Method for diagnostic marker development
A technology for identifying markers and markers, which is applied in the field of identifying markers and can solve problems such as linkage barriers and DNA polymorphism difficulties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
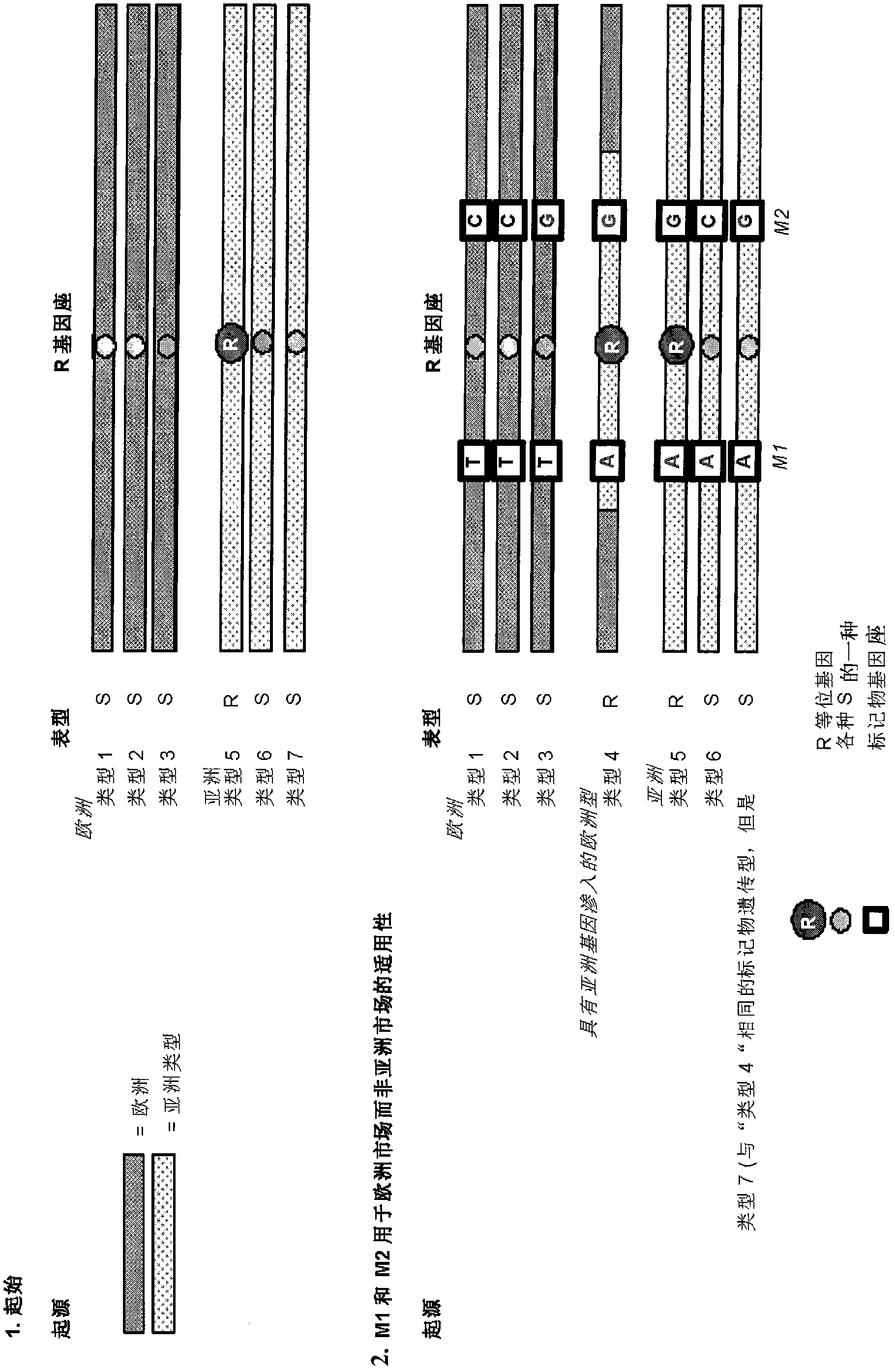
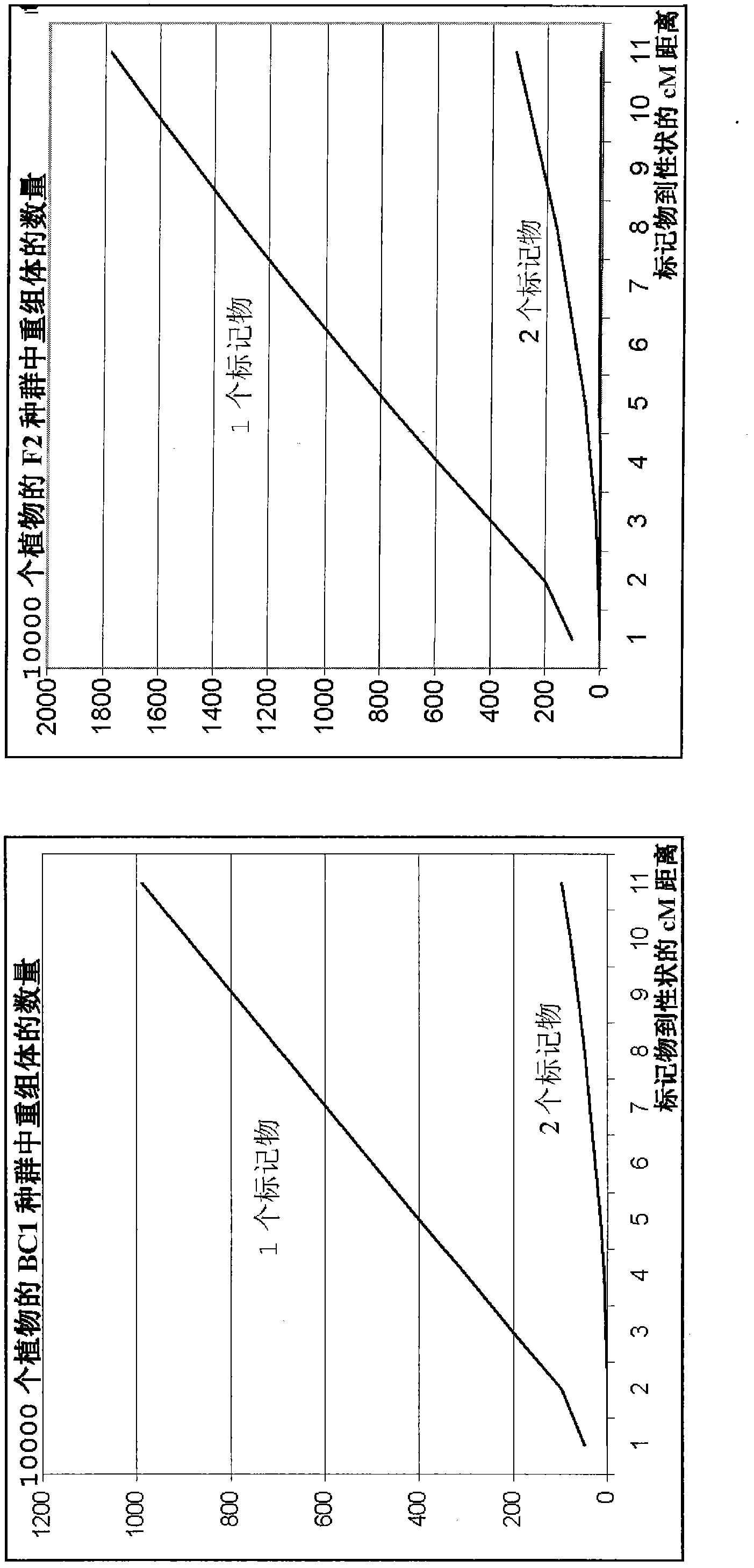
[0067] The principle of the current invention is to generate markers in the vicinity of the target trait. These markers are unique within the germplasm and were designed based on the sequence knowledge available for the selected DNA segment.
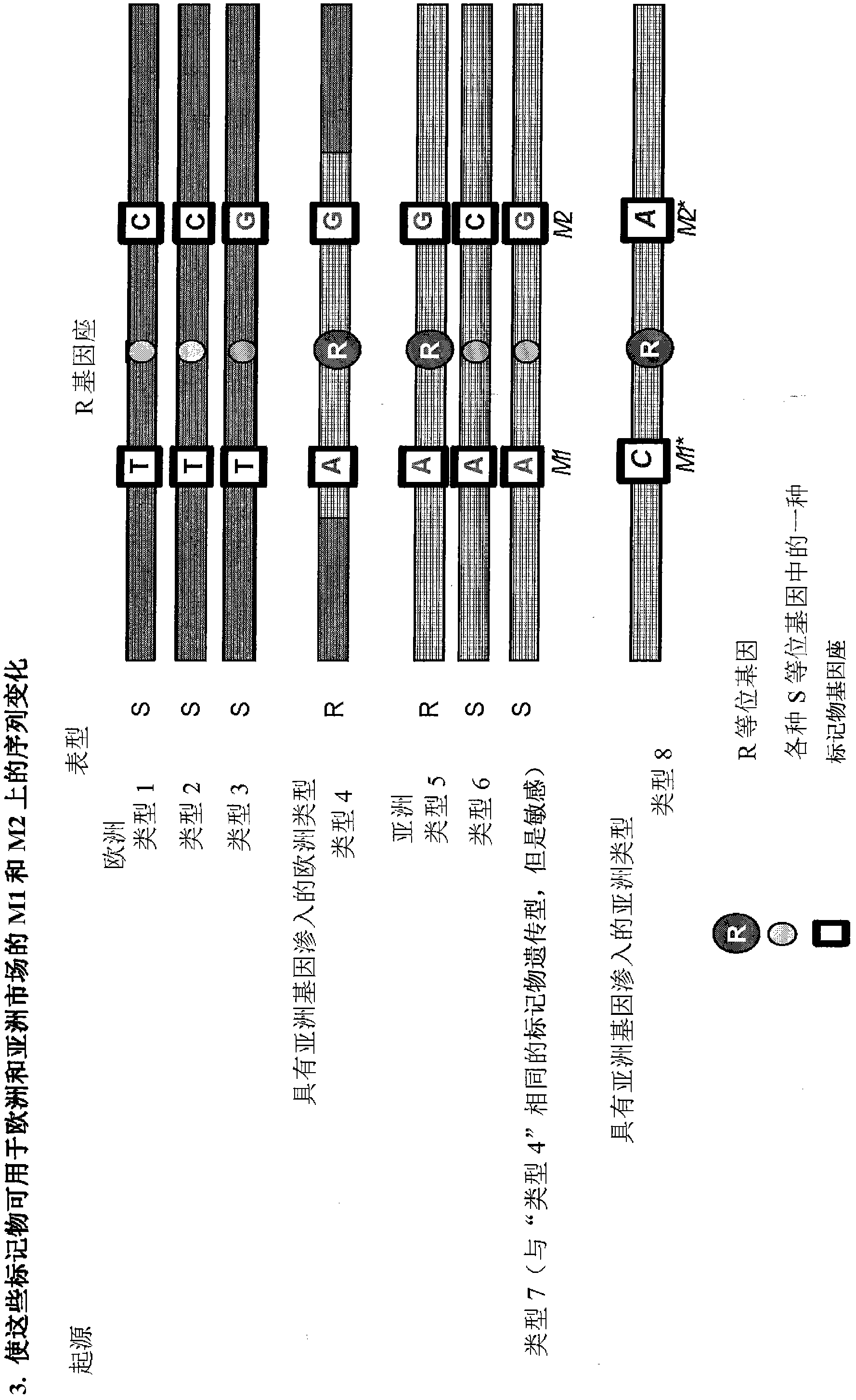
[0068] As a first example describing the starting environment, STS markers M1 and M2 have been developed for the disease resistance trait R obtained from a wild ancestor of the crop of interest ( figure 1 ). This disease resistance trait R was derived from an Asian accession ("Type 5") and has been introgressed into a cultivated European background, resulting in the European breeding line "Type 4". STS markers M1 and M2 were formed based on the sequence of marker loci M1 and M2 flanking the R gene. Only marker M1 has a good predictive value for trait R in segments of the target crops commercially available in Europe. Linkage disorders containing Asian resistant haplotypes were relatively large in European backgrounds.
[0069] Weak ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com