A zero calibration method for an industrial robot
An industrial robot and zero calibration technology, which is applied in the direction of manipulators, manufacturing tools, program control manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming precision, lack of time, complicated operation process, etc., to save operating time, improve zero alignment accuracy, The effect of saving manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
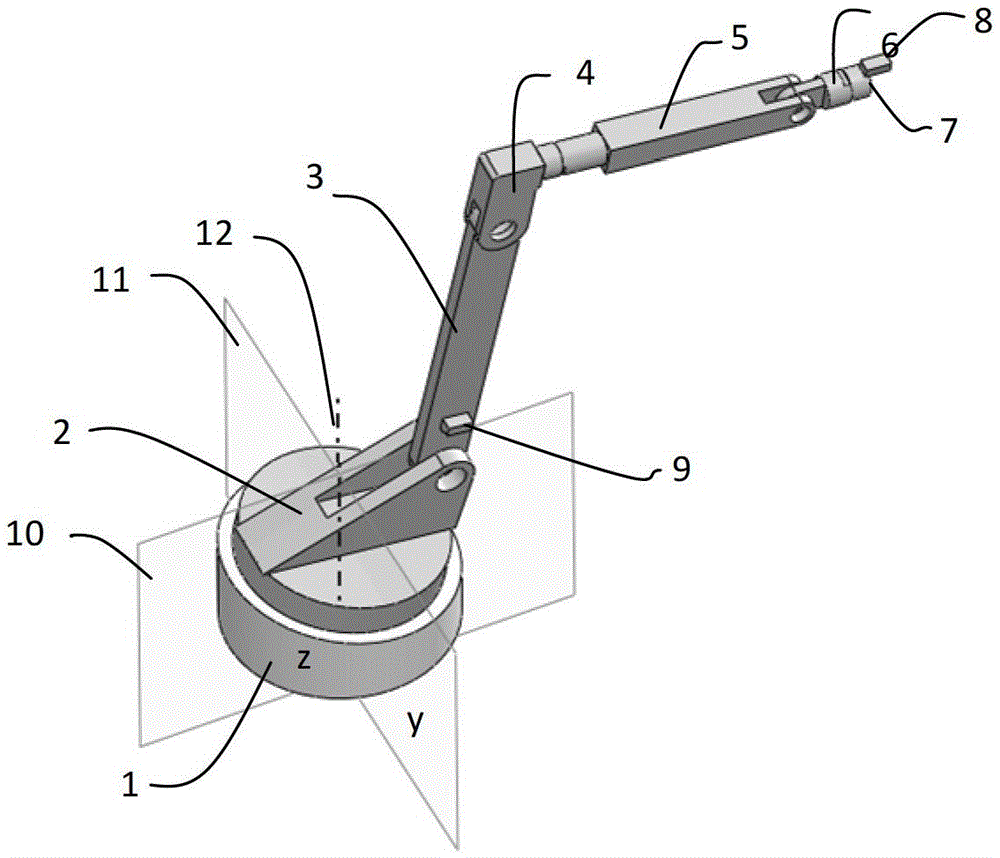
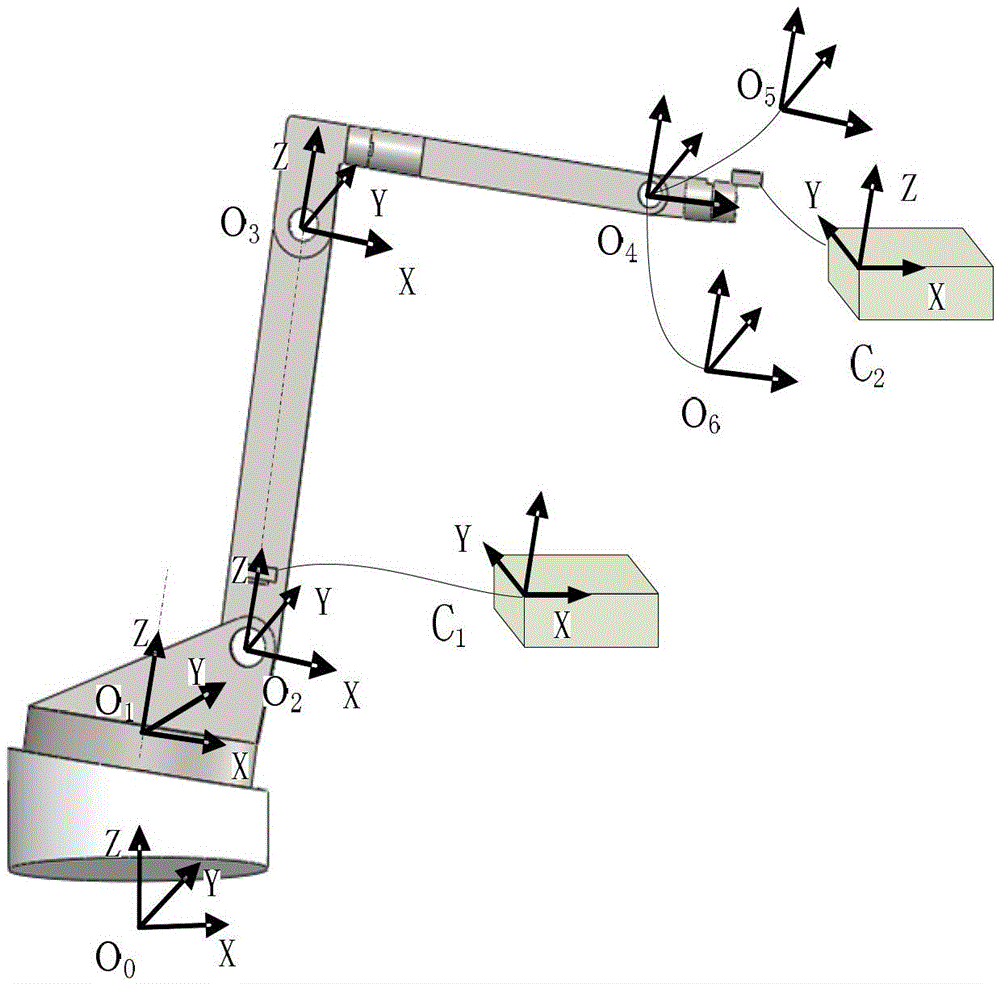
[0019] Typical industrial robots such as figure 1 As shown, the robot body is installed on a workbench (not shown) through a base, and the 1-6 axes of the robot are connected in series above the base, and each axis is connected by a rotary joint. figure 2 At the same time, the positions of the two installations of the inclination sensor on the 2-axis and 6-axis of the robot in the new method are given.
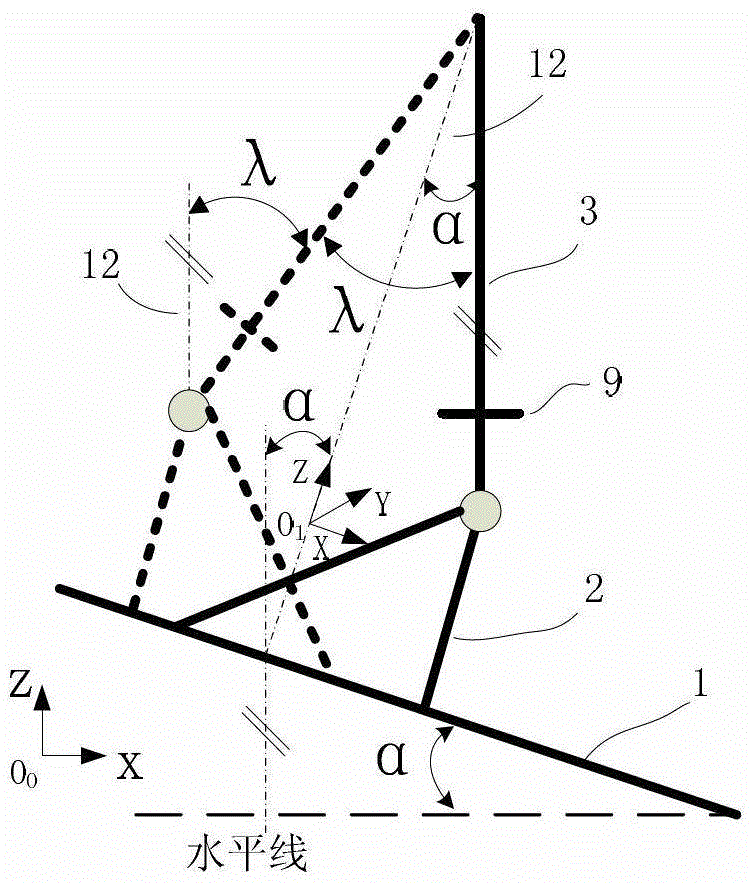
[0020] After the robot is installed, since the workbench cannot be guaranteed to be in an absolutely horizontal position, it can be considered that the robot base is always installed in an inclined state. In order to quantify the inclination of the robot base, it is assumed that the dotted line 12 is parallel to the direction of the gravity line, the reference plane a passes through the dotted line 12 and is parallel to the axis of the rotary joint between ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com