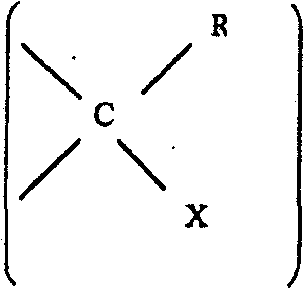Process for pre-tanning and tanning skins with organic tanning agent
A rawhide and pre-tanning technology, applied in the field of tanning, can solve the problems of lengthening the overall tanning process and environmental impact, and achieve the effects of avoiding mechanical strength and excessive relaxation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
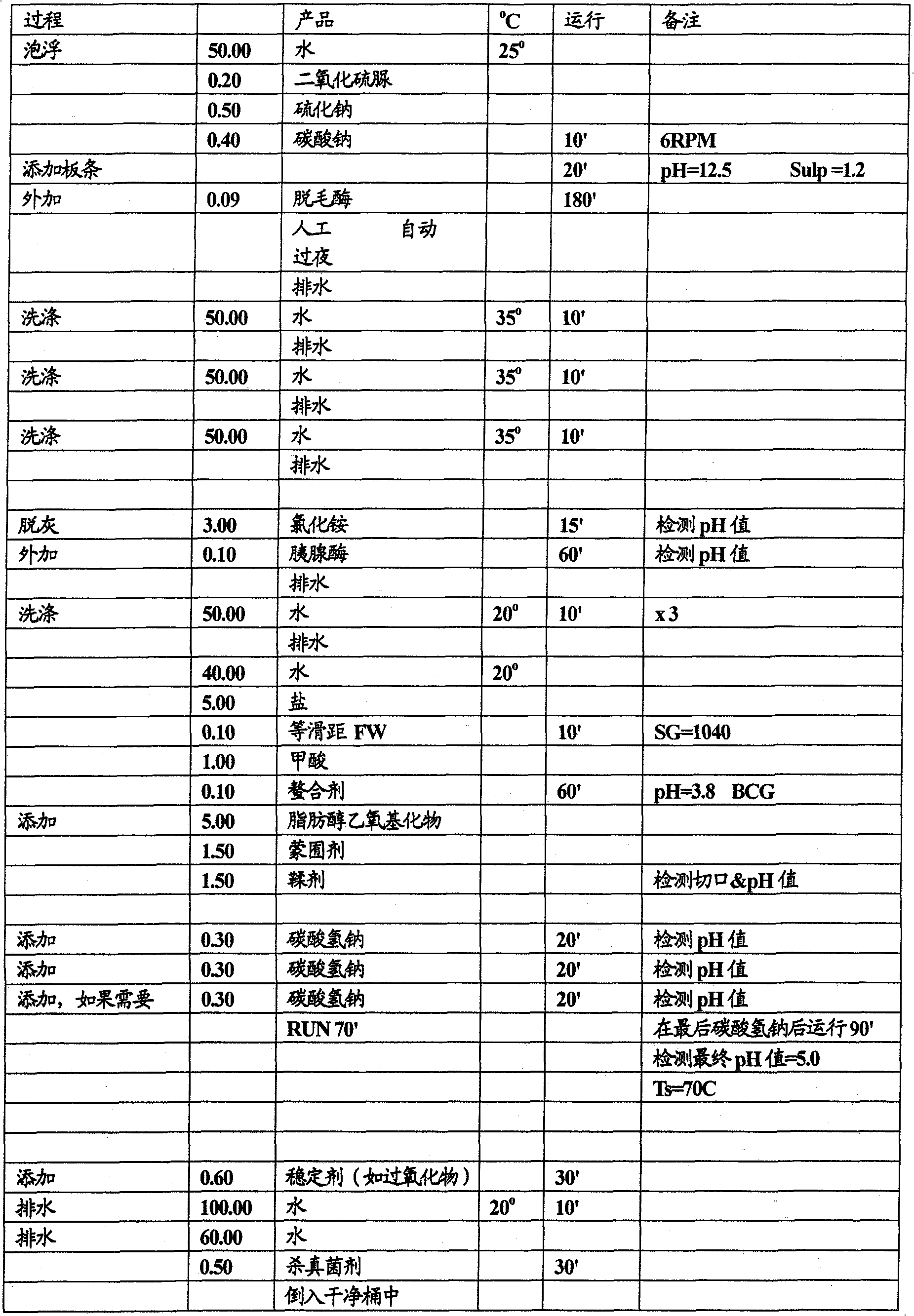
[0121] Pre-tanning of wet white lamb skins at low temperatures using aqueous degreasing
[0122] method
[0123]
[0124] result
[0125] Independent analysis of the wet white lamb skins obtained gave the following results (determined by using the BS 1309 test method):
[0126] 3.9% oil (target is <5%)
[0127] • 0.62% free fatty acids (target is <1%).
[0128] in conclusion
[0129] The inventive method, which does not require an acid leaching stage and performs aqueous degreasing at low temperatures, gives good results both in terms of grease levels and free fatty acid levels, both of which are significantly below the target values.
Embodiment 2
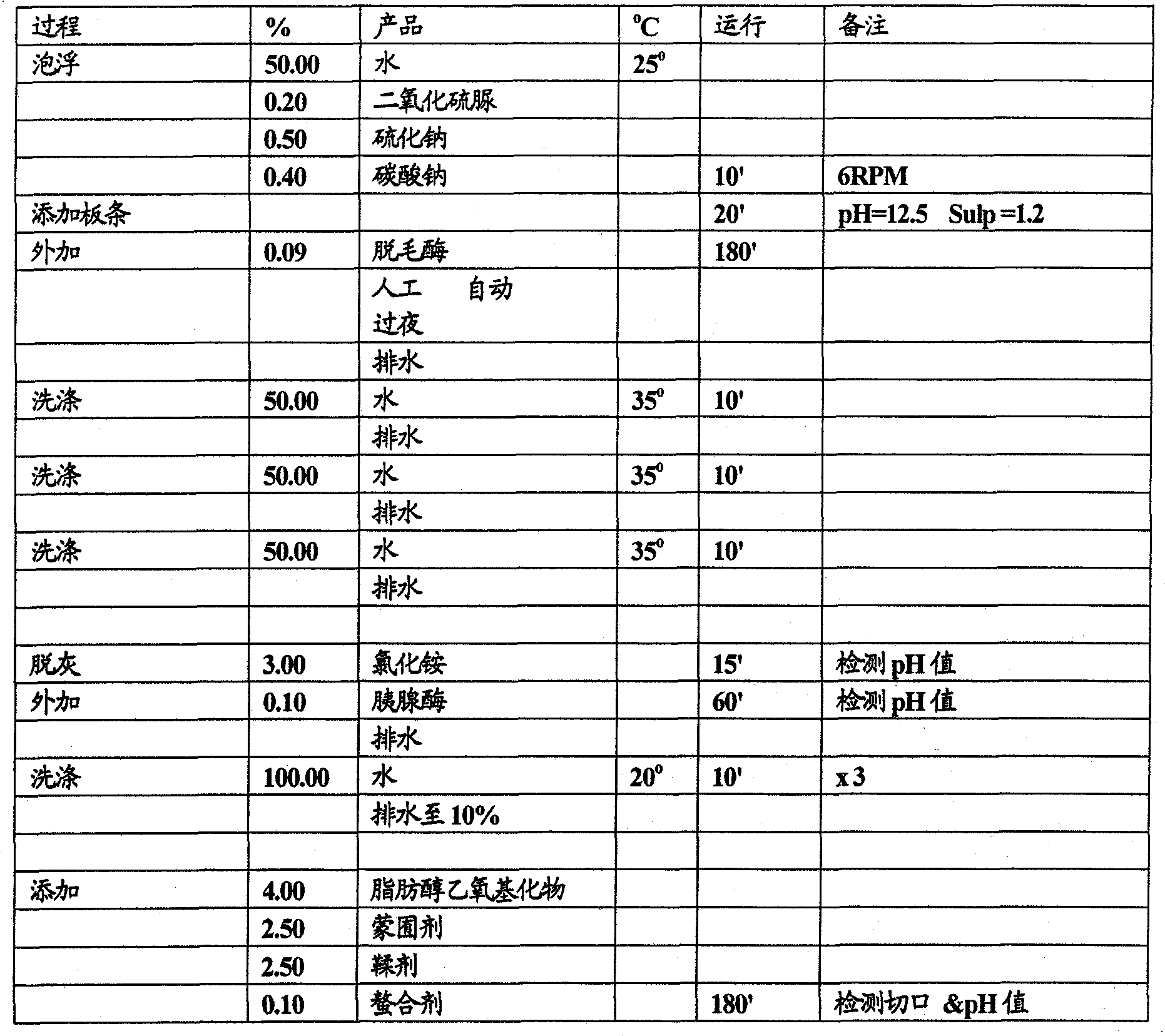
[0131] Pre-tanning of wet white lamb skins at high pH (directly after deliming - no pH adjustment)
[0132] method
[0133]
[0134]
[0135] result
[0136] Analysis of the wet white lamb skins obtained gave the following results (determined by using the BS 1309 test method):
[0137] - 0.43% residual free fatty acid (target is <1%).
[0138] in conclusion
[0139] The process of the invention without the pickling stage and with pretanning at high pH (i.e. avoiding the need for pH adjustment steps before and after pretanning and the associated use of acids and bases) gave good results in terms of free fatty acid levels, significantly lower than the target value.
Embodiment 3
[0141] Tanning of cowhide
[0142] method
[0143]
[0144]
[0145] result
[0146] THPx successfully tans hides and hides directly from deliming and softening without the need for a pickling step.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap