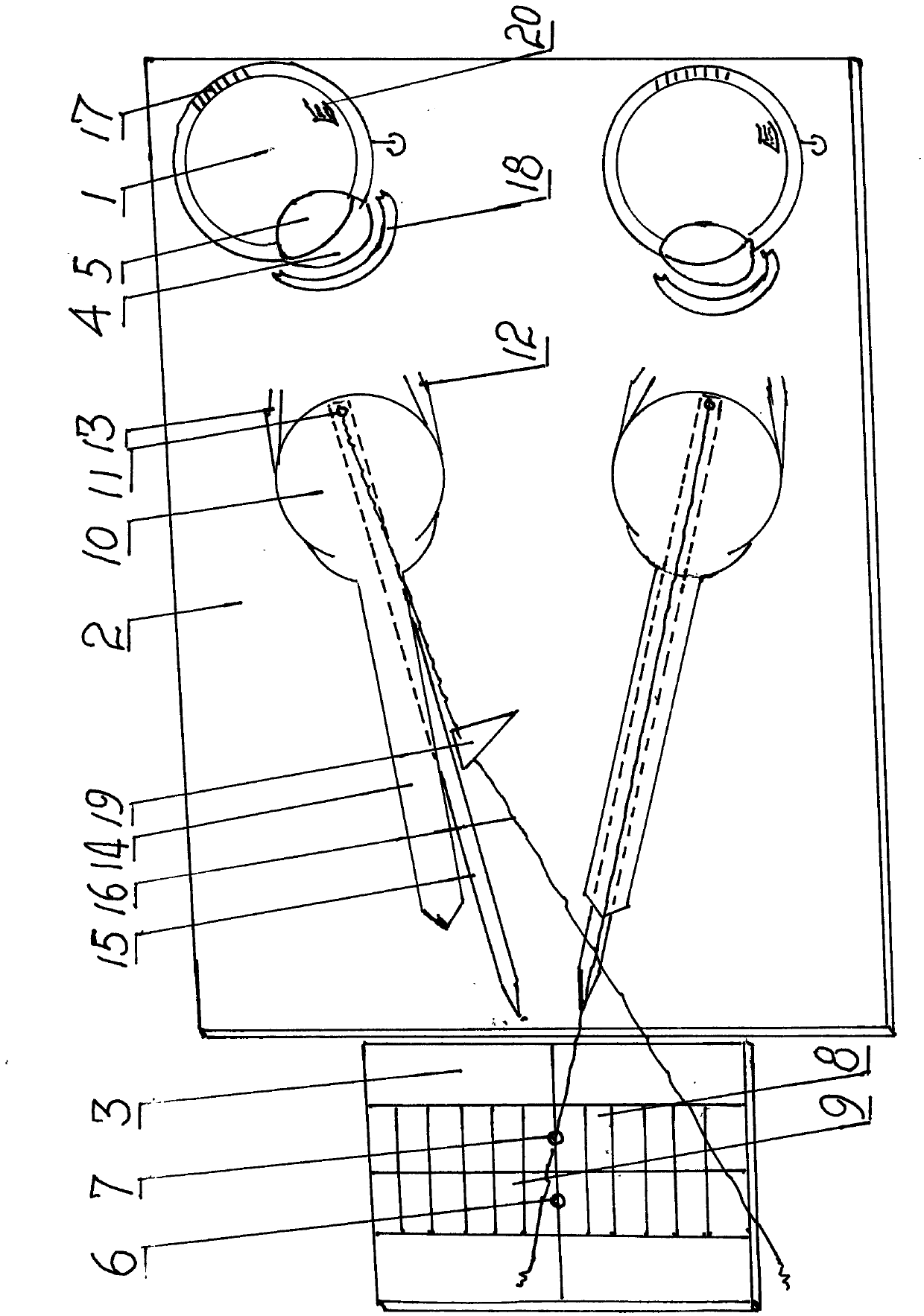
Demonstrator with two-eye visual function
A demonstration device and binocular vision technology, which is applied in the field of optometry and can solve the problems of complex abstraction and difficulty in understanding of binocular vision.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1, combined with the demonstration of Maldives rods.
[0054] A Maldox rod for optometry, cut 1 / 2 into a semicircle along the direction of the columella lens, and place it on the right simple eye 1 semicircle bracket 18, that is, place it in front of the lower cornea 4. The two lamps of the sub-board 3 are energized. Make the patient glance, adjust up and down to be, lower cornea 4 is the vertical light beam that lower lamp 7 becomes by Maldives rod, and cornea empty 5 is upper lamp 6. Adjust left and right again for the vertical light beam that is aimed at to coincide with the light 6 on the cornea space 5, that is, the vertical light beam and the light 6 are all in the vertical line, and now the right simple eye 1 is the horizontal upright position. As simple and easy eye 1 deflects left and right, then vertical light beam leaves the upper light 6 of corneal space 5, and the deflection is bigger, and light beam is farther away from small light 6.
[0055]...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 demonstrates myopia with systemic symptoms and exophoria caused by adjustment factors.
[0060] When the simple eye 1 in the upright position is turned outward, the lower light 7 seen by the lower cornea 4 moves to the left, and is misaligned with the upper light 6 seen by the cornea empty 5, and some bars of the right red 9 also move to the left. The bar grid changes from the upper and lower same colors of the positive position to the upper blue and the lower red. The lower light 7 is a false image (a double image) caused by the outward deflection of the simple eye 1 .
[0061] Then adjust the left eye to be the right eye, then the same lower light 7 seen by the left and right eyes of the "owner" of the two simple eyes is: the lower light 7 whose right eye has changed its position and moved to the left—false image , and the two images of lamp 7 under the same position of the left eye, - diplopia occurred. When the "belonging person" is watching with both ey...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Embodiment 3, plane demonstration of exophorin.
[0066] The right side wants to look at the lower light 7 that line 15 wants to look at. The planar slice 10 turns outwards, that is, the visual axis 14 that is attached also points to the right side of the lower light 7, and does not coincide with the line 15 that you want to see, and there is an angle between the two lines. When looking close, the image line 16 has moved to the left, and is placed on the inside of the line 15, which is the position of the false image of the lower light 7. And the left eye is in the right position: the visual axis, want to see, and image lines of the left flat section overlap, and point to the lower light 7 (as shown in the left eye of the accompanying drawing) together. The two image lines 16 of the two eyes should point to the lower lamp 7 at the same time, but they form an upright left eye pointing to the lower lamp 7, and another false image is the inward displacement of the lower l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com