Optical receiver for multimode communications
An optical receiver, multi-mode communication technology, applied in the direction of electromagnetic receiver, multi-mode transmission, optical fiber transmission, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
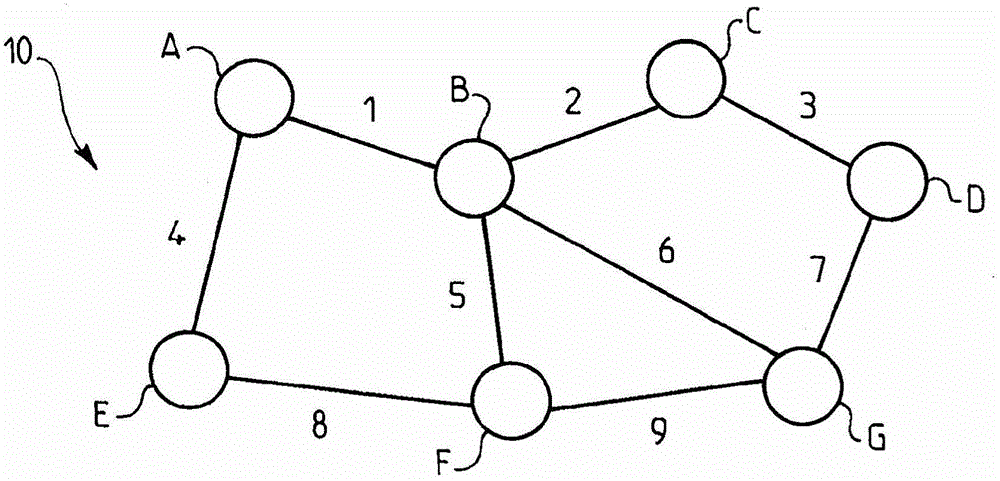
[0059] Example 1: Two modulated optical signals are sent from node A to node G via two modes LP01 and LP11. Propagate the two modes through spans 1 and 6 in that order. The resulting delay between the two modes is (see Table 2):
[0060] (50*4.25+80*2.5)=412.5ns.
example 2
[0061] Example 2: Three modulated optical signals are sent from node A to node G through three modes LP01, LP11 and LP02. All patterns are propagated through spans 1, 5 and 9 in that order because routing through span 6 is not available, eg span 6 does not support pattern LP02.
[0062] The resulting delay for LP11 is (see Table 2):
[0063] (50*4.25+50*4.25+60*4.22)=678.2ns.
[0064] The resulting delay for LP02 is (see Table 2):
[0065] (50*6.32+50*6.28+60.6.31)=10008.6ns.
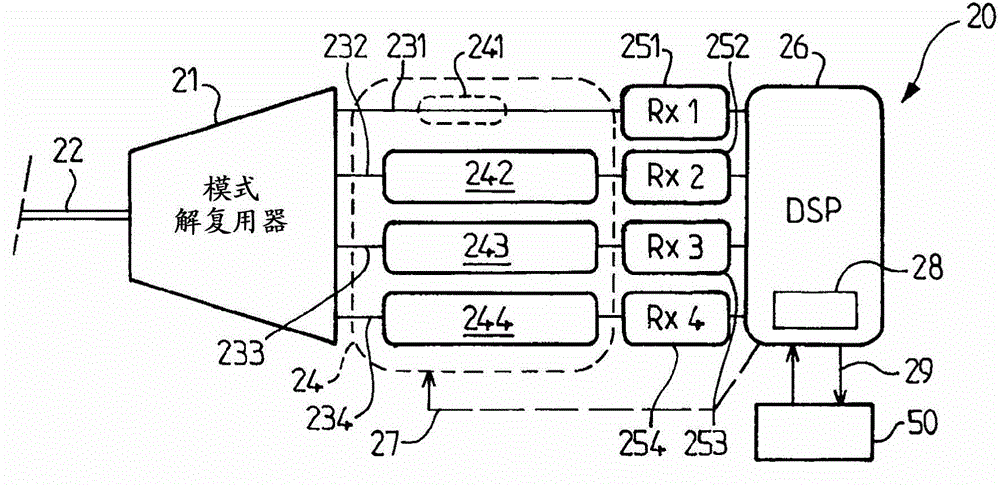
[0066] In one embodiment, delay control module 28 can also perform an update function for updating the lookup table in database 50 as indicated by arrow 29 . The data in Table 2 can be updated in several ways.
[0067] In one embodiment, the DSP 26 algorithmically determines the physical parameters upon receipt of a pre-known training sequence. Any modulation format can be used for this purpose. Such an update using data-aided algorithms is performed over time, for example weekly or monthly accord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com