Modified omci as complement inhibitor
A complement inhibitor and variant technology, applied in anti-inflammatory agents, nervous system diseases, non-central analgesics, etc., can solve problems such as short half-life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
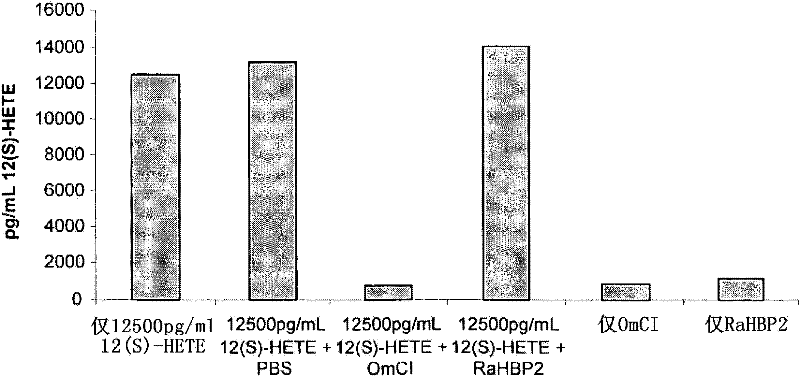
[0132] Example 1: Binding of wild-type OmCI to 12(S)-HETE (12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid) in a competitive ELILSA
[0133] background:
[0134] OmCI can bind fatty acids ( figure 1 ). Mass spectrometry analysis showed that ricinoleic acid (C 18 h 34 o 3 ) and palmitoleic acid (C 16 h 30 o 2 ) are the dominant forms found in OmCI expressed by Pseudomonas methanosa and E. coli, respectively. However, the true physiological ligand is more likely to be one or more of the many eicosanoids derived from host cell membranes that mediate inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and cell signaling.
[0135] A competitive enzyme immunoassay (EIA) from Assay Designs Inc. can be used to quantify a number of eicosanoids. One of the EIA kits described above uses a polyclonal antibody against 12(S)-HETE to bind alkaline phosphatase-labeled 12 that competes with unlabeled 12(S)-HETE in a sample or in a standard of known concentration. (S)-HETE. After simultaneous incubation at...
Embodiment 2
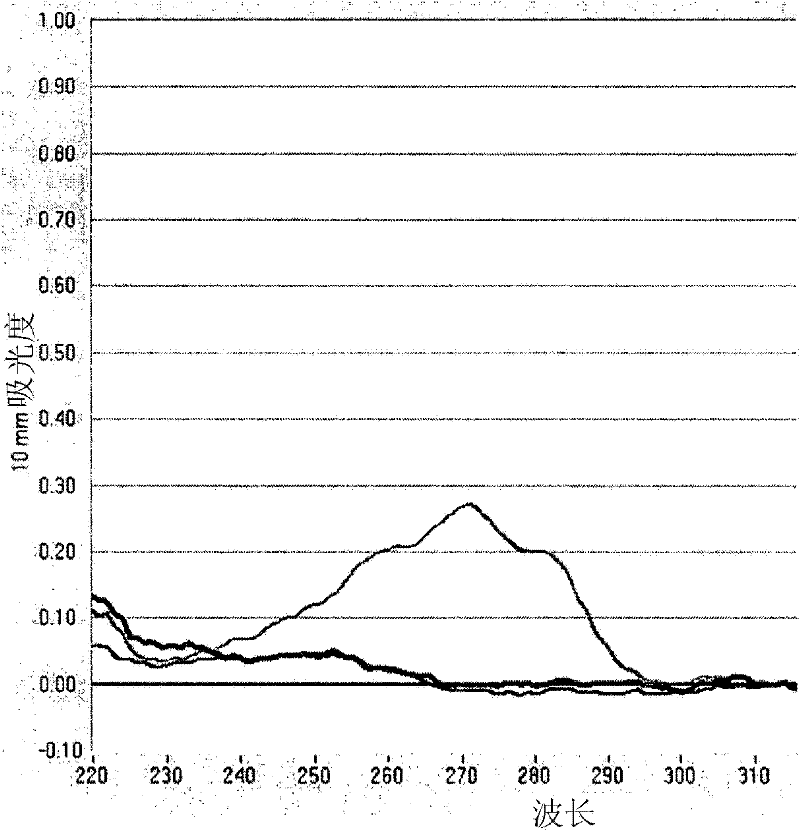
[0143] Example 2: Absorbance confirms binding of wild-type OmCI to LTB 4
[0144] background:
[0145] Leukotrienes have a characteristic strong UV absorption spectrum due to their conjugated double bond system (triene chromophore). In aqueous media, LTB 4 The absorption peak is at 271nm, and the "shoulder peaks" are at 262nm and 282.5nm. Protein absorption peak at 280nm. Combined with LTB 4 The protein should show increased UV absorbance around 280nm compared to the protein alone, and the LTB 4 The characteristic shoulders of are located 10 nm on each side of the absorption peak.
[0146] method:
[0147] Make bOmCI (4.5mg) with 1.8ml LTB 4 (50 ng / [mu]l stock solution in absolute ethanol, Biomol International) was incubated in 39 ml PBS with shaking at room temperature for 10 minutes. OmCI and LTB in this mixture 4 The molar ratio is 1:1. The mixture was concentrated to 200 μl in a Vivaspin (Sartorious) 5 kDa cut-off ultrafiltration device. The retentate was washe...
Embodiment 3
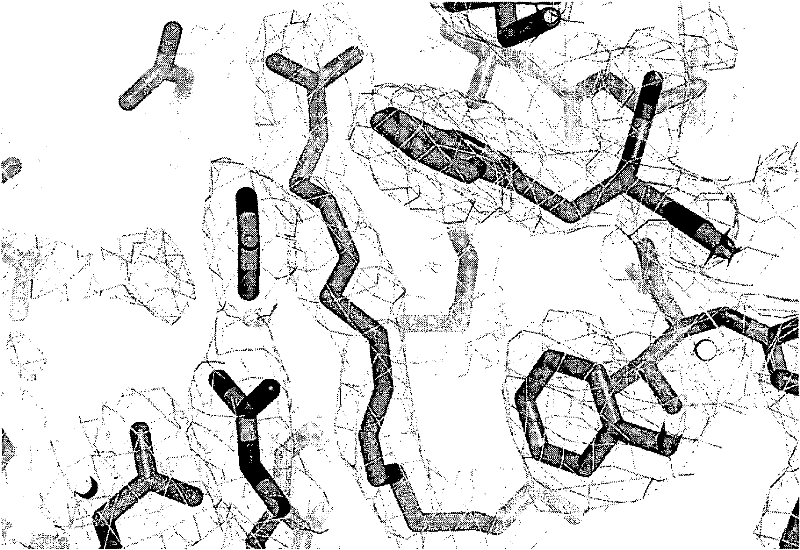
[0151] Example 3: Crystallographic structural data showing LTB in the binding pocket of wild-type bOmCI 4
[0152] method:
[0153] Loaded with LTB 4 The bOmCI protein was prepared as described above (Example 2), then concentrated to 25 mg / ml, buffer exchanged to Tris-HCl at pH 7, 30 mM NaCl, and used to grow crystals. From P21OmCI:LTB on BM14ESRF in July 2008 4 The monoclinic crystal (a=41.76 b=112.81 c=62.40 β = 101.89°, 4 repeats / asymmetric unit) to collect diffraction data sets. The data has been processed to 2.0 resolution, the structure was initially determined by molecular replacement, and OmCI:LTB was established 4 model and refine it to R=20.7, R free = 23.7, rmsd bonds = 0.005, rmsd angles = 0.9.
[0154] result:
[0155] Figure 4 LTB in the bOMCI binding pocket is shown 4 display of the bat. The following residues are directly involved in the interaction with LTB 4 A combination of:
[0156] · Arg54, Thr85, Trp87: These residues are related to L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com