Method for producing ethanol by fermentation of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain
A technology for recombining Saccharomyces cerevisiae and engineering strains, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation and other directions, can solve problems such as lack of and inability to utilize xylose, and achieve high expression, reduced unit time, and high activity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain
[0020] 1. Clone the xylose reductase gene (xyl1) fragment (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) from Candida parapsilosis, and make a Blast comparison with the Candida parapsilosis xylose reductase gene sequence released by Genebank , for homology comparative analysis, the results showed that the homology between the cloned xyl1 gene fragment and the Candida parapsilosis xylose reductase gene released by the gene bank was 100%.
[0021] 2. Clone the xylitol dehydrogenase gene (xyl2) fragment (as shown in SEQ ID NO.2) from Candida tropicalis, and compare the sequence obtained by sequencing with xyl2 in the gene bank (Pubmed+NCBI+Nucleotide) Homology analysis of the gene sequence showed that the sequence was completely consistent with the Genomic DNA sequence of Candida tropicalis xyl2 released by Genebank.
[0022] 3. Cloning of GAP gene fragment from Pichia pastoris GS115
[0023] Primer seque...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Expression identification and activity analysis of xylose reductase gene xyl1 and xylitol dehydrogenase gene xyl2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0042] Select several robust bacterial strains screened in Example 1 for shake flask culture, break the wall, and analyze the expression situation by SDS-PAGE; select the bacterial strain with the highest expression level, cultivate it in large quantities, purify the target protein, and measure the enzyme activity in vitro, wherein xylose reduction The specific enzyme activity of the enzyme gene xyl1 is about 0.521±0.008; the specific activity of the xylitol dehydrogenase gene xyl2 is about 0.401±0.004.
experiment example 1
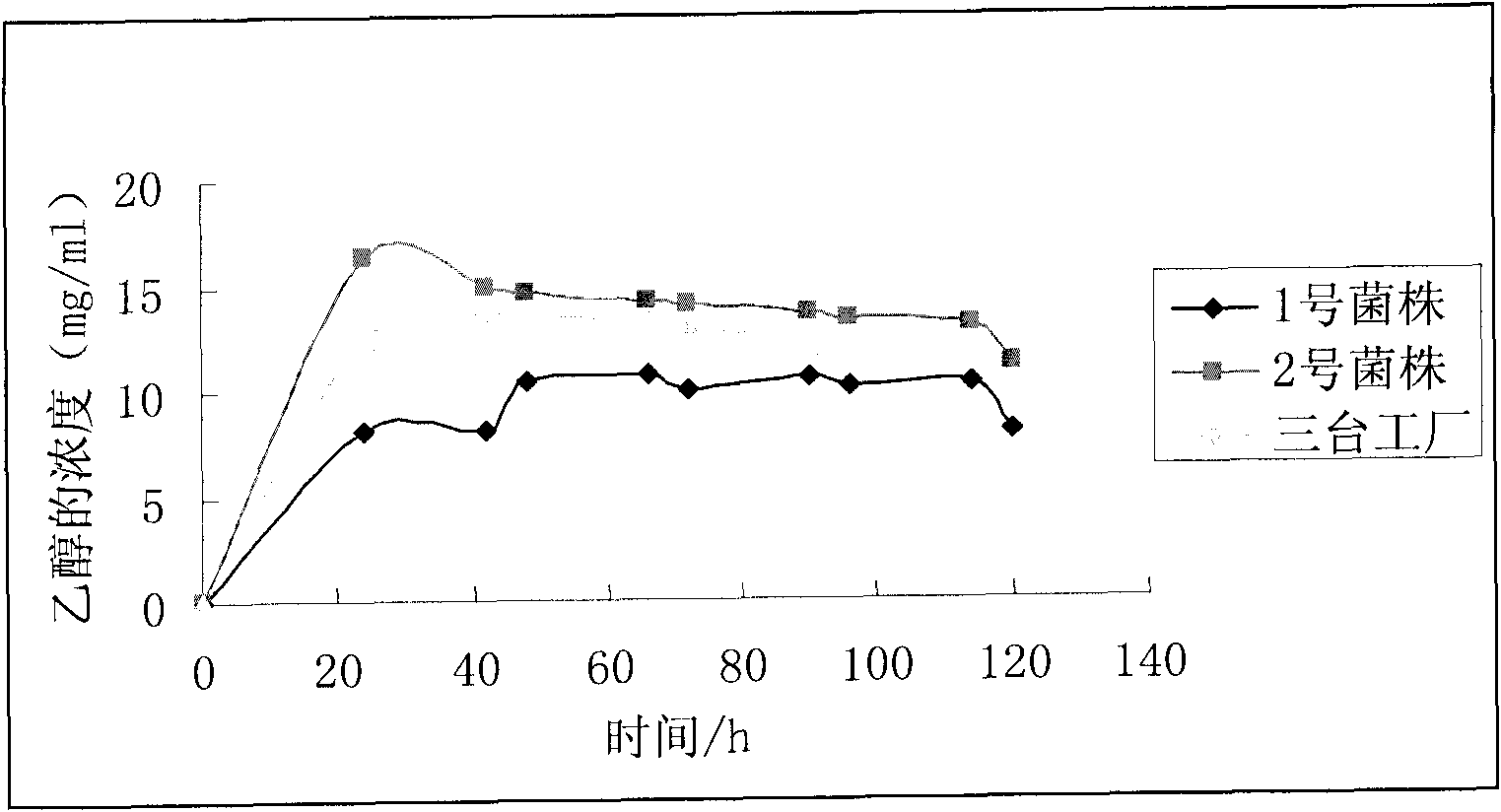
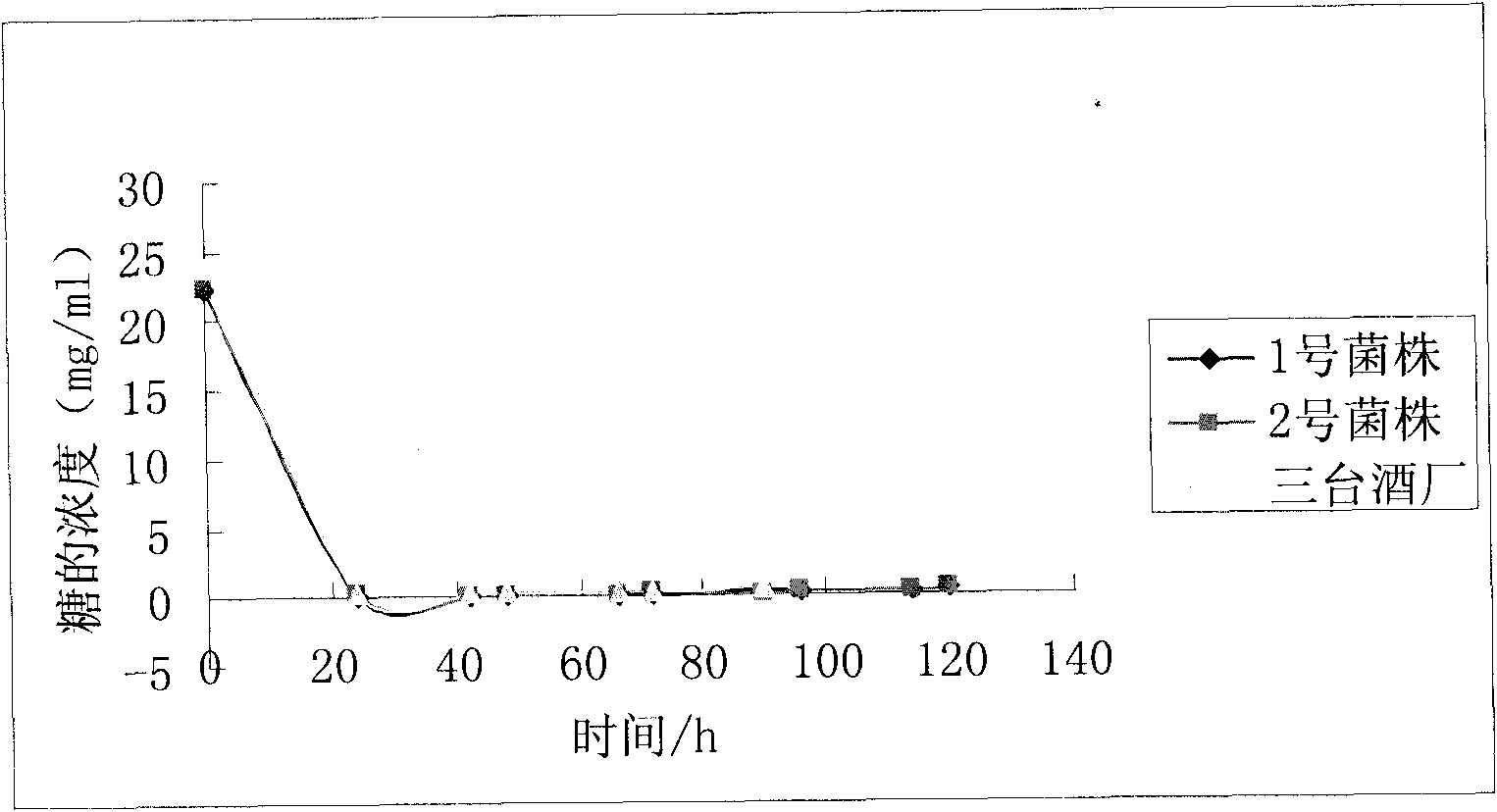
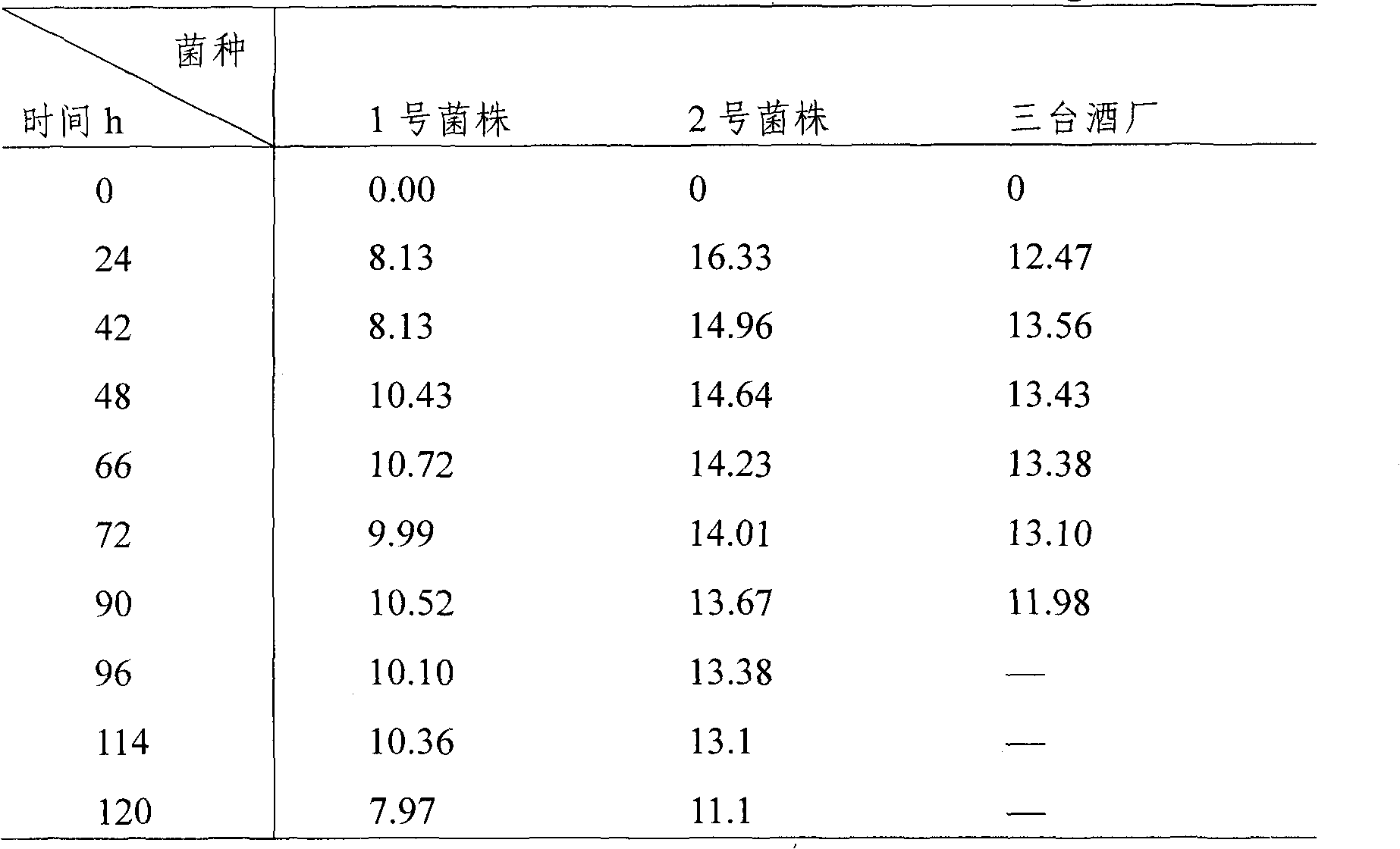
[0044] Xinjiang Jimusar Santai Winery Experiment
[0045] The purpose of the experiment: to carry out large-scale fermentation under the same conditions as possible, the amount of fermentation straw is 1 ton, and timely detect the changes of sugar and alcohol in the fermentation liquid during the fermentation process, so as to test the strains in the actual production process of the three wineries The final yield effect of alcohol.
[0046] Experimental equipment and reagents: 722S spectrophotometer, water bath, electric furnace, Φ15mm×180mm test tube, 1.5ml centrifuge tube. Ethanol (analytical pure), glucose (analytical pure), potassium dichromate (analytical pure), pure water, Xinjiang sweet sorghum straw.
[0047] Experimental steps:
[0048] 1. Prepare 15 fermentation vats, divided into 3 groups of 1, 2, and 3, with 5 fermentation vats in each group, numbered: 11, 12, 13, 14, 15; 21, 22, 23, 24, 25; 31 , 32, 33, 34, 35.
[0049] 2. Break up 3 tons of stalks, divide the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com