Antigen-binding proteins
An alpha antagonist and antagonist technology, which can be used in drug combinations, antibodies, fusion polypeptides, etc., to solve problems such as blood vessel growth, hemorrhage and edema, and loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
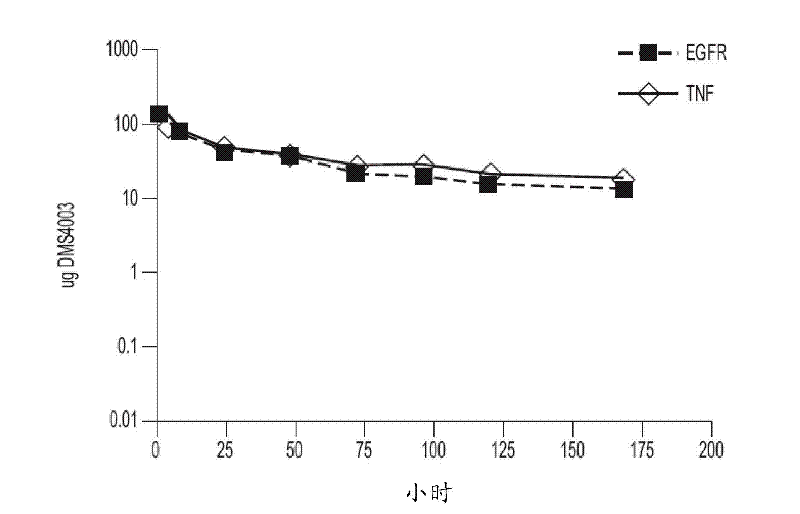
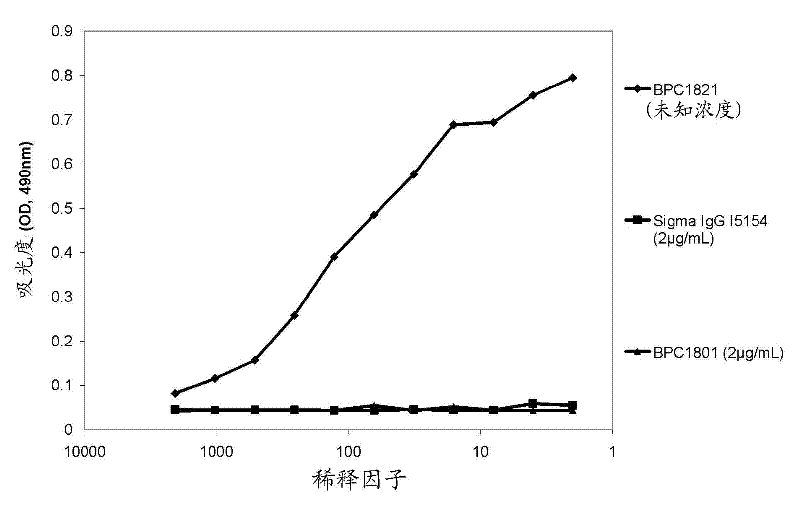
[0338] 1.1 Preparation of dual targeting anti-TNFα / anti-VEGF mAbdAb (DMS4000)
[0339] An anti-TNFα / anti-VEGF mAbdAb (designated DMS4000) was produced by fusing the dAb to the C-terminus of the mAb (adalimumab) heavy chain. To construct the heavy chain expression cassette, the vector DNA encoding the heavy chain of the alternative mAbdAb was used as a starting point. The dAb portion was excised using restriction enzymes SalI and HindIII. DOM15-26-593 (anti-VEGF dAb) was amplified by PCR (using primers encoding SalI and HindIII ends) and ligated into the vector backbone from which the dAb had been excised using the same restriction sites to generate mAb and dAb 'STG' (serine, threonine, glycine) linker between.
[0340] Sequence-verified clones (SEQ ID NO: 11 and 13 for the light and heavy chains, respectively) were selected and large-scale DNA preparations were performed and, using transient transfection techniques, passed through the light and heavy chains (SEQ ID NO: Co...
Embodiment 2
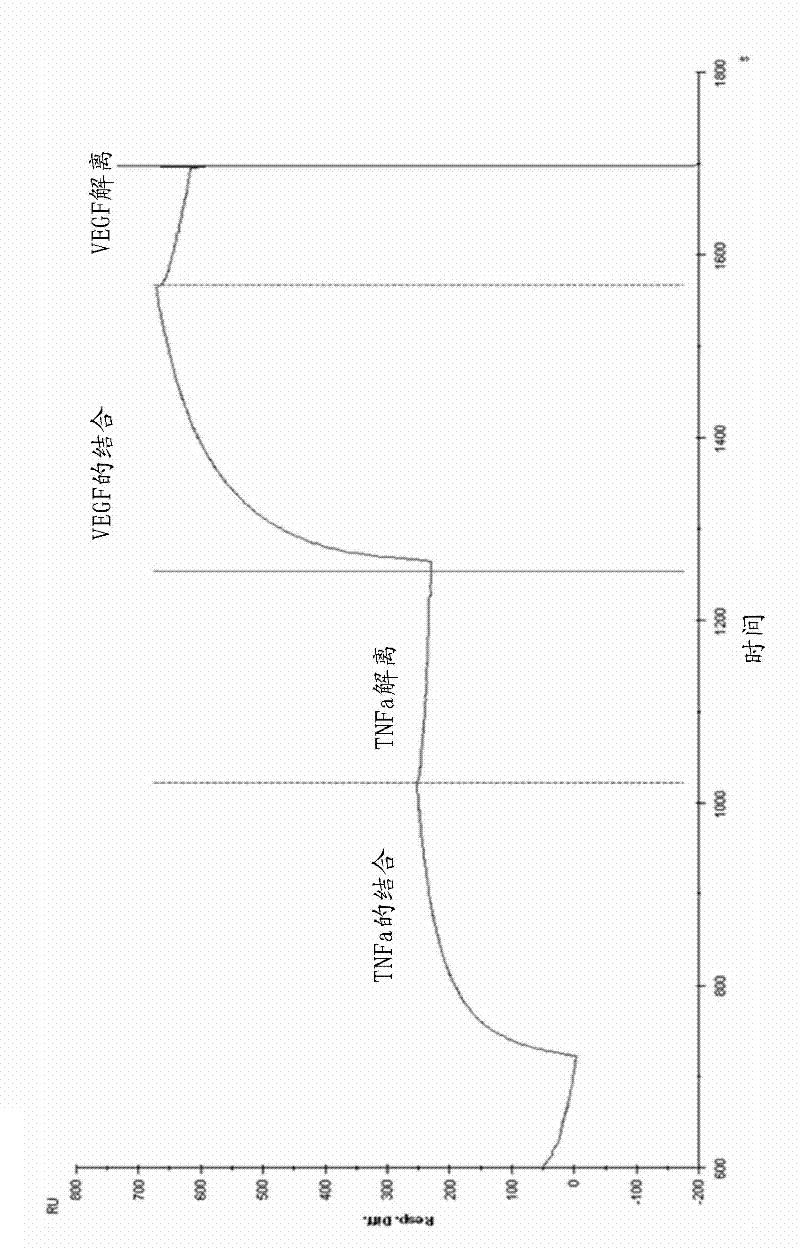
[0359] Biacore analysis of dual targeting anti-TNFα / anti-VEGF mAbdAb
[0360] Experimental mAbdAbs were subjected to BIAcore analysis to determine their kinetic association and dissociation constants for binding their corresponding antigens. at BIAcore TM 3000 devices for analysis. The equipment temperature was set at 25 °C. HBS-EP buffer was used as running buffer. Collect experimental data at the highest possible rate for the equipment. Using standard amine coupling chemistry according to the manufacturer's instructions, one flow cell on a research-grade CM5 chip was coated with protein A, and a second flow cell was similarly treated, but with buffer instead of protein A to generate a reference surface. A flow cell coated with Protein A was then used to capture mAbdAbs. Antigen was injected as 2x serial dilutions as detailed in Table 2. Several dilutions were run in duplicate. A separate buffer injection instead of ligand is used for background subtraction. Samples...
Embodiment 3
[0364] Stoichiometric assessment of antigen-binding proteins (using Biacore™)
[0365] This example is predictive. It provides guidance for conducting other assays in which the antigen binding proteins of the invention can be tested.
[0366] Anti-human IgG was immobilized on the CM5 biosensor chip by primary amine coupling. The antigen-binding protein is captured on this surface and then passed through with a single concentration of TNFα or VEGF sufficient to saturate the binding surface and the observed binding signal to full R-max. Then using the formula given, the stoichiometry is calculated:
[0367] Stoichiometry = Rmax*MW(ligand) / MW(analyte)*R(immobilized or captured ligand)
[0368] In cases where the stoichiometry of more than one analyte binding is calculated simultaneously, the different antigens are passed sequentially at saturating antigen concentrations and the stoichiometry is calculated as above. The work can be performed on a Biacore 3000 at 25°C using H...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com