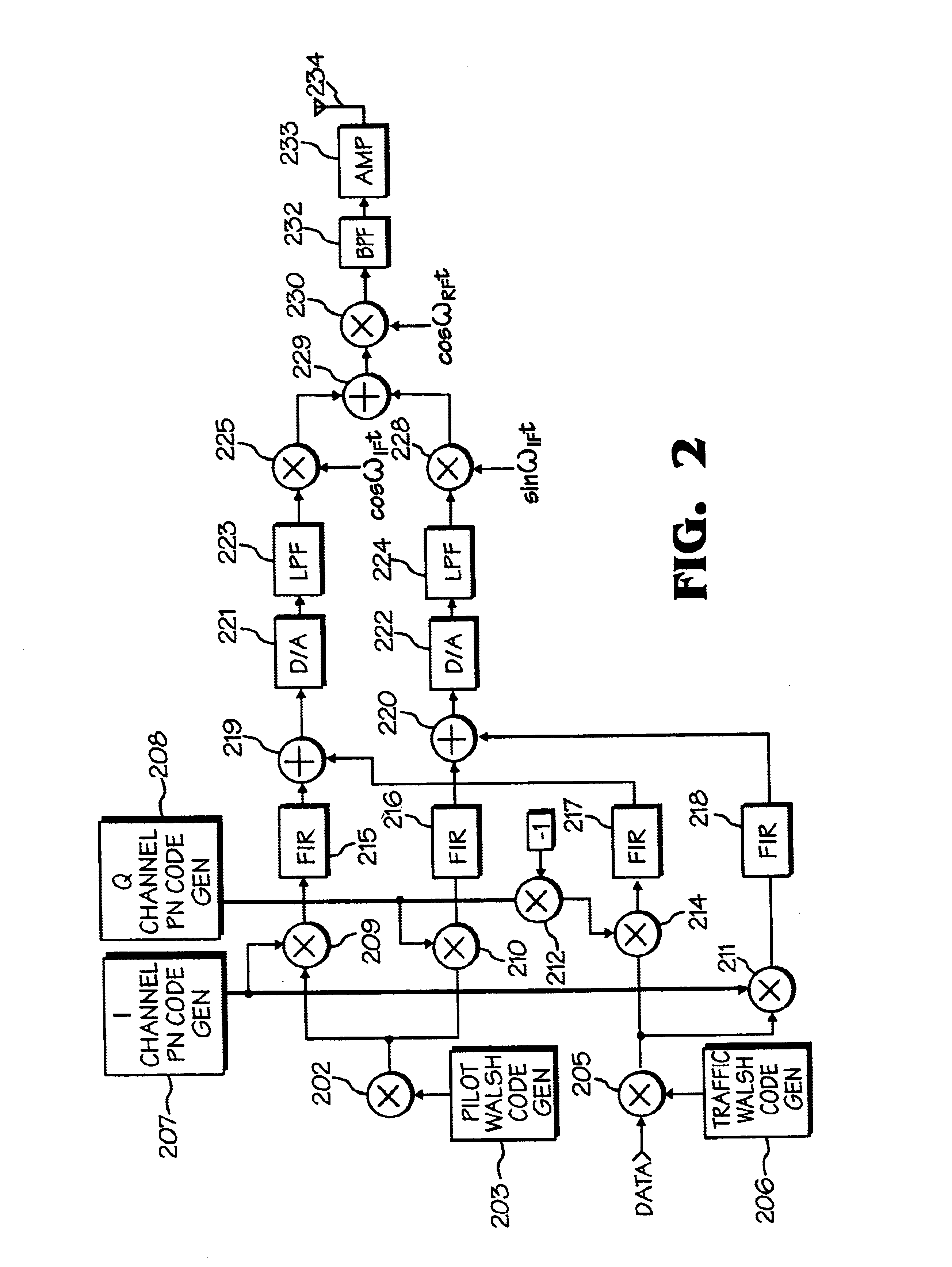
Data transmitter and receiver of a spread spectrum communication system using a pilot channel
InactiveUSRE38603E1The synchronization process is simpleMinimizing PN code acquisition timeSynchronisation information channelsMultiplex code generationFinite impulse responseIntermediate frequency
An improved spread spectrum communication system includes a transmitter and a receiver utilizing a pilot channel for the transmission of pure rather than modulated PN codes for code acquisition or tracking purposes with a lower bit error rate. The pilot signal is used to obtain initial system synchronization and phase tracking of the transmitted spread spectrum signal. At the transmitter side, a Walsh code generator, a Walsh modulator, a first PN code generator, a first band spreader, a second band spreader, finite impulse response filters, digital-analog converters, low-pass filters, an intermediate frequency mixer, a carrier mixer, a band-pass filter are used to transmit a spread spectrum signal. At the receiver side, a corresponding band-pass filter, a carrier mixer, an intermediate-frequency mixer, low-pass filters, analog-digital converters, a second PN code generator, an I channel despreader, a Q channel despreader, a PN code synchronization controller, a Walsh code generator, a first Walsh demodulator, a second Walsh demodulator, accumulator & dump circuits, a combiner, and a data decider are used to demodulate a received spread spectrum signal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
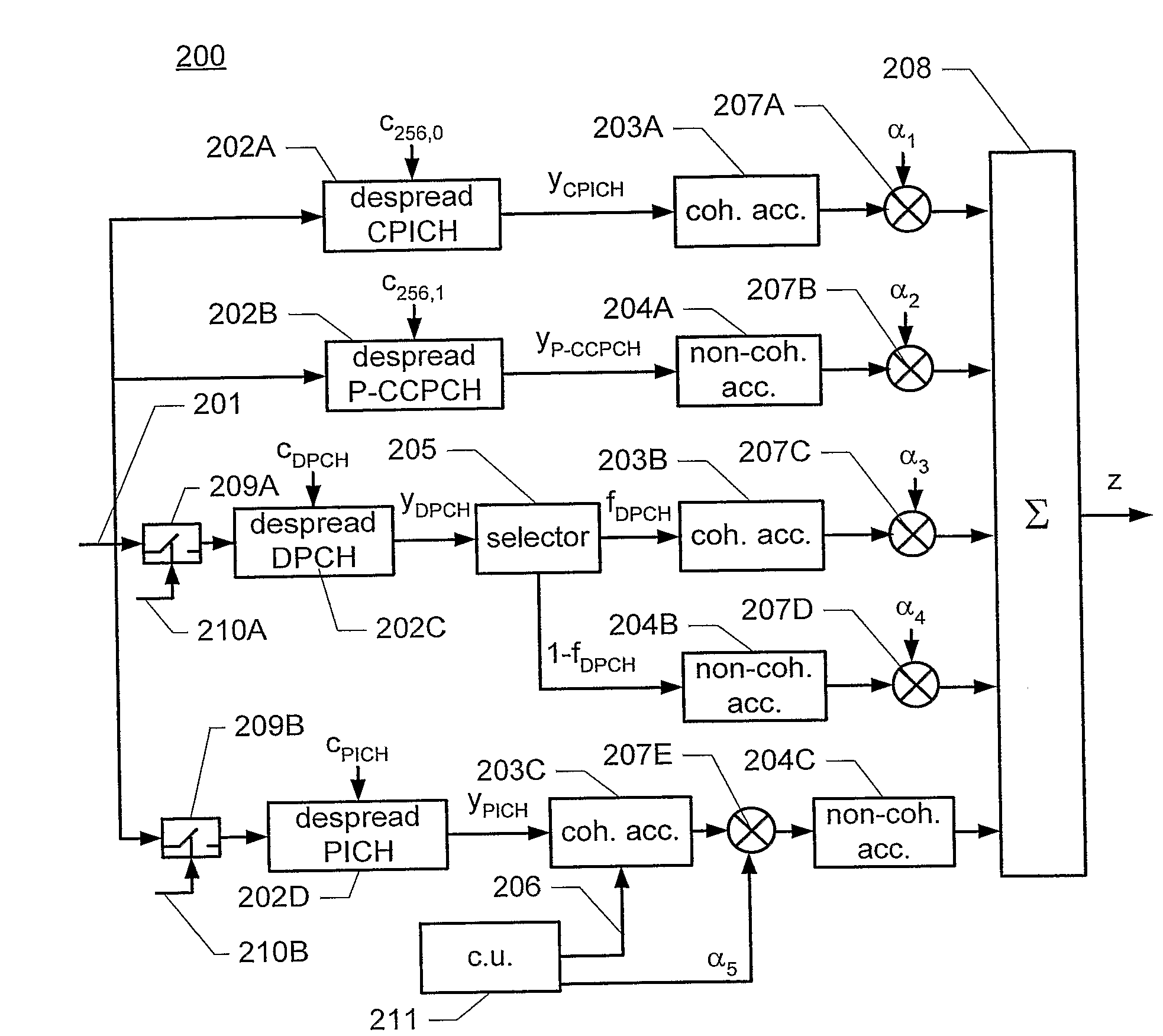
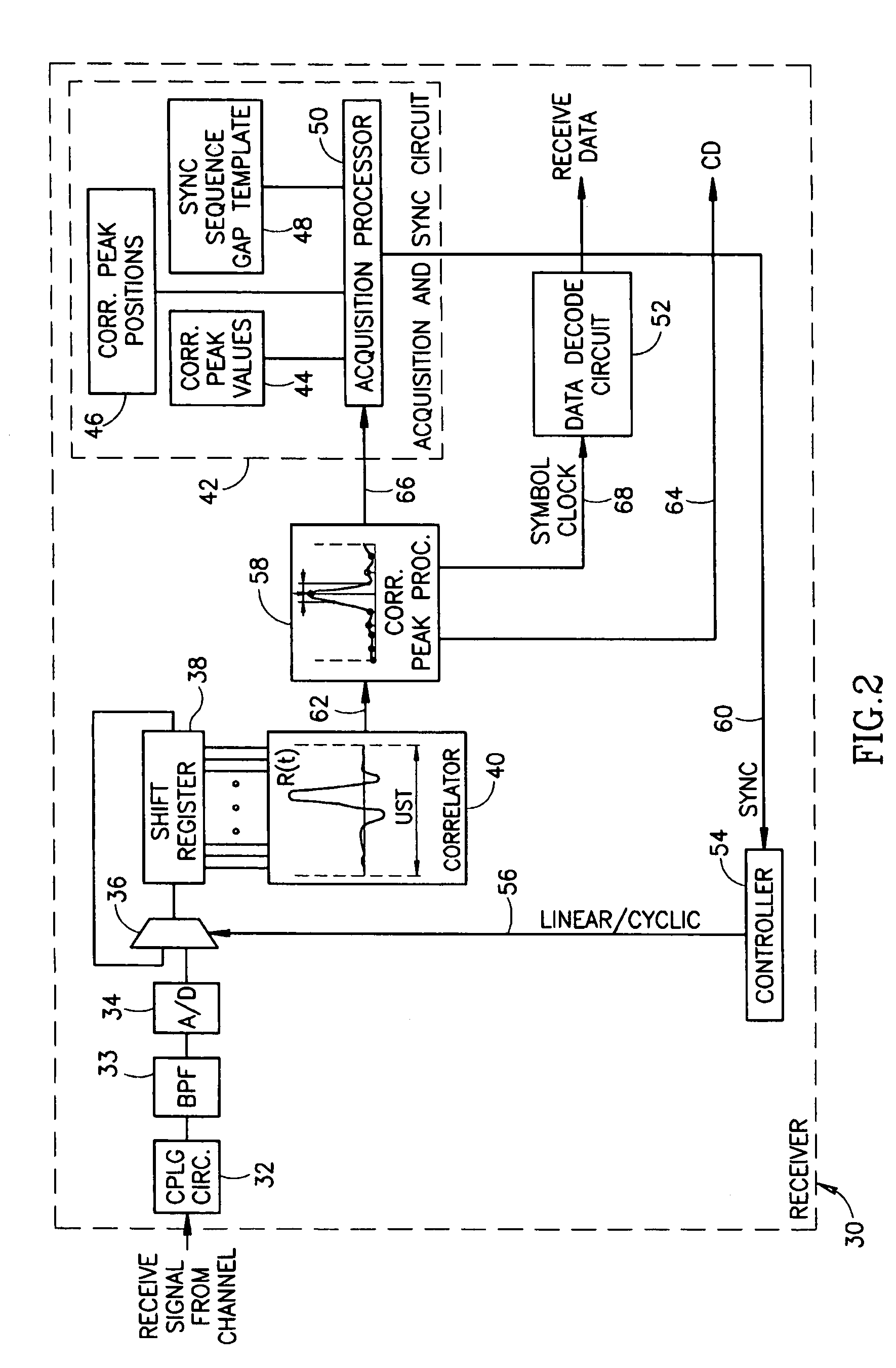
Determinting a Detection Signal in a Spread Spectrum Communications System
InactiveUS20080212654A1Easy to detectEasy to combineMultiplex code allocationTransmissionCommunications systemComputer science
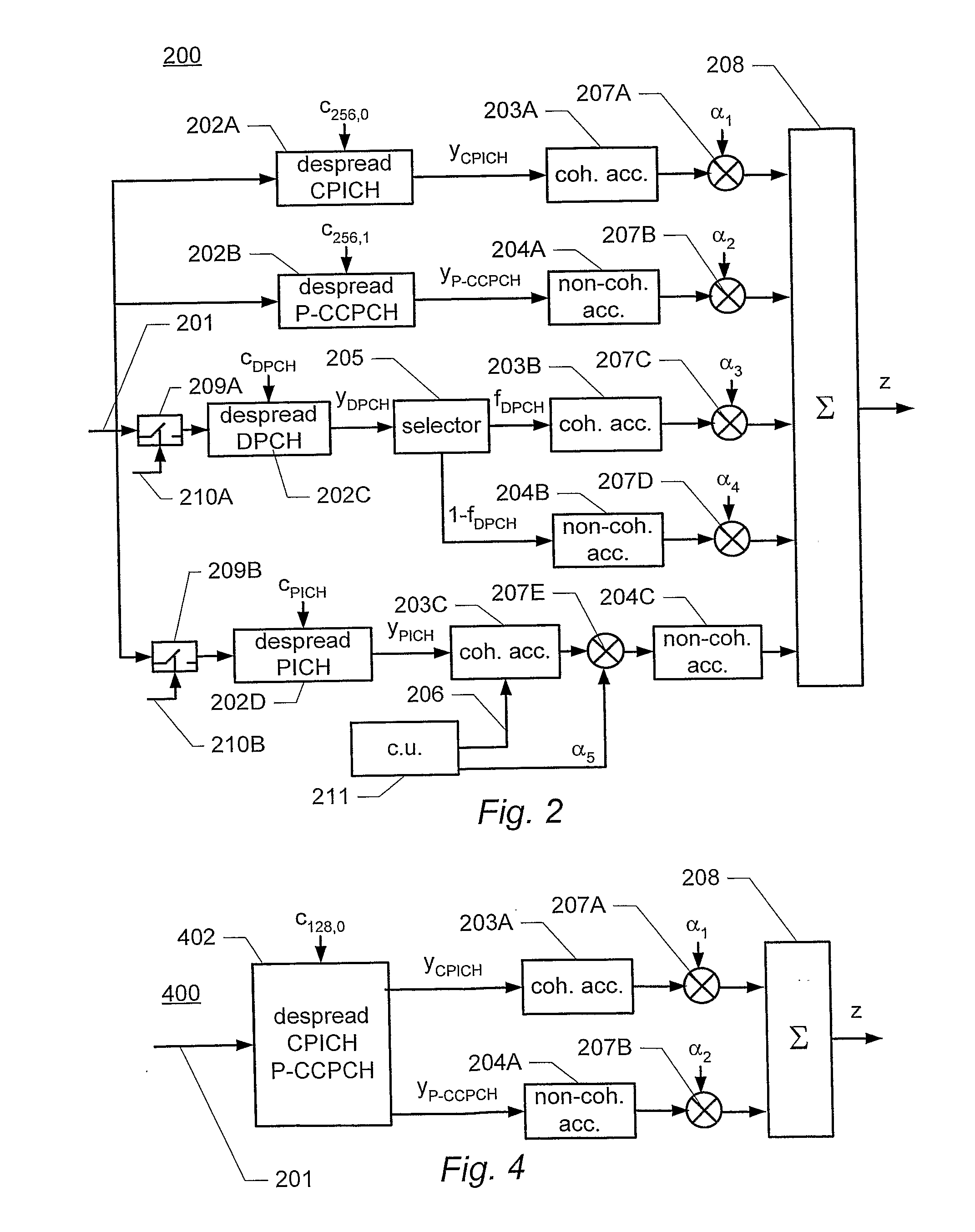
Disclosed is a method of generating a detection signal for detecting energy in a spread-spectrum signal, comprising: de-spreading the spread-spectrum signal by applying a predetermined spreading code to obtain a sequence of de-spread signal symbols (202A-202D); accumulating a number of said signal symbols to obtain a single detection signal. The accumulation includes: obtaining a first and a second subset of said de-spread signal symbols, wherein the symbols of the first subset have values that are known to the receiver or at least known to be the same for all symbols of the first subset, and wherein the symbols of the second subset have unknown values; coherently accumulating the symbols of the first subset to obtain a first partial detection signal (203A, 203B, 203C); non-coherently accumulating the symbols of the second subset to obtain a second partial detection signal (204A, 204B, 204C); and combining the first and second partial detection signals to obtain the single detection signal (208).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
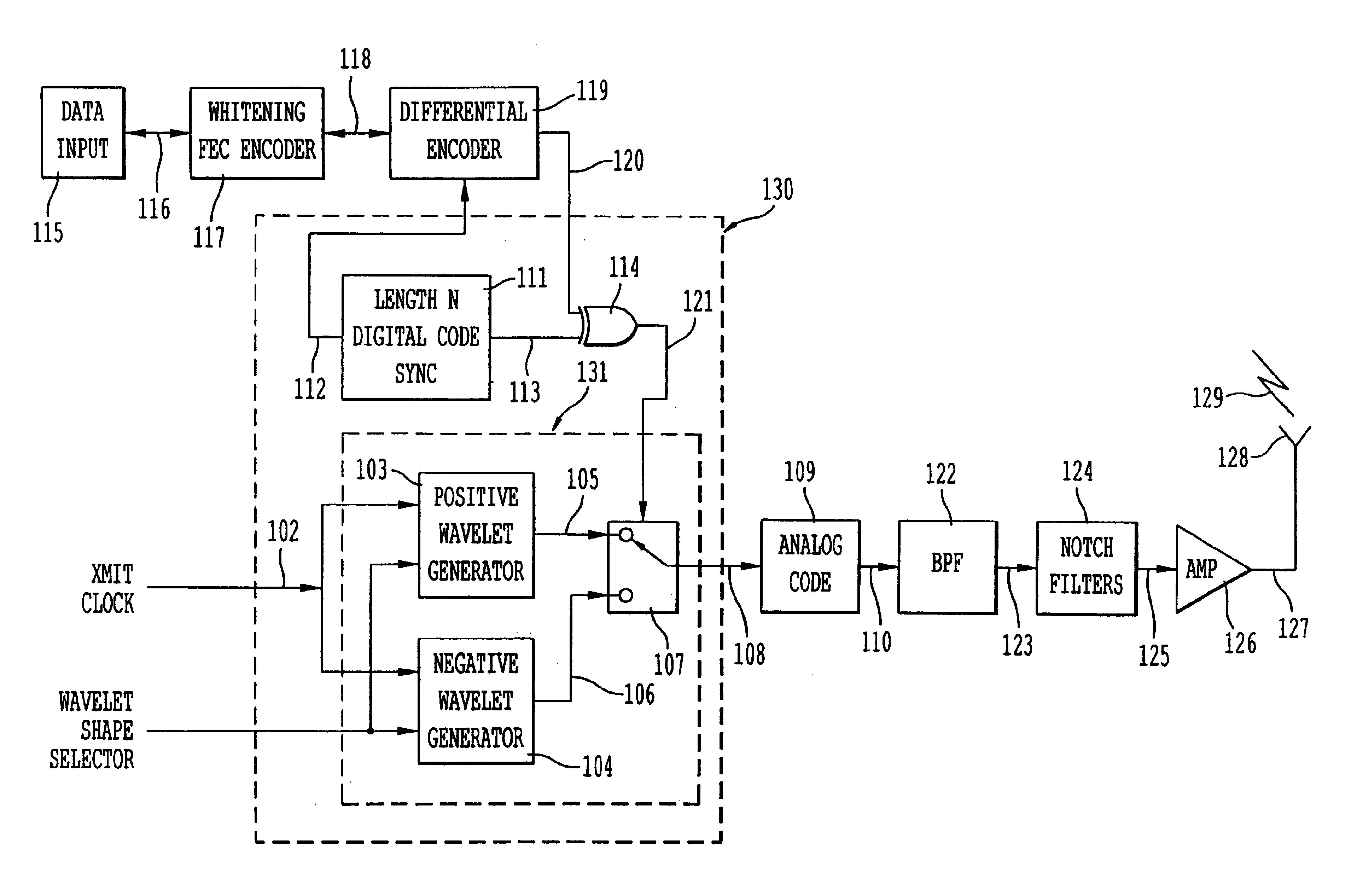
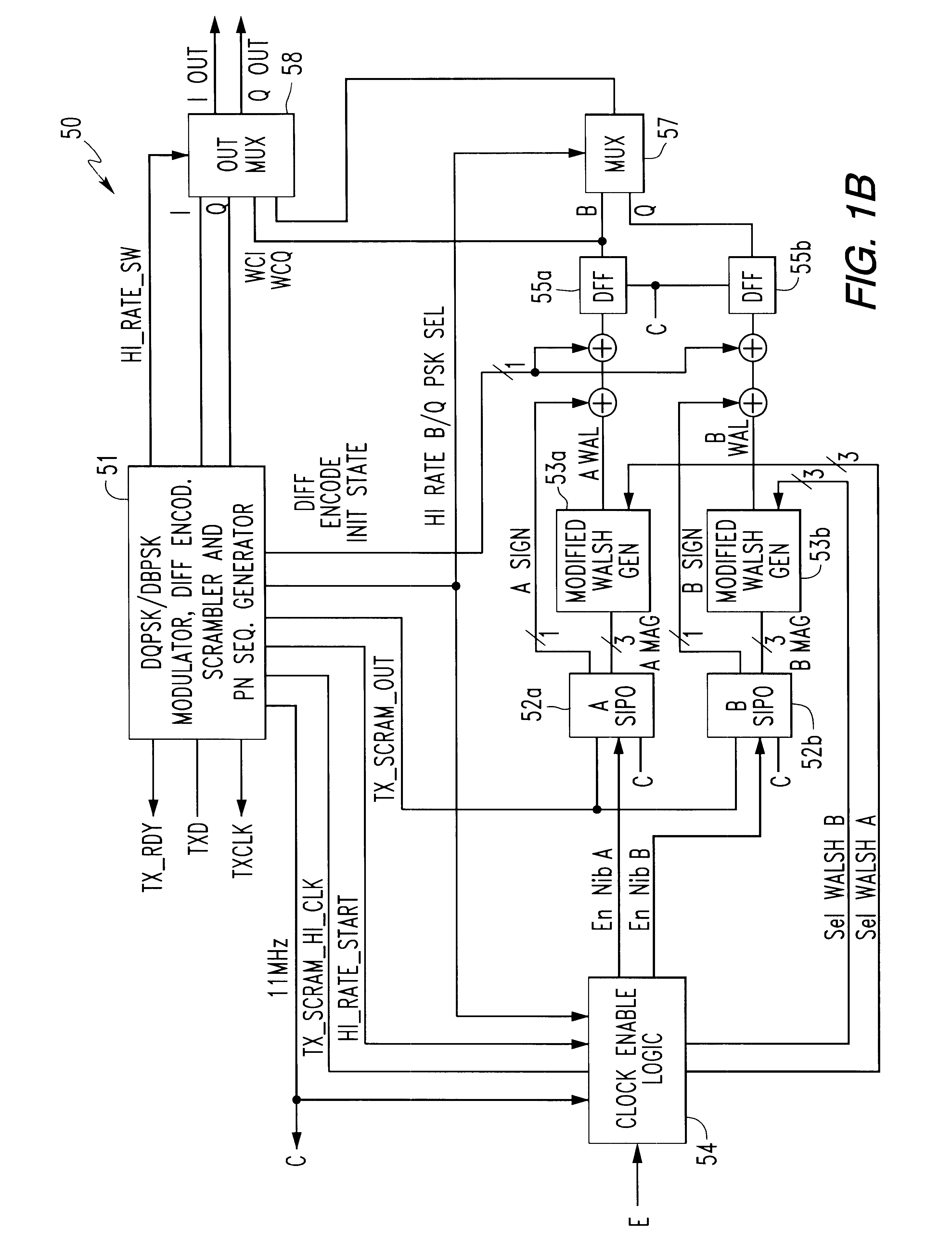
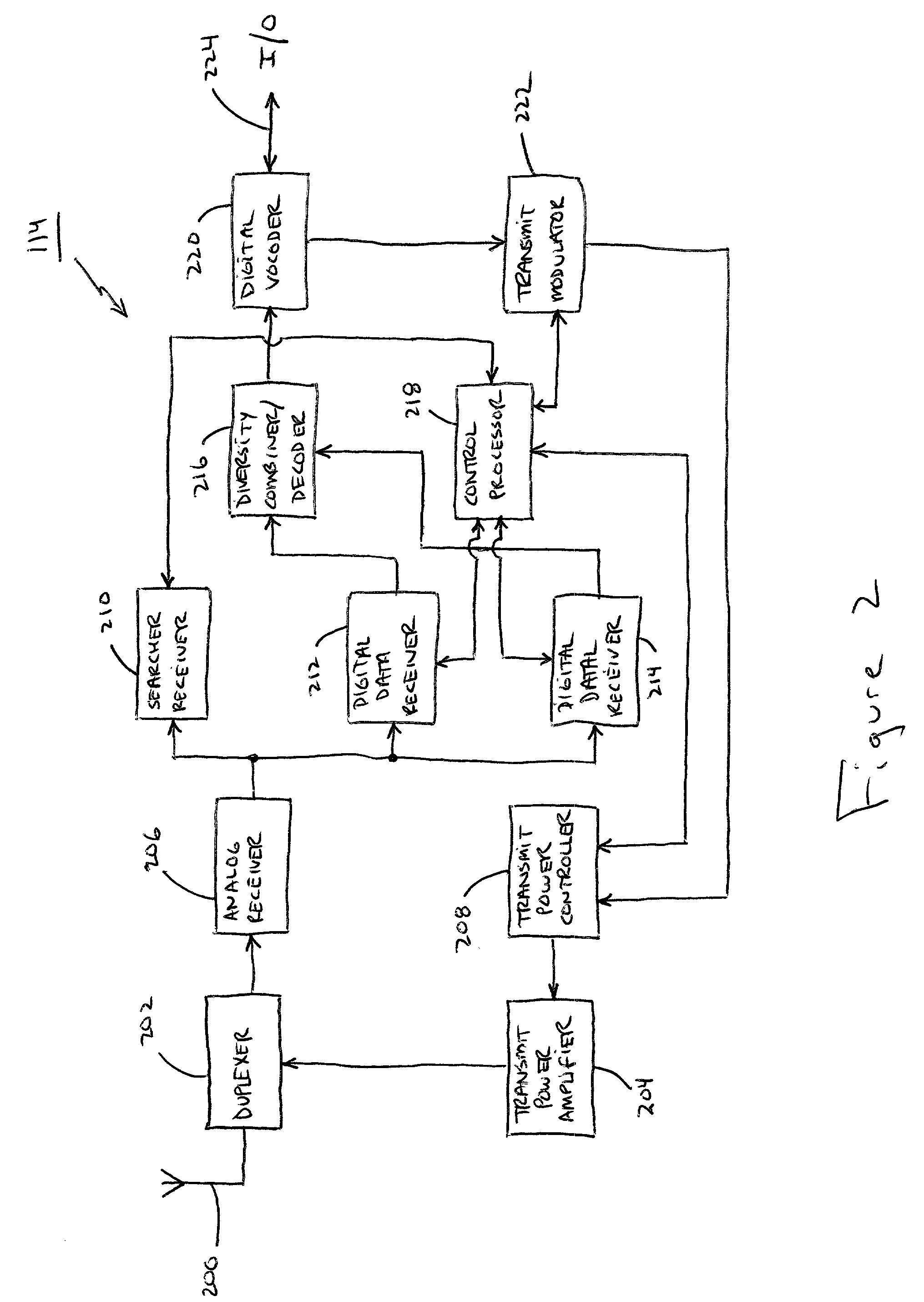
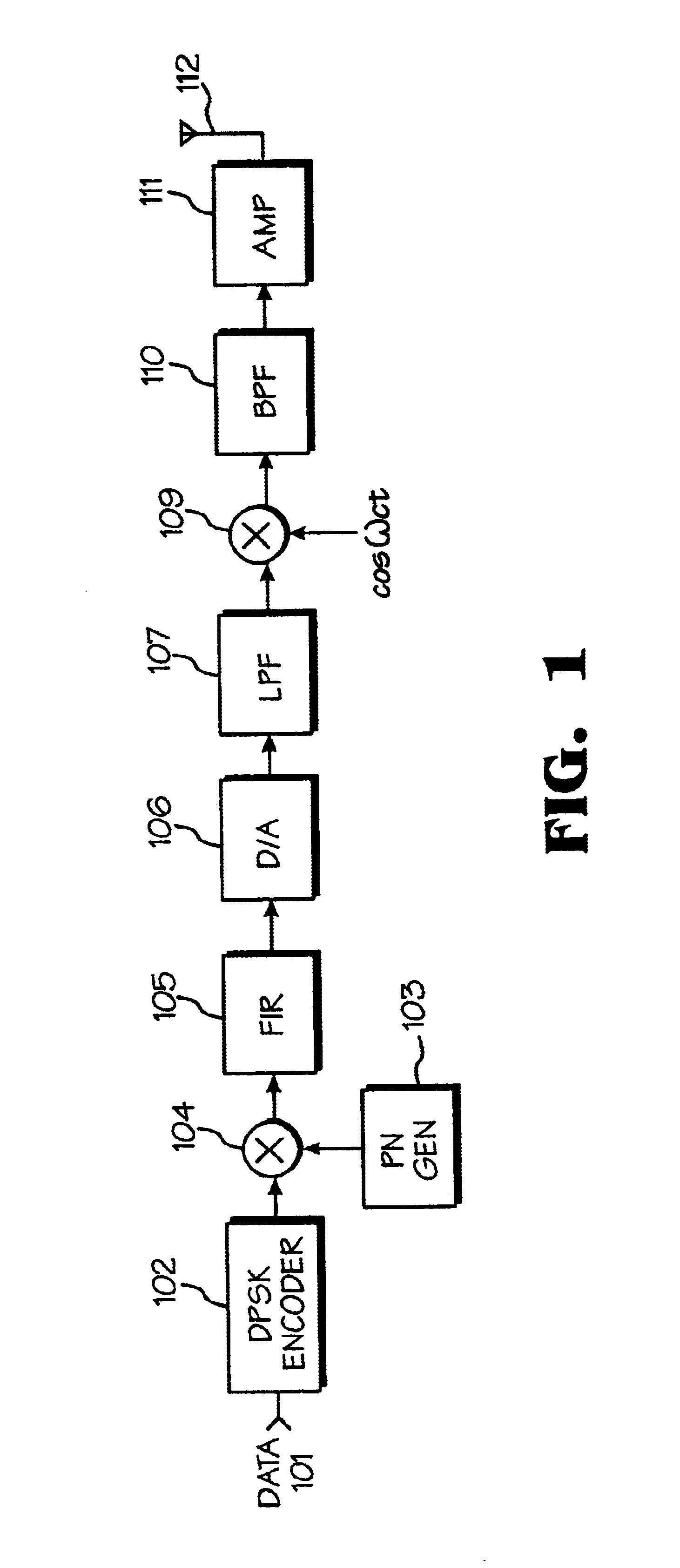
Spread spectrum transmitter, spread spectrum receiver, and spread spectrum communications system
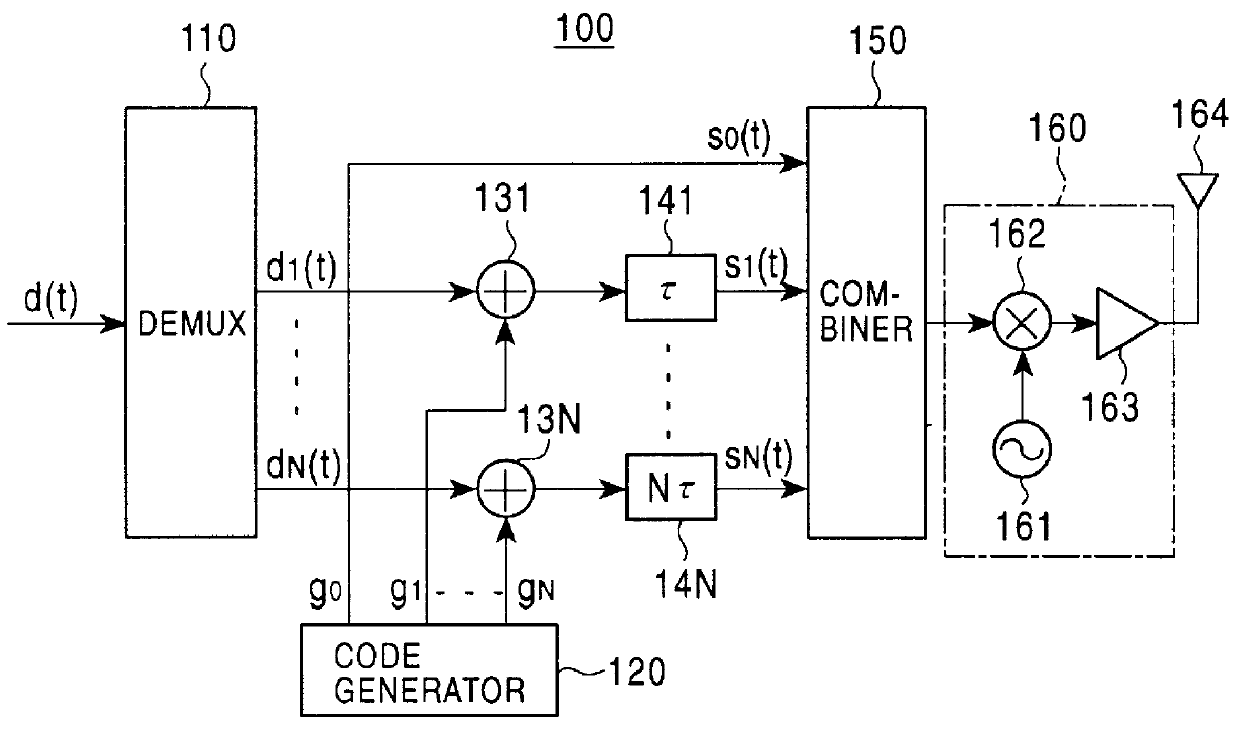
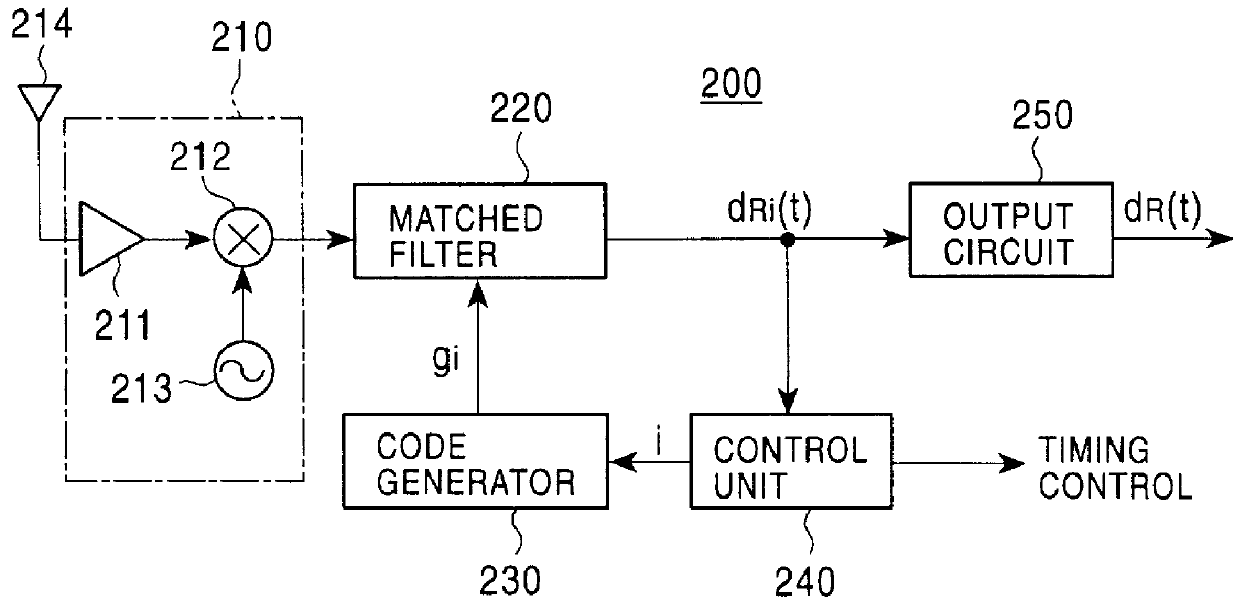
InactiveUS6163566ASimple configurationCode division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemSpread spectrum radar
A spread spectrum communications system is provided for reducing the number of required matched filters to simplify the configuration associated with the reception. In a spread spectrum transmitter, a plurality of spread channel signals are synthesized by shifting their respective phases by a time sufficiently shorter than one symbol period. In a spread spectrum receiver, a plurality of spread code sequences are set one by one at a tap of a single matched filter in one symbol period in a time division manner to recover transmitted data.
Owner:CANON KK
Responding to changes in measurement of system load in spread spectrum communication systems
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for responding to changes in measurement of a system load in a spread spectrum communication system. Using a load control algorithm, for example, the spread spectrum communication system may handle sudden changes or variations, such as spikes or steps in system load measurements for an uplink and / or a downlink between a mobile unit and an access network. The load control algorithm determines whether a sudden variation of a measured system load is generated by a source not under a power control or is caused by a variation of a spread spectrum communication system load. A load control measure may be selectively applied to adjust one or more parameters associated with the system load. That is, an increase of a first new measurement value may be limited to a given maximum increment for one sampling time period of a plurality of sampling time periods in response to a spike in the system load or a desired response to a sudden increase of the system load may be delayed by a given maximum number of measurement samples. By allowing a limited increase, the response of the spread spectrum communication system to sudden changes of a system load may be controlled such that some blocking may occur but dropping of calls may be avoided. In this manner, the load control algorithm may avoid unnecessary dropping of calls.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
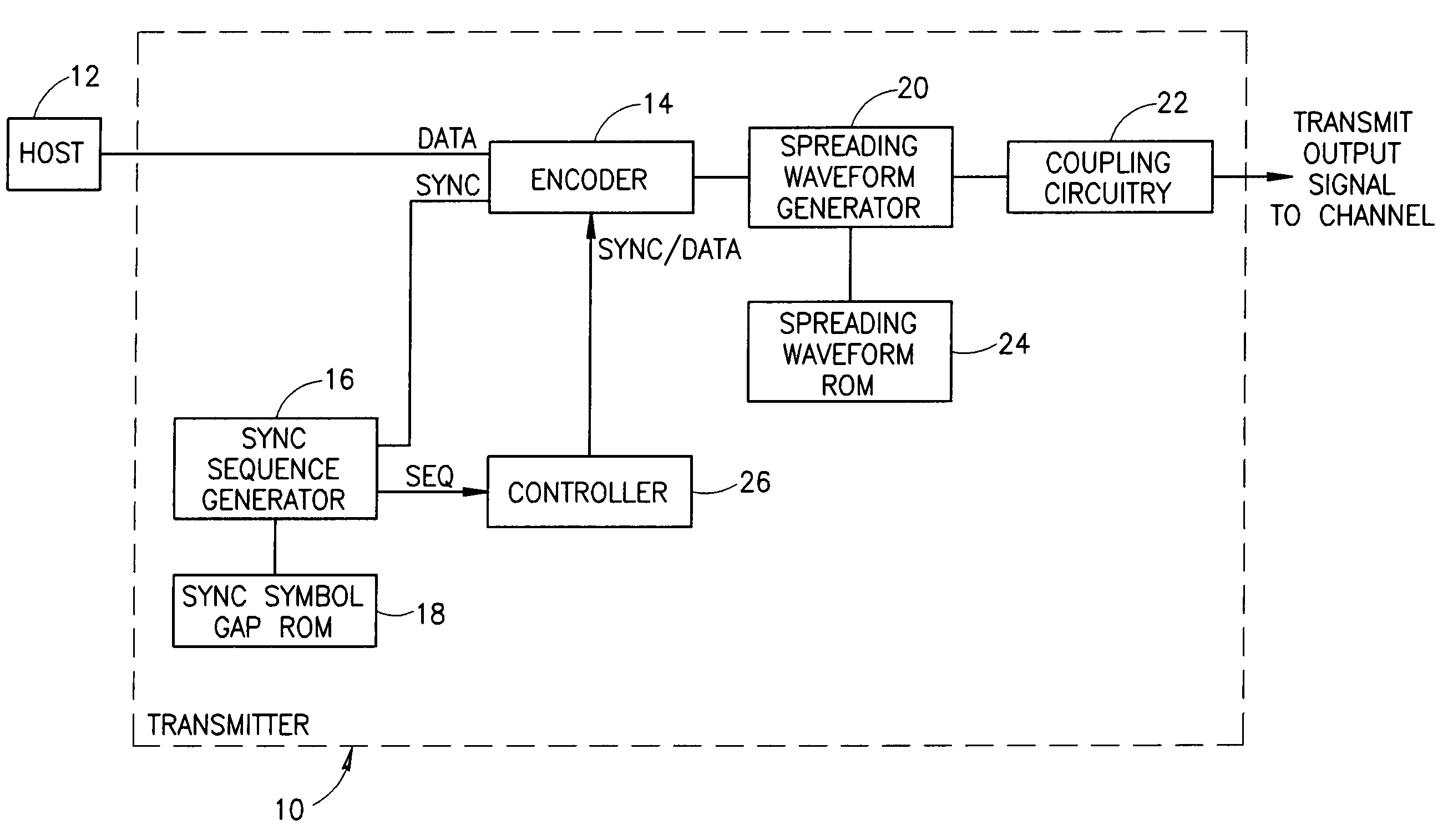
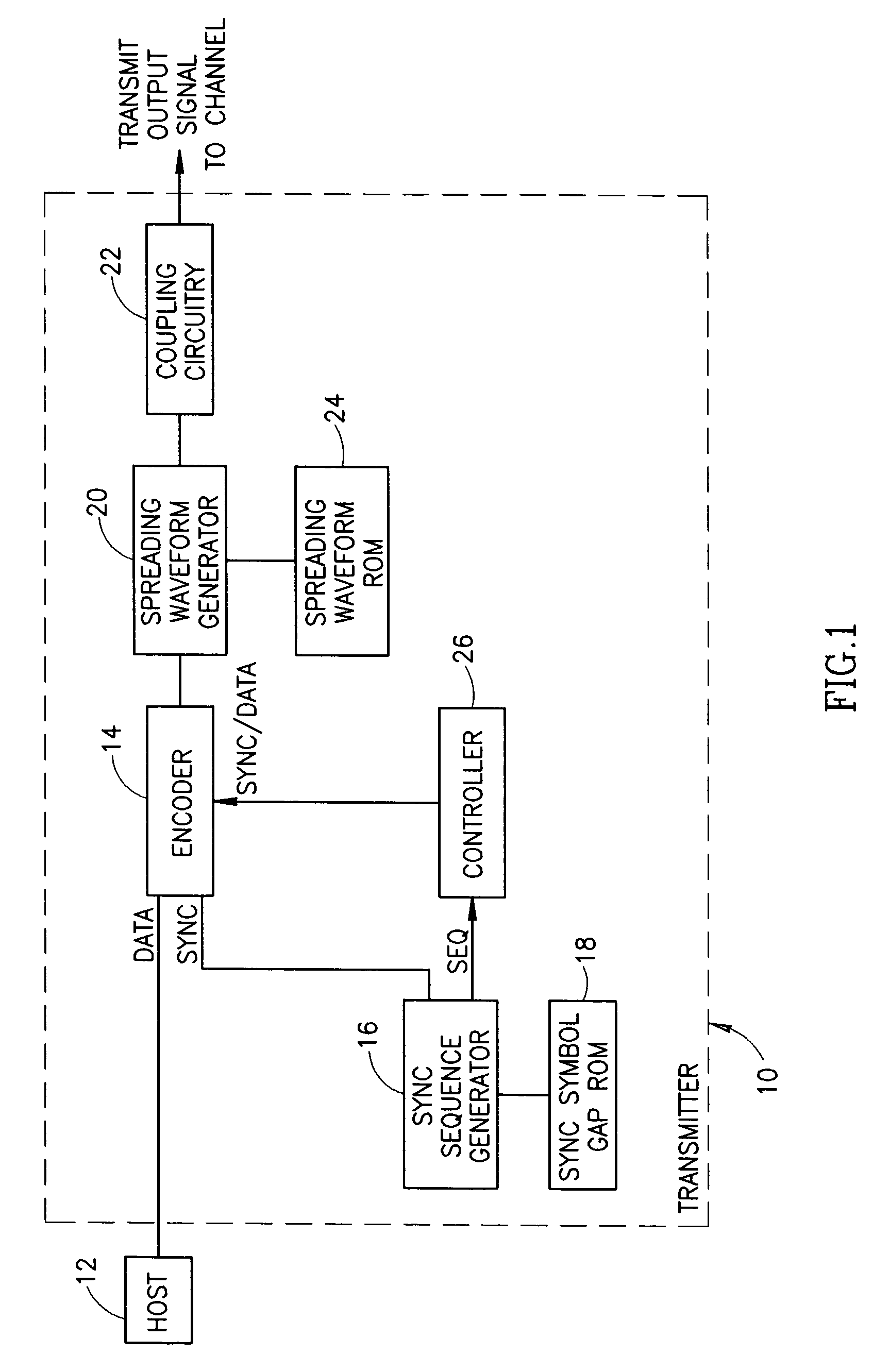
Method and apparatus for generating a synchronization sequence in a spread spectrum communications transceiver
InactiveUS7463709B2Reduce probabilityTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTransceiverTime delays
A novel and useful acquisition and synchronization mechanism for spread spectrum communication systems whereby a synchronization sequence comprising a plurality of known symbols spaced apart by predefined time delay intervals is transmitted as the start of packet signal. At the transmitter, a synchronization sequence is transmitted at the beginning of each packet. A synchronization sequence is generated which includes a plurality of symbols with predefined time gaps between each of the symbols. Multiple synchronization sequences may be generated wherein each sequence comprises a unique set of time delays or gaps between each of the symbols. Each set of unique time delays or gaps between symbols of a sequence is stored as a synchronization sequence gap template in memory. When required to generate a synchronization sequence, the sequence generator outputs the plurality of synchronization symbols and inserts a specific time delay between each of the symbols in accordance with the contents of the gap template for the particular synchronization sequence.
Owner:ITRAN COMM
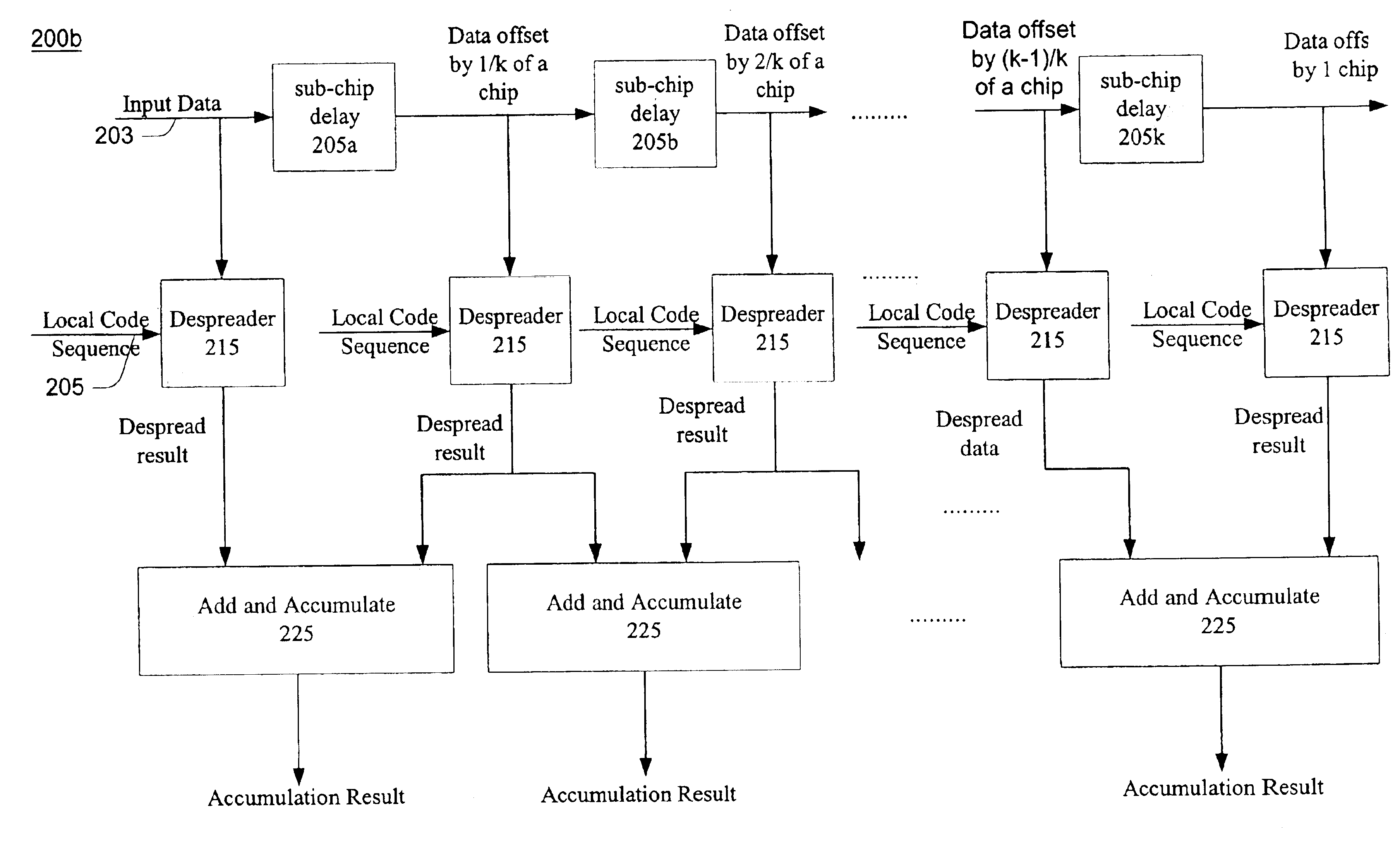
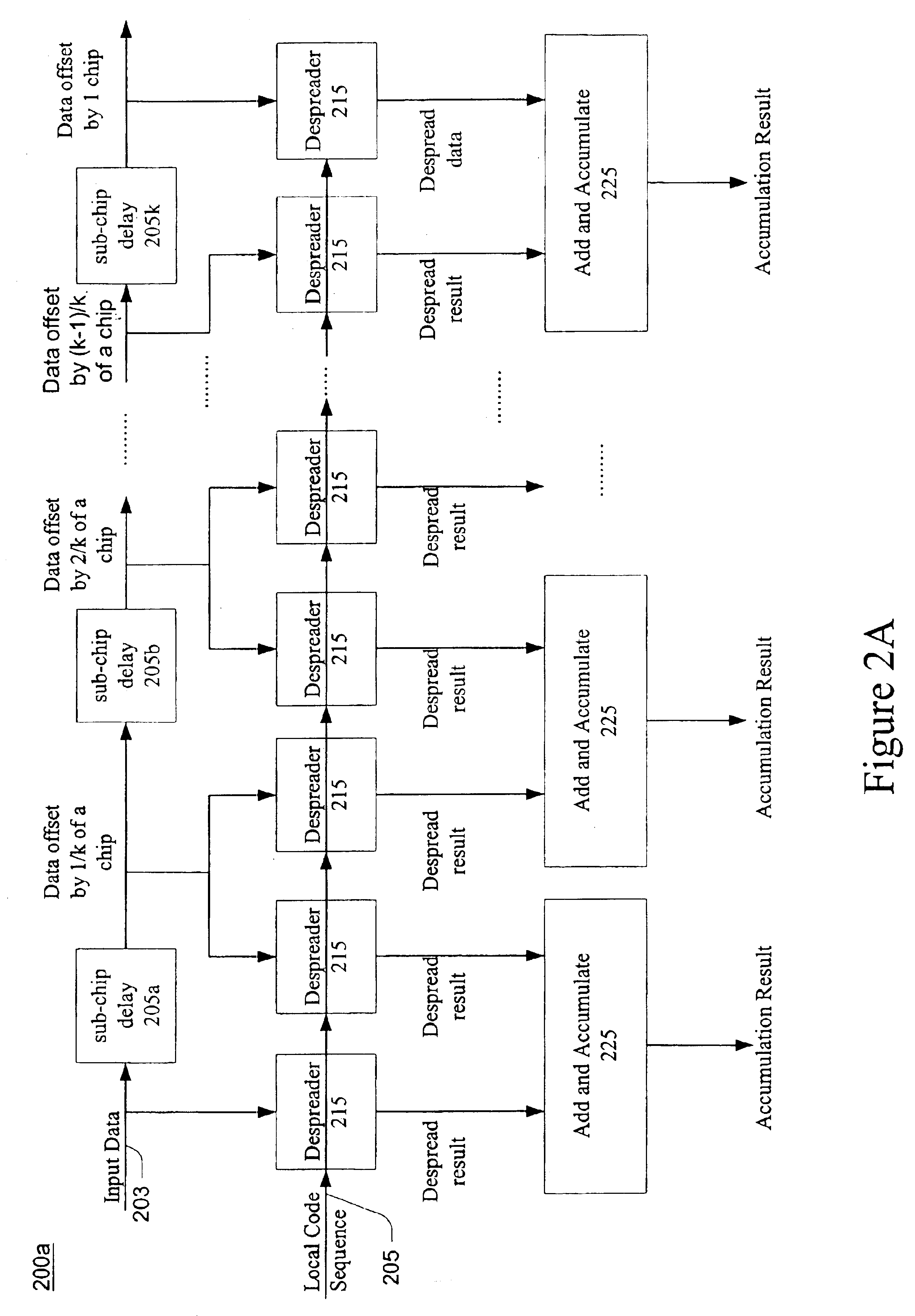
Apparatus and method for sub-chip offset correlation in spread-spectrum communication systems
InactiveUS6895036B2Reduction in “ miss ” probabilityReduction in maximum mean timeAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationComputer scienceData sequences
An embodiment of the present invention described in the specification and the drawings is an apparatus and method for code correlation in spread spectrum communication systems. The apparatus receives a data sequence, and offsets the data sequence with a fixed sub-chip delay. The data sequence and the offset data sequence are each despread with a locally generated code sequence. The despread results are summed and accumulated. The accumulated results may then be used to achieve a lower “miss” probability during code correlation.
Owner:MORPHICS TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com