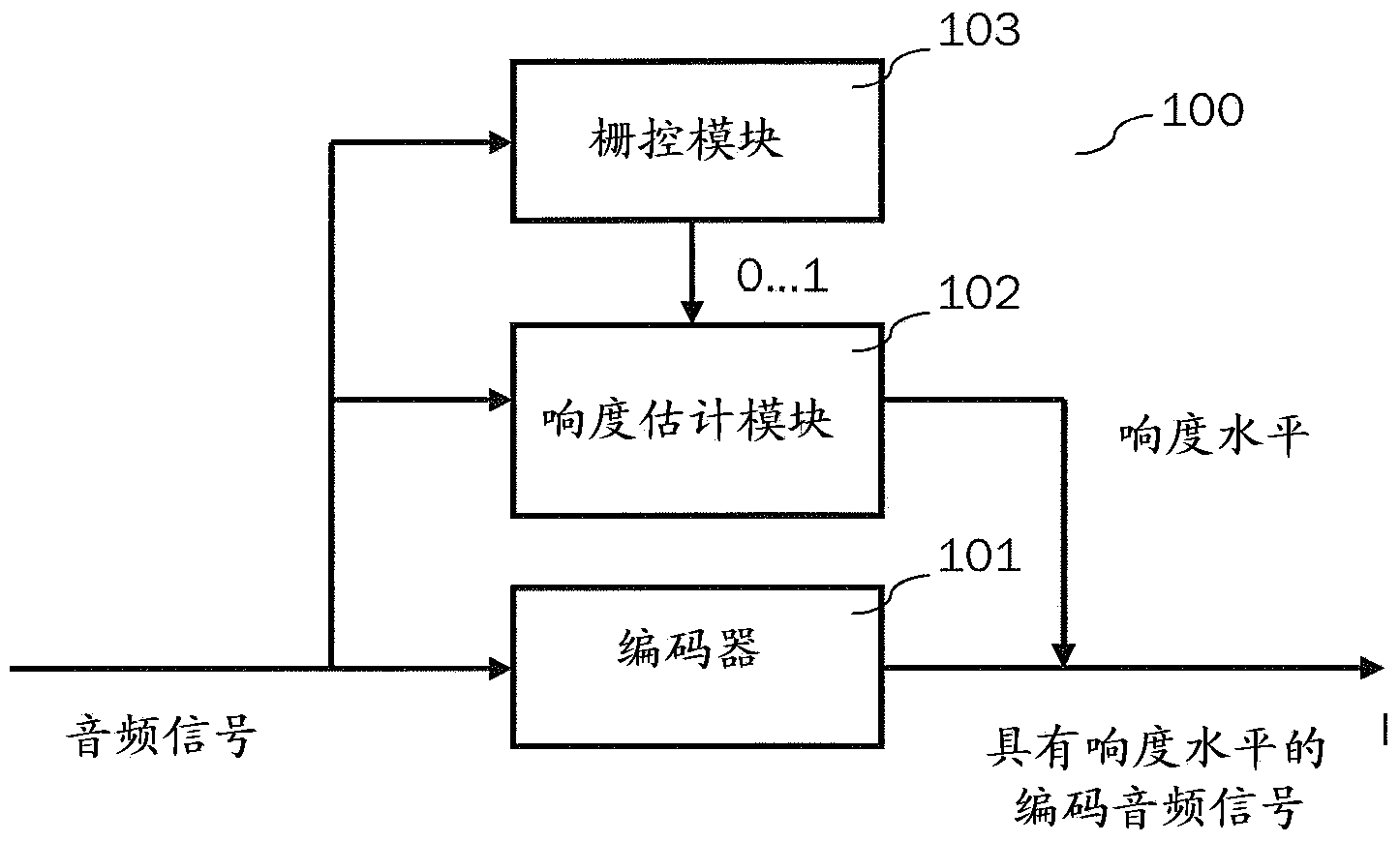
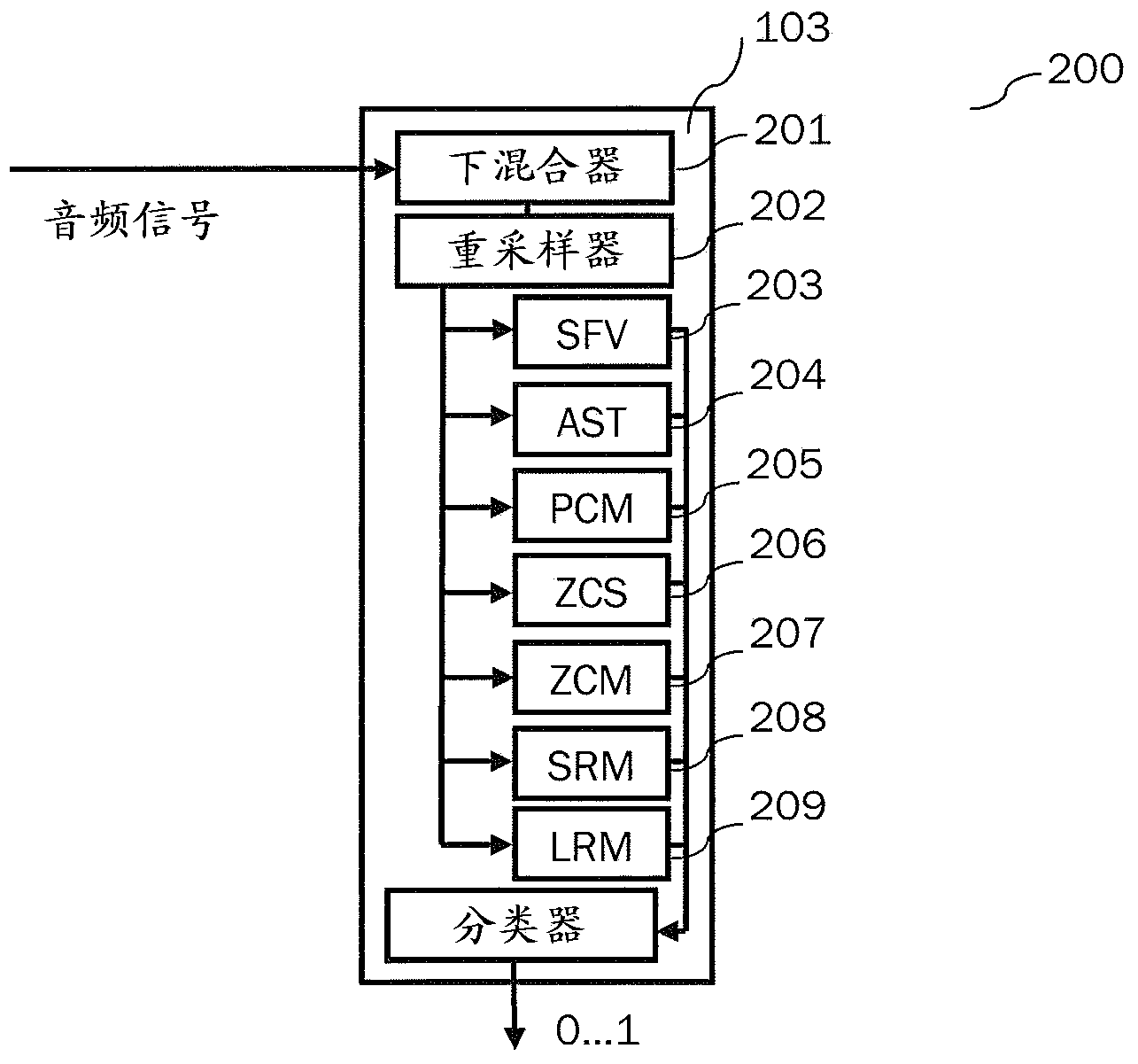
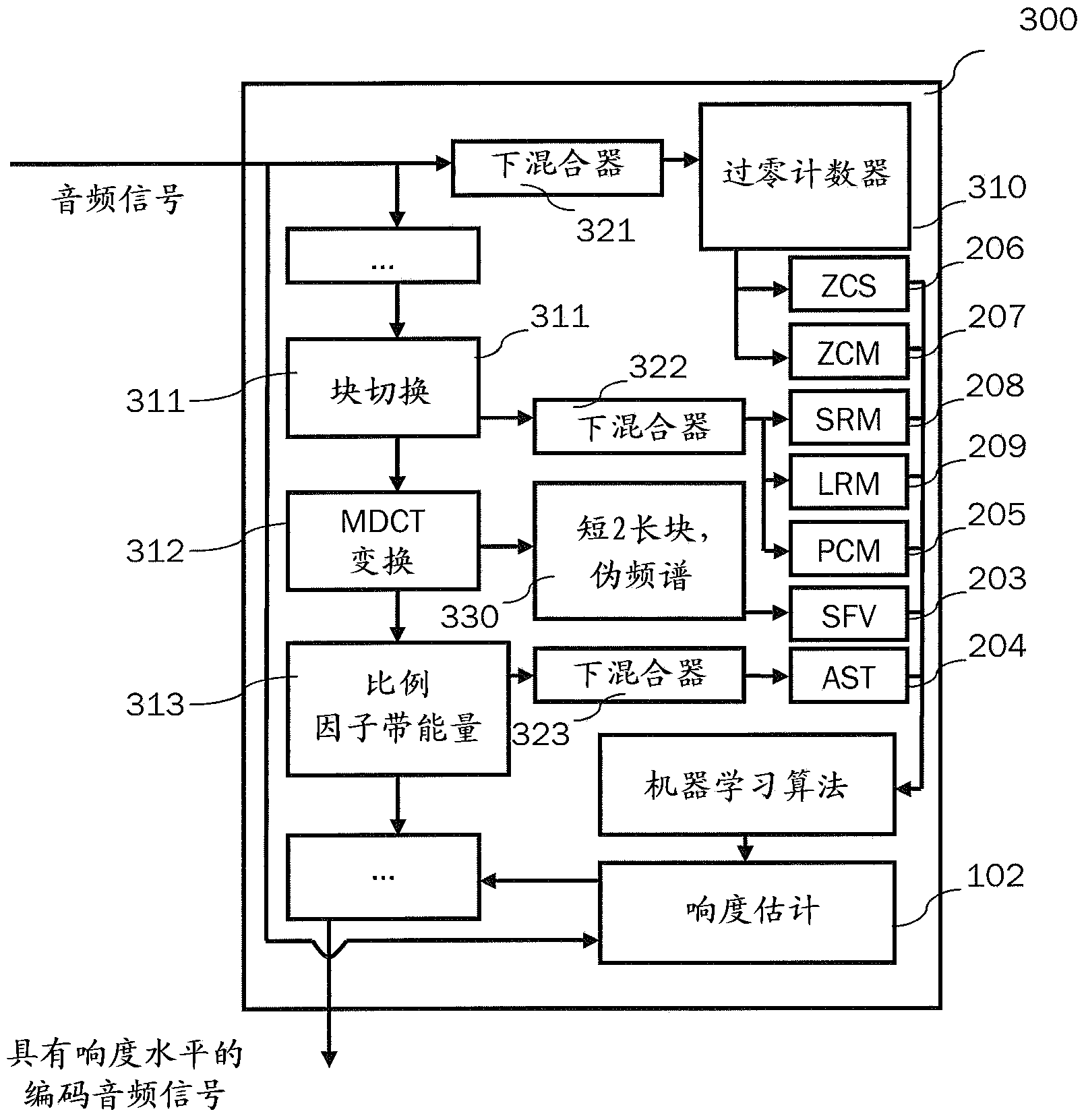
Efficient content classification and loudness estimation
A loudness, payload technology, used in speech analysis, instrumentation, etc., to solve problems such as imperfection, misclassification that affects loudness calculations, and no additional processing work expected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0166] According to one embodiment, the scale factor band energy is used instead of the spectral power density used to calculate the average spectral slope described above. An example table of MDCT index 0 sets (Nm) for a sampling rate of 48kHz is shown in the table below. The scaling factor band energy is calculated as follows:
[0167] Z m = Σ n = N m N m + 1 - 1 | x n 2 | for 0 m ≤ 46
[0168] Z m = scale factor band (sfb) energy of index m
[0169] x n = MDCT coefficient of index n, 0
[0170] N m = MDCT index offset of sf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com