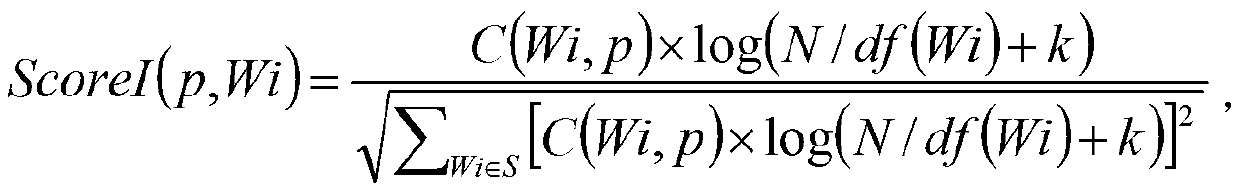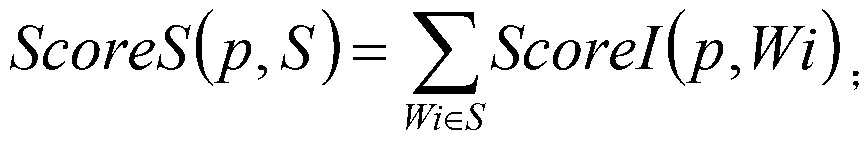Estimation method of biological sample completeness
A technology of biological samples and evaluation methods, which is applied in the field of evaluating the completeness of samples in the biological sample bank system, can solve the problems of expensive storage space, occupation, waste of precious samples and storage space, etc., and achieve the effect of improving utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
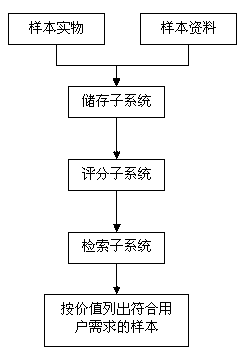
[0044] A tumor biological sample bank system is selected. The storage subsystem of the sample bank saves the inventory of physical objects and the collection of data, and manages them in units of cases. Each case includes corresponding sample objects and sample materials. For the convenience of display, 11 samples in the library are selected for scoring, and the specific information of these samples taken from the storage subsystem is shown in Table 1.
[0045] Table 1
[0046]
[0047]
[0048] The information in Table 1 is explained as follows, serum: 0 = no serum sample, 1 = serum sample; mutation detection: 0 = no mutation detection data, 1 = mutation detection data; follow-up data: -1 = no follow-up, 0 = Unable to follow up, 1=1 follow-up record, 2=2 follow-up records, and so on; serial samples: 0=no serial samples, 2=2 serial samples, 3=3 serial samples , and so on;.
[0049] Step 1 lists the suspended cases nP={case k}, because case k is a case that has not been...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The example sample library in Example 1 is selected, but no field is disabled in Step 1, that is, nW={}, the subsequent calculation steps and formulas are the same as in Example 1, and the calculation results are shown in Table 5. It can be seen from Table 5 that the score of case g rises sharply without using the deactivated field. The reason is that case g contains the field “RH negative”, while other cases do not, which gives case g more scores. However, this field has basically nothing to do with the disease of tumor and will not be used for research. Therefore, it is necessary to deactivate such fields that have nothing to do with user needs to avoid affecting the score.
[0077] table 5
[0078] order
Embodiment 3
[0080] The sample sample library in Example 1 was selected, but in step 1 only the field "RH Negative" was disabled, that is, nW={RH Negative}, the subsequent calculation steps and formulas were the same as in Example 1, and the calculation results are shown in Table 5. It can be seen from Table 5 that the “name” and “sex” fields that are not disabled have no significant impact on the completeness ranking of cases, but the score gap between cases becomes smaller, and the ability to distinguish completeness of cases decreases when the sample size is large , it is also necessary to deactivate such mandatory data.
[0081] Table 6
[0082] order
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com