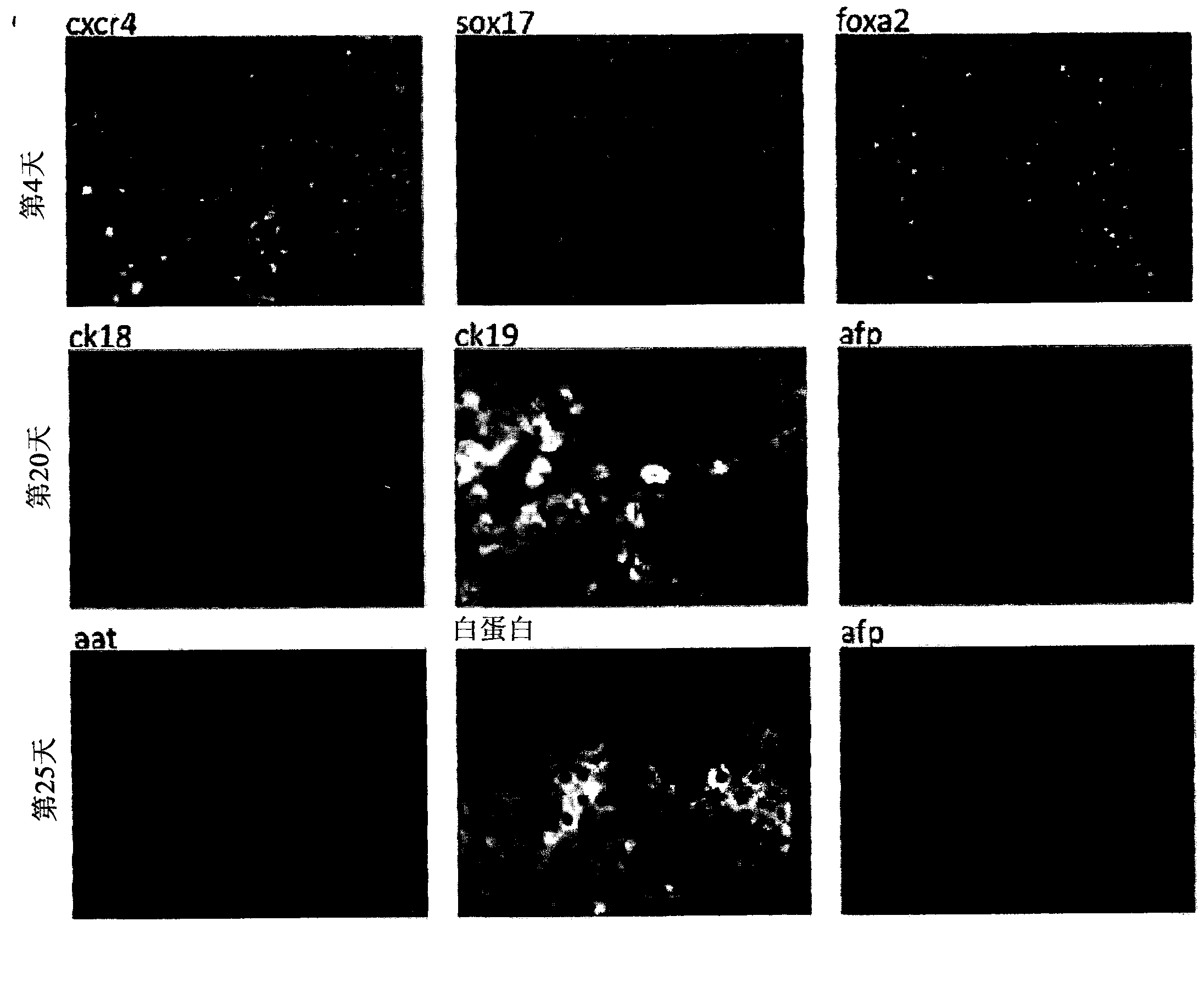
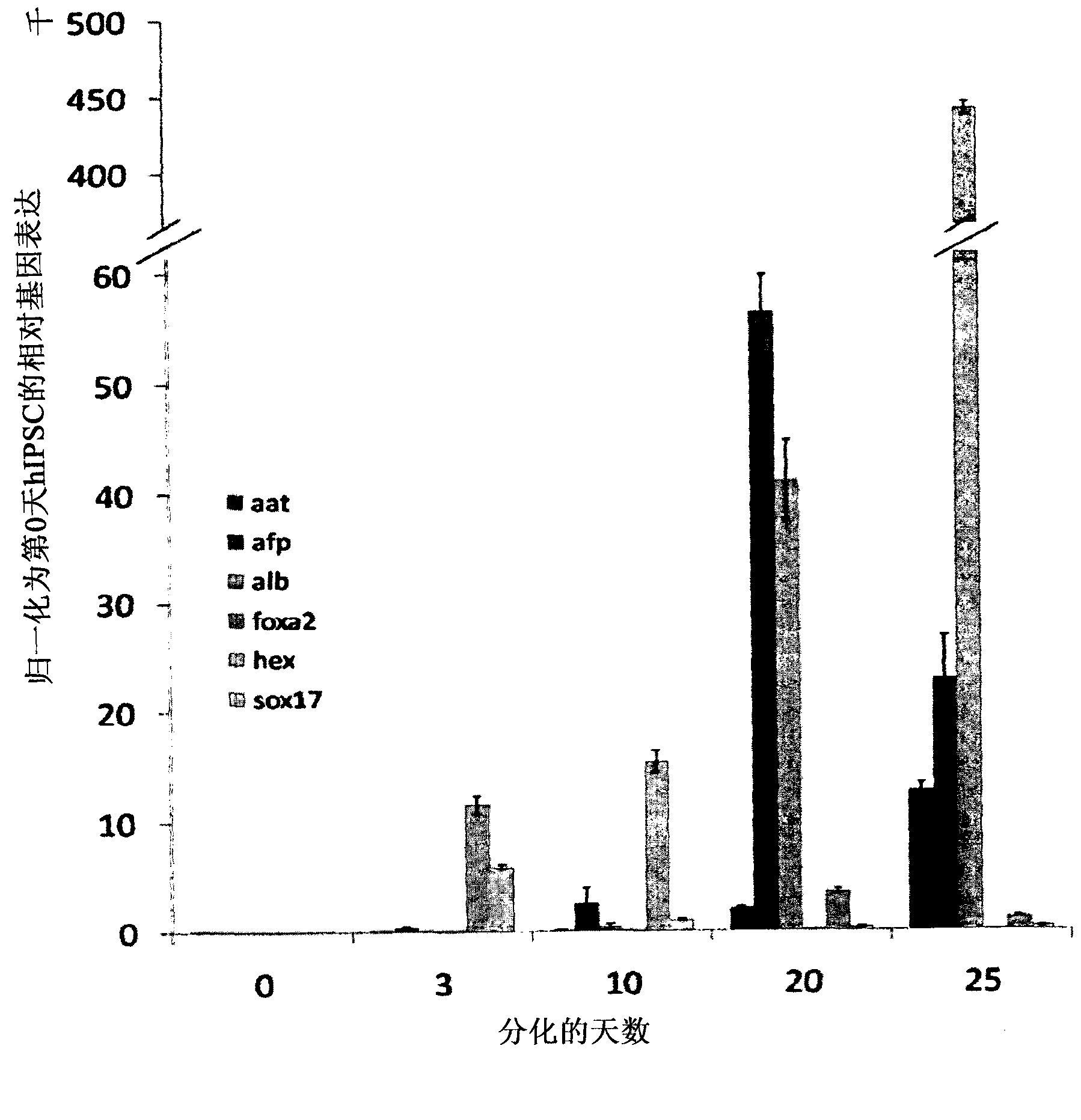
Vitro hepatic differentiation
A Liver Differentiation, Population Technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0189] experiment
[0190] method
[0191] hIPSC derivation and culture
[0192] After appropriate ethical review and patient consent, 8 mm skin punch biopsies were obtained from volunteer patients attending Addenbrooke's Hospital (Ethics Committee No. 08 / H0311 / 201; R&D No: A091485). Fibroblasts were obtained from tissue donations under GMP conditions using standardized laboratory protocols and expanded in standard fibroblast medium. Additional fibroblast samples were obtained from INSERM (France) and Coriell Biorepository. As detailed in Table 1, a total of 5 different disease samples were obtained from 7 different patients. Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived vectors each contained the coding sequence for one of four human genes (Oct-4, Sox2, c-Myc, and Klf4), while the corresponding viral particles were produced by Vectalys (Toulouse, France). ) were generated and used to infect fibroblasts with a 10-fold multiplicity of infectivity, as originally described by Y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com