A wireless sensor network lifetime optimization method for mobile multi-sink nodes
A wireless sensor network and optimization method technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, advanced technology, etc., can solve problems such as energy holes, limited network survival time, and large network delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0085] As another embodiment of the present invention, formula (1-1) can also be used to calculate the potential value of each grid:
[0086]
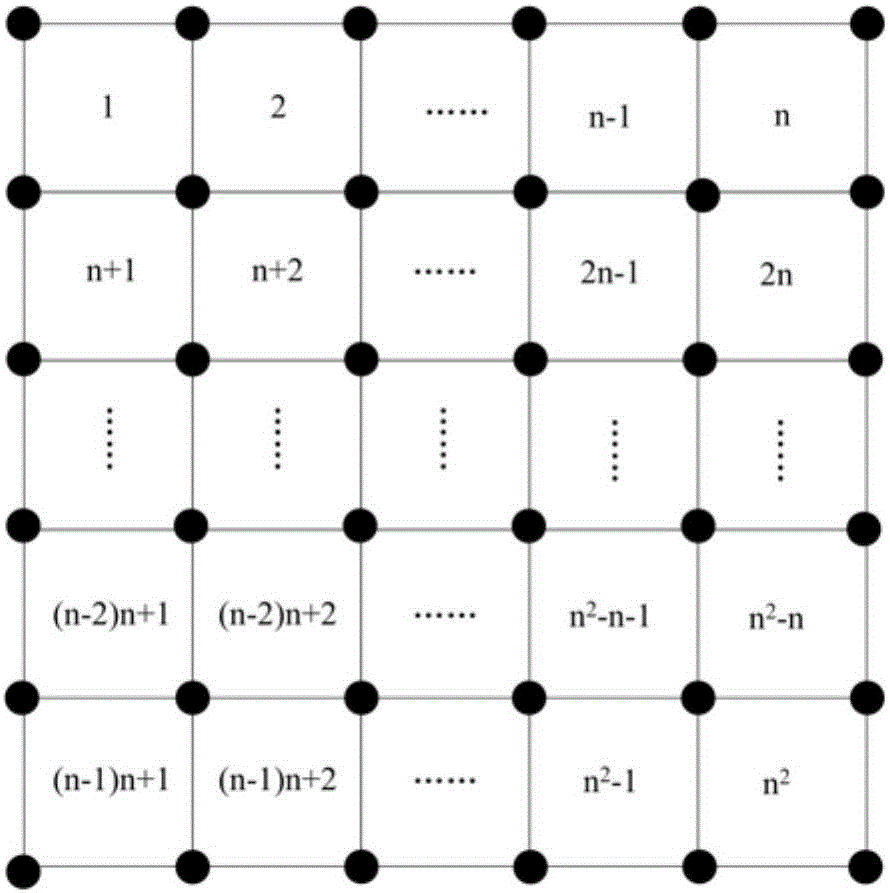
[0087] In formula (1-1), P(v) represents the potential value of grid v, grid v Indicates the grid center of grid v, d vj Represents the sensor node j in the set N(v) to the grid center grid of the grid v v distance, d max Indicates the maximum communication distance of the sensor node, N(v) indicates the grid center grid of the grid v in the monitoring area of the wireless sensor network v The distance does not exceed d max (that is, the set of all sensor nodes within the communication range of one hop). alpha 1 Indicates the distance potential factor, which ranges from 1 to 3, and the preferred empirical value is 2. Equation (1-1) does not consider the remaining energy of sensor nodes, which will cause the imbalance of node energy consumption and shorten the network generation time.
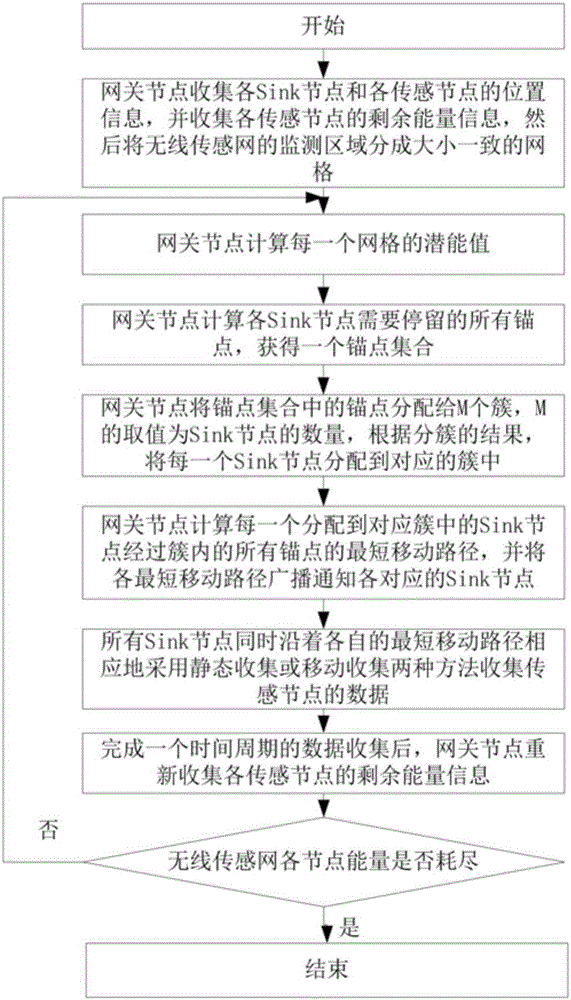
[0088] Step 3: The gateway node calcul...
Embodiment approach
[0089] The specific preferred implementation method of this step is as follows:
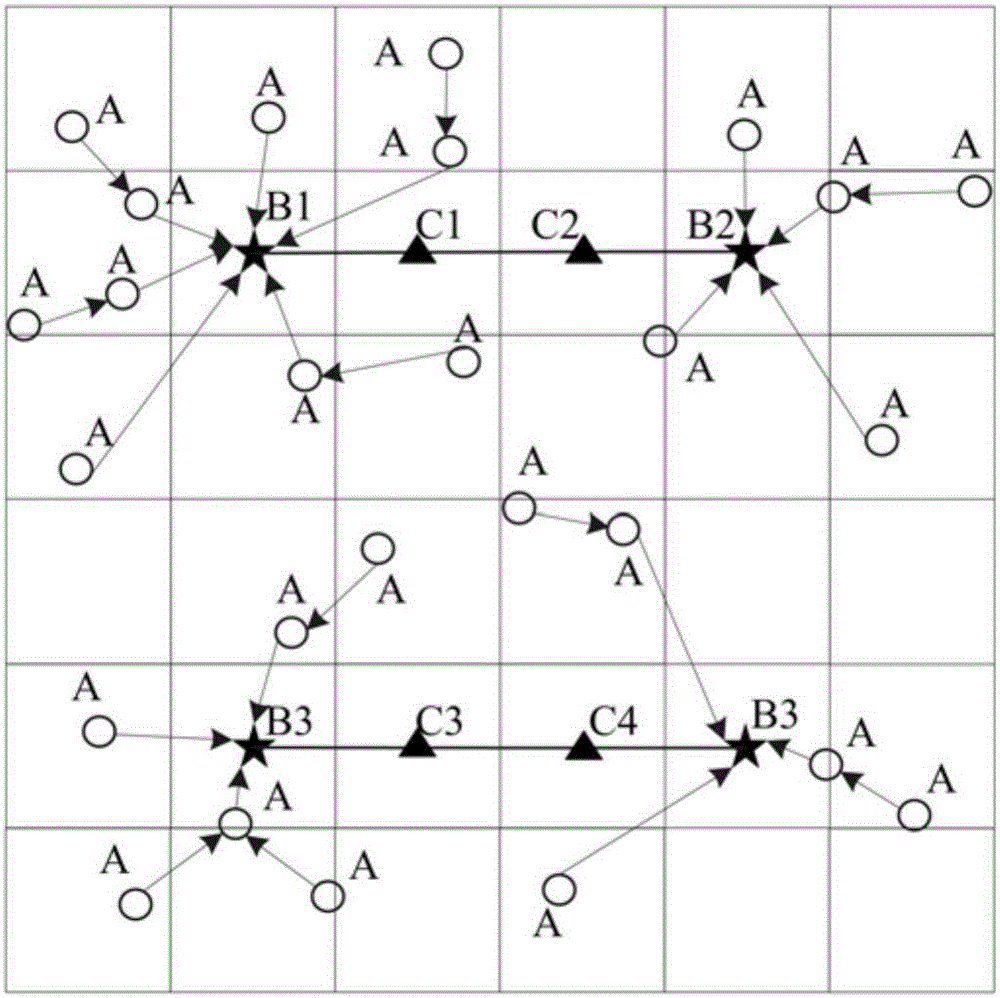
[0090] a1) Select the center of the grid with the largest potential value as the current anchor point among all the grids in the monitoring area of the entire wireless sensor, and record the potential value P of the grid where the current anchor point is located * (1), adding the current anchor point to an empty anchor point set P at this time;
[0091] a2) With the current anchor point as the current convergence point, determine all sensor nodes whose minimum transmission hops to the current convergence point do not exceed 2, and all the grids in the maximum communication coverage area of these sensor nodes form a set Q 1 ;According to the method shown in formula (2), the set Q 1 Subtract the potential value P of the grid where the current anchor point is located from the potential value of each grid in * , thus correspondingly get the set Q 1 New potential values for each grid in :
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com