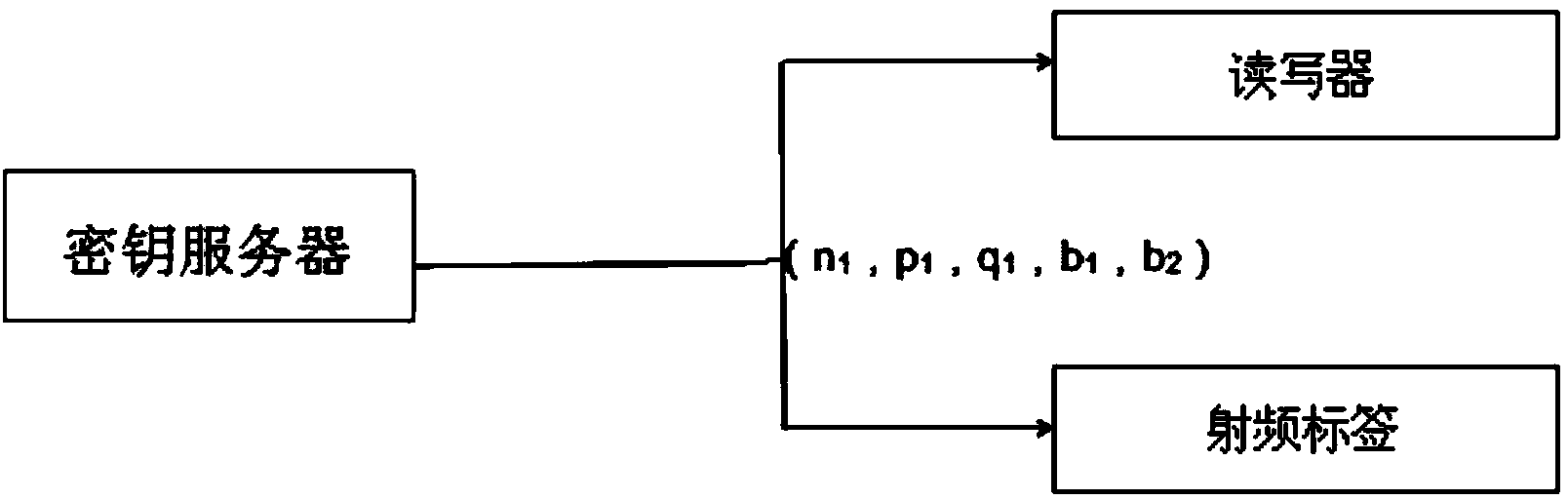Chinese remainder theorem based location privacy method in Internet-of-Things sensing layer authentication
A technology of the Chinese remainder theorem and the Internet of Things, applied in electromagnetic radiation induction, user identity/authority verification, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of label location exposure, data source location exposure, etc., and achieve the effect of hiding the label location
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment completes the initialization phase of the system. The purpose of this stage is to generate the key material, and then write it into the radio frequency tag and reader to provide the basis for the subsequent stage. represented by the following steps:
[0028] steps
content
100
The key server generates two prime numbers (p 1 ,q 1 ).
102
calculate b 1 , b 2 , n 1 .
104
(n 1 ,p 1 ,q 1 , b 1 , b 2 ) into the reader and RF tags.
[0029] The specific description in the first embodiment is as follows:
[0030] Step 100: The key server randomly generates two large prime numbers (p1, q1).
[0031] Step 102: Calculate b 1 =q 1 -1 modp 1 , b 2 =p 1 -1 modq 1 , n 1 =p 1 q 1 .
[0032] Step 104: the key server writes (n1, p1, q1, b1, b2) into the reader-writer and the radio frequency tag.
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment completes the search and authentication process. The purpose of this stage is to ensure that only legitimate readers can find tags nearby and hide the location of tags. represented by the following steps:
[0035]
[0036] The specific description in embodiment two is as follows:
[0037] Step 106: The reader generates two numbers randomly Then calculate V 1 =r 1 b 1 q 1 + r 2 b 2 p 1 modn 1 , and M 1 =(r 1 , r 2 , V 1 ) to the label.
[0038] Step 108: Tag receives M 1 After verifying If the above formula is established, it means that the reader is legal. Otherwise, the reader is considered to be an attacker and does not make any response, thereby preventing the attacker from knowing its own position. The purpose of location privacy protection is achieved.
[0039] Step 110: The tag randomly generates two numbers Then calculate V 2 = r 3 b 1 ·q 1 + r 4 b 2 ·p 1 modn 1 , and M 2 =(r 3 ,r 4 ,V 2 ) to the reader.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0042] This embodiment is the symmetric key negotiation generation stage. The purpose of this stage is to generate a shared key and transmit information such as tag ID under the protection of this key. represented by the following steps:
[0043] steps
content
114
The reader and the tag calculate the shared key k 1 .
116
Tag ID transmission.
[0044] The specific description in embodiment three is as follows:
[0045]Step 114: After the search phase and the tag response phase, the reader and the tag can respectively calculate the shared key as follows: k 1 =h(r 1 | r 2 | r 3 | r 4 |p 1 |q 1 ). h(-) is a hash function and exists as a key algorithm. This key is used to protect the integrity and confidentiality of subsequent communications.
[0046] Step 116: In this process, the tag and the reader share the key k 1 Under the protection of the label, information such as tag ID can be transmitted.
[0047] It can be seen fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com