Indirect branch prediction
A branch prediction and indirect technology, applied in the direction of instruments, computing, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve time-consuming and difficult problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
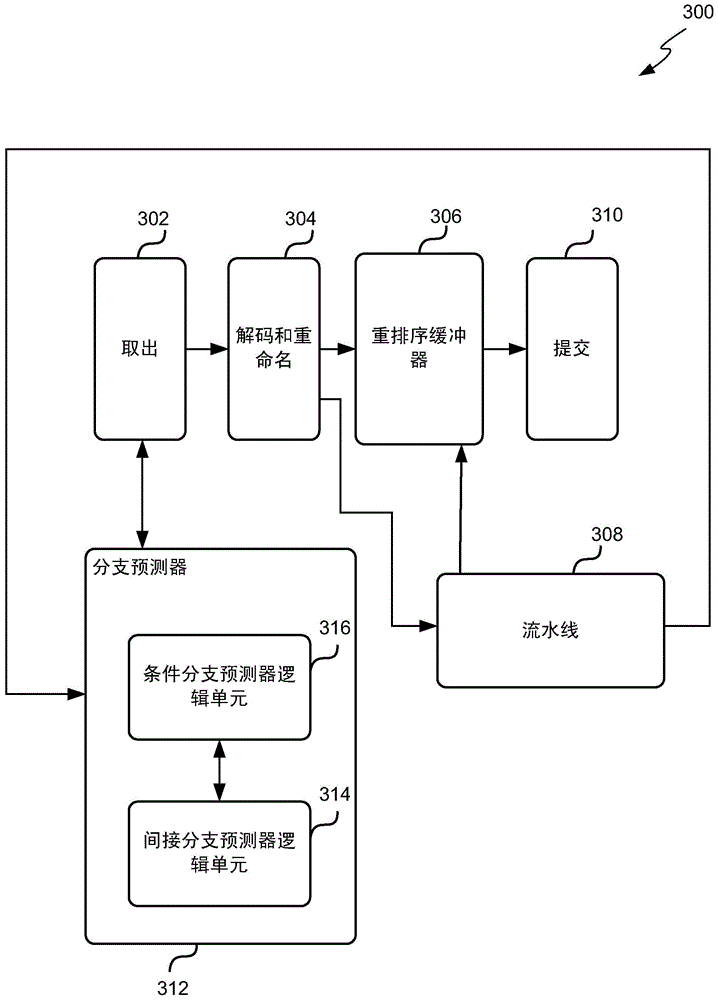
[0034] Embodiments of the invention are described below by way of example only. These examples represent the best mode currently known to applicants for putting the invention into practice, although these best modes are not the only ways in which the invention can be practiced. This description presents the functionality of the example and the sequence of steps used to construct and operate the example. However, different examples may perform the same or equivalent functions or sequences.
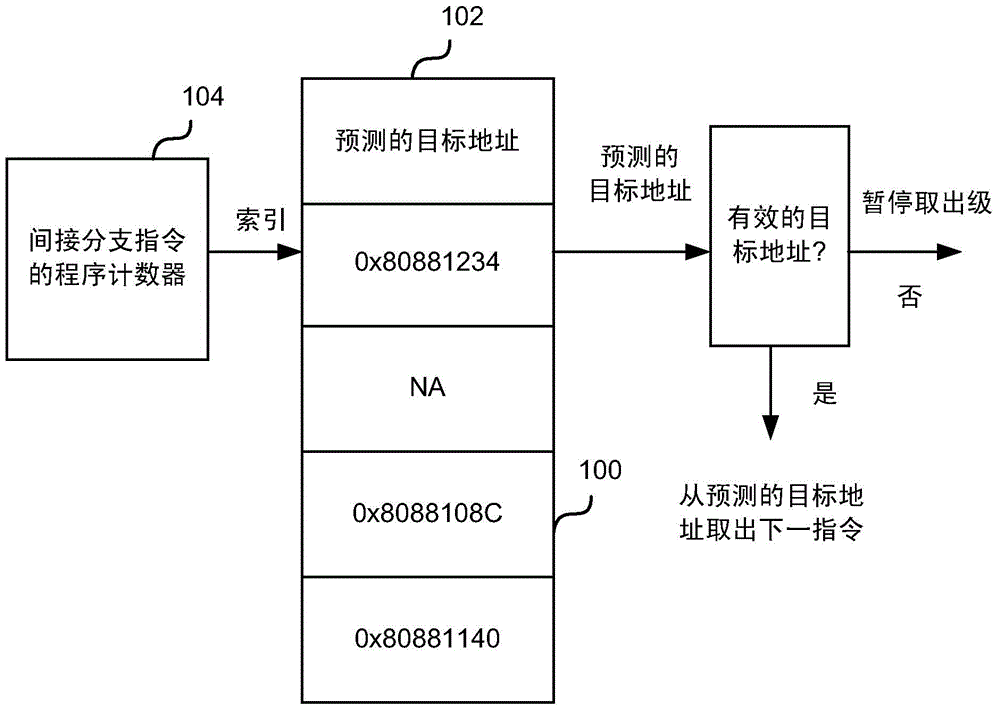
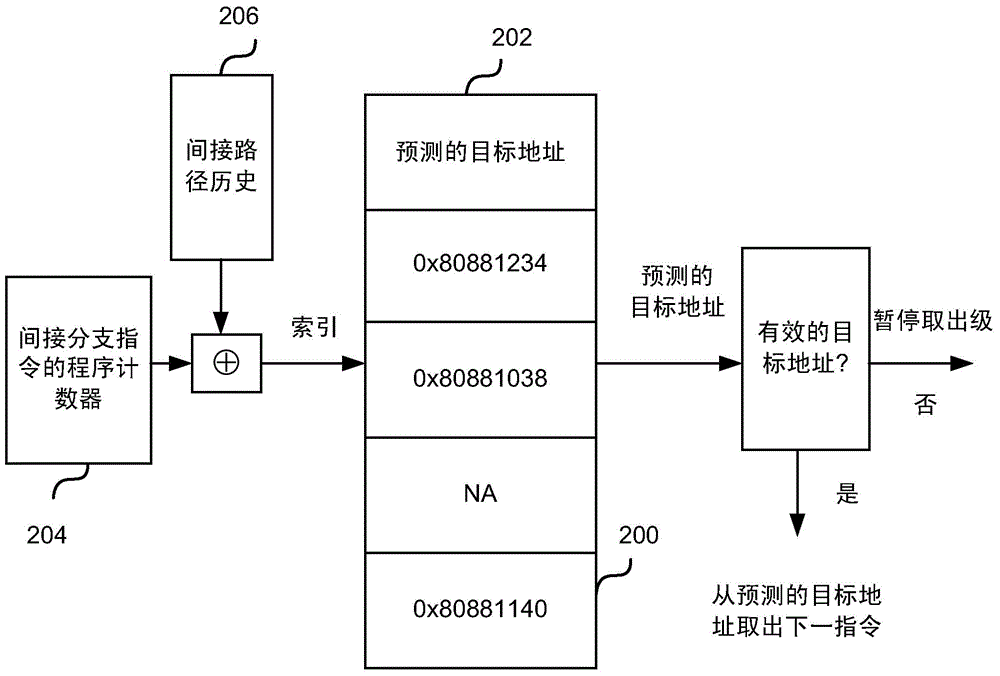
[0035] As described above, indirect branches (eg, branches based on variables rather than constant values) are harder to predict because the branch predictor has to predict where the target will be. Targets are especially difficult to predict because they are usually based on register values that change periodically.
[0036] The most common way to predict an indirect branch is to use a branch target buffer (BTB), which stores the most recent target address of an indirect branch instruc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com