Building sample rate independent timing diagrams using digital edge averaging
An averaging and edge technology, applied in digital variable display, digital transmission system, digital variable/waveform display, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
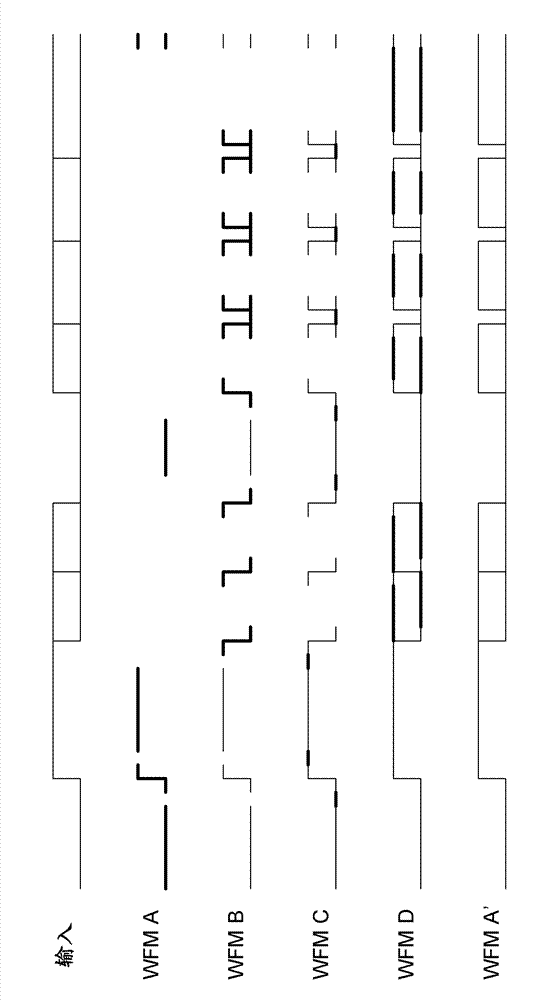
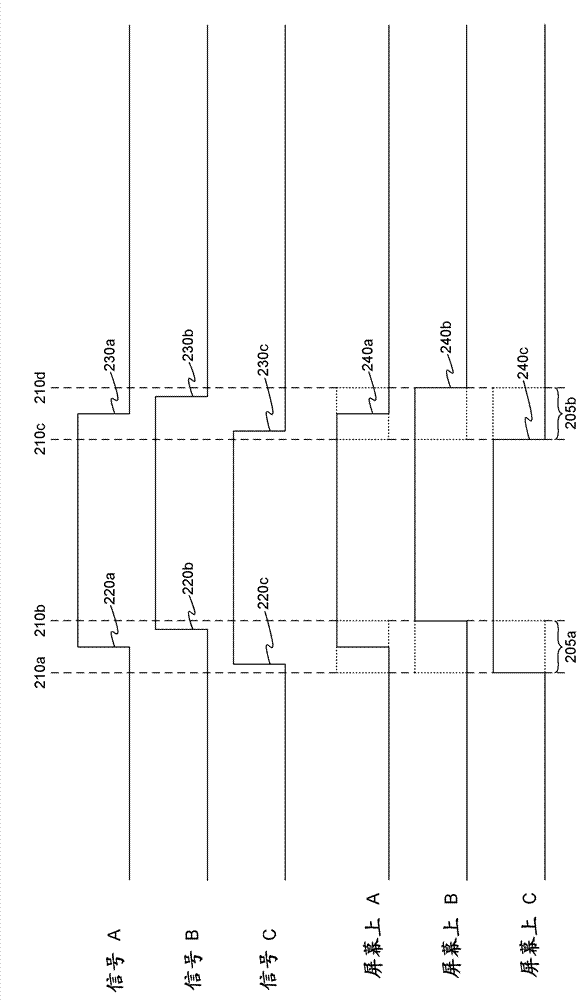
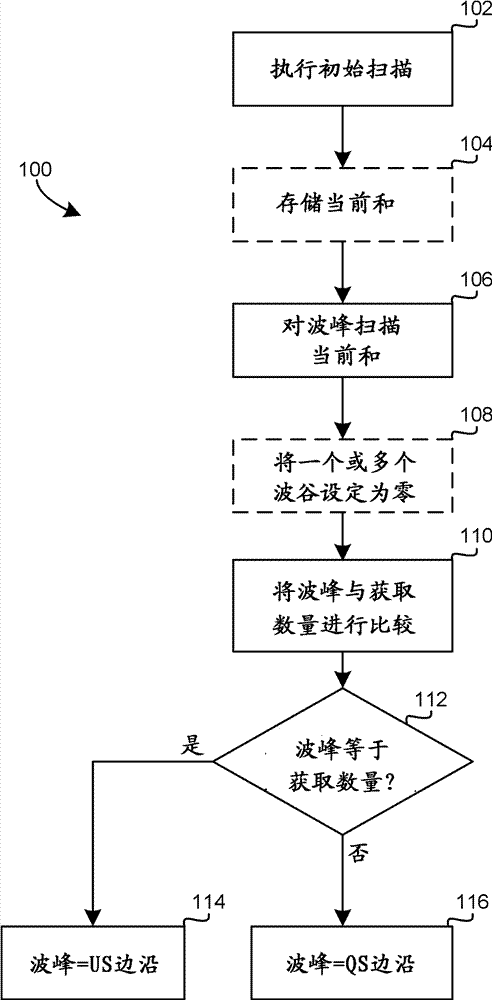
[0012] In the current system, the digital edge average (DEA) of any single transition means that it can only be calculated if the edge appears within each repeated DEA aperture. Through conventional methods, the tested signal has many opportunities to synchronize, but it is not uniformly synchronized (US). This requires the quasi-synchronous (QS) edge type concept described below.
[0013] QS edges as used herein generally refer to edges that appear in the DEA aperture but do not appear in each repeated acquisition. The data bus, the stroboscope whose width is a clock whose width changes in number, and the edge of a clock whose number changes according to the trigger event are all examples of edge events that are conventionally synchronized with the trigger event (for example, they can all be based on the same system clock ), but in the DEA sense, it is only QS.
[0014] Digital Edge Mapping (DEM) usually uses repeated and directional DEA operations to resolve QS edges and uses t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com