Solar simulator and measurement method using same
The technology of a solar simulator and measurement method is applied in the field of solar simulators to achieve the effects of prolonging lamp life, shortening measurement time, and shortening luminous time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
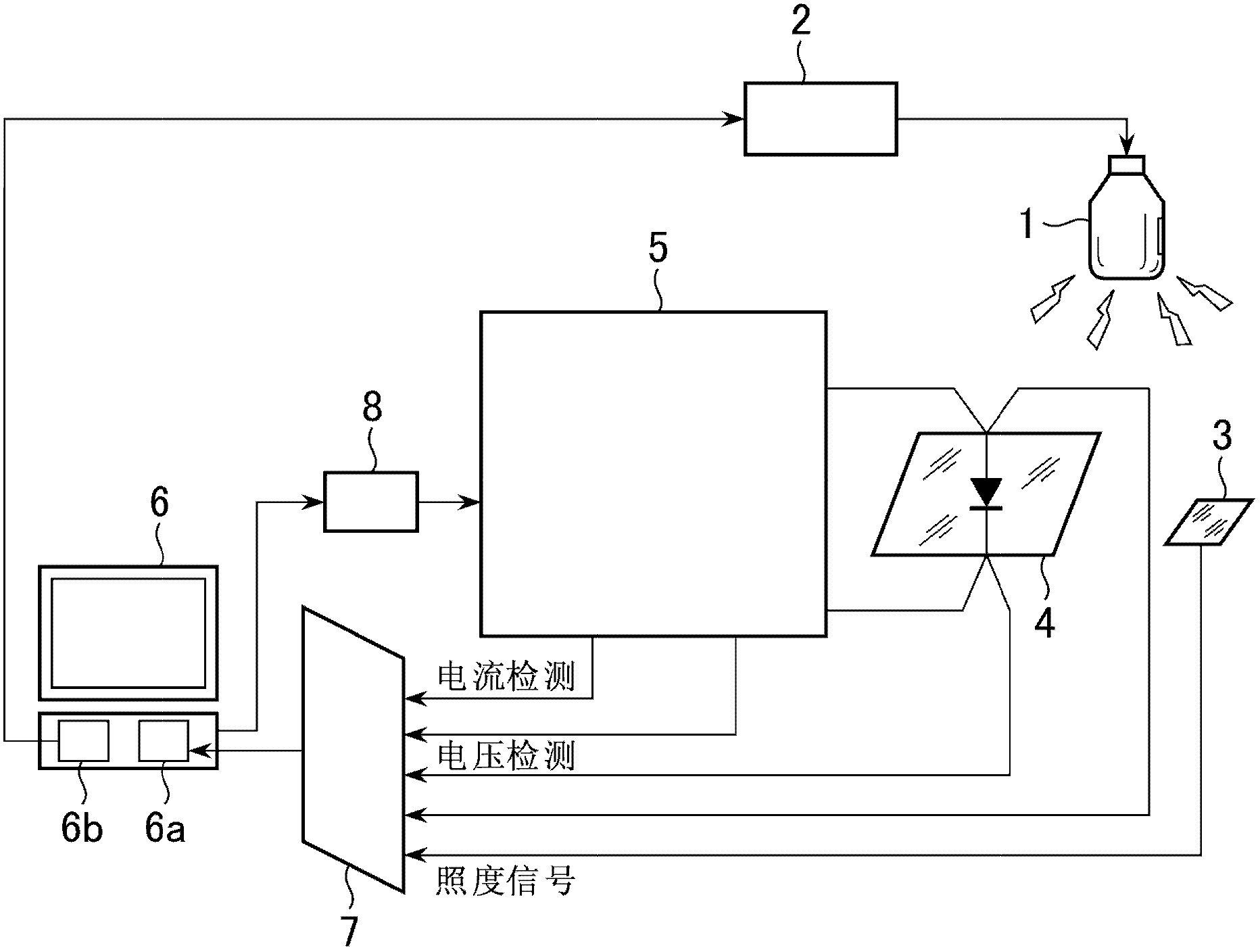
[0082] according to Figure 5 An example of a solar cell in the vicinity of a current / voltage value (optimum operating point) showing maximum power ( Figure 9 The area M) responds slowly, while in other load areas ( Figure 9 The area N1 and area N2) respond quickly. In this embodiment, the electronic load command is controlled by current. The operating current of the solar cell is manipulated according to the electronic load command, and the voltage value output from the solar cell as the object to be measured is measured. Figure 5 (b) represents the patterns a, b, and c in which the current command changes with time. Figure 5 (a) is the output characteristic curve obtained according to the modes a, b, and c of the current command changing with time.
[0083] exist Figure 5 In (a) and (b), pattern a (dotted line) represents a conventional measurement method of measuring a solar cell with a current command at a constant speed. Pattern b (single-dashed line) represent...
Embodiment 2
[0090] according to Figure 7 Next, an example of a solar cell in another mode will be described. The solar cell is in the vicinity of the current / voltage value (optimum operating point) showing the maximum power ( Figure 9 The area M) responds slowly, while in other load areas ( Figure 9 Region N1 and region N2) solar cells with fast response. In this embodiment, the electronic load command is controlled by voltage. The operating voltage of the solar cell is controlled according to the electronic load command, and the current value output from the solar cell as the object to be measured is measured. Figure 7 (b) represents the patterns a, b, and c of the voltage command changing with time. Figure 7 (a) is the output characteristic curve obtained according to the modes a, b, and c of the voltage command changing with time.
[0091] exist Figure 7 In (a) and (b), pattern a (dotted line) represents a conventional measurement method of measuring a solar cell with a volt...
Embodiment 3
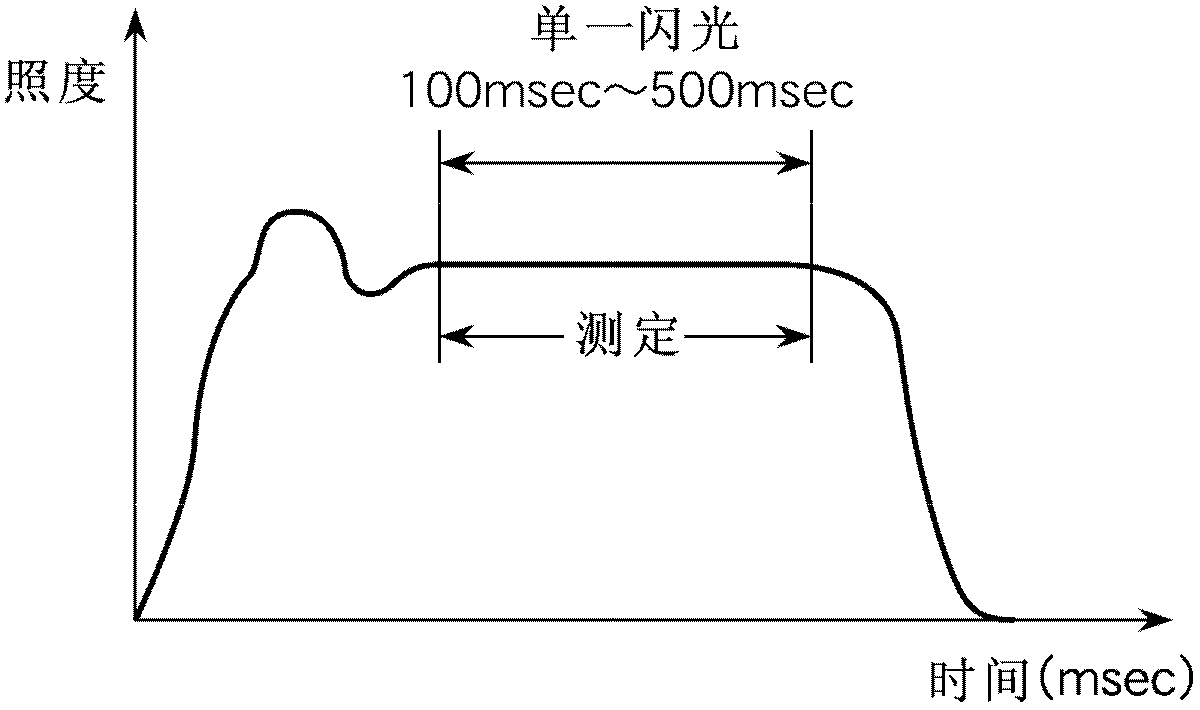
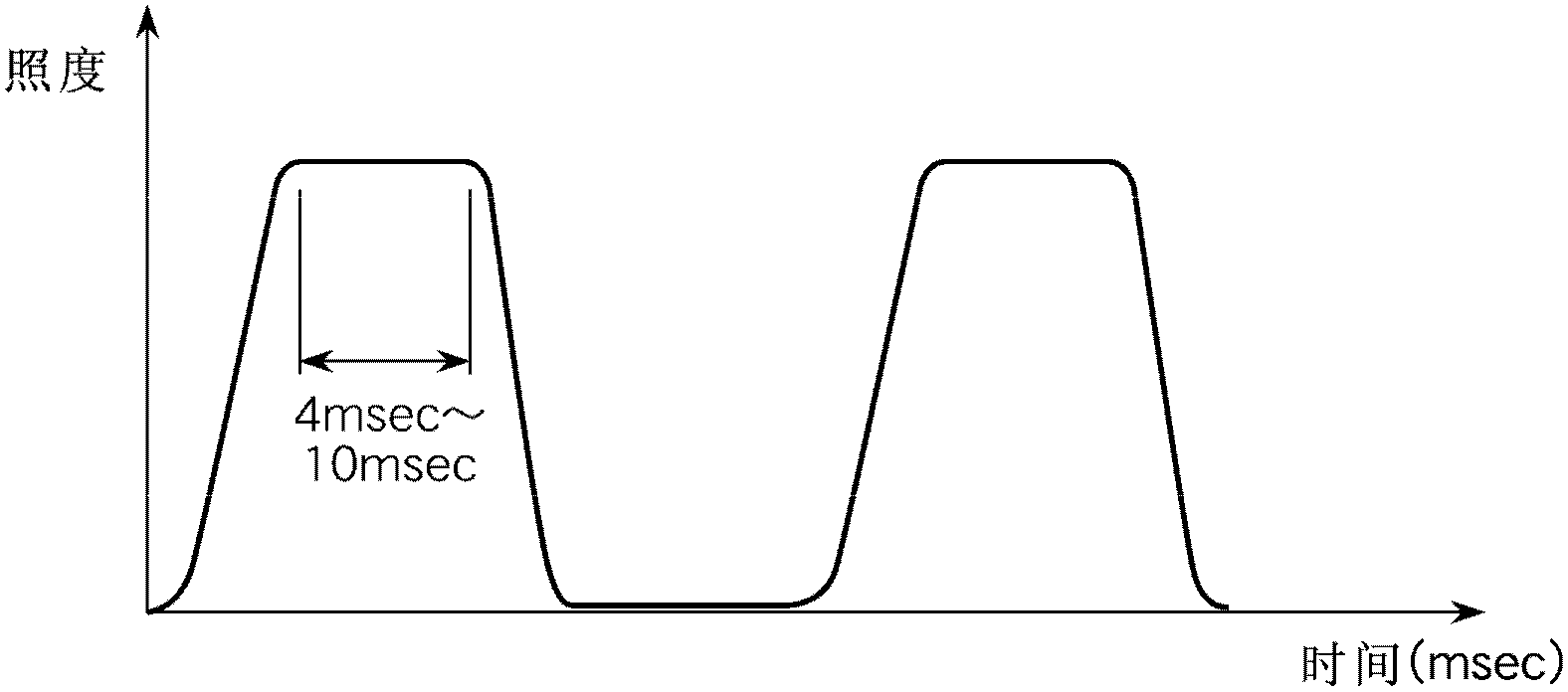
[0098] When using a light source with a short light emitting time, such as Figure 8 As shown, multiple flashes can be made to perform split measurement. For example, in the case of changing the current with time according to the single-dot chain line b of the conventional measurement method in Example 1, when measuring the output characteristics of a solar cell with a relatively slow response characteristic, the pulse waveform can be divided into and Figure 8 Measurement points corresponding to parts A and B of the pulse waveform in (a). exist Figure 8 (b) at the first luminous place, according to the assay method of the present invention Figure 8 (a) The measurement point of part A is measured. exist Figure 8 (b) at the second luminous place, according to the assay method of the present invention Figure 8 (a) The measurement point of part B is measured. and Figure 5 (b) and Figure 7 As in mode c of (b), after the load command speed is properly adjusted by the me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com