See-through display brightness control
A see-through display and see-through display technology, applied to static indicators, cathode ray tube indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as discomfort or damage to the user's eyes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
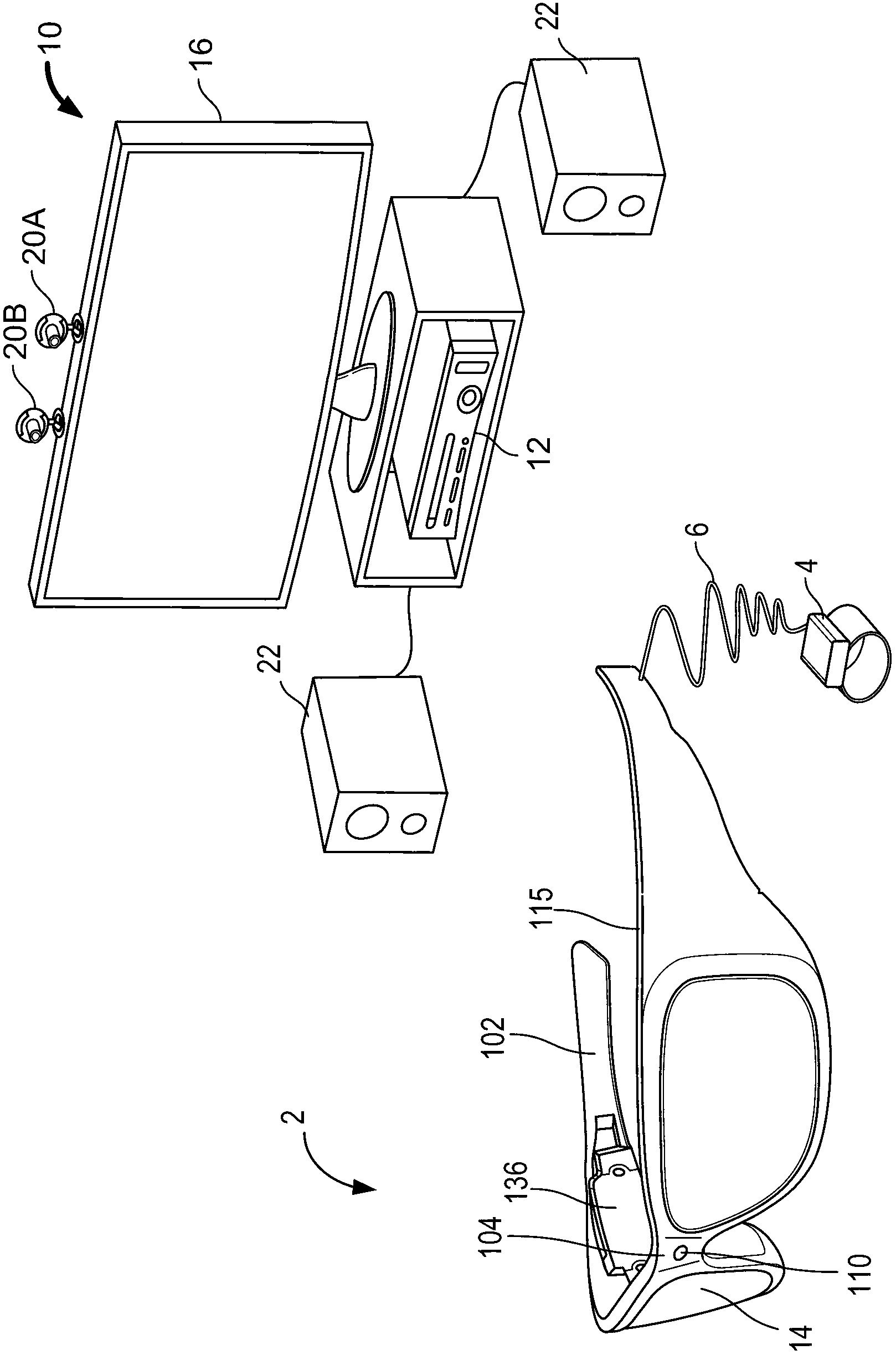
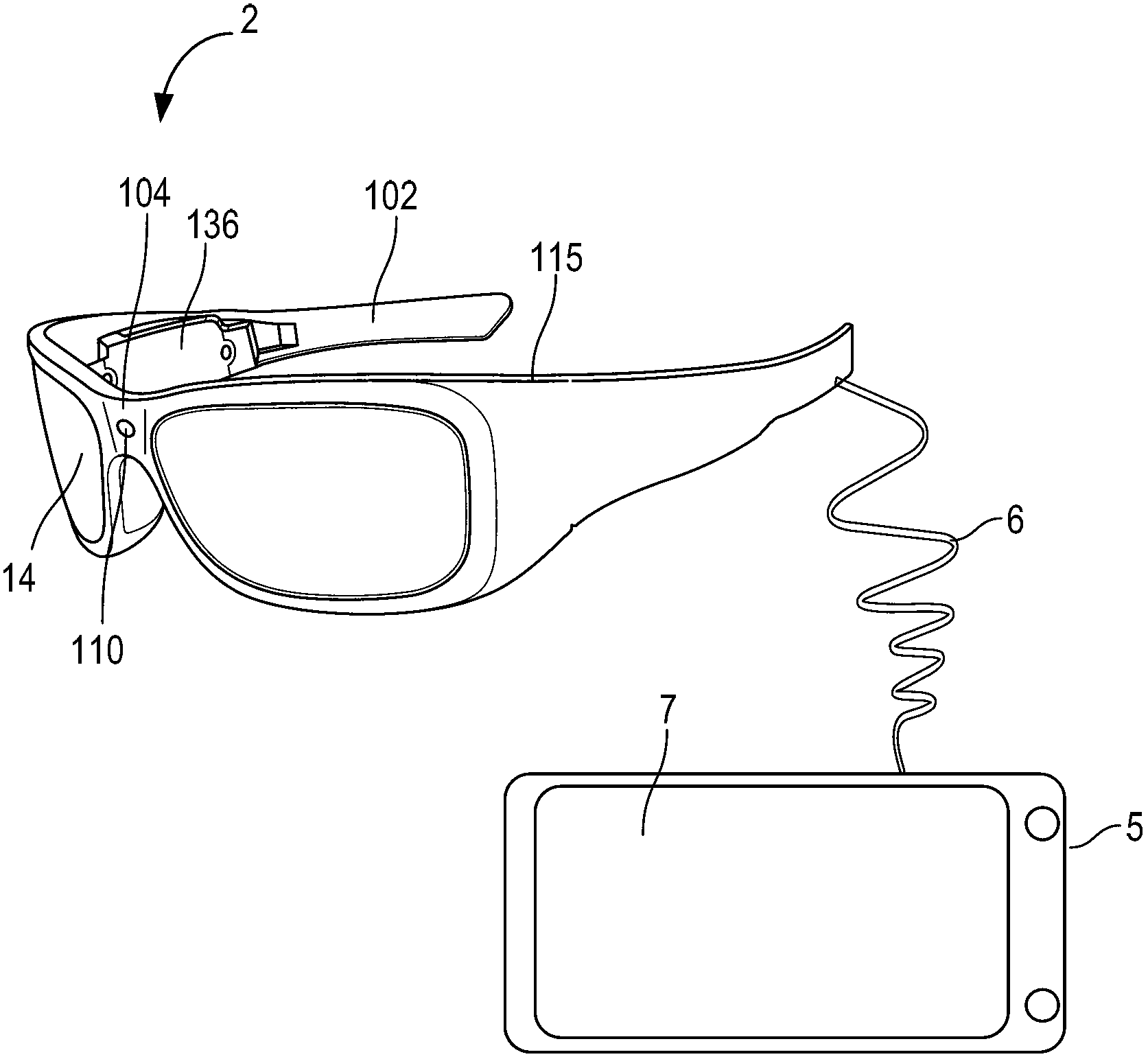
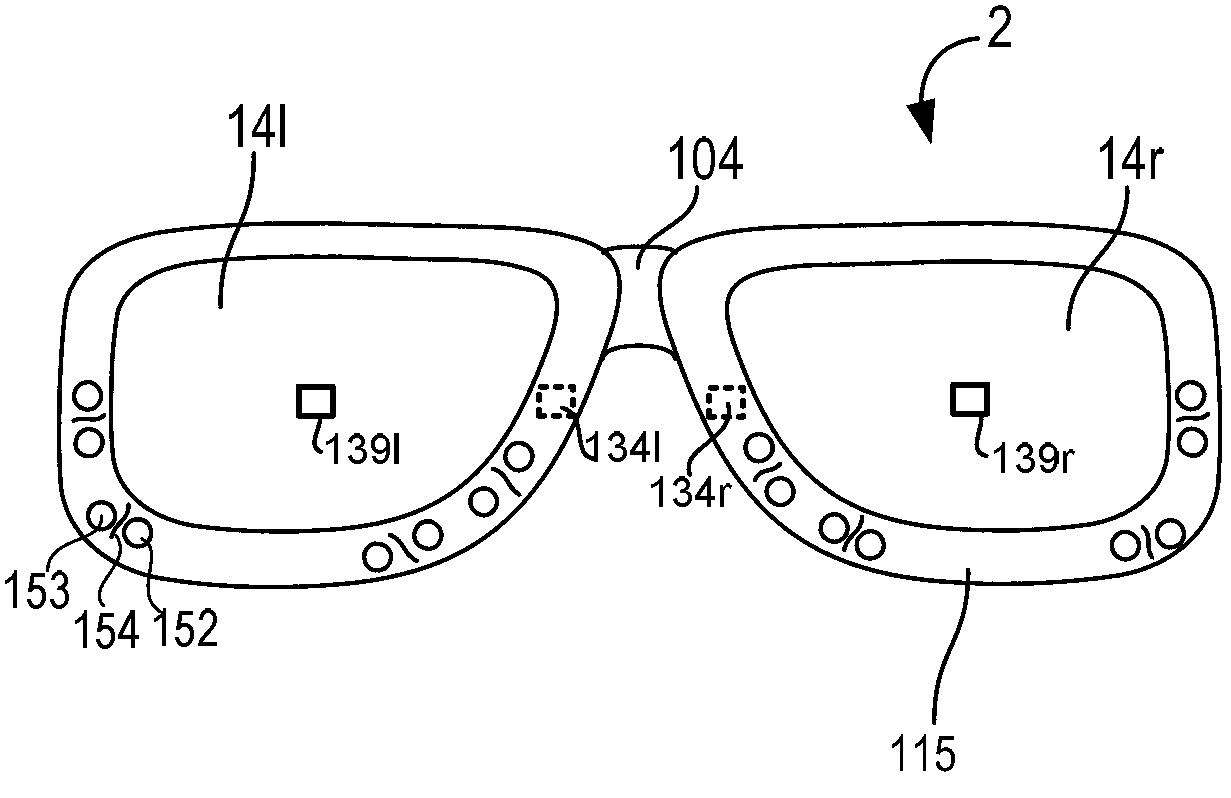
[0053] The techniques described herein provide various embodiments for adjusting the brightness of see-through, near-eye displays. One possible adjustment is to change the brightness used to display the image ("image brightness"). Another possible adjustment is to change the opacity of the display so that more or less external light will pass through into the wearer's eyes. These adjustments can be balanced against each other so that real and virtual objects are properly viewed.
[0054] In one embodiment, the wearer's eyes are tracked to determine where the user is looking. The light intensity of the real world object the user is looking at is then determined. Light intensity can be used to adjust opacity and / or image brightness. In one embodiment, the wearer's pupil size is tracked. Pupil size can be used to determine how to adjust opacity and / or image brightness. Note that both light intensity from the object and pupil size can be taken into account in the determinatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com