Method for obtaining a structure factor of an amorphous material, in particular amorphous glass
A technology of amorphous materials and structure factors, applied in the direction of using wave/particle radiation for material analysis, analyzing materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to identify mathematical artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
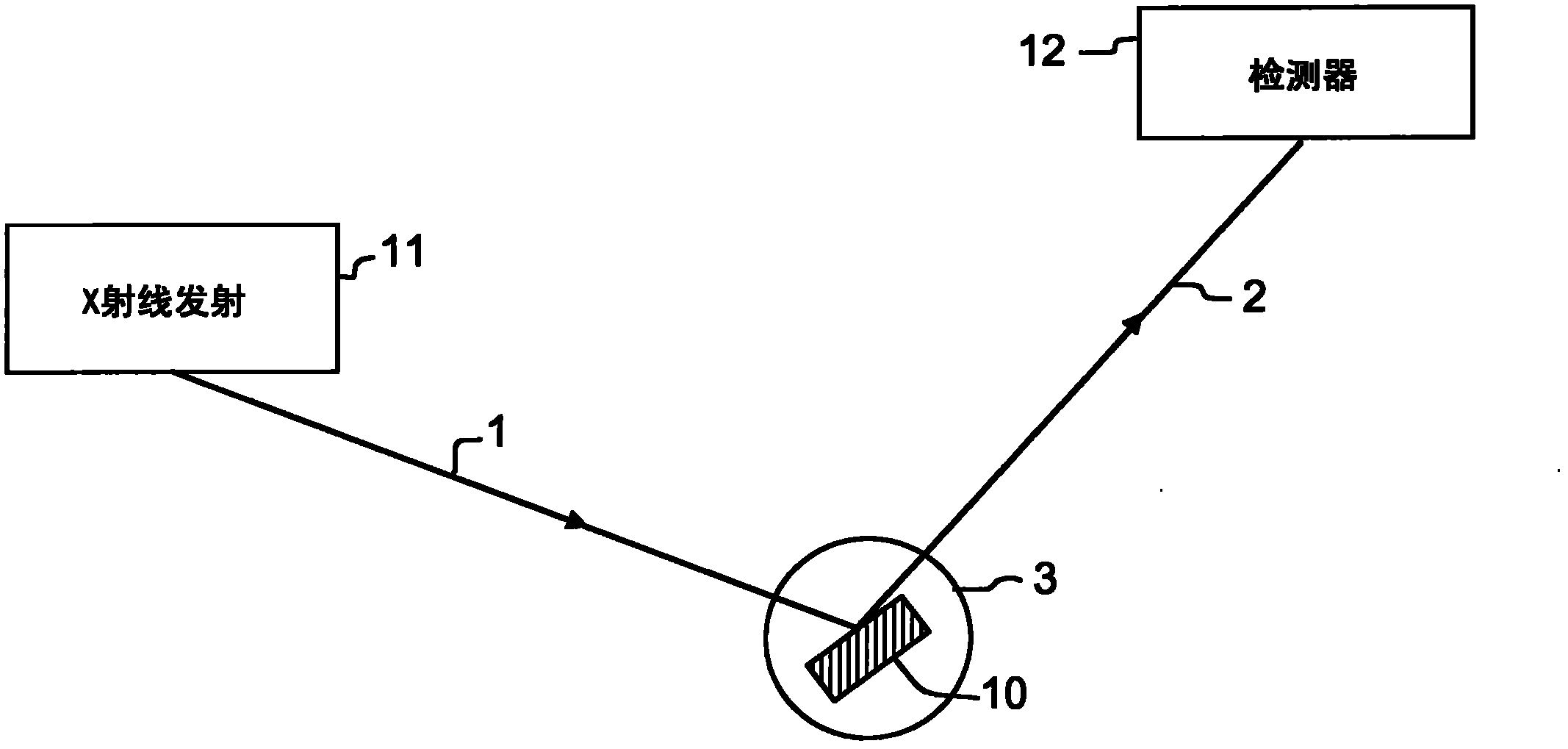
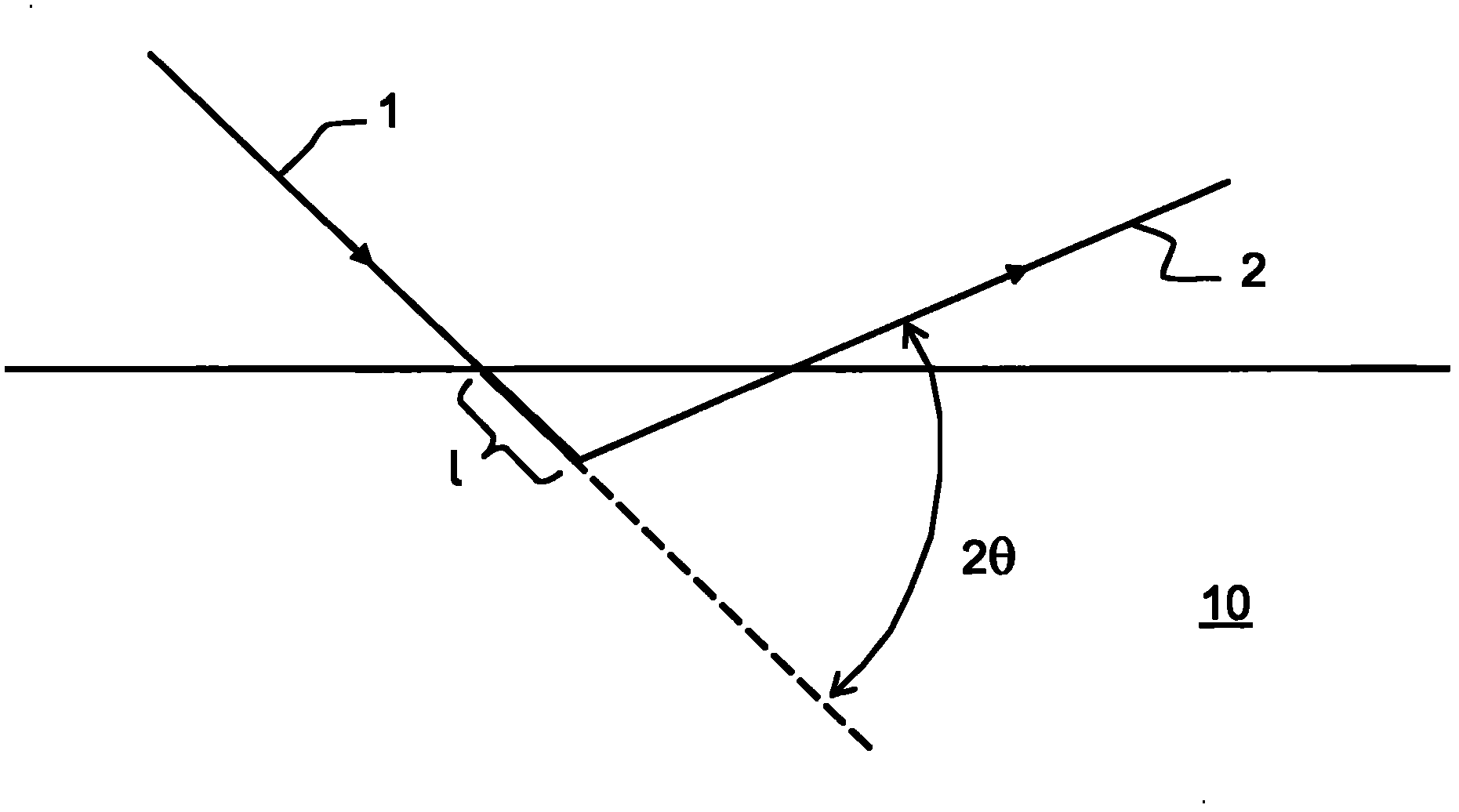
[0022] figure 1 Example The principle of X-ray scattering used in the method according to the invention. An incident beam 1 of X-photons emitted by a source 11 towards a glass sample 11 is backscattered or reflected by the glass sample.
[0023] A glass sample 10 is placed on the diffractometer 3 . The presence or absence of a post-monochromator can be considered in the configuration of the diffractometer.
[0024] Incident X-rays 1 are reflected by the glass. figure 1 The ray 2 reflected by the sample 10 is depicted. The detector 12 is arranged in the direction of propagation of the reflected ray 2 . This detector 12 makes it possible in particular to measure the intensity of the reflected photons.
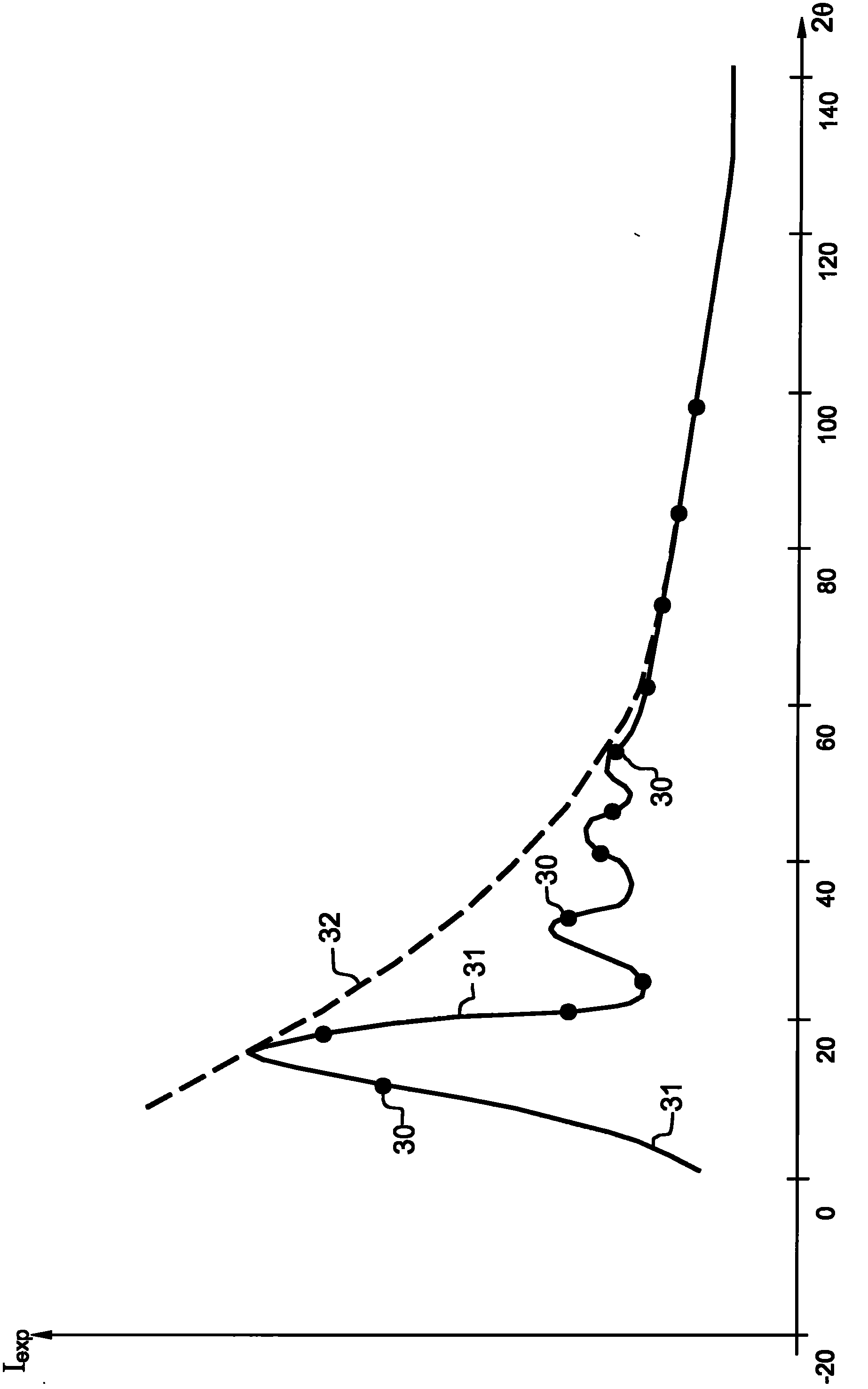
[0025] In methods of the WAXS type, the angle of incidence of the emitted X-rays 1 is varied over a relatively large angular range such that the scattering angle θ is varied over a relatively large angular range. The intensity of the reflected photons then varies as a funct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com