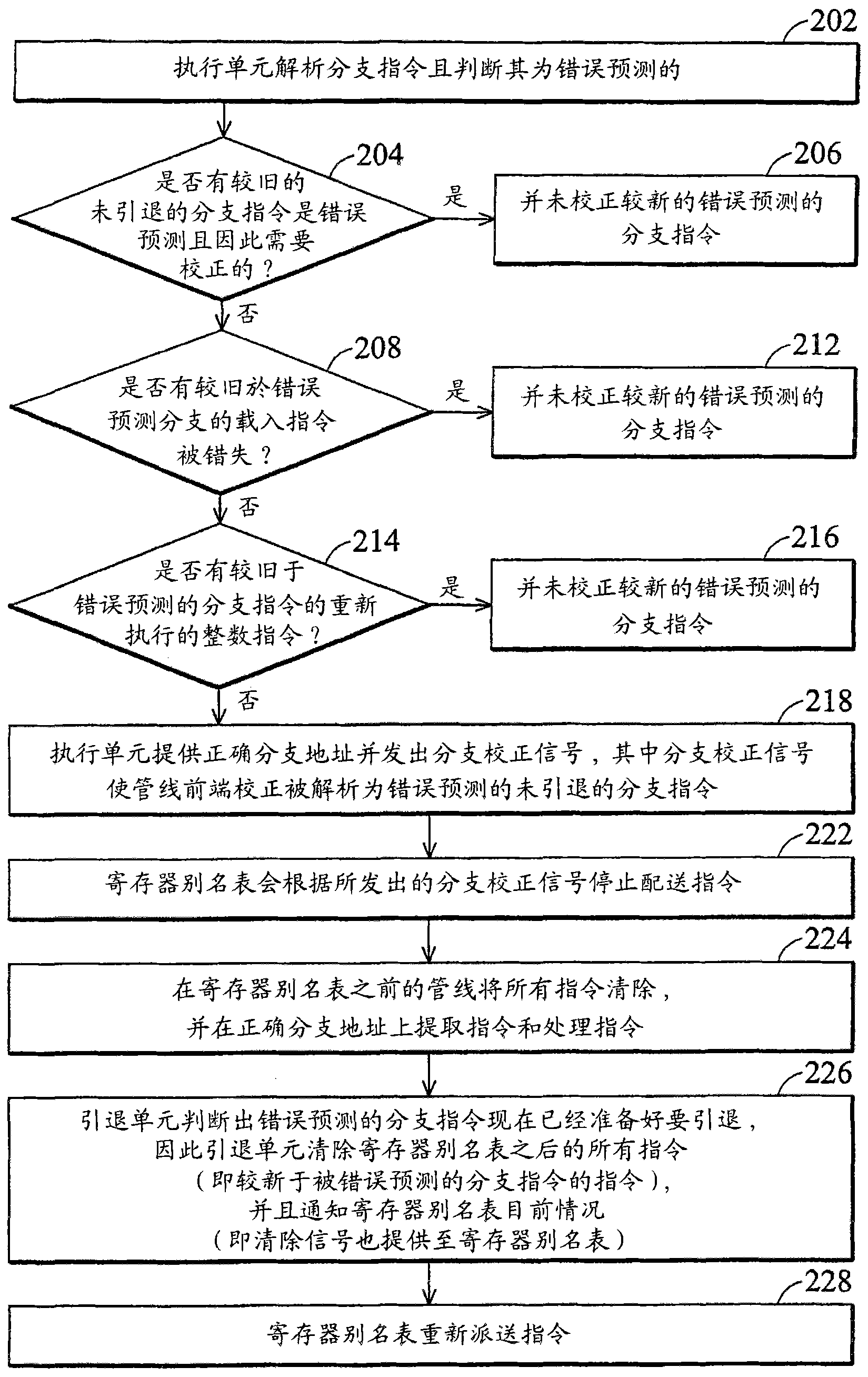
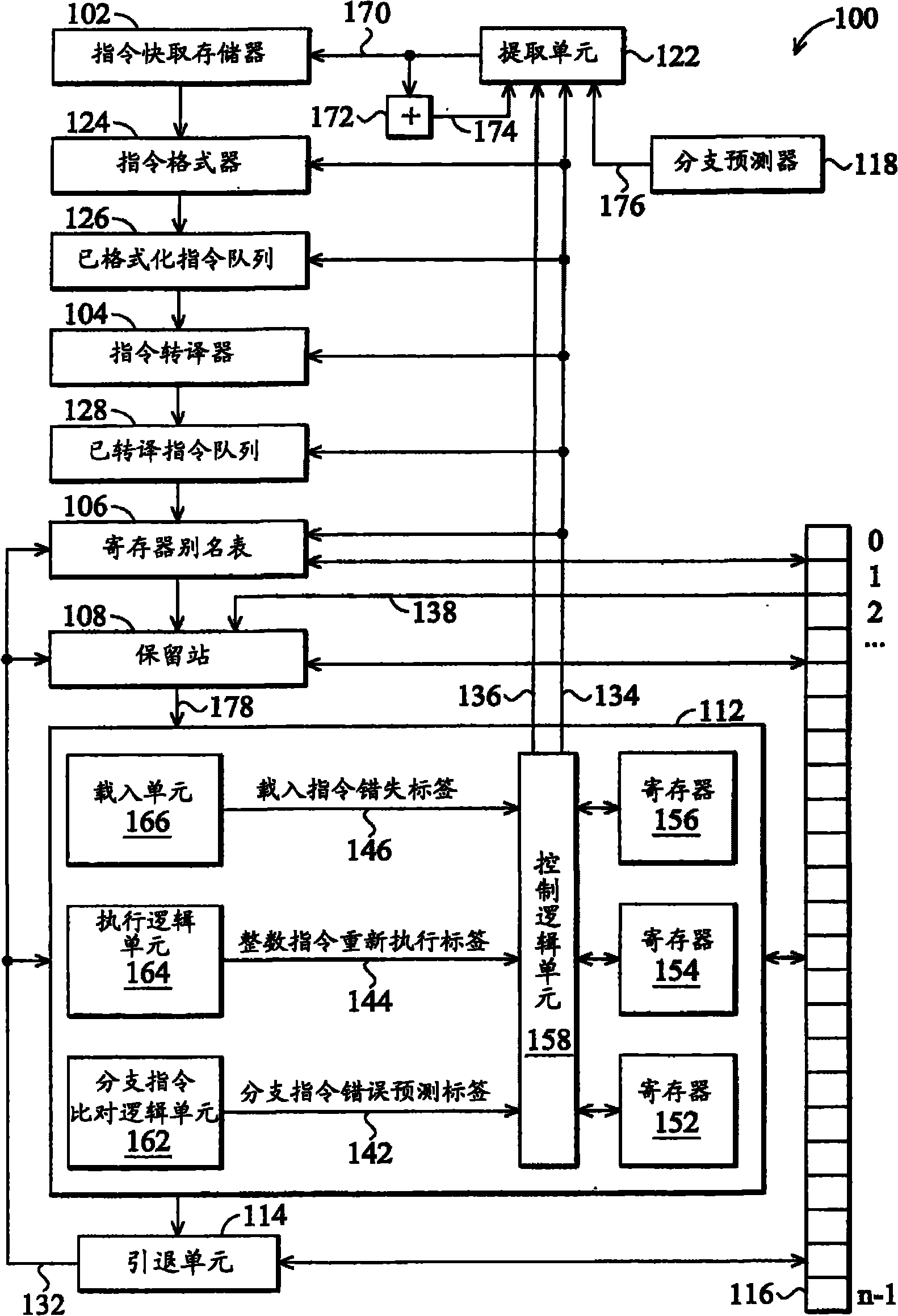
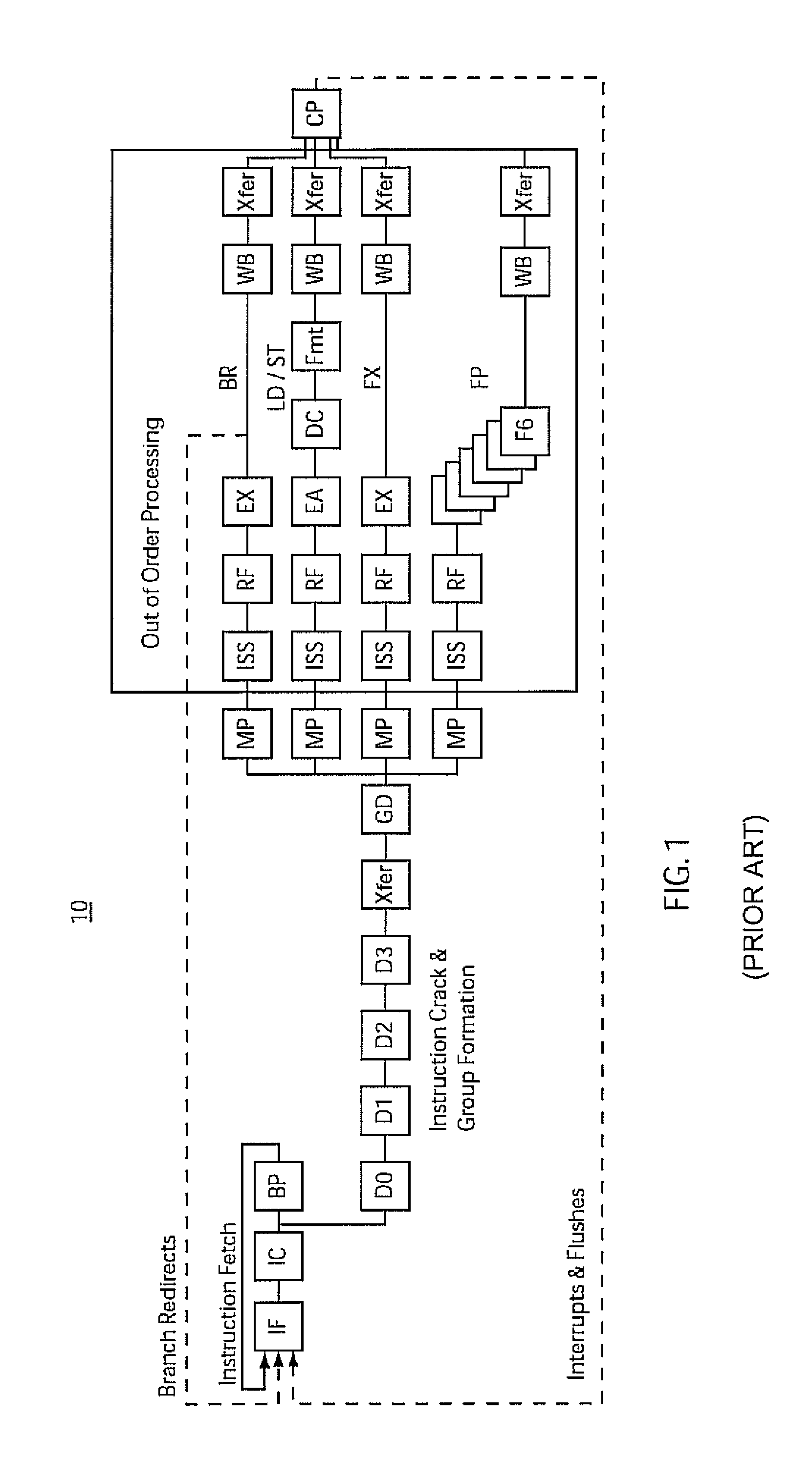
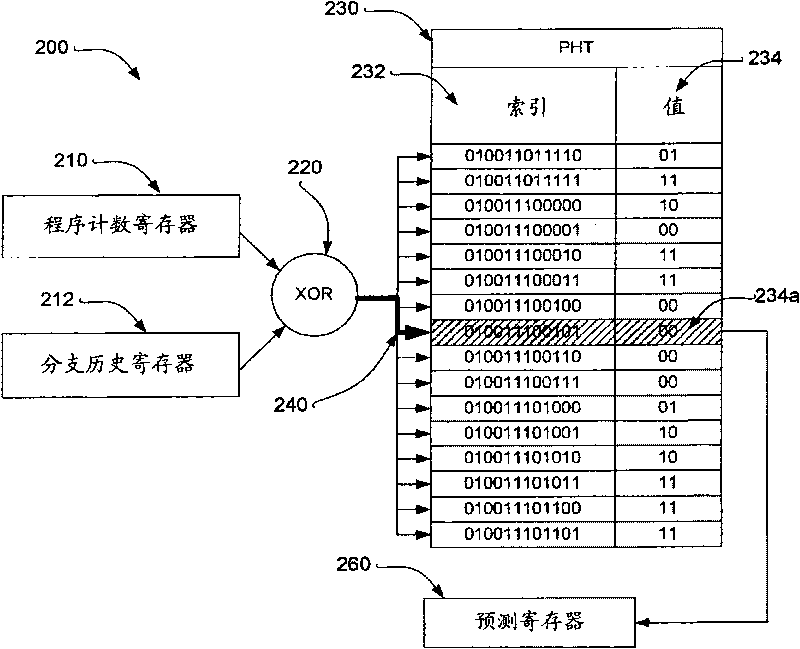
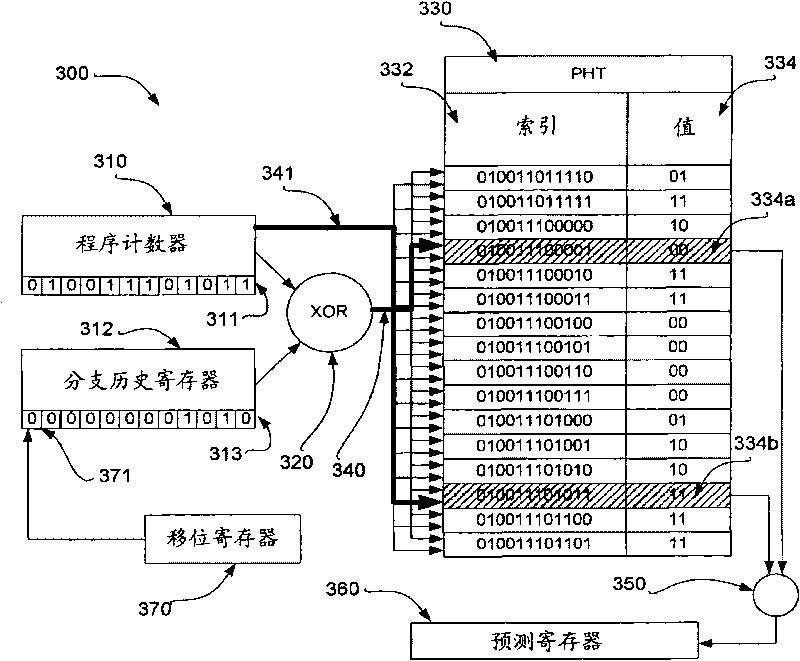
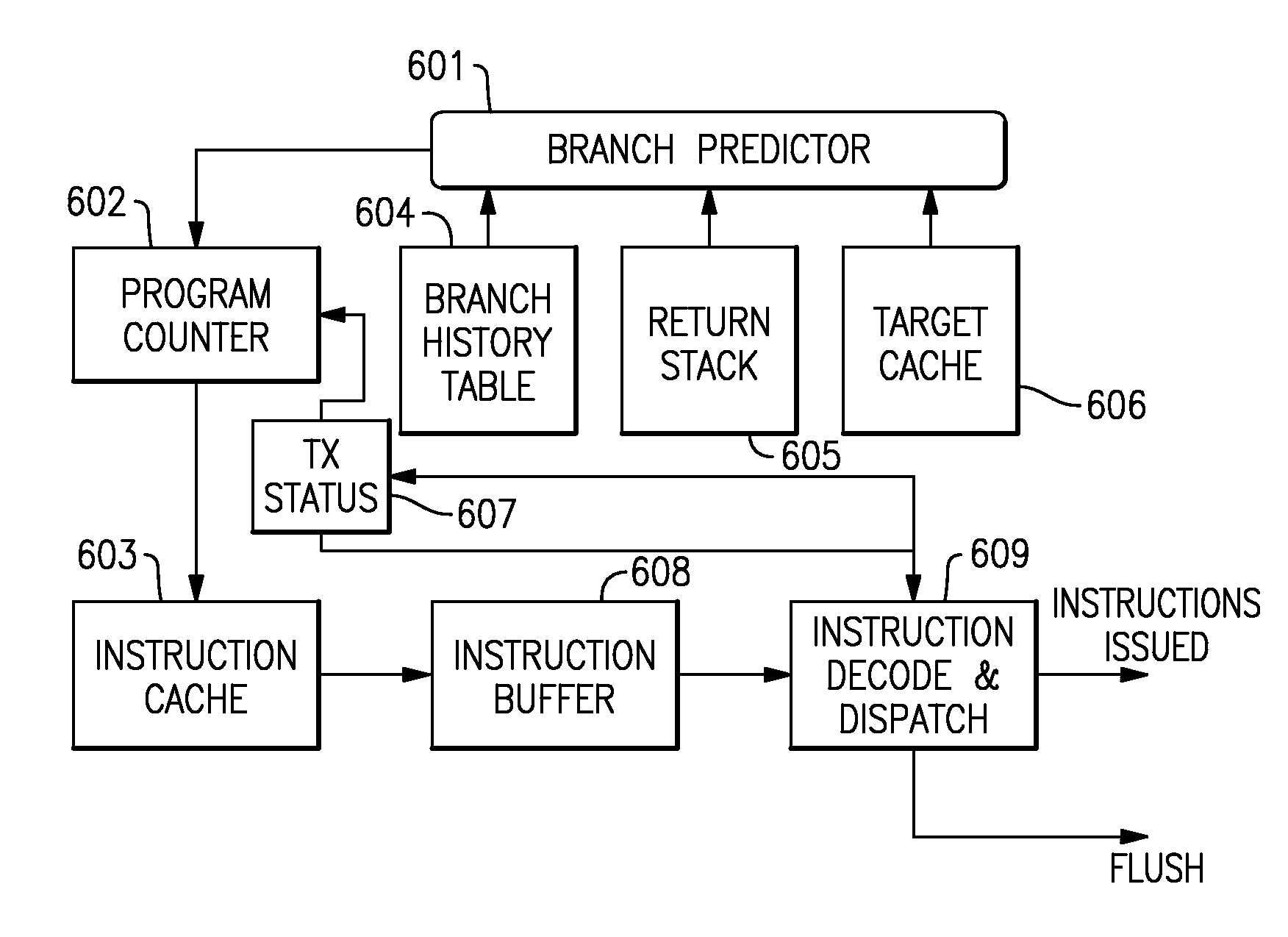
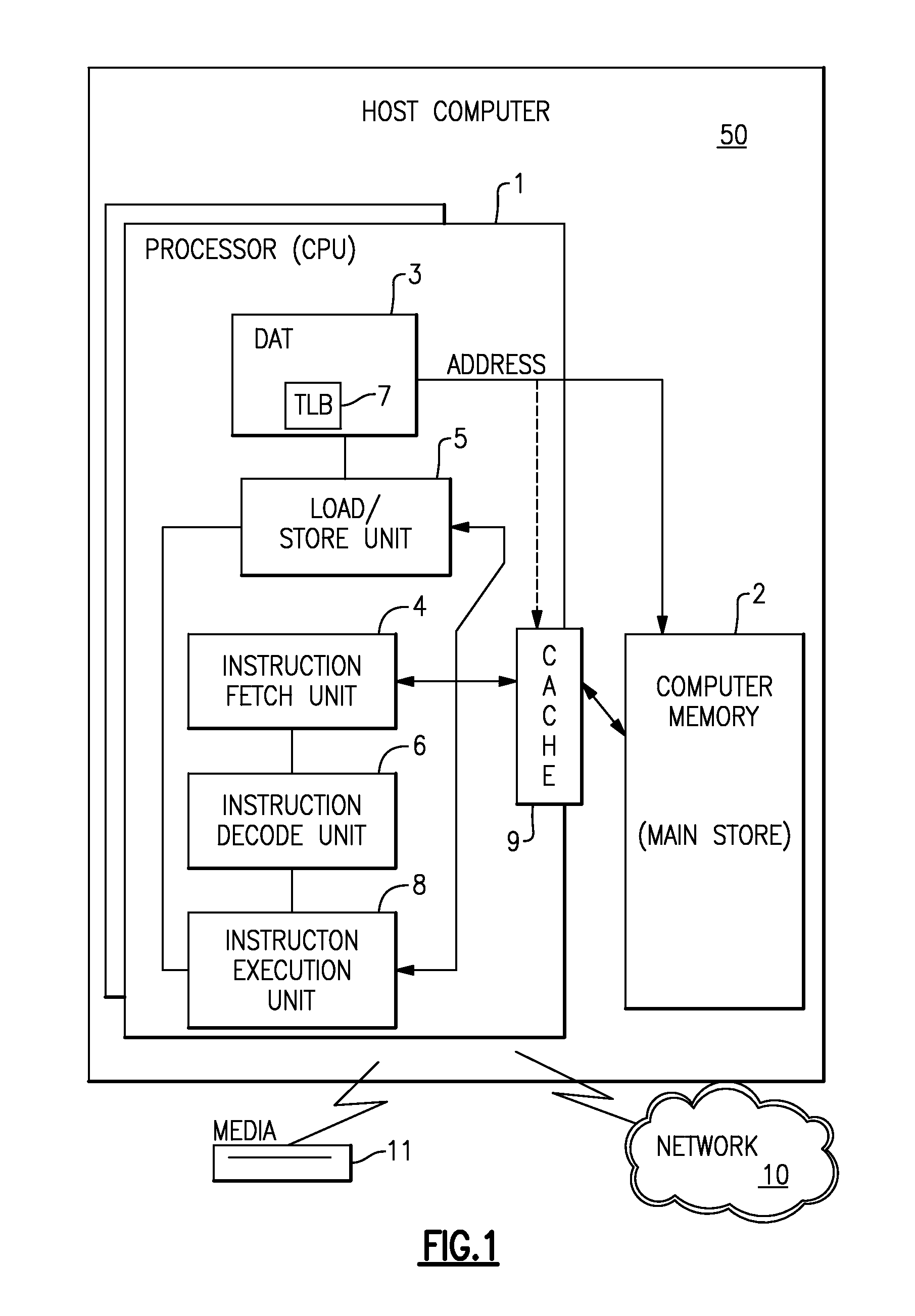
Patents
Literature
177 results about "Branch predictor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
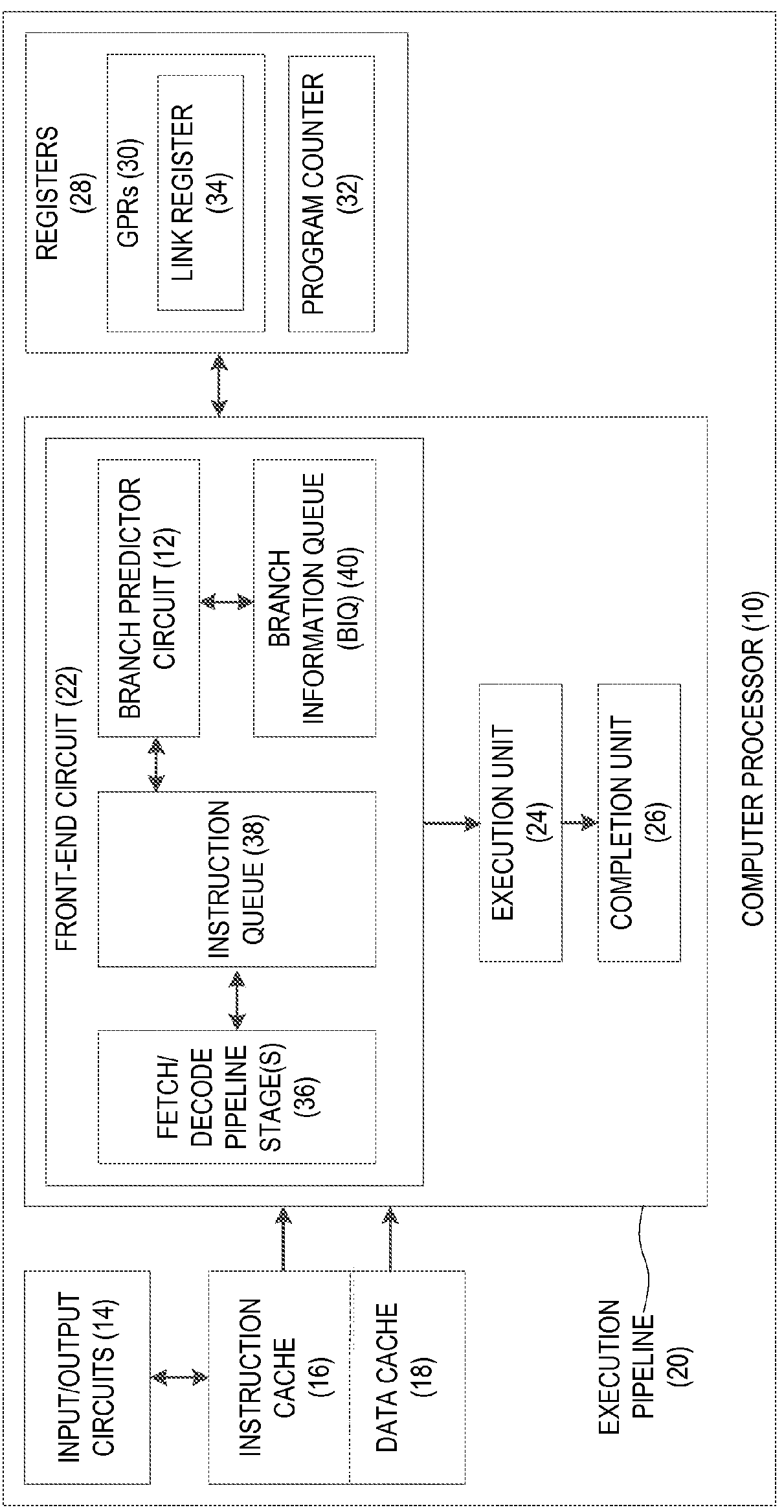
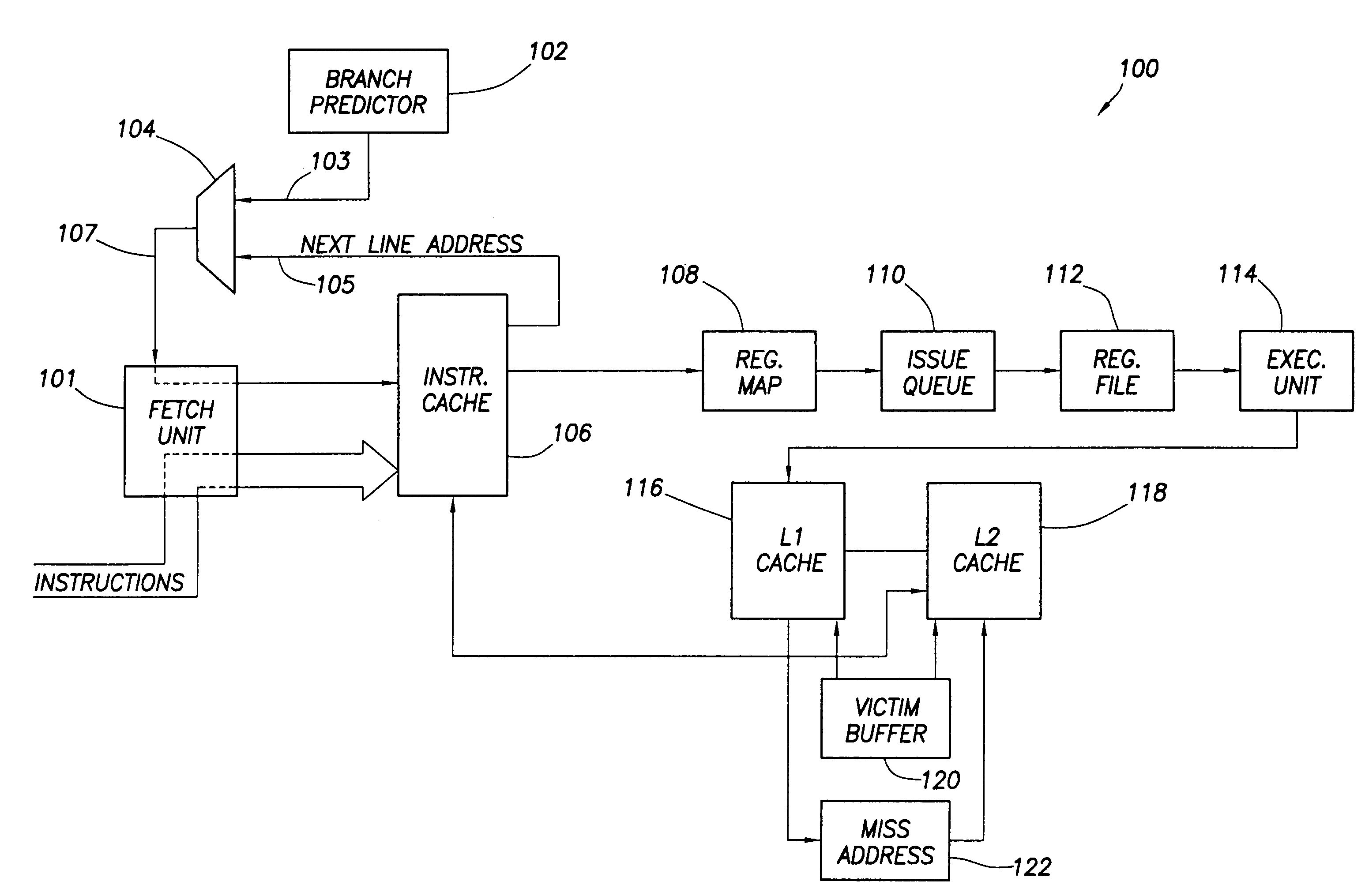
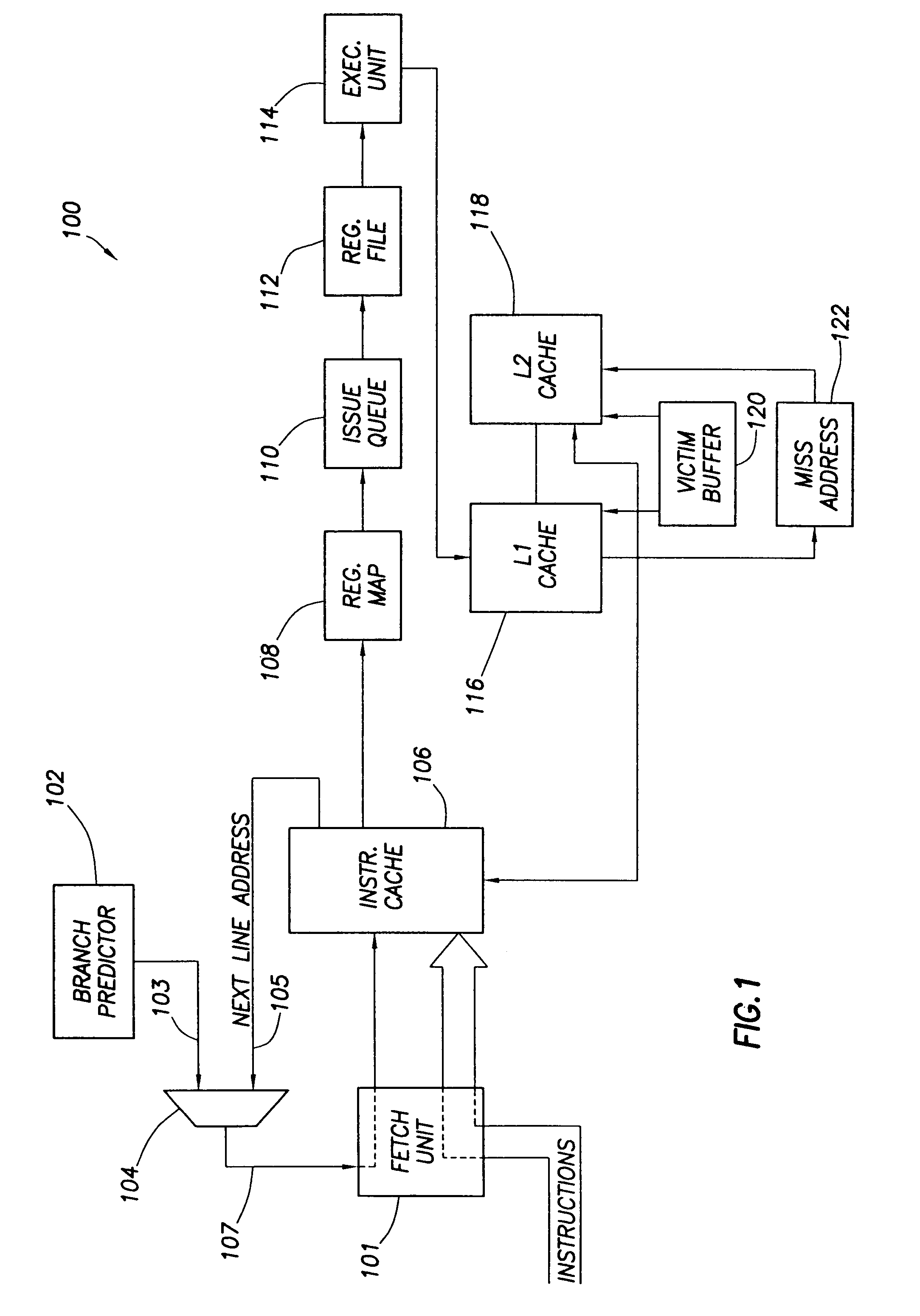
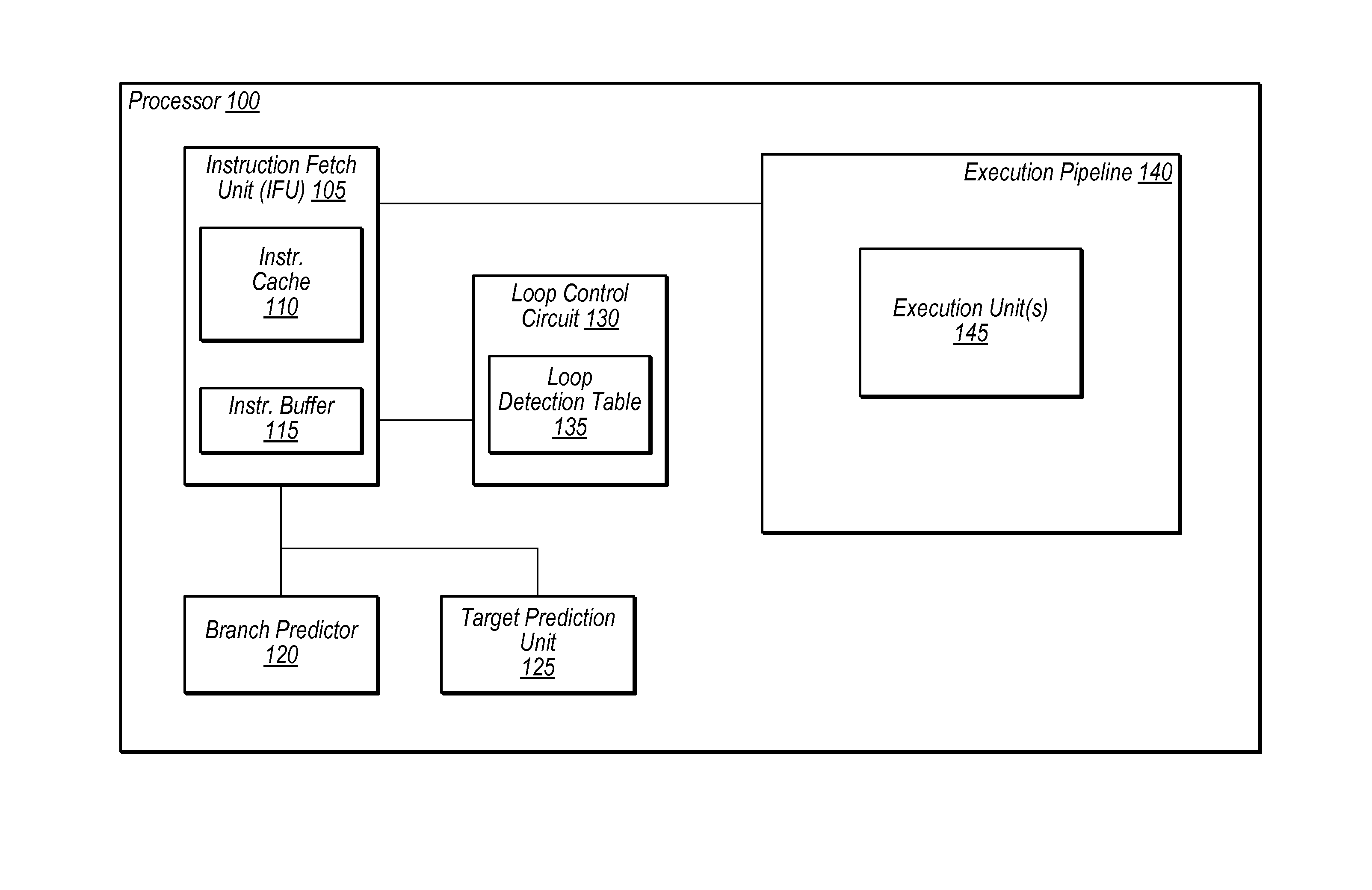
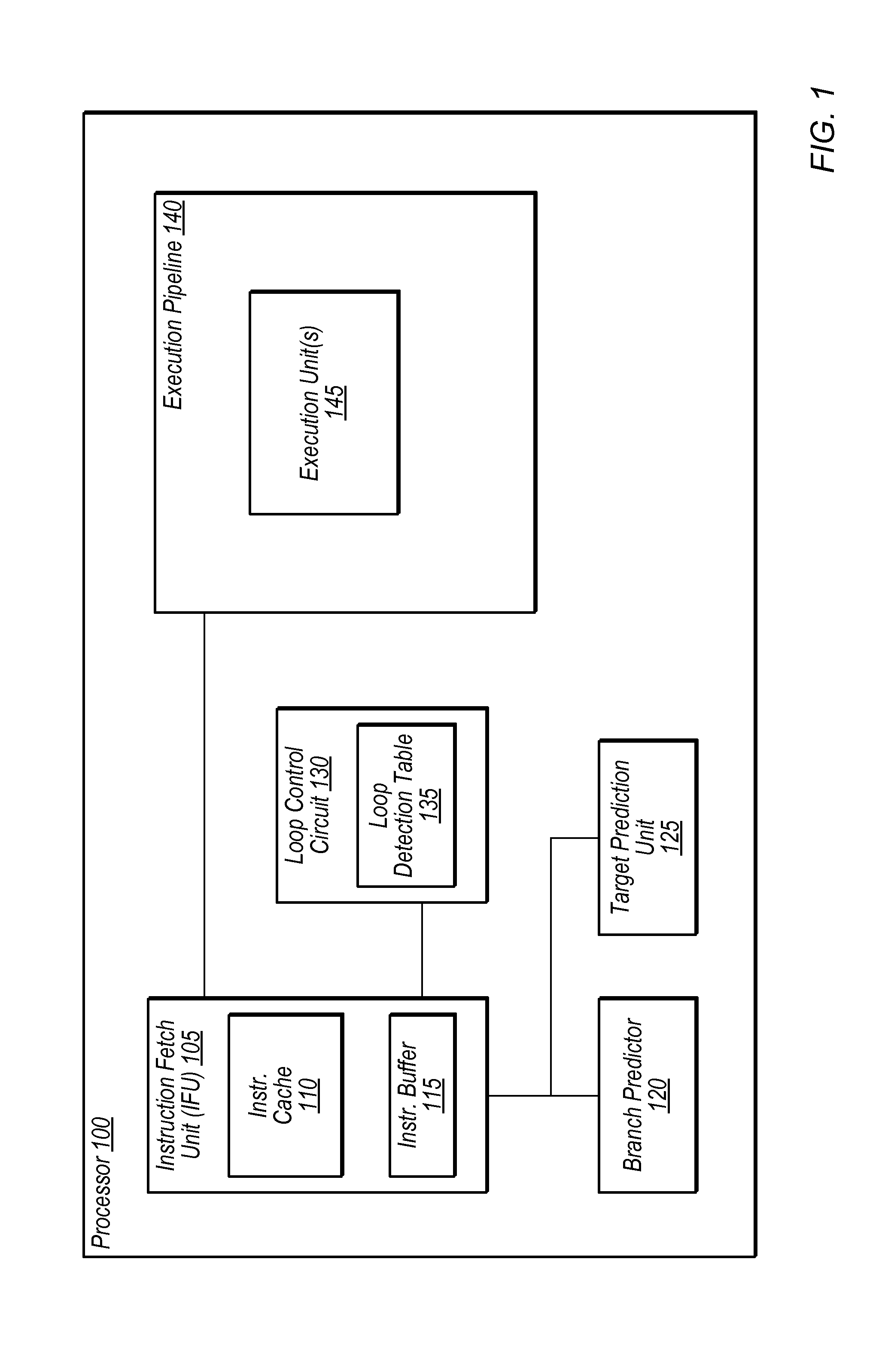
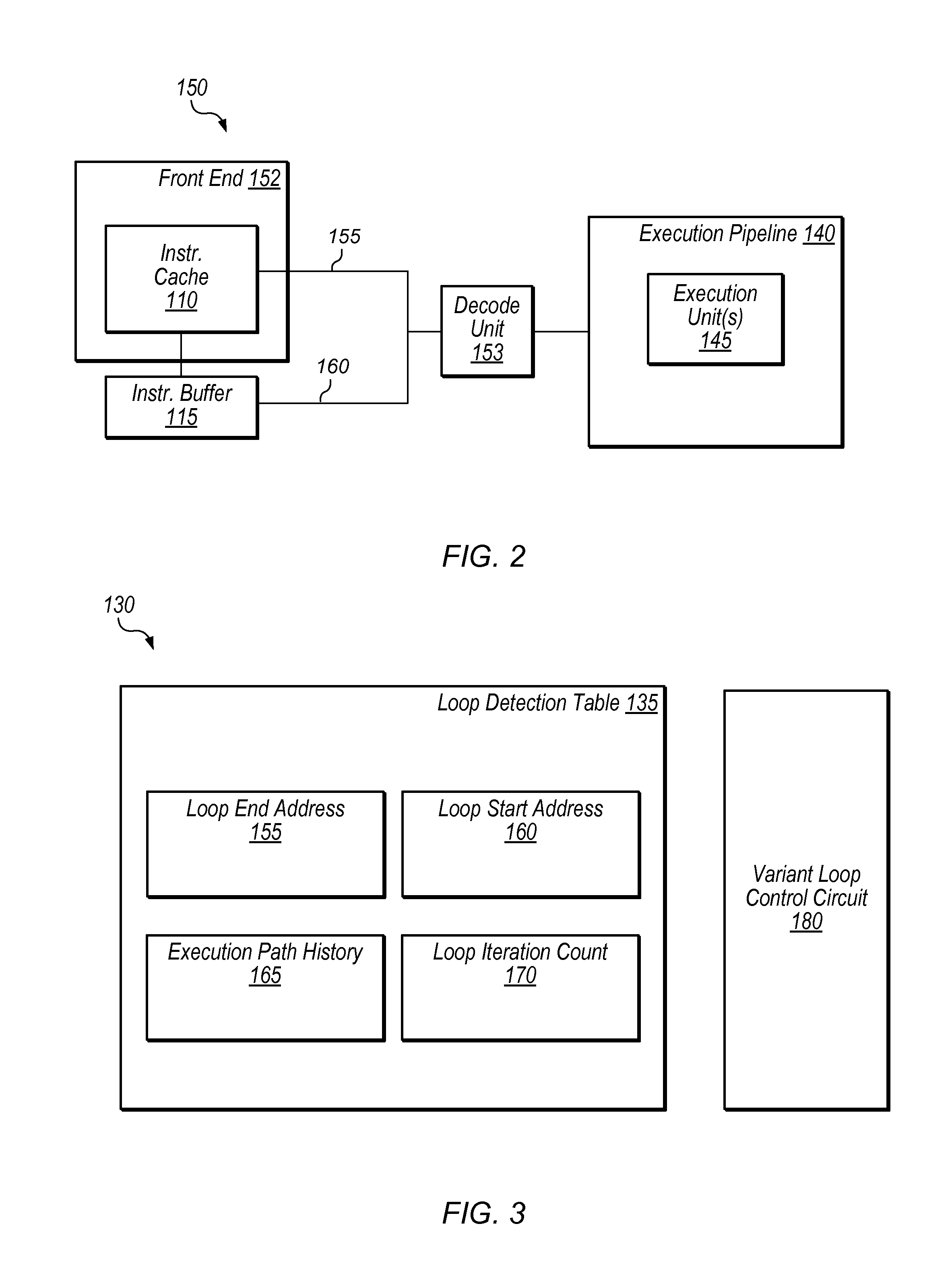
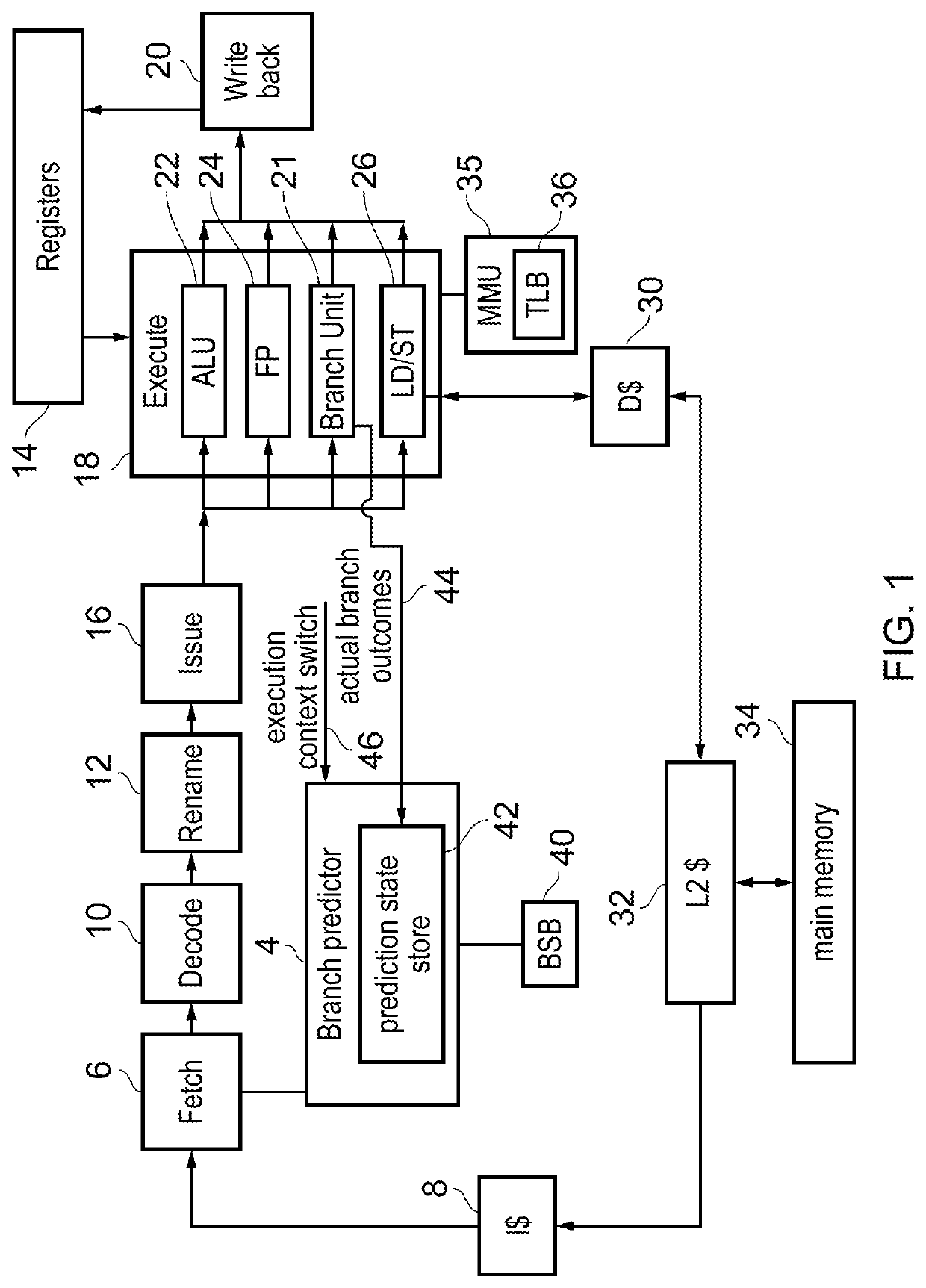
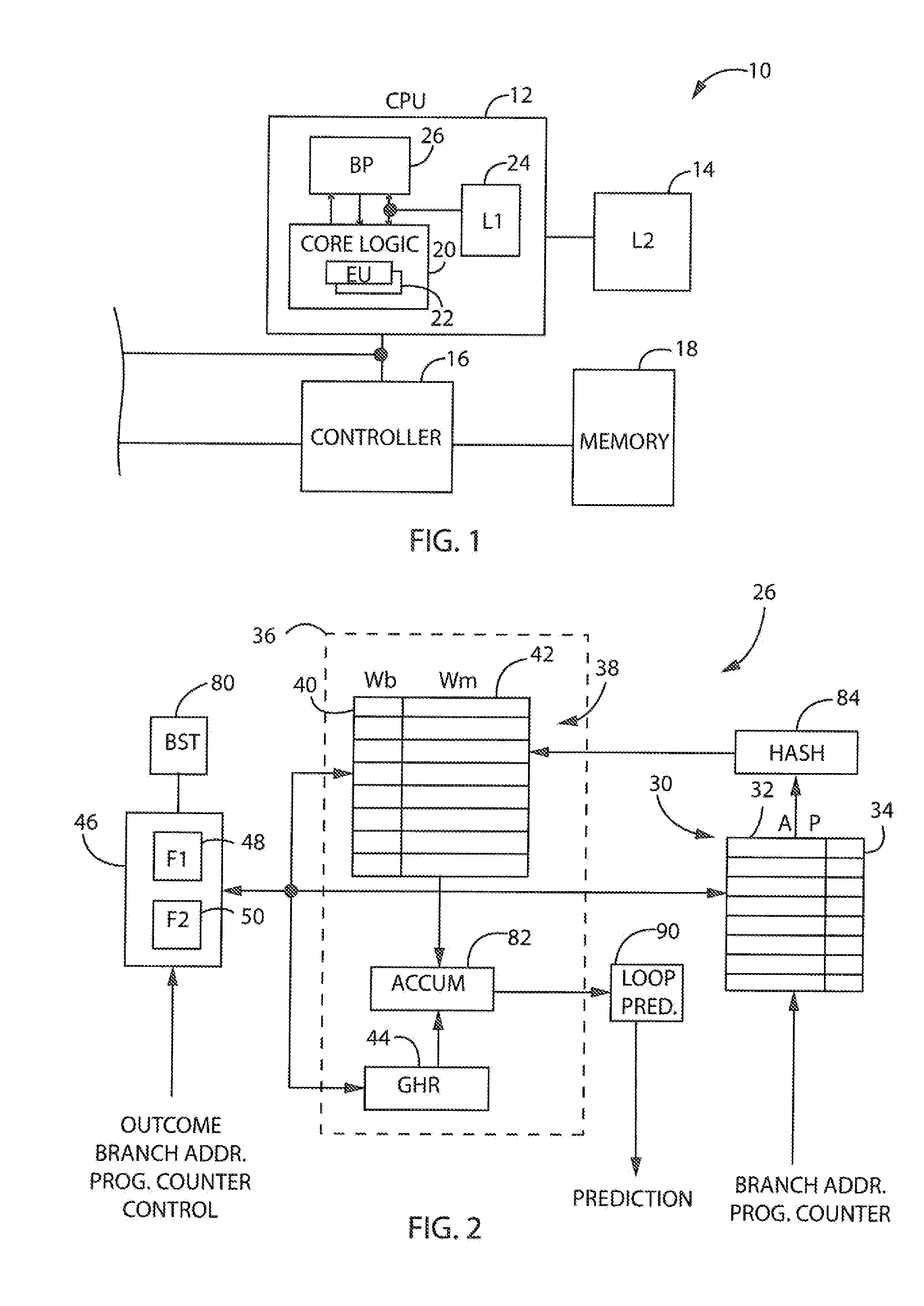
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g. an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow in the instruction pipeline. Branch predictors play a critical role in achieving high effective performance in many modern pipelined microprocessor architectures such as x86.
Branch prediction architecture
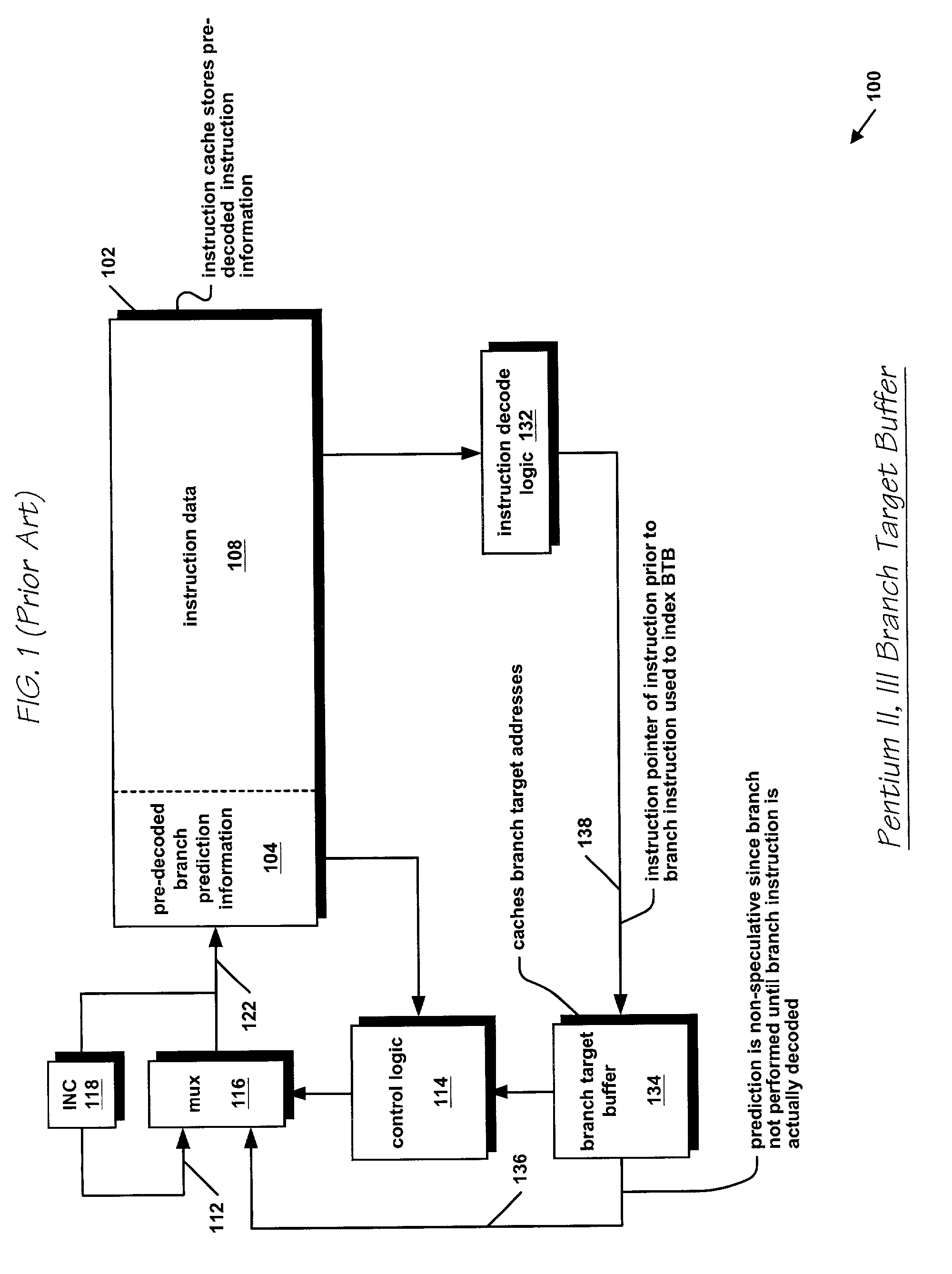
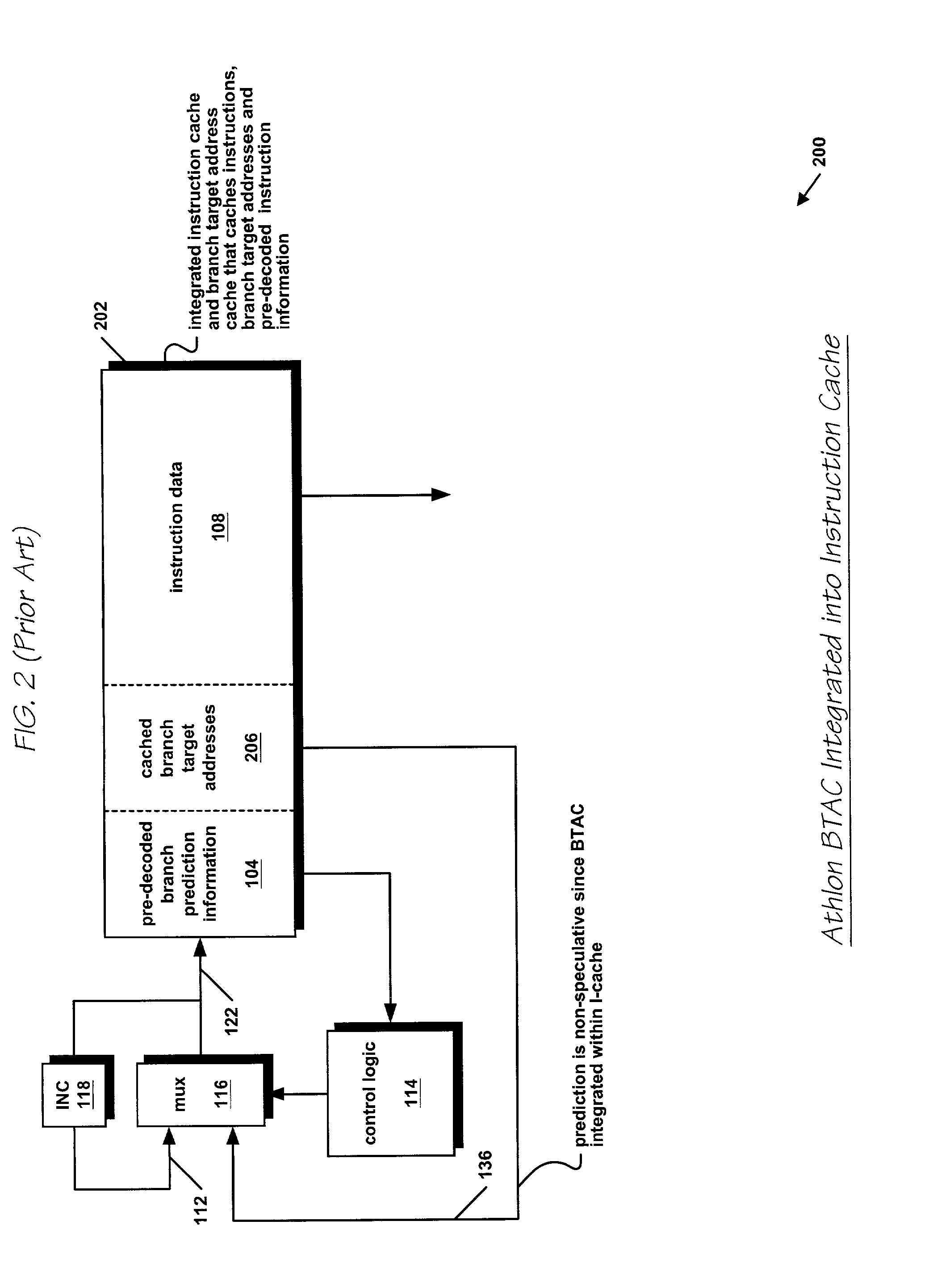
InactiveUS6332189B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationProcessor registerTrace Cache
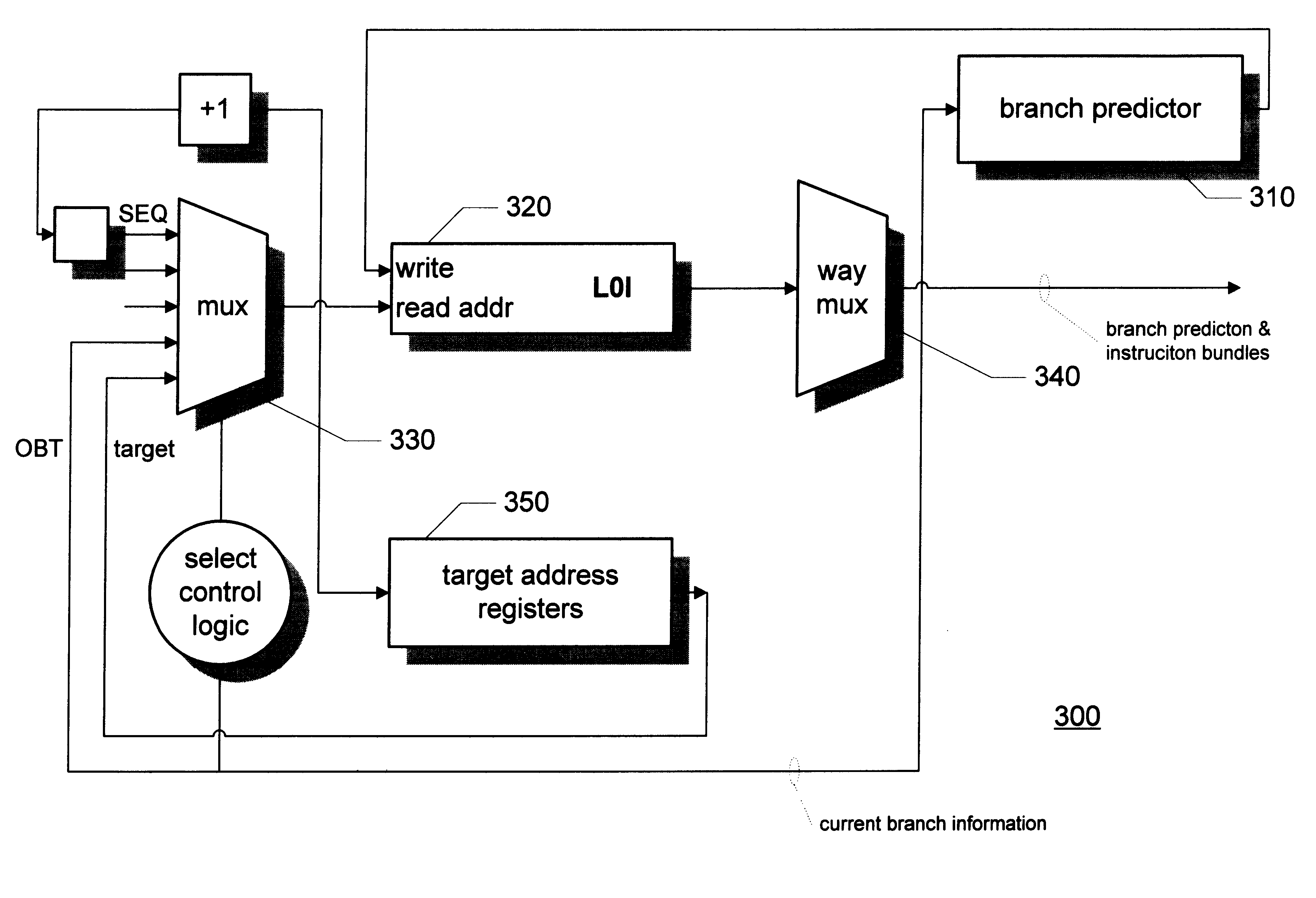
A branch prediction architecture is disclosed, having a branch predictor, a target address register, first and second multiplexors, a cache memory, and a trace cache. The branch predictor may advantageously be a series-parallel branch predictor, and alternatively may be a serial-BLG branch predictor or a choosing branch predictor. The first multiplexor receives an input from the target address register, and provides an output to the cache memory. The cache memory receives output from both the branch predictor and the first multiplexor, and provides an output to the second multiplexor. The trace cache receives the output from the branch predictor, and provides an output received by the second multiplexor. The second multiplexor, receiving input from both the trace cache and the cache memory, outputs branch predictions and instruction bundles.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Bad branch prediction detection, marking, and accumulation for faster instruction stream processing
ActiveUS20100299502A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsVariable lengthByte
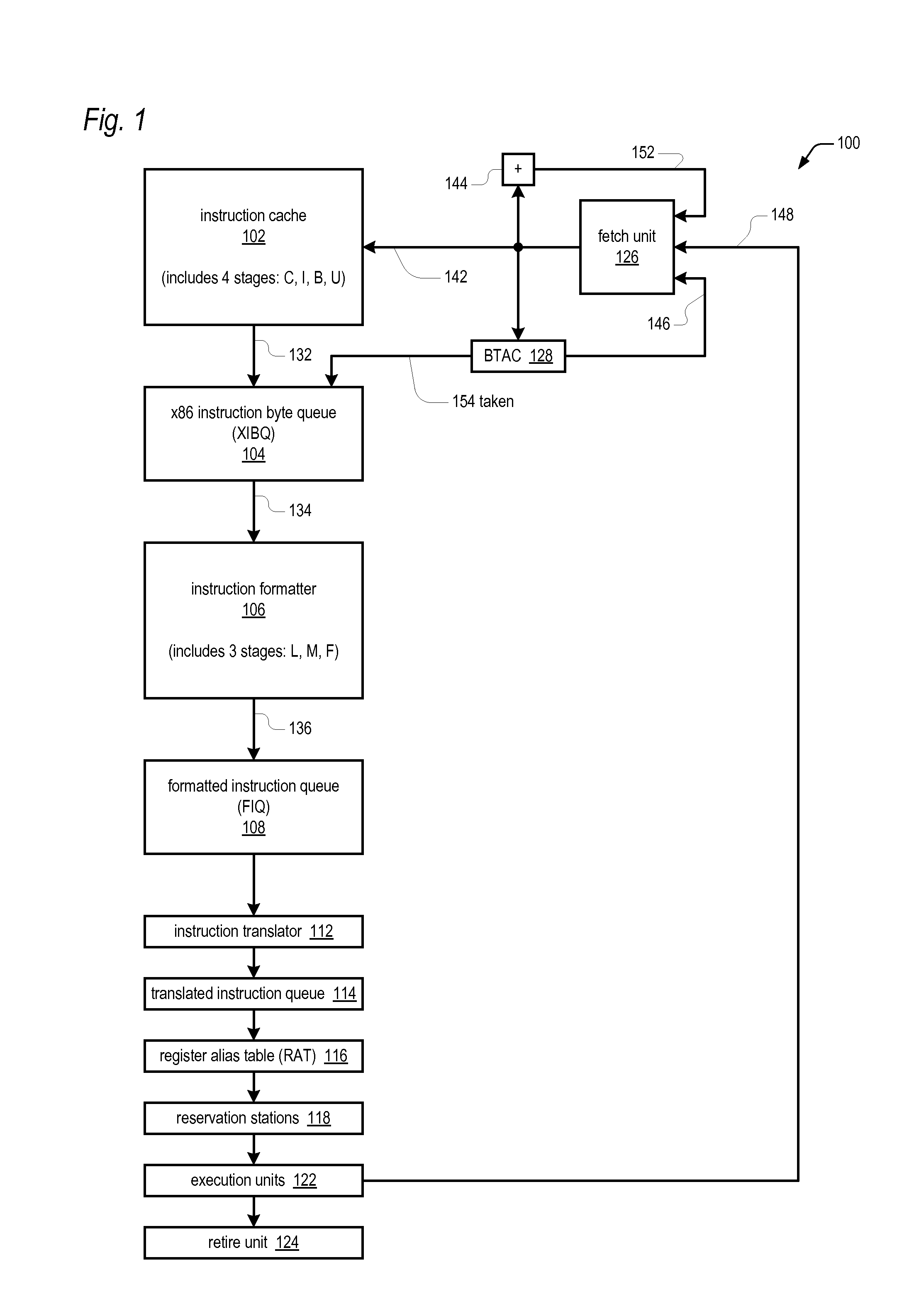
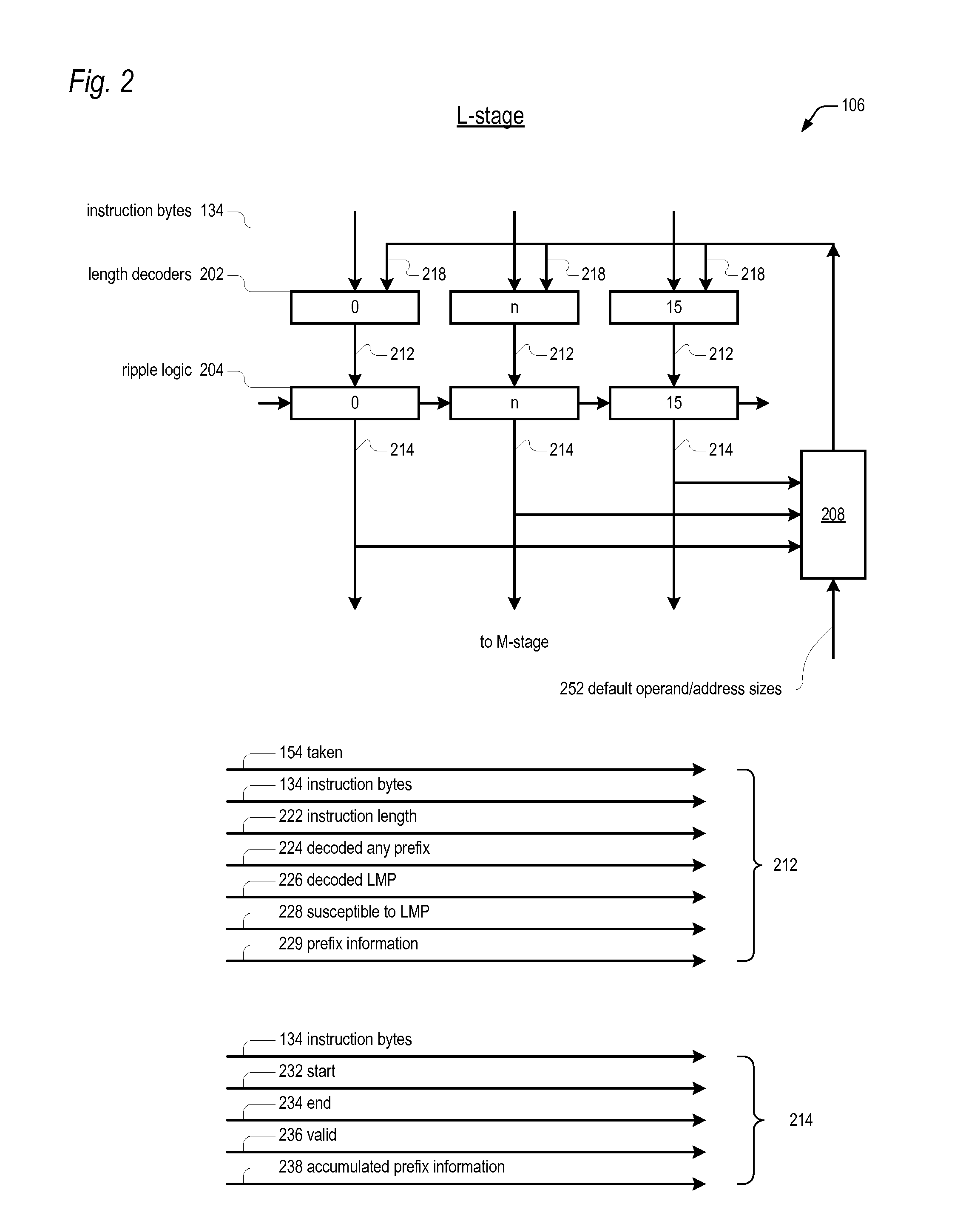
An apparatus for extracting instructions from a stream of undifferentiated instruction bytes in a microprocessor having an instruction set architecture in which the instructions are variable length. Decode logic decodes the instruction bytes of the stream to generate for each a corresponding opcode byte indictor and end byte indicator and receives a corresponding taken indicator for each of the instruction bytes. The taken indicator is true if a branch predictor predicted the instruction byte is the opcode byte of a taken branch instruction. The decode logic generates a corresponding bad prediction indicator for each of the instruction bytes. The bad prediction indicator is true if the corresponding taken indicator is true and the corresponding opcode byte indicator is false. The decode logic sets to true the bad prediction indicator for each remaining byte of an instruction whose opcode byte has a true bad prediction indicator. Control logic extracts instructions from the stream and sends the extracted instructions for further processing by the microprocessor. The control logic foregoes sending an instruction having both a true end byte indicator and a true bad prediction indicator.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Suppression of control transfer instructions on incorrect speculative execution paths
ActiveUS20120290820A1Suppresses resultEliminates spurious flushDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionExecution control
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for segmented sequential storage
InactiveUS20160098279A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureSequential data
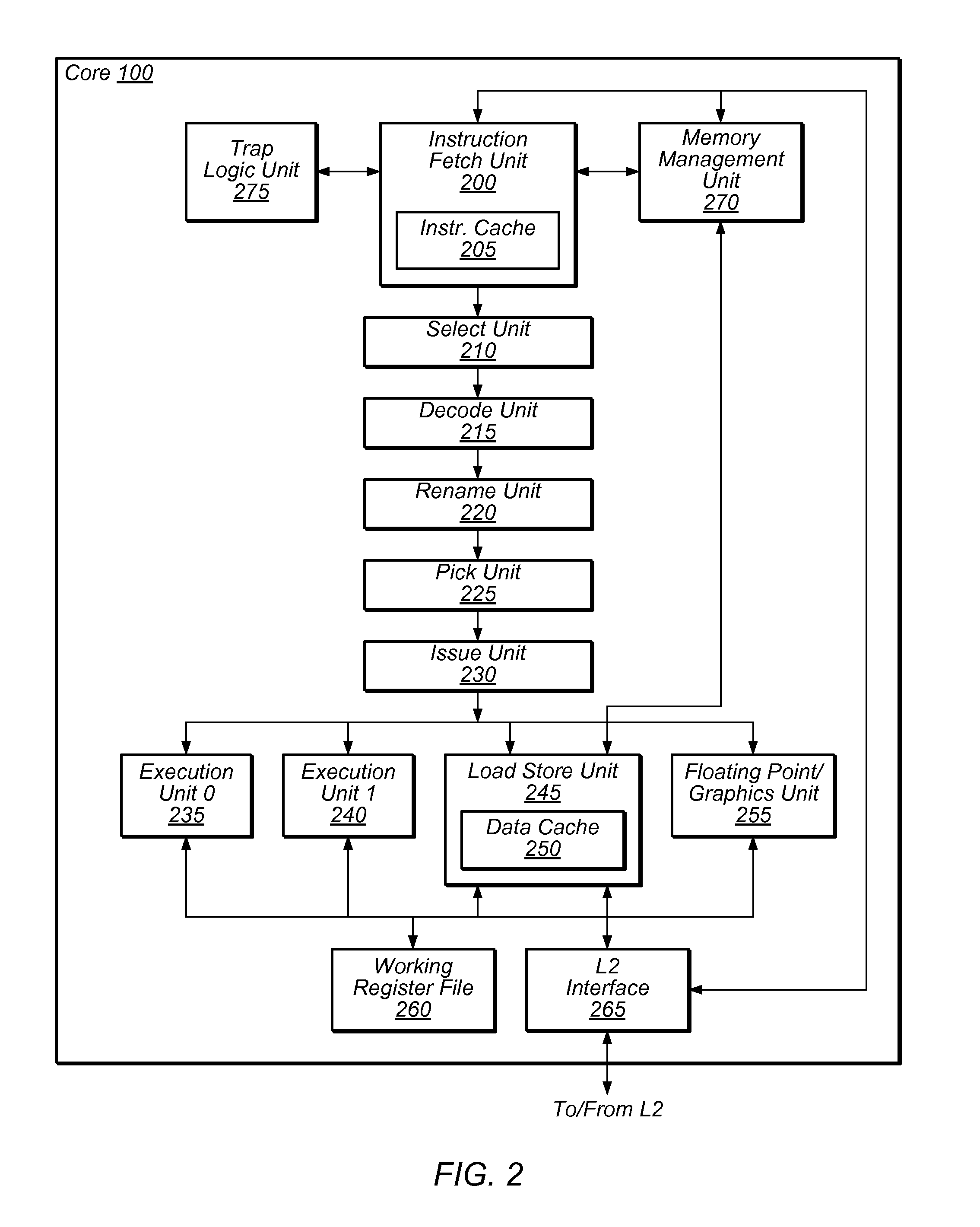
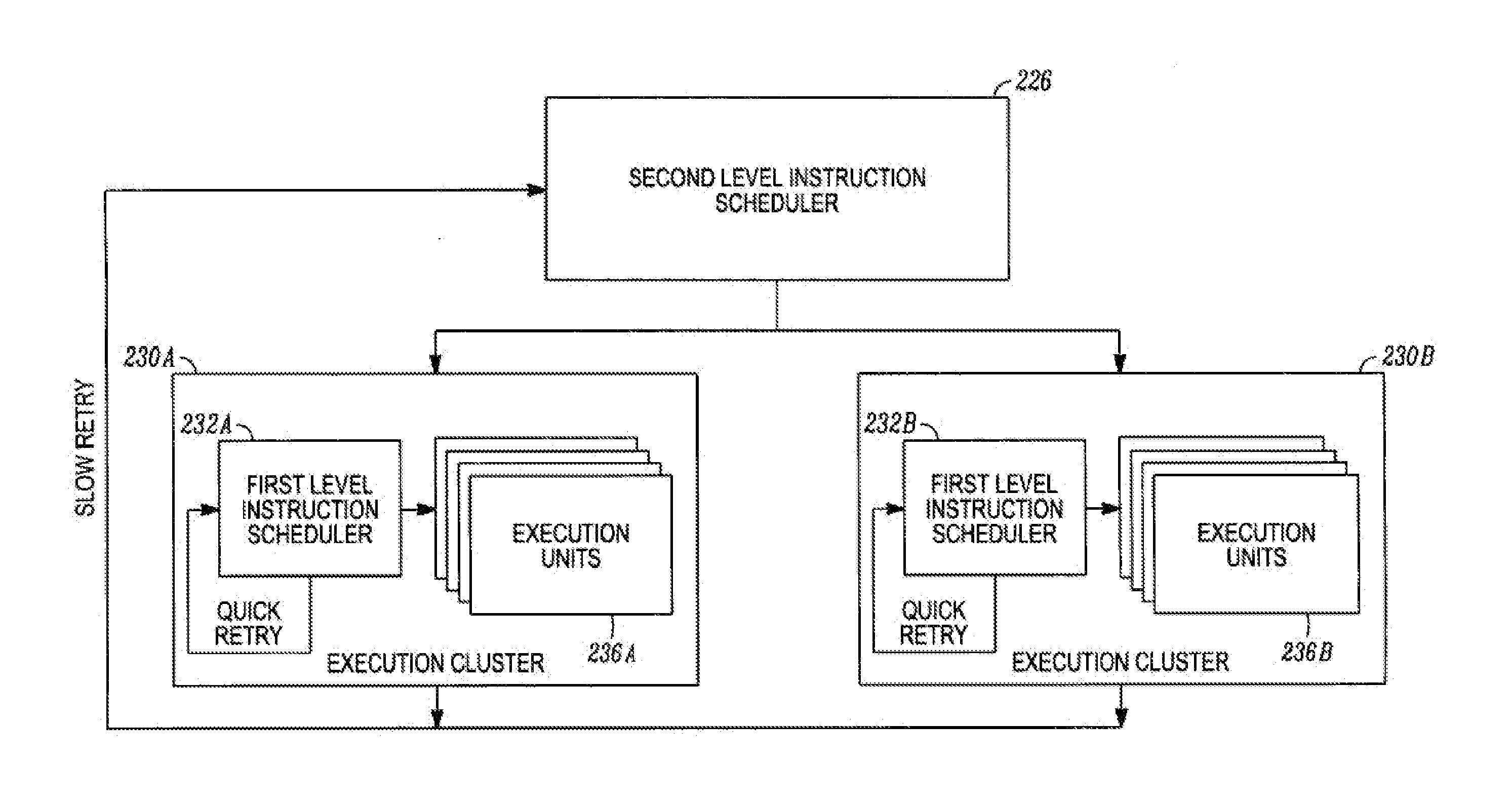
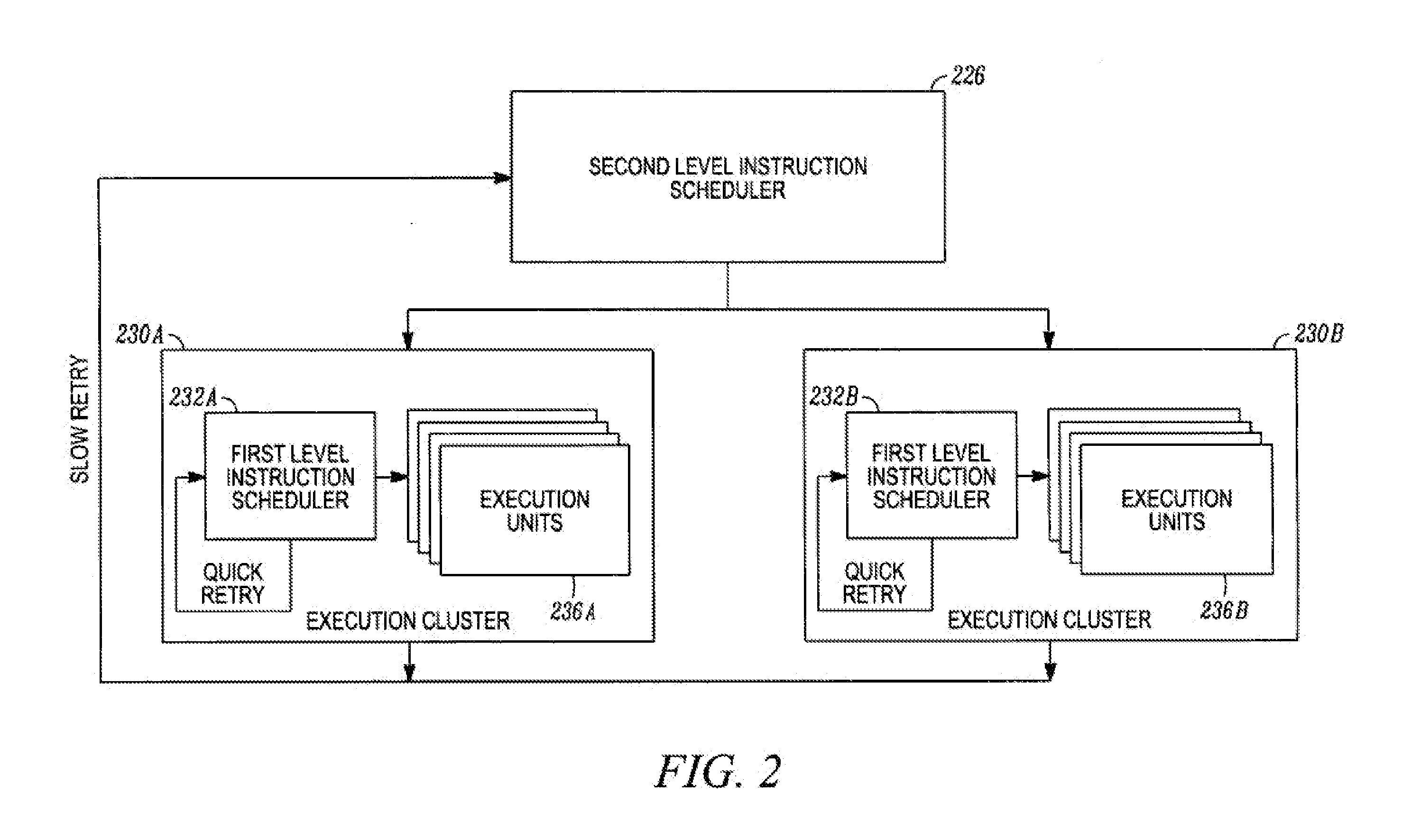
Various embodiments are described relating to processors, hierarchical processors, branch predictors, branch prediction systems, and computing systems. Some or all of a hierarchical instruction scheduler, hierarchical register file, or a hierarchical store buffer may be included in a hierarchical microprocessor. Some or all aspects of the hierarchical microprocessor may be implemented, partially or fully, using a method for sequential data storage.
Owner:RPX CORP
Branch prediction using least-recently-used (LRU)-class linked list branch predictors, and related circuits, methods, and computer-readable media
InactiveUS20160055003A1Decrease sensitivity to speculative corruptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerLeast recently frequently used
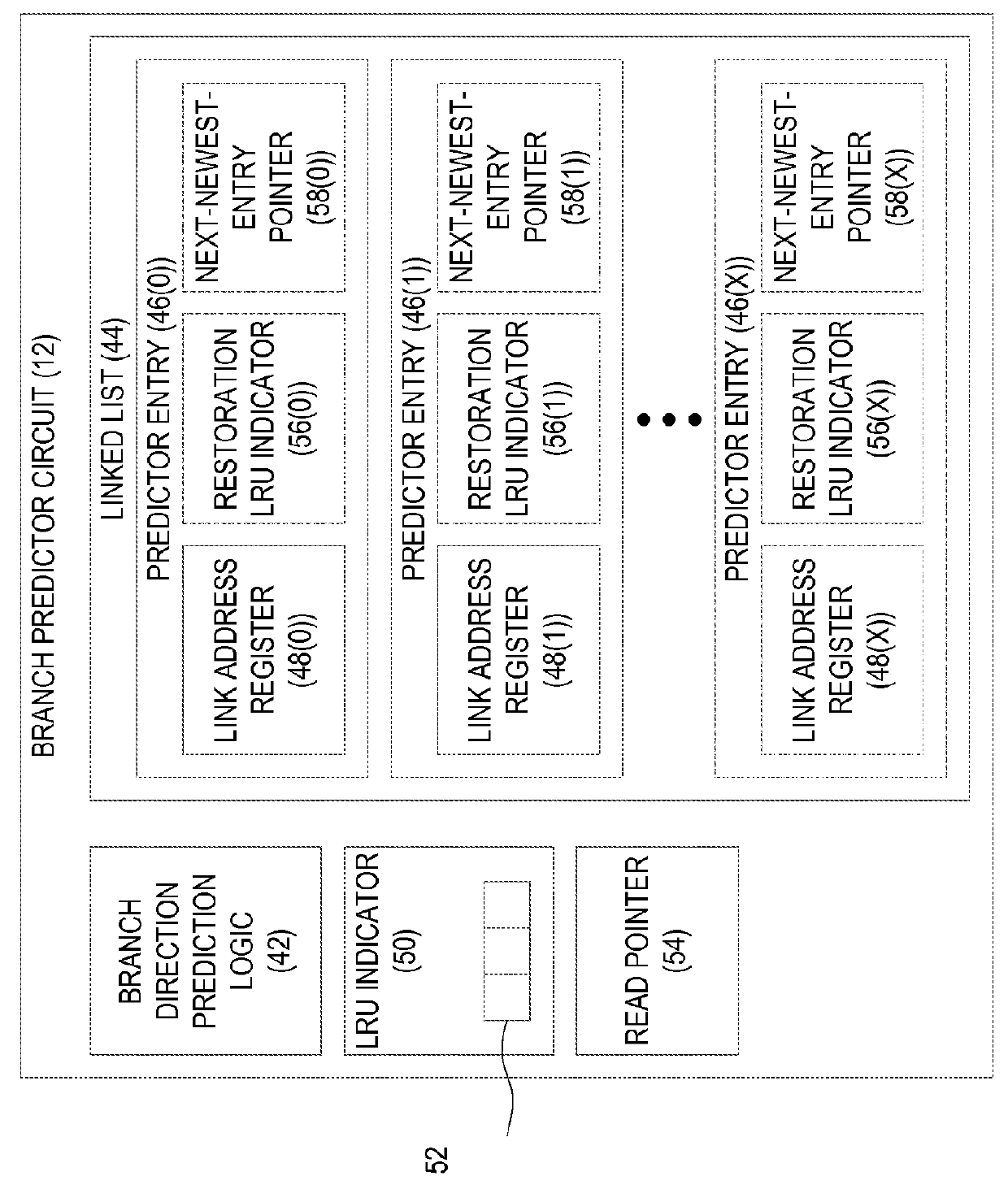
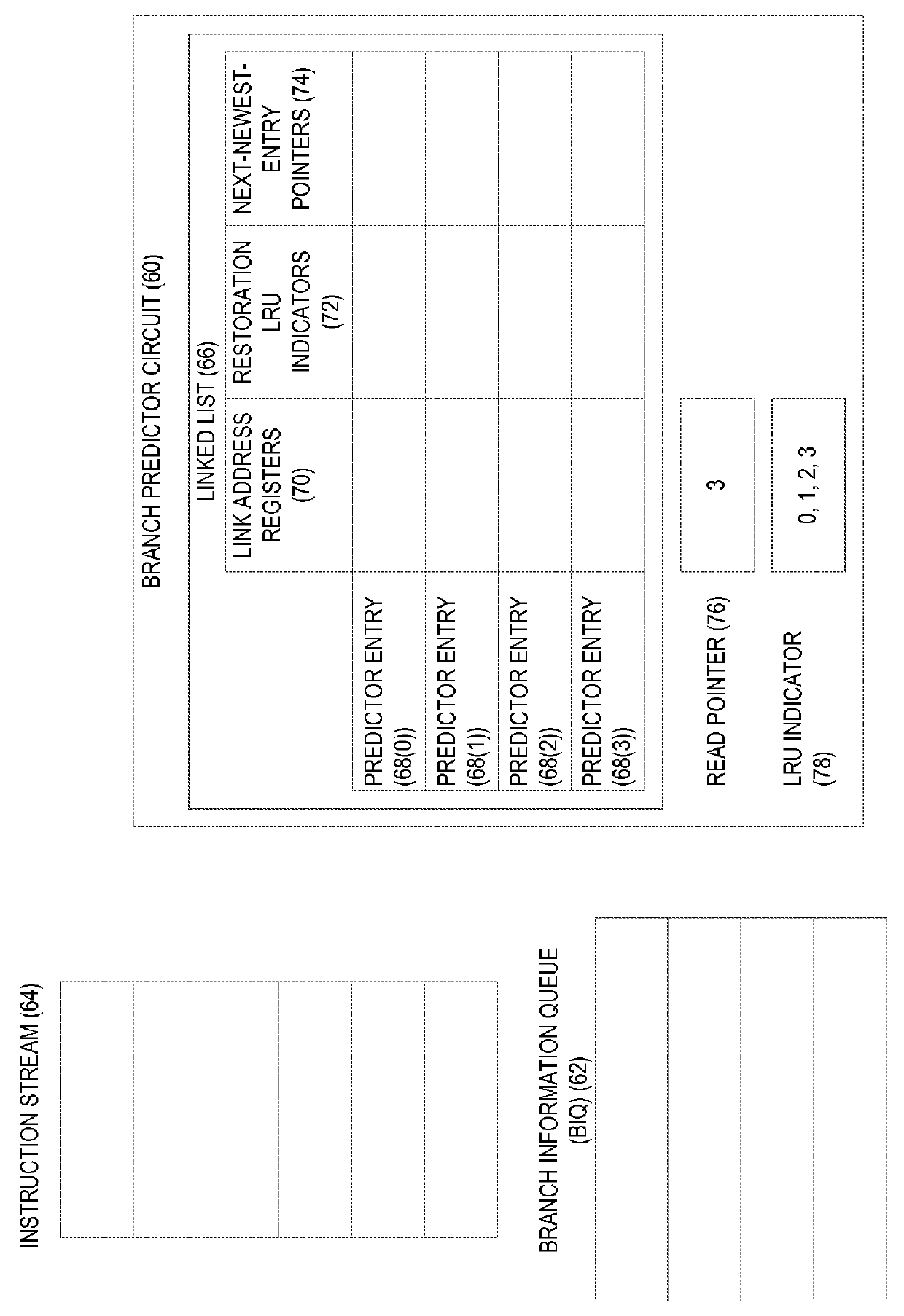
Branch prediction using Least-Recently-Used (LRU)-class linked list branch predictors, and related circuits, methods, and computer-readable media are disclosed. In one aspect, a branch predictor circuit comprises branch direction prediction logic and a linked list comprising a plurality of predictor entries, each comprising a link address register. The branch predictor circuit also comprises a LRU indicator indicative of a relative age of each of the predictor entries. The branch predictor circuit is configured to detect a first branch instruction in an instruction stream, and determine whether the first branch instruction is predicted to be taken. Responsive to determining that the first branch instruction is predicted to be taken, the branch predictor circuit allocates a least-recently-used entry of the plurality of predictor entries of the linked list based on the LRU indicator, and stores a sequential address for the first branch instruction in the link address register of the least-recently-used predictor entry.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Instruction acquisition control method based on simultaneous multithreading
InactiveCN102566974AImprove superiorityAdvancing Predictive Execution SpeedConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsFailure ratePattern matching
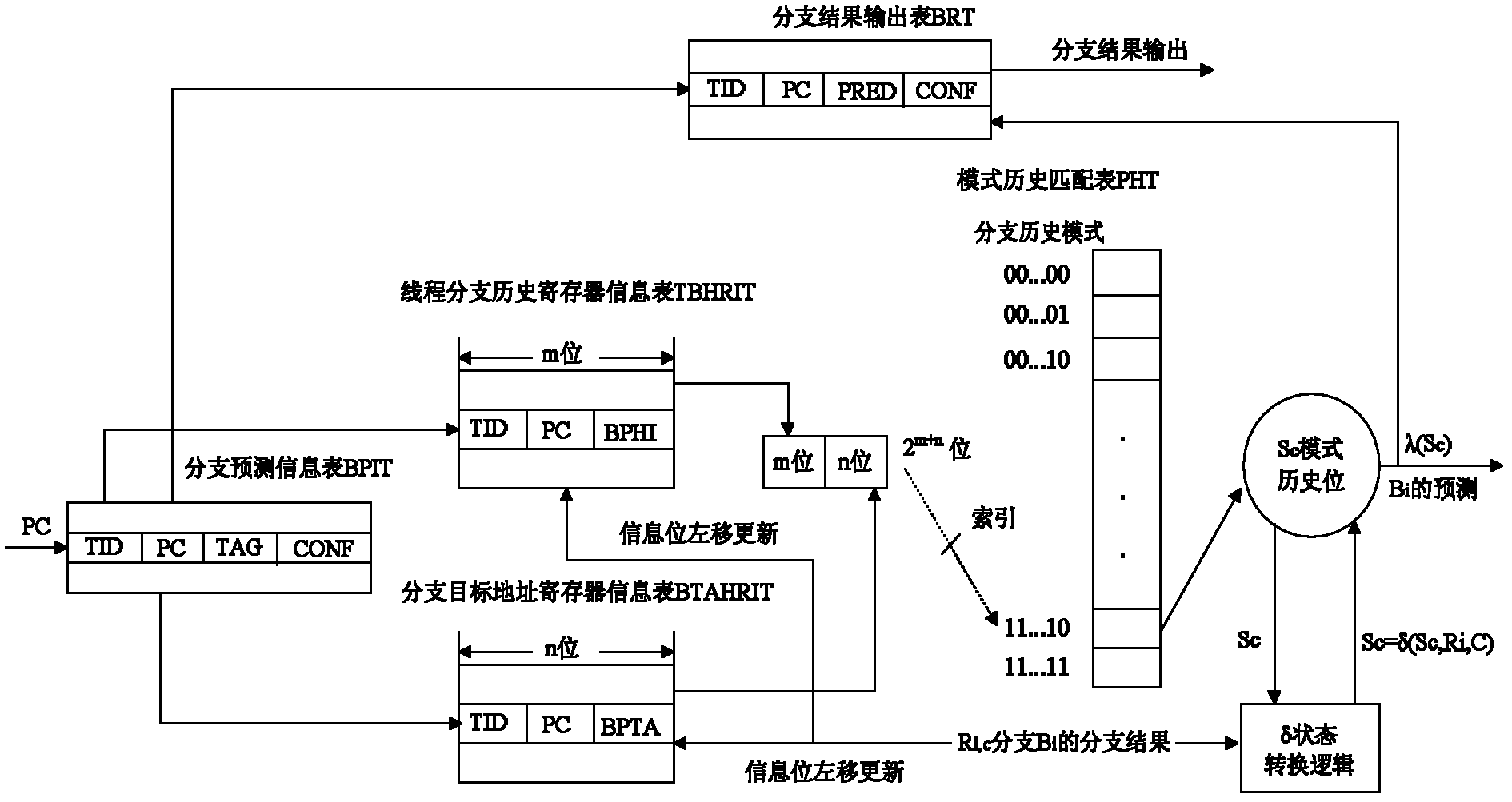
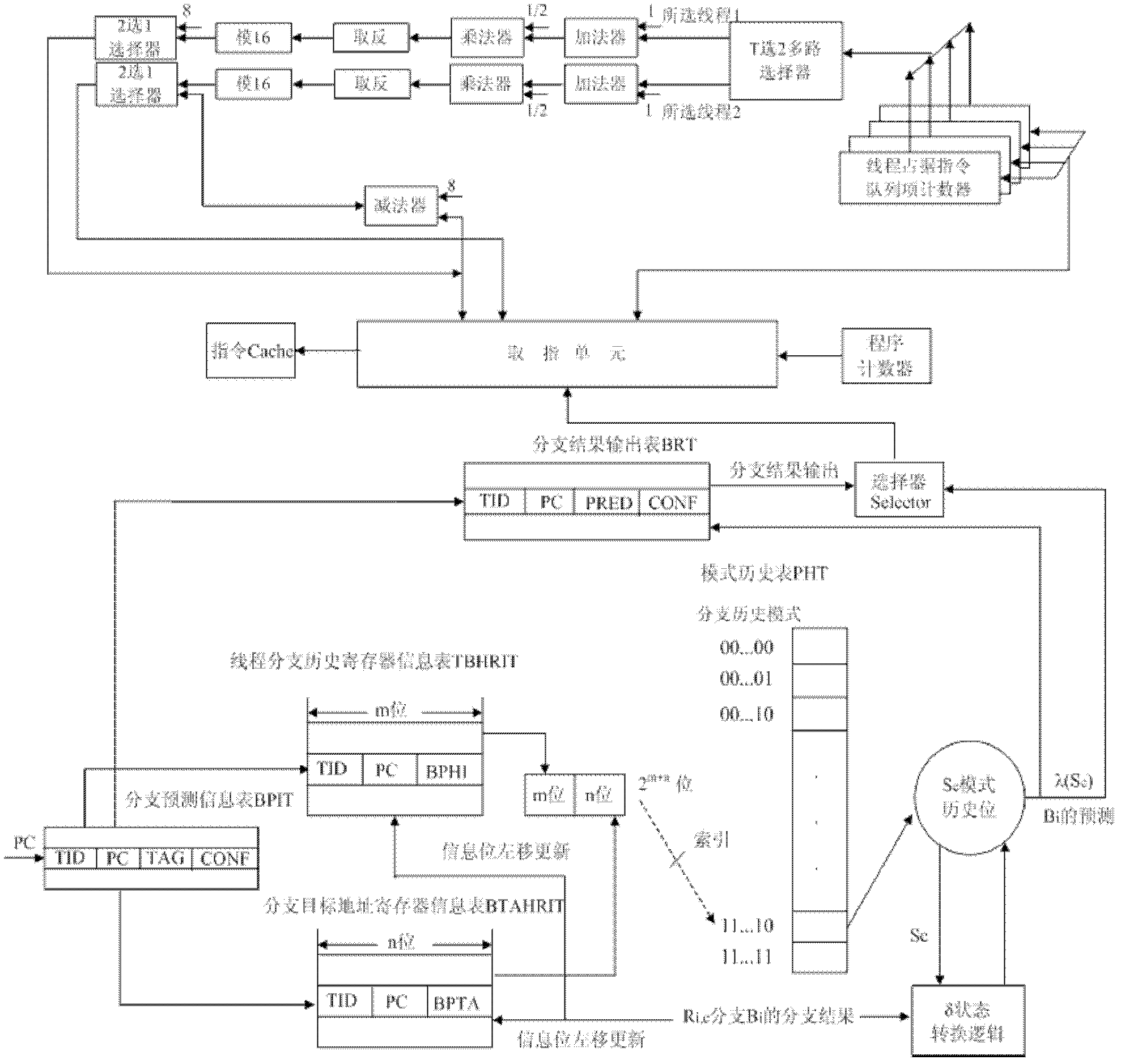
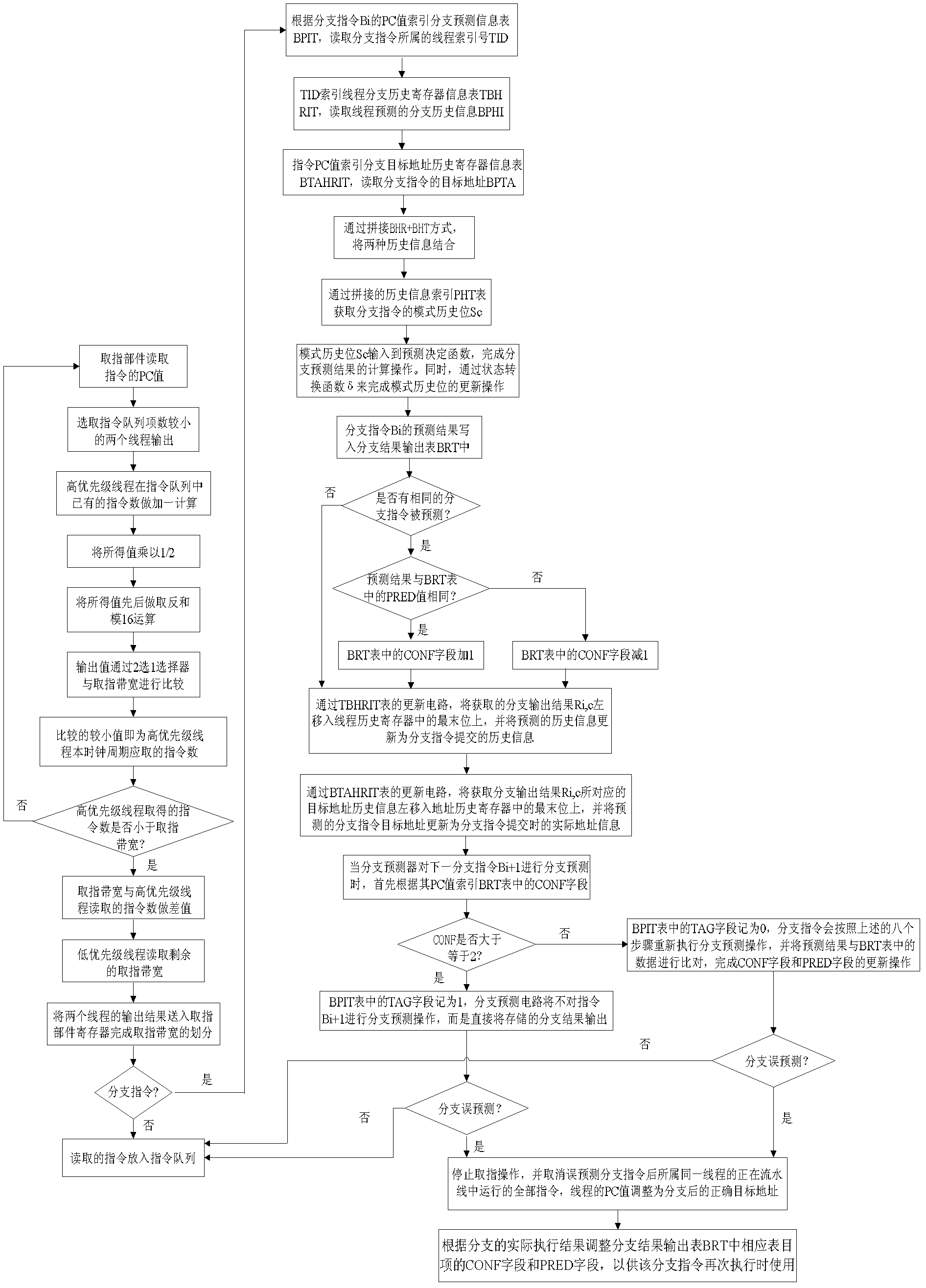
The invention provides an instruction acquisition control method based on simultaneous multithreading, which includes the steps: in each clock cycle of a processor, reading a PC (personable computer) value of instructions by an instruction acquisition component according to a program counter, selecting two threads with high priority as instruction acquisition threads firstly, and then computing the actual instruction number required by each instruction acquisition thread so as to read the instructions; according to an IPC (inter-process communication) value and the Cache failure rate, enabling a dual-priority resource allocation mechanism to compute system resources required by the threads in an instruction acquisition stage and complete dynamic allocation of the resources; matching a TBHBP (thread branch history branch predictor) with the instruction acquisition operations of the instruction acquisition component, acquiring a pattern type match position Sc by connecting global historical information with local historical information read by a branch instruction Bi to utilize as an index of a secondary PHT (pattern history table), and inputting computed results to a BRT (branch result table); and when the branch instruction Bi is executed again, judging whether CONF fields are larger than or equal to 2 or not by the aid of a selector, directly outputting the recorded branch results if the CONF fields are larger than or equal to 2, and finally placing the acquired instruction into an instruction Cache, so that all operations of instruction acquisition control are completed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Suppression of control transfer instructions on incorrect speculative execution paths
Techniques are disclosed relating to a processor that is configured to execute control transfer instructions (CTIs). In some embodiments, the processor includes a mechanism that suppresses results of mispredicted younger CTIs on a speculative execution path. This mechanism permits the branch predictor to maintain its fidelity, and eliminates spurious flushes of the pipeline. In one embodiment, a misprediction bit is be used to indicate that a misprediction has occurred, and younger CTIs than the CTI that was mispredicted are suppressed. In some embodiments, the processor may be configured to execute instruction streams from multiple threads. Each thread may include a misprediction indication. CTIs in each thread may execute in program order with respect to other CTIs of the thread, while instructions other than CTIs may execute out of program order.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Memory violation prediction
InactiveUS20180081806A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsLoad instructionPerformed Procedure
Disclosed are methods and apparatuses for preventing memory violations. In an aspect, a fetch unit accesses, from a branch predictor of a processor, a disambiguation indicator associated with a block of instructions of a program to be executed by the processor, and fetches, from an instruction cache, the block of instructions. The processor executes load instructions and / or store instructions in the block of instructions based on the disambiguation indicator indicating whether or not the load instructions and / or the store instructions in the block of instructions can bypass other instructions of the program or be bypassed by other instructions of the program.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
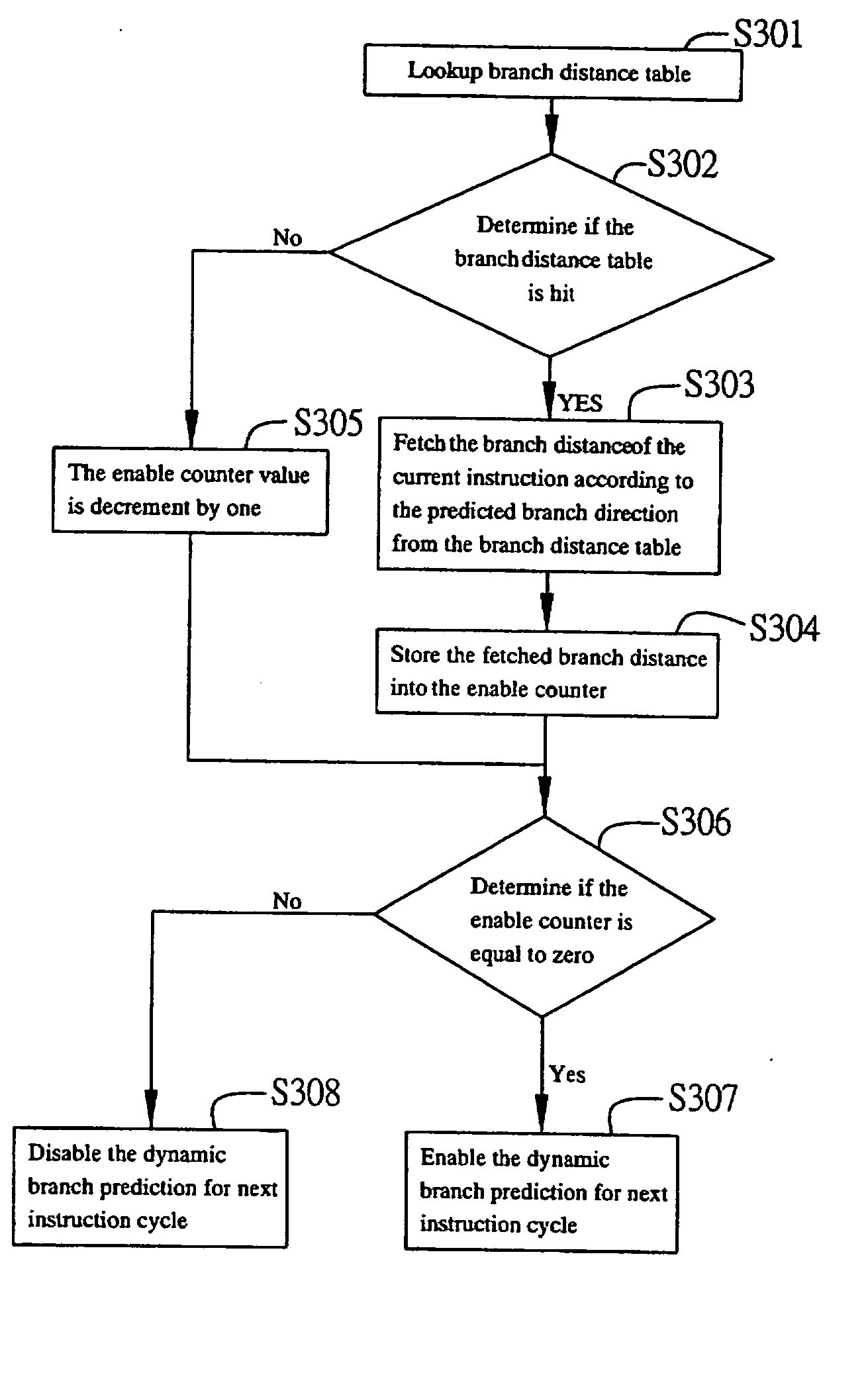
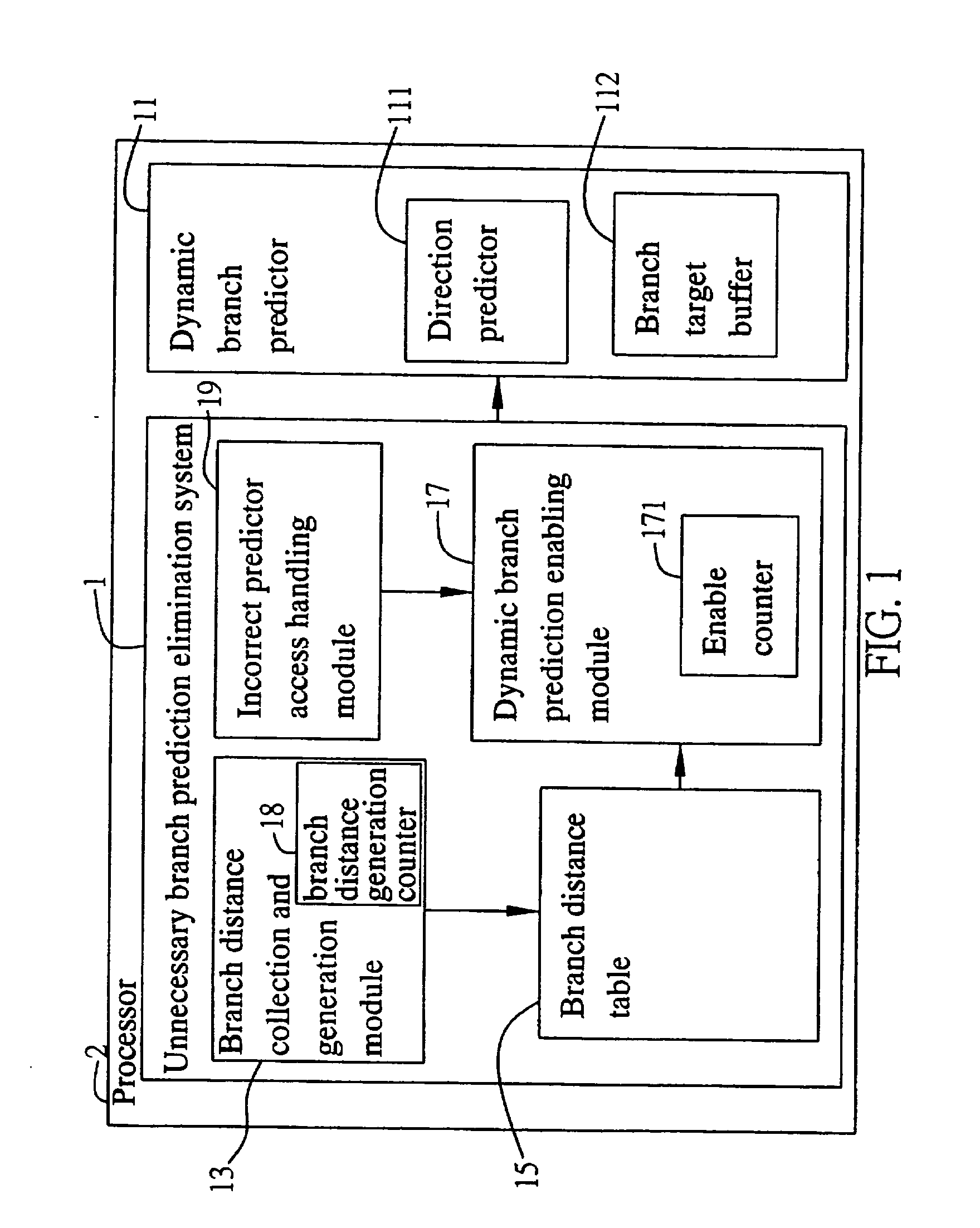
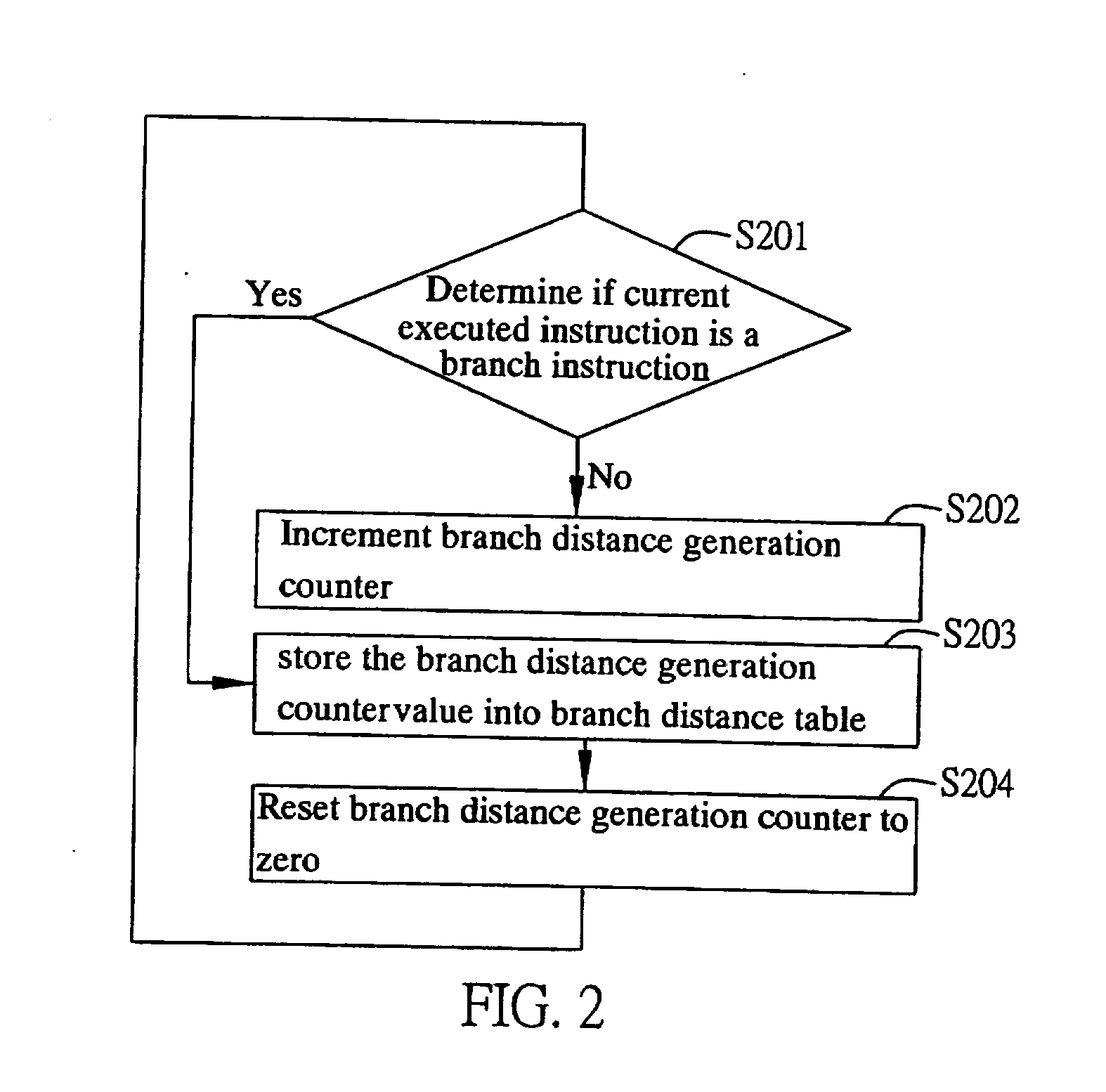
Unnecessary dynamic branch prediction elimination method for low-power
InactiveUS20070130450A1Branch prediction accuracy is not affectedEfficient powerDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsElimination methodBranch predictor
A system and method for unnecessary dynamic branch prediction elimination in a processor with a dynamic branch predictor, includes a branch distance generation module for generating a branch distance between two consecutive branch instructions, a branch distance table for storing the branch distance generated by the branch distance generation module, and a dynamic branch predictor enabling module for determining enable or disable the dynamic branch prediction by using the branch distances stored in the branch distance table for the next incoming instructions. Through the configuration of the system, the dynamic branch prediction is performed only for branch instruction, so as to save power consumption due to unnecessary dynamic branch predictions.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Allocating threads to resources using speculation metrics
ActiveCN103942033AAnalogue/digital conversionResource allocationReservation stationResource allocation
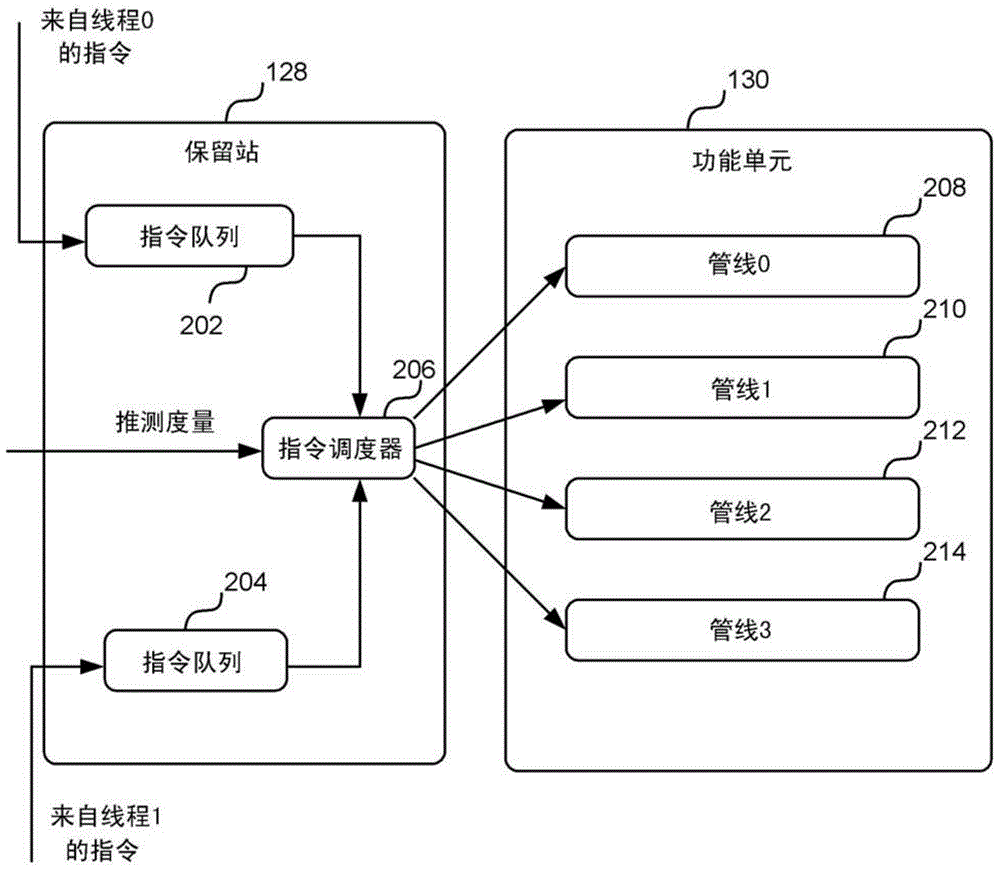
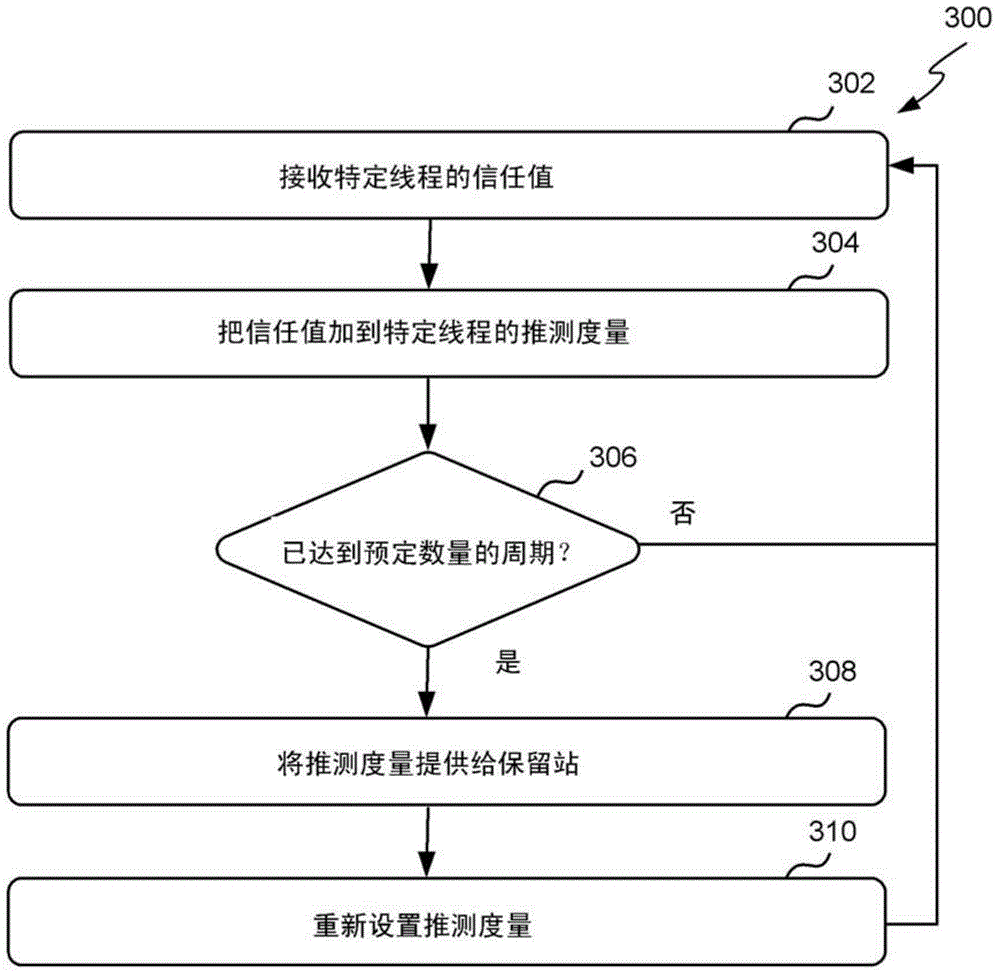
The invention describes allocating threads to resources using speculation metrics. A method, a reservation station and a processor for allocating resources to a plurality of threads based on the extent to which the instructions associated with each of the threads are speculative. The method comprises receiving a speculation metric for each thread at the reservation station. Each speculation metric represents the extent to which the instructions associated with a particular thread are speculative. The more speculative an instruction, the more likely the instruction has been incorrectly predicted by a branch predictor. The reservation station allocates functional unit resources (e.g. pipelines) to the threads based on the speculation metrics, and selects a number of instructions from one or more of the threads based on the allocation. The selected instructions are then issued to the functional unit resources.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
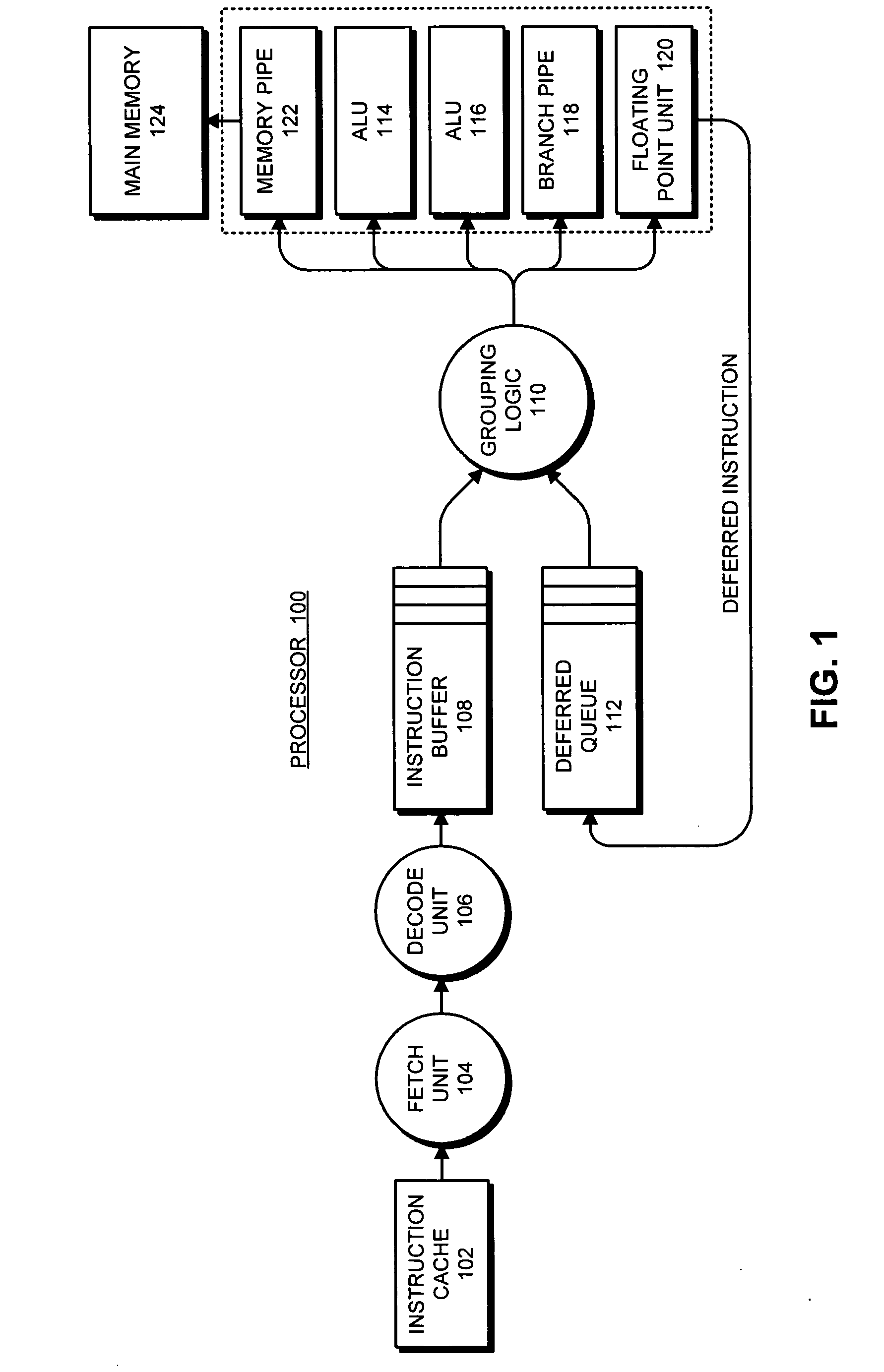
Run-ahead program execution with value prediction
InactiveUS7188234B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionLine tubingLoad instruction
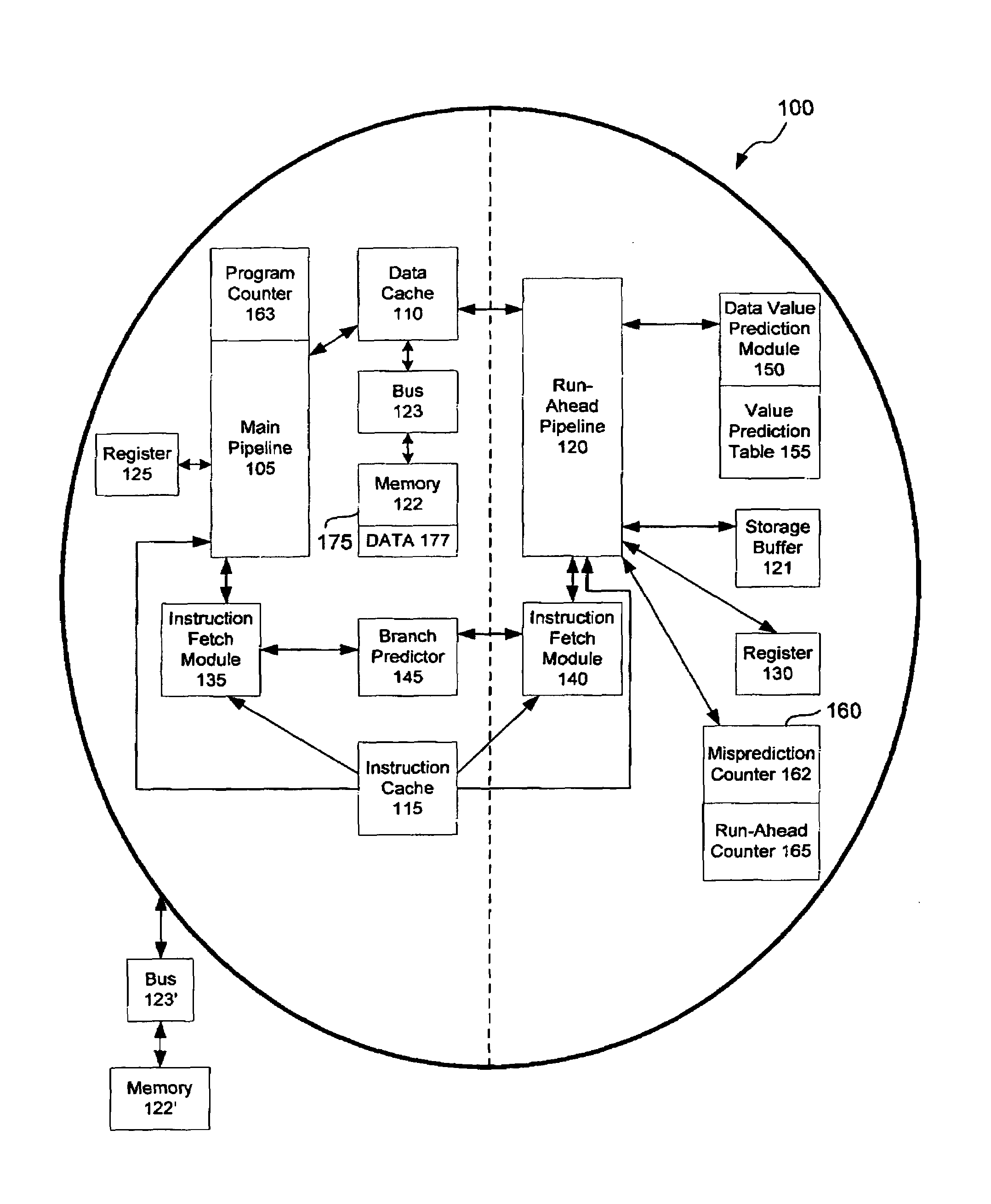
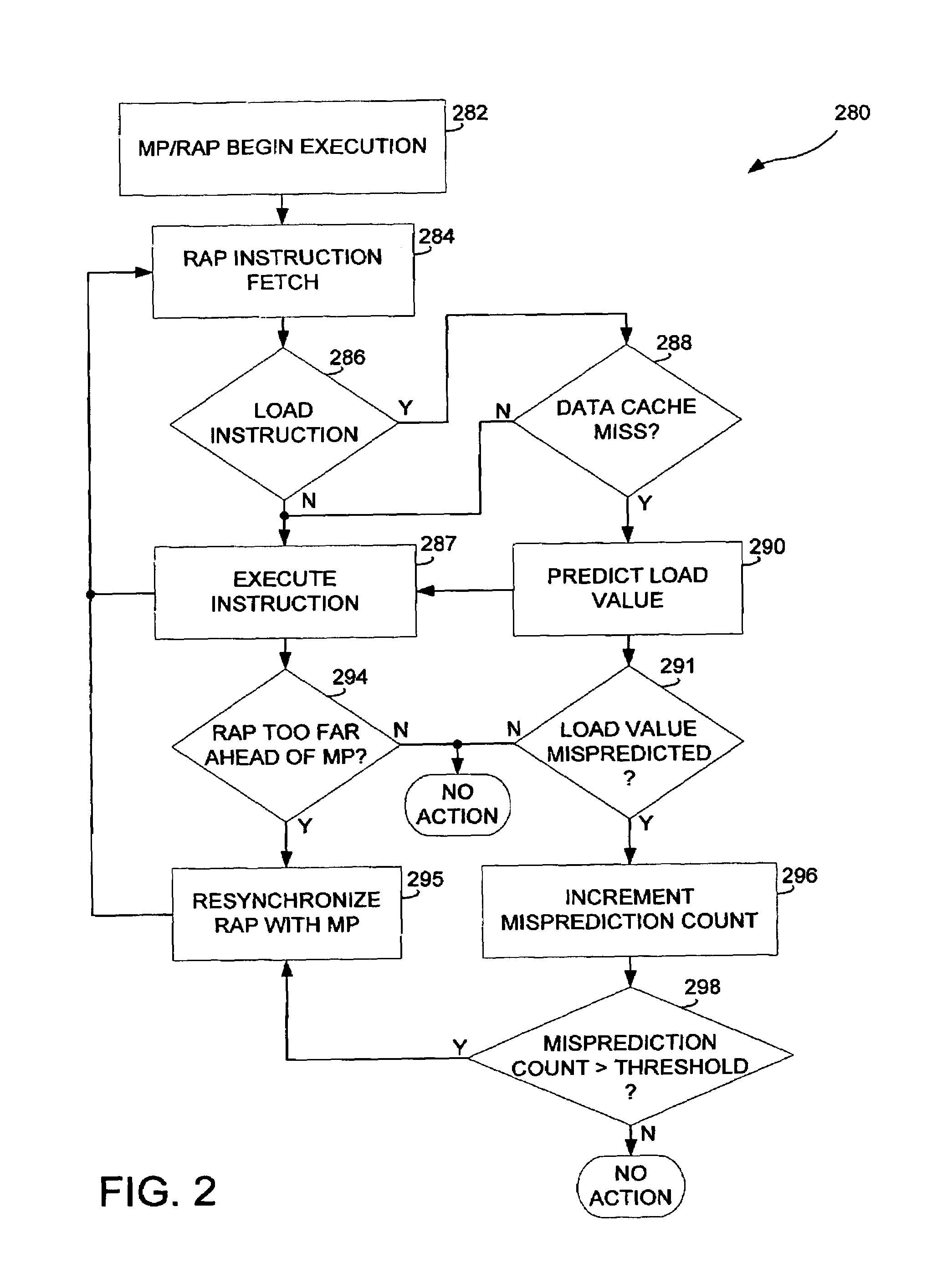
A data processing apparatus, a computer, an article including a machine-accessible medium, and a method of processing data are disclosed. The data processing apparatus may include a pair of pipelines sharing an instruction cache, data cache, and a branch predictor with the second pipeline running ahead of the first pipeline using a data value prediction module. The pipelines may be included in one or more processors and coupled to a memory to form a computer. The method includes executing a plurality of instructions using the pipeline pair, such that when a cache miss is encountered by the second pipeline during execution of a LOAD instruction, the data value prediction module supplies a predicted load value in lieu of a cached value, enabling continued execution of the plurality of instructions by the second pipeline without waiting for the return of the cached value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Branch predictor directed prefetch
ActiveUS20080209173A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsInstruction streamBranch predictor
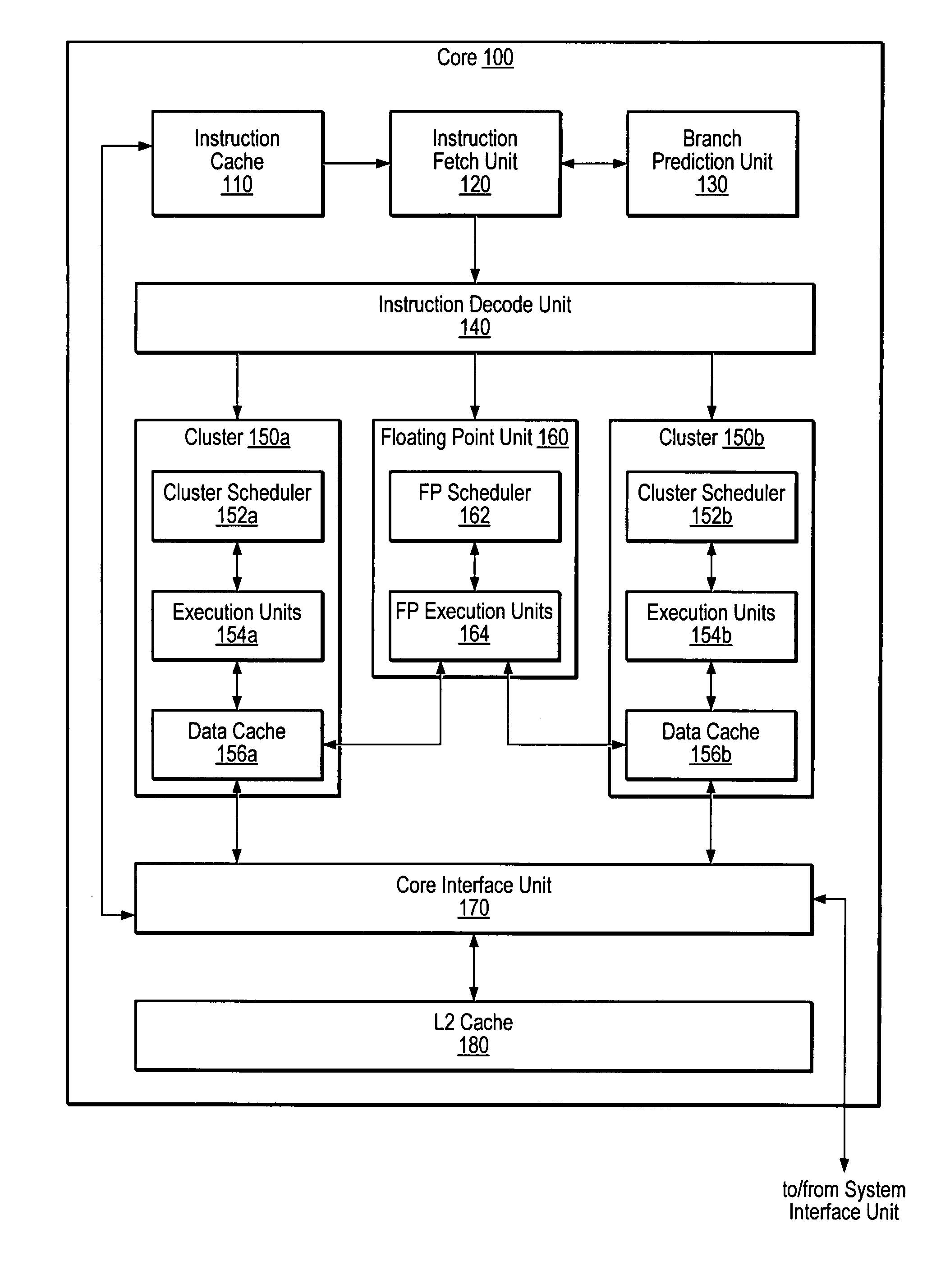
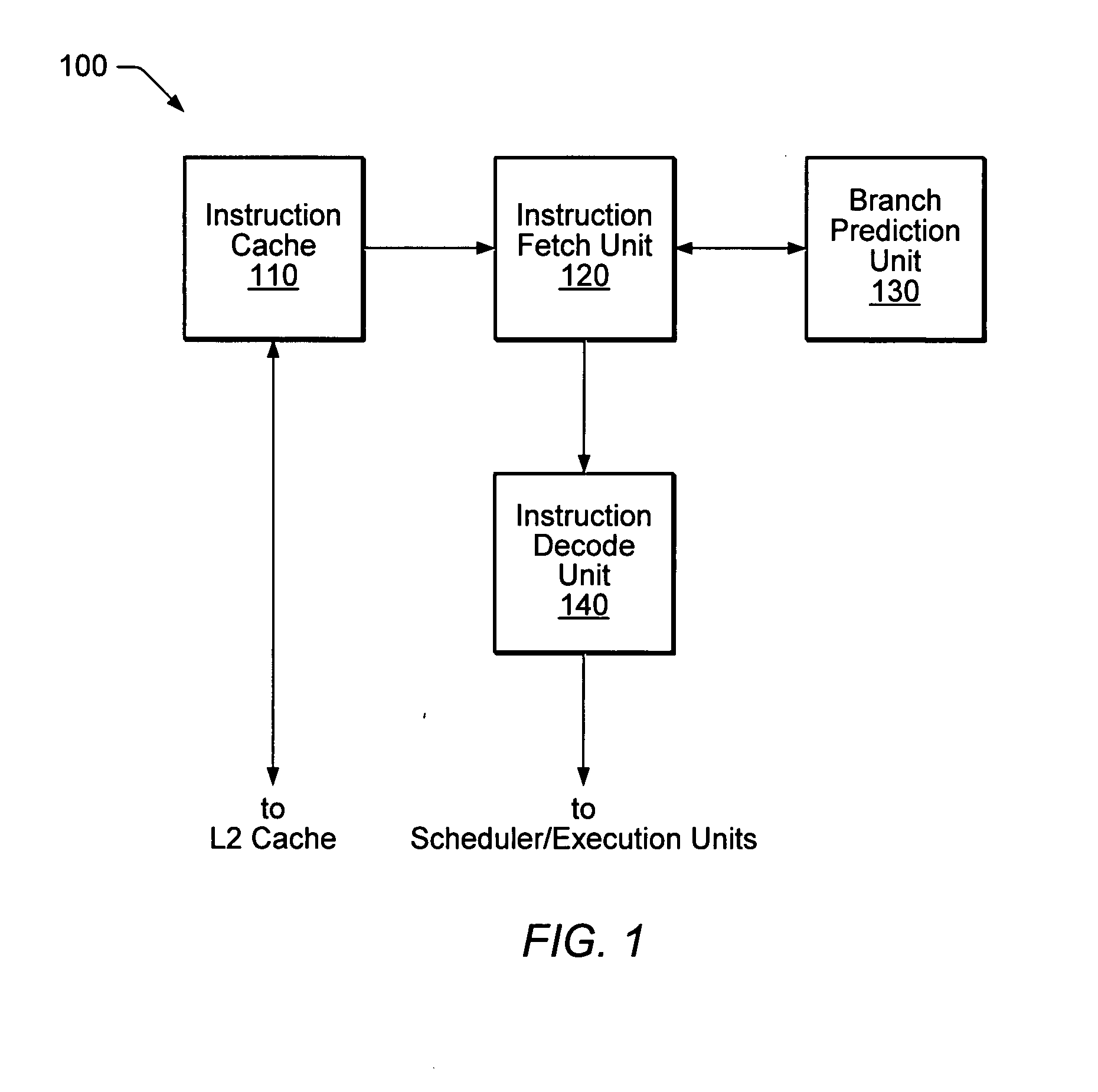
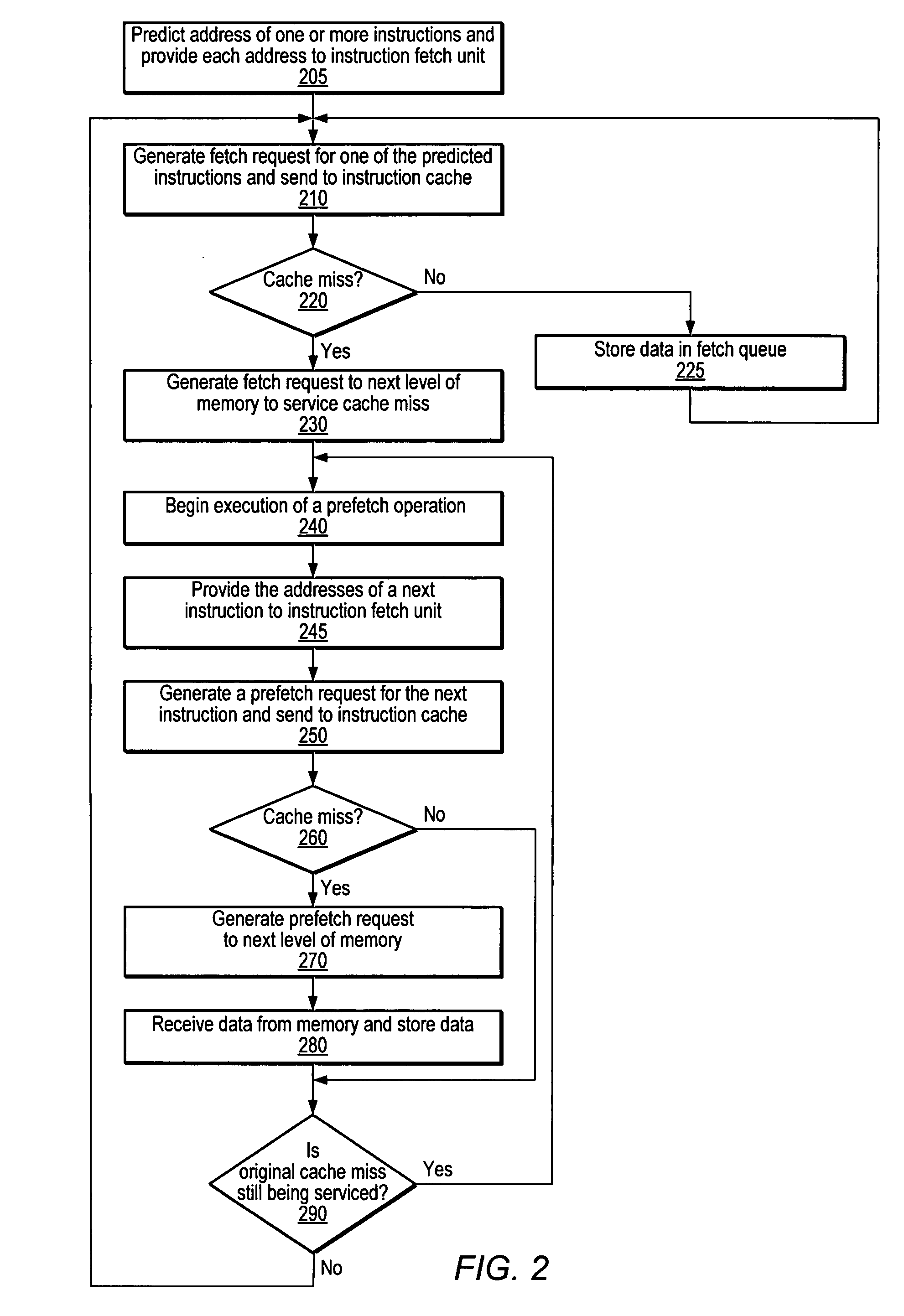
An apparatus for executing branch predictor directed prefetch operations. During operation, a branch prediction unit may provide an address of a first instruction to the fetch unit. The fetch unit may send a fetch request for the first instruction to the instruction cache to perform a fetch operation. In response to detecting a cache miss corresponding to the first instruction, the fetch unit may execute one or more prefetch operation while the cache miss corresponding to the first instruction is being serviced. The branch prediction unit may provide an address of a predicted next instruction in the instruction stream to the fetch unit. The fetch unit may send a prefetch request for the predicted next instruction to the instruction cache to execute the prefetch operation. The fetch unit may store prefetched instruction data obtained from a next level of memory in the instruction cache or in a prefetch buffer.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Branch prediction apparatus and method for low power consumption
InactiveUS20050066154A1Reduce power consumptionDigital computer detailsNext instruction address formationShift registerPrediction algorithms
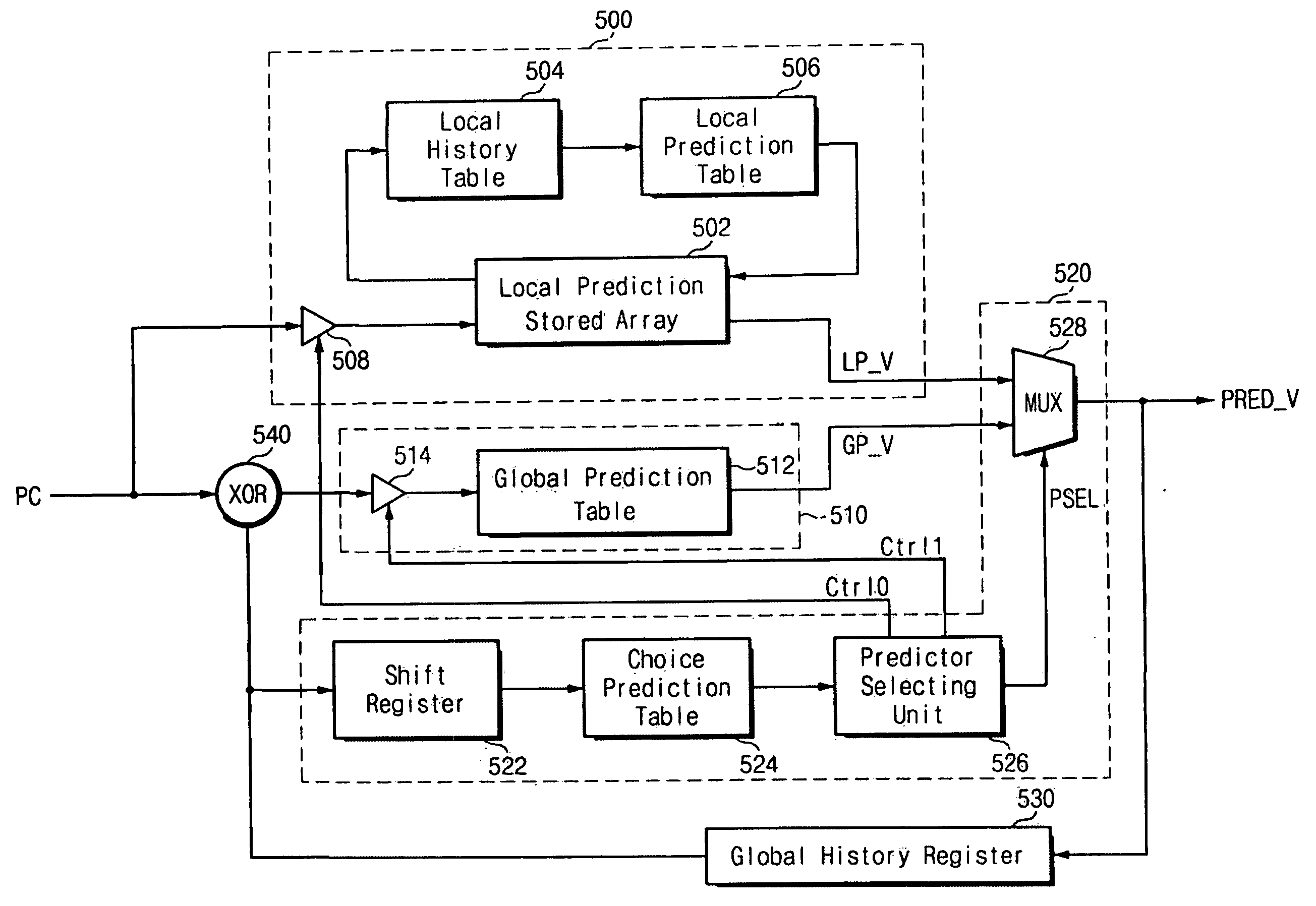
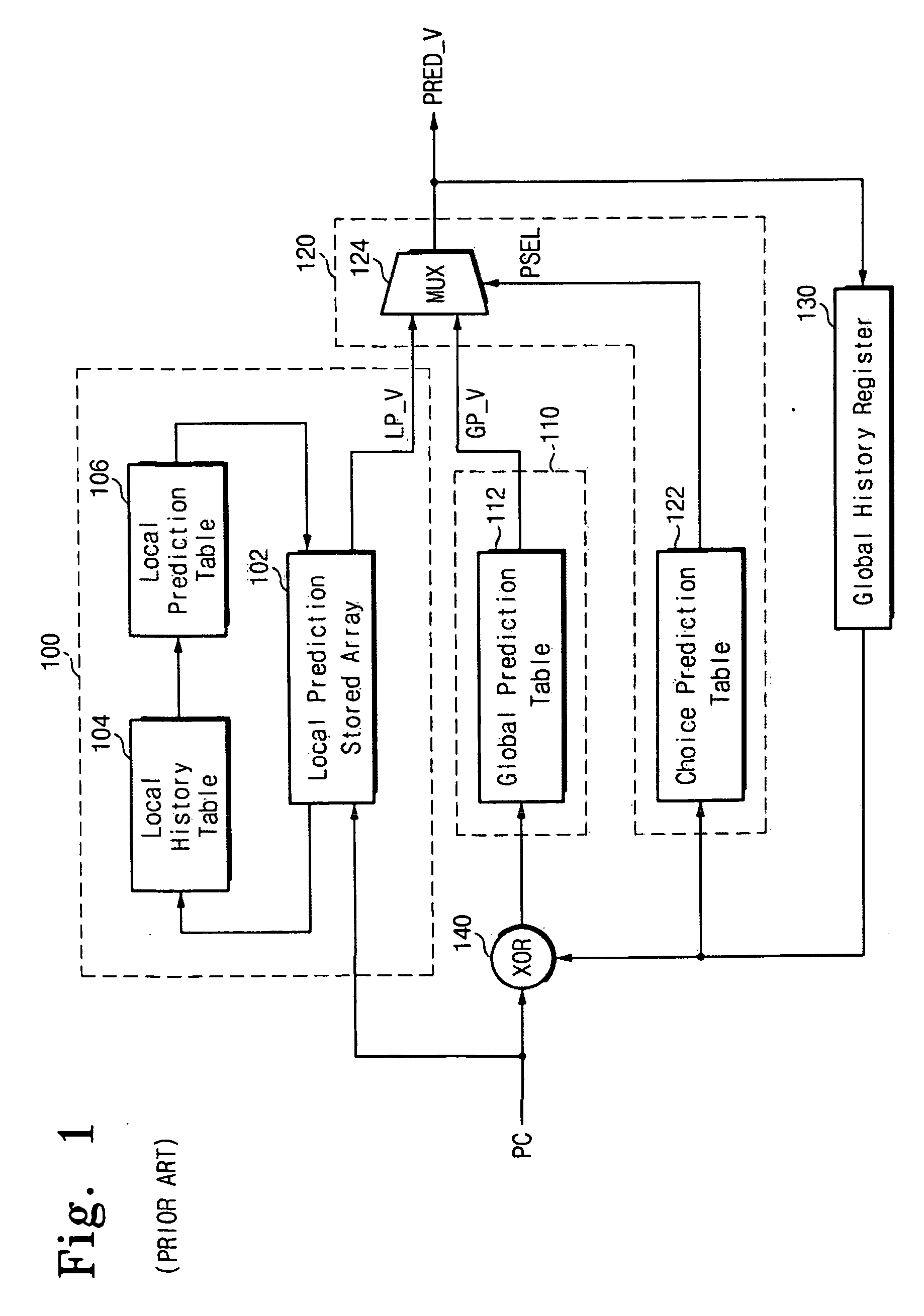
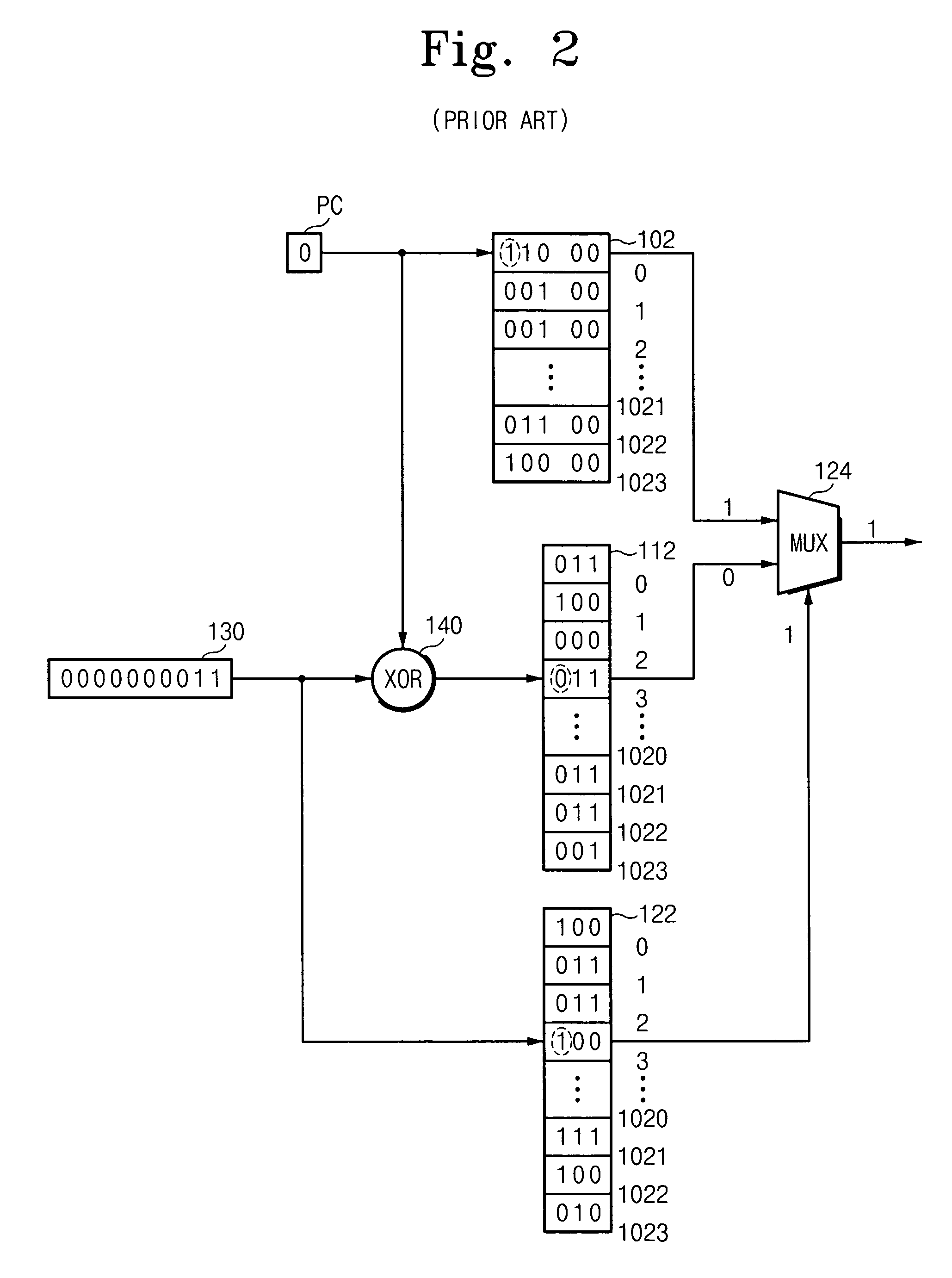
A branch prediction apparatus may include a first branch predictor for executing a first branch prediction algorithm and a second branch predictor for executing a second branch prediction algorithm. A choice predictor may generate a control signal for controlling operations of the first branch predictor and the second branch predictor. The choice predictor may also select and output a prediction result of the first branch predictor or the second branch predictor. The first branch predictor and the second branch predictor may respectively execute the prediction algorithms depending on the control signal. The choice predictor may include a shift register for shifting stored branch prediction values of the branch prediction apparatus to the left by one bit. A choice prediction table may be indexed by a value of the shift register to output a predictor selection value. A predictor selecting unit may generate the control signal and a selection signal for selecting an output of one of the first and the second branch predictors. An MUX circuit may output a branch prediction value of the first branch predictor or a branch prediction value of the second branch predictor depending on the selection signal. A computer-readable medium may include instructions causing a computer to perform the functions of selecting one branch predictor from among a plurality of branch predictors by using previous branch prediction results, and executing a branch prediction for a branch instruction by using the selected branch predictor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microprocessor and execution method thereof
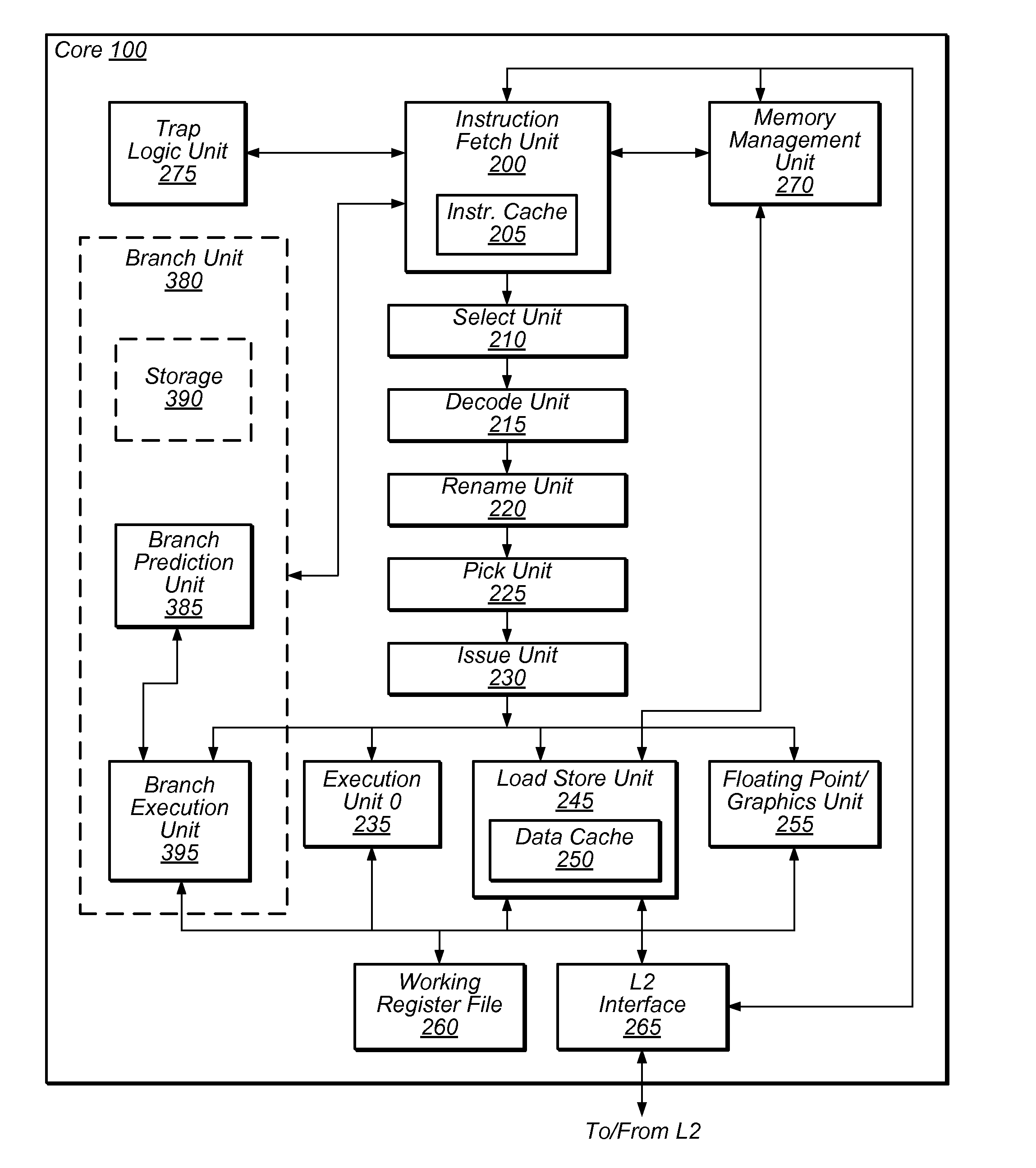
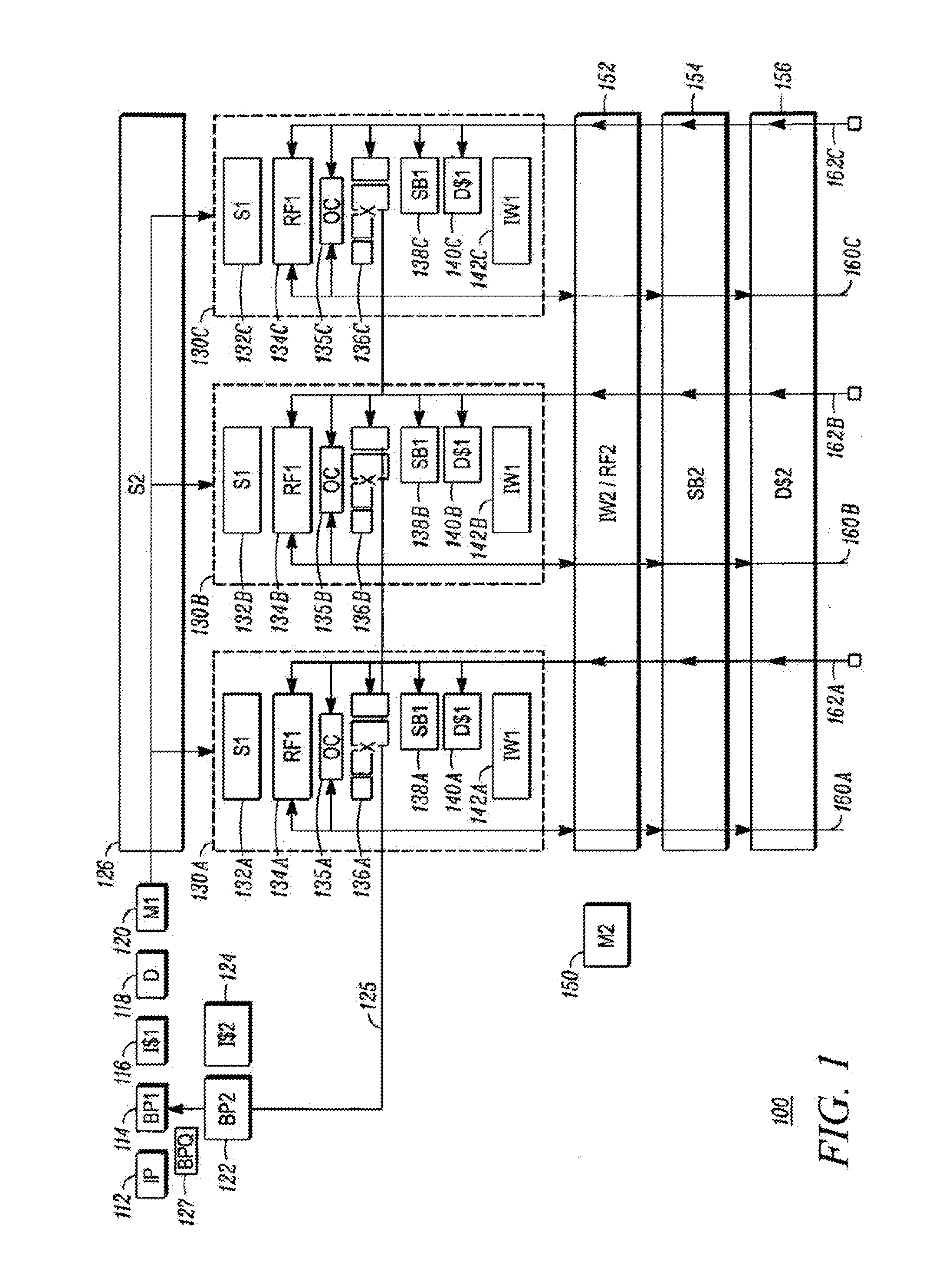
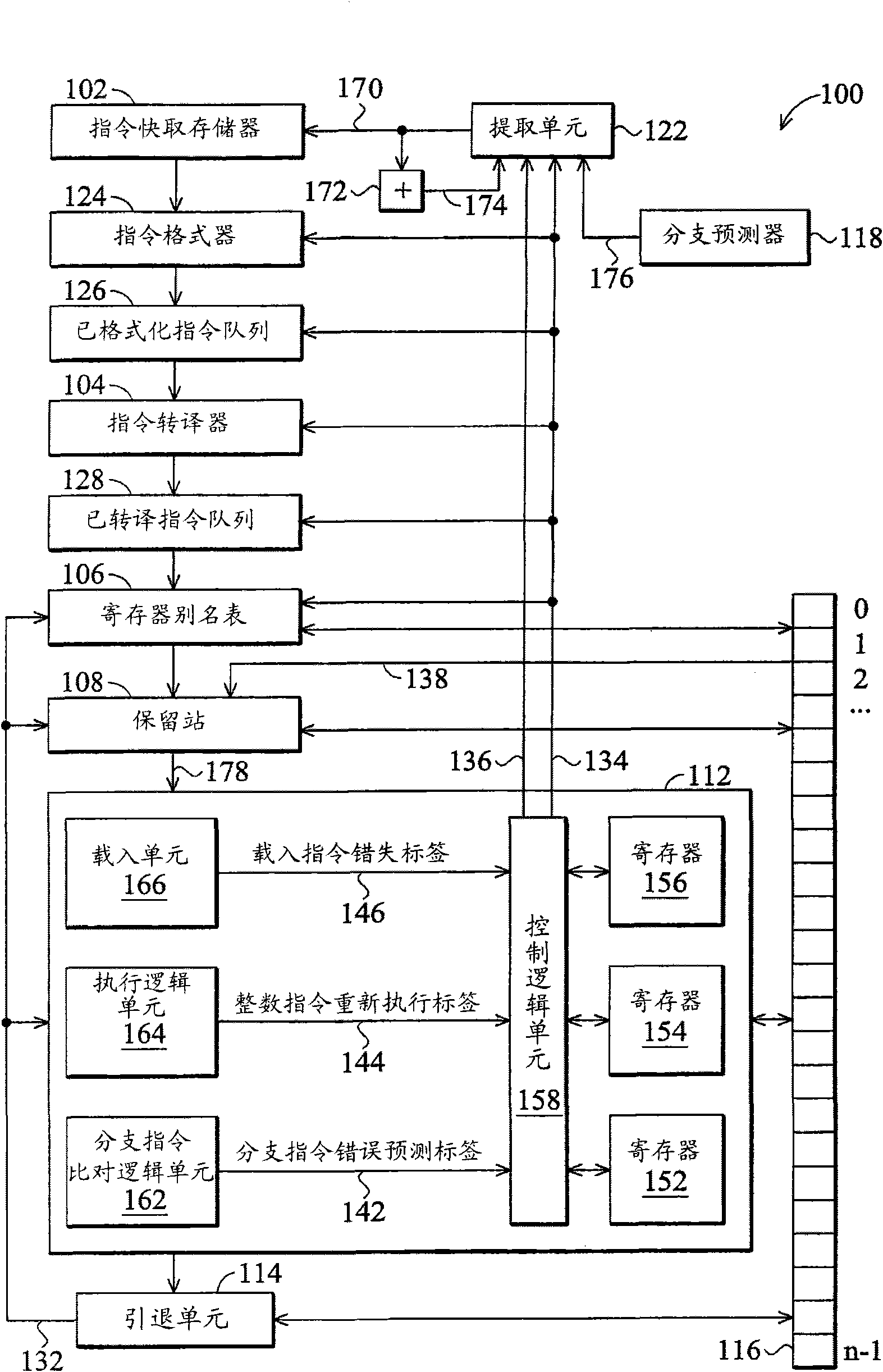
A microprocessor and an execution method thereof are used for pipelined out-of-order execution in-order retire. The microprocessor includes a branch predictor that predicts a target address of a branch instruction, a fetch unit that fetches instructions at the predicted target address, and an execution unit that: resolves a target address of the branch instruction and detects that the predicted and resolved target addresses are different; determines whether there is an unretired instruction that must be corrected and that is older in program order than the branch instruction, in response to detecting that the predicted and resolved target addresses are different; execute the branch instruction by flushing instructions fetched at the predicted target address and causing the fetch unit to fetch from the resolved target address, if there is not an unretired instruction that must be corrected and that is older in program order than the branch instruction; and otherwise, refrain from executing the branch instruction.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
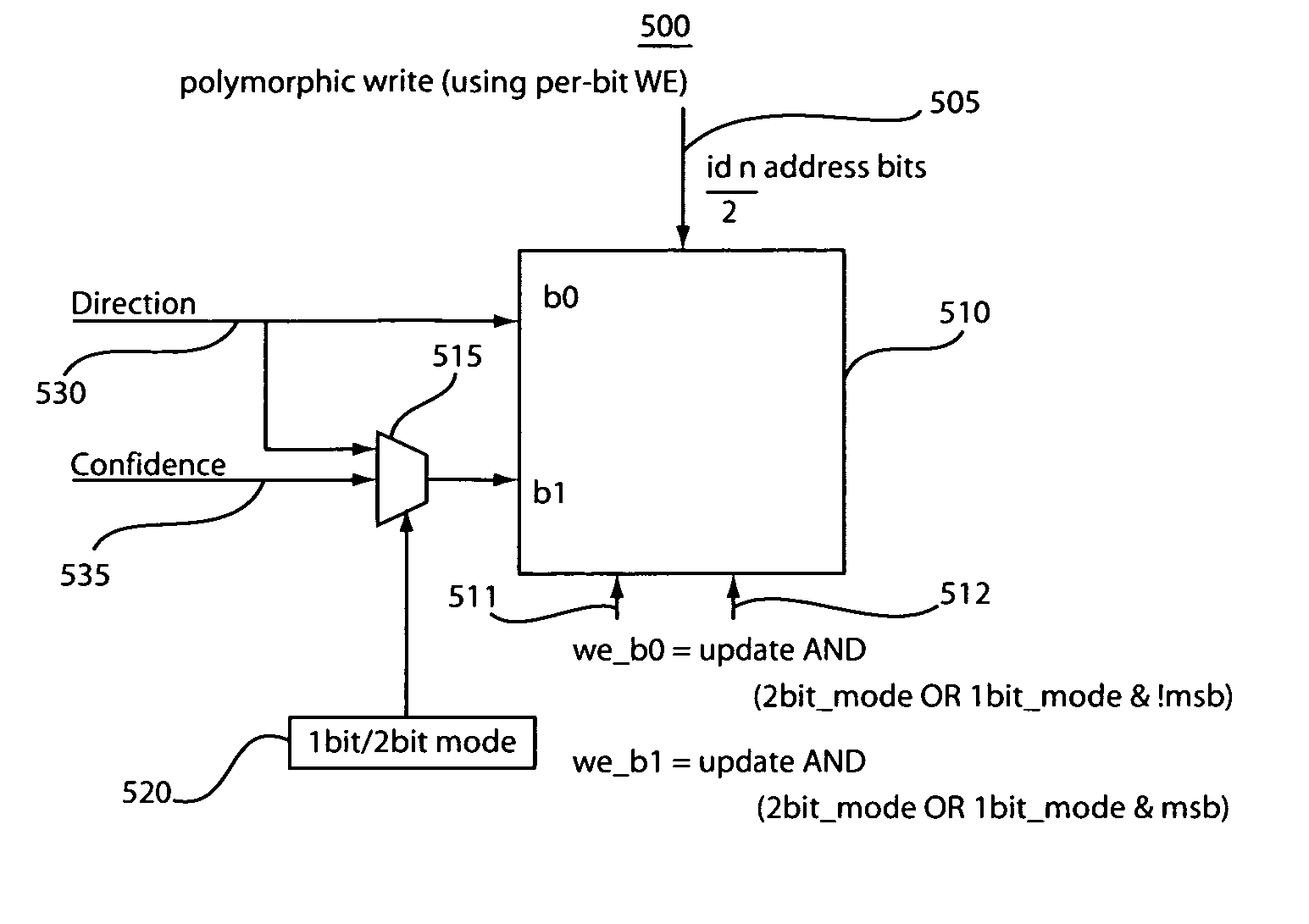
Polymorphic branch predictor and method with selectable mode of prediction
InactiveUS7523298B2Avoid poor resultsImprove performanceDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsBranch predictor
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
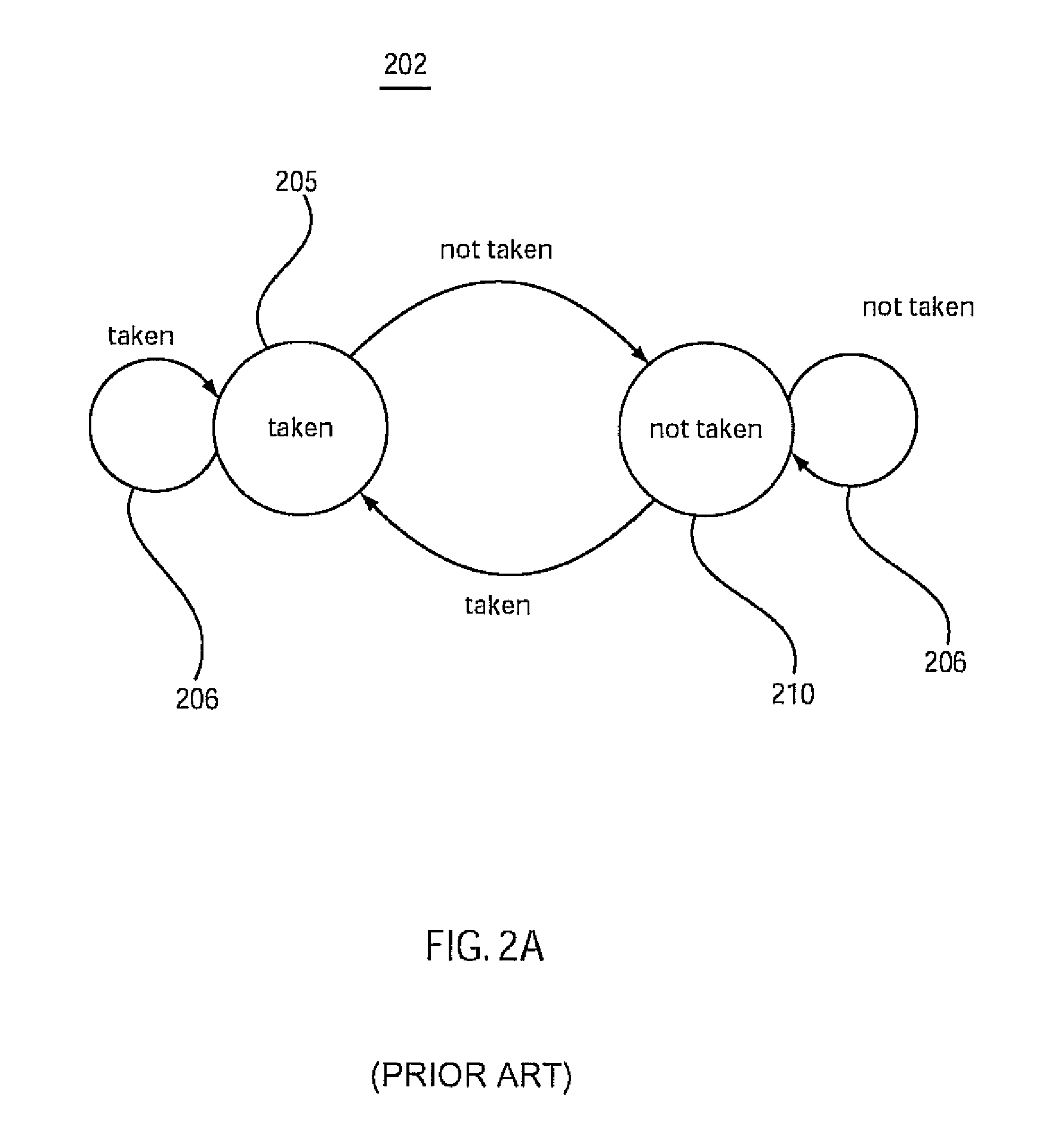
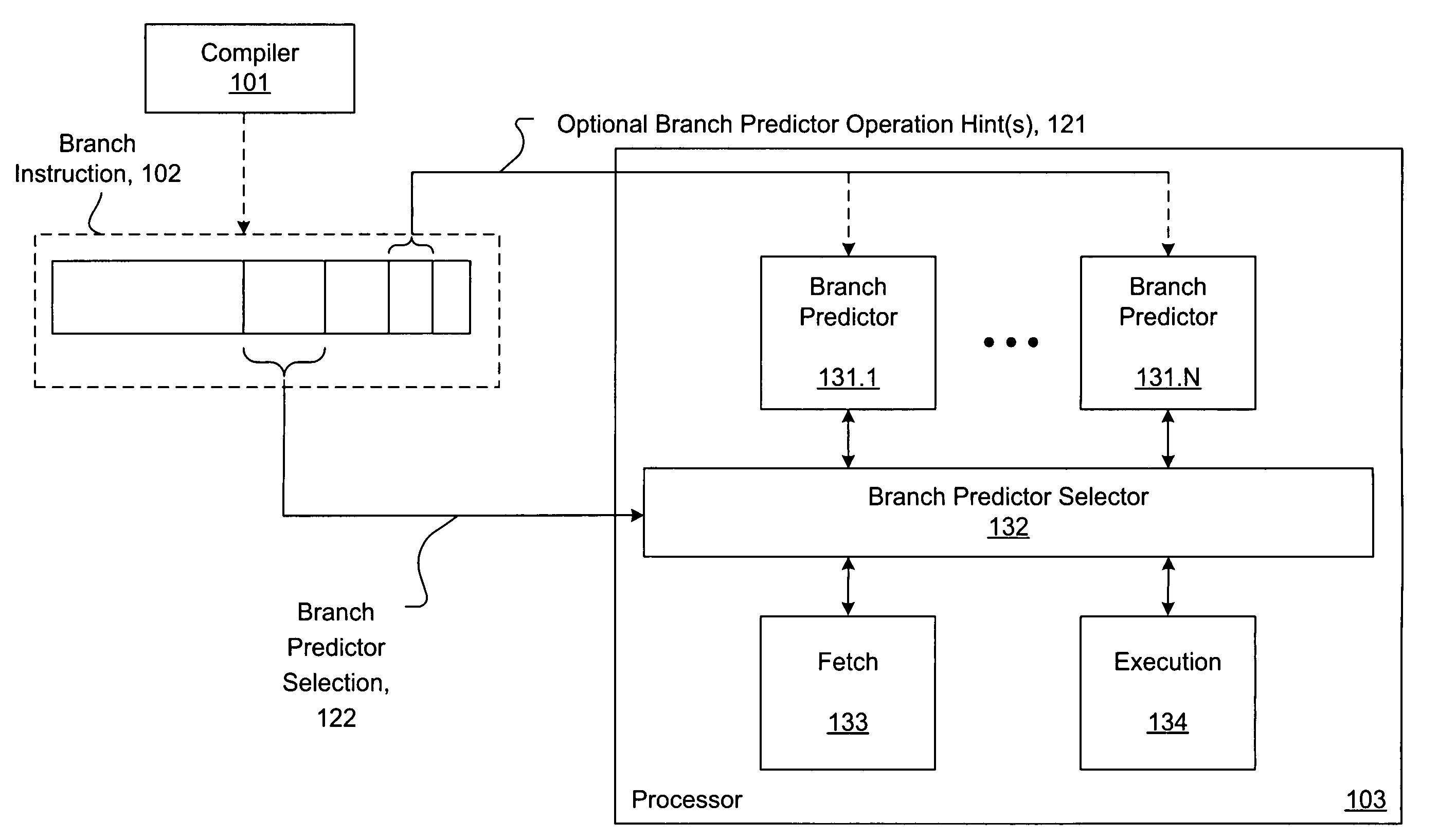
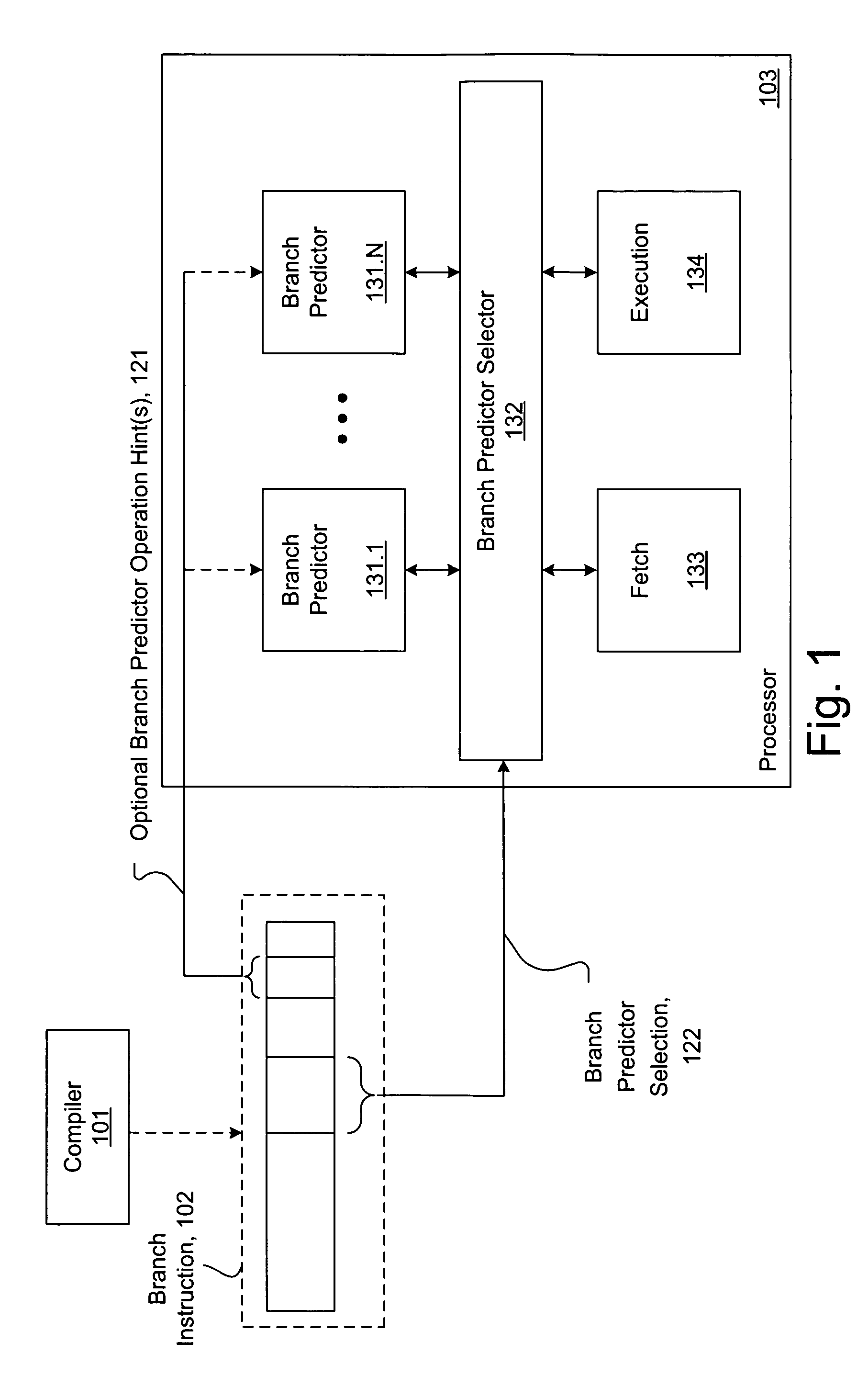
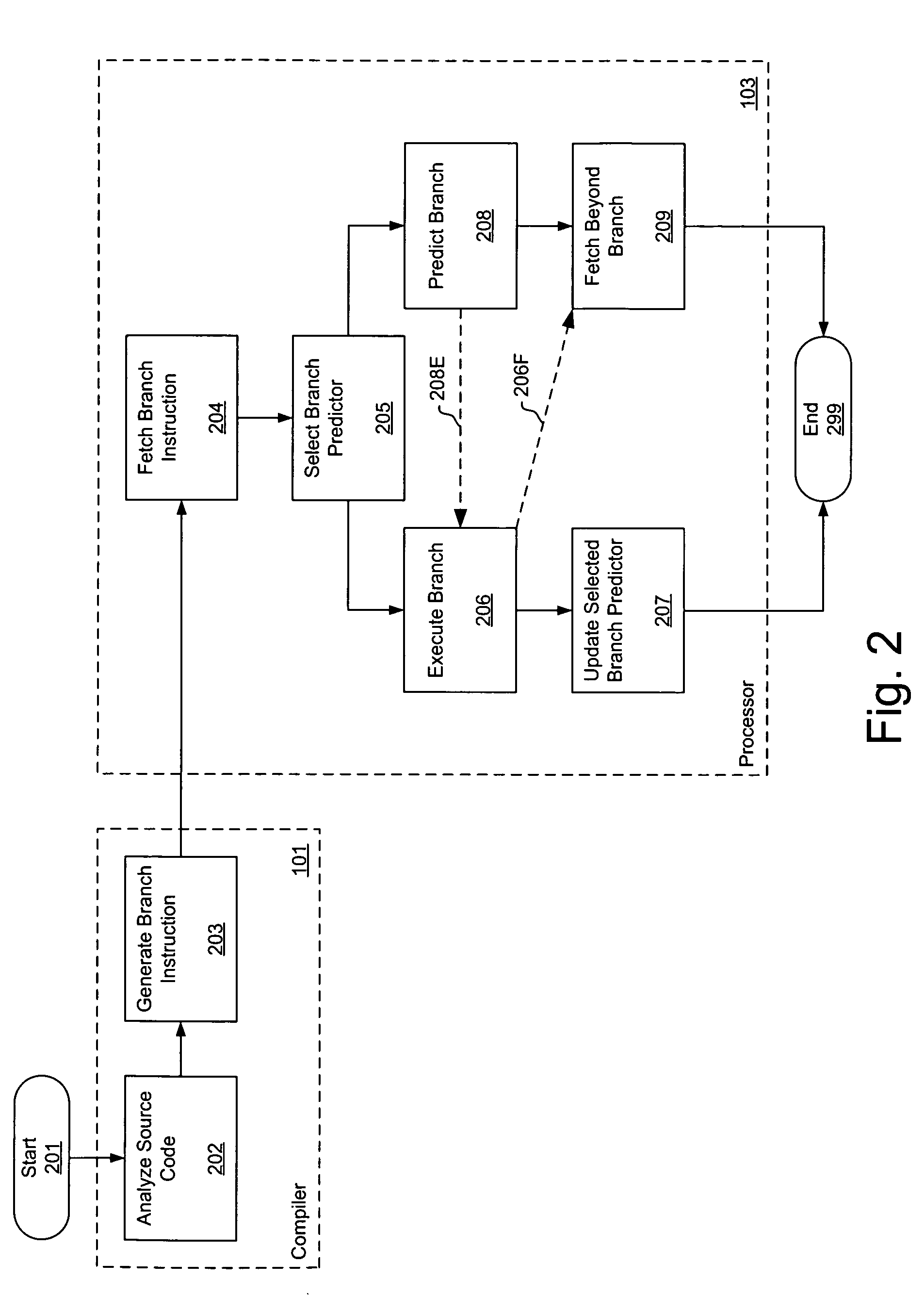
Software hint to specify the preferred branch prediction to use for a branch instruction
ActiveUS7673122B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsBranch predicationSoftware agent
Software hints embedded in branch instructions direct selection of one of a plurality of branch predictors to use when processing the branch instructions, leading to improved branch prediction (i.e. fewer mis-predictions) over conventional schemes. A software agent assembles branch instructions having associated respective branch predictor control fields compatible with a branch predictor selector and a plurality of branch predictors. Each branch predictor control field is used to perform branch predictor selection, branch predictor control, or both. Branch predictor selection enables selective branch prediction according to an appropriate one of the branch predictors as determined by the software agent by examining context surrounding the branch instruction. Branch predictor control enables control of operation of one or more of the branch predictors. For example, a history-based branch predictor may be instructed to provide branch prediction according to a history-depth specified by the branch predictor control.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
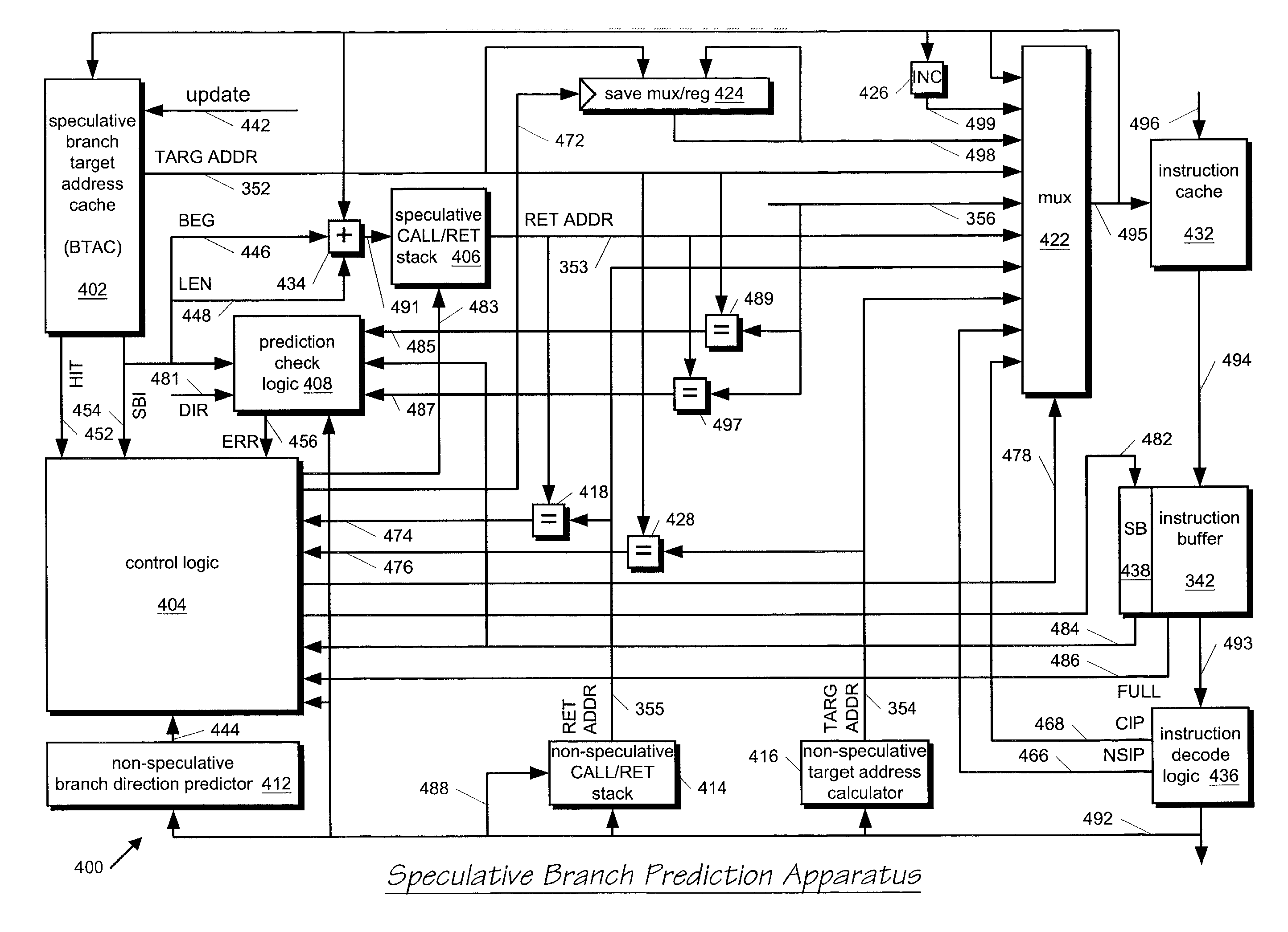
Speculative branch target address cache with selective override by secondary predictor based on branch instruction type
InactiveUS7165169B2Reduce negative impactAccurate predictionDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionBranch target address cacheProgram counter
A branch prediction apparatus having a primary predictor and a secondary predictor that selectively overrides the primary predictor based on the type of branch instruction decoded. A branch target address cache in the primary branch predictor speculatively predicts a branch target address and direction based on an instruction cache fetch address prior to decoding the instruction, and the processor branches to the speculative target address if the speculative direction is predicted taken. Later in the pipeline, decode logic decodes the instruction and determines the branch instruction type, such as whether the branch instruction is a conditional branch, a return instruction, a program counter-relative type branch, an indirect branch, etc. Depending upon the branch type, if the primary and secondary predictions do not match, the processor branches based on the secondary prediction to override the branch taken based on the primary prediction.
Owner:IP FIRST
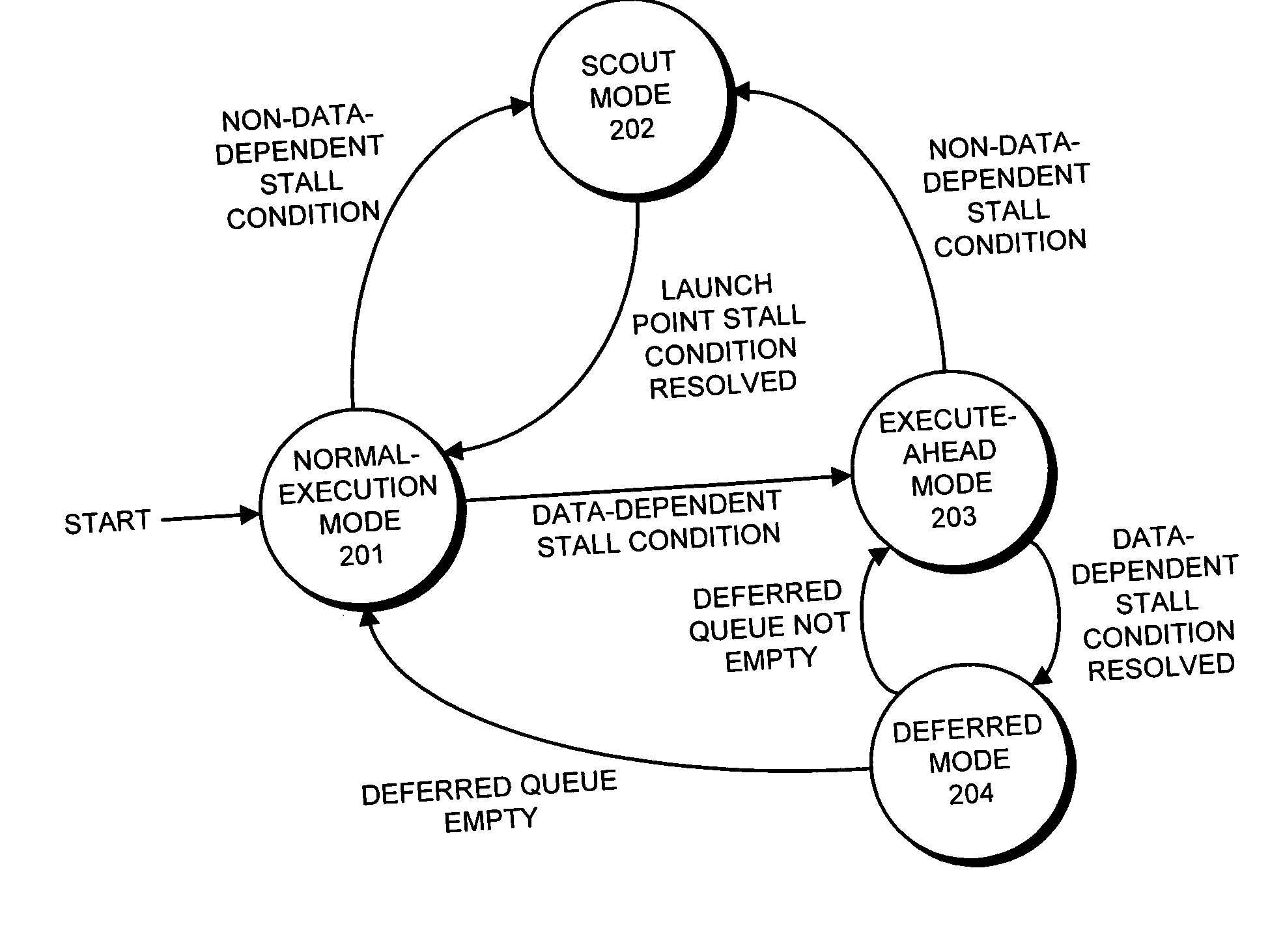
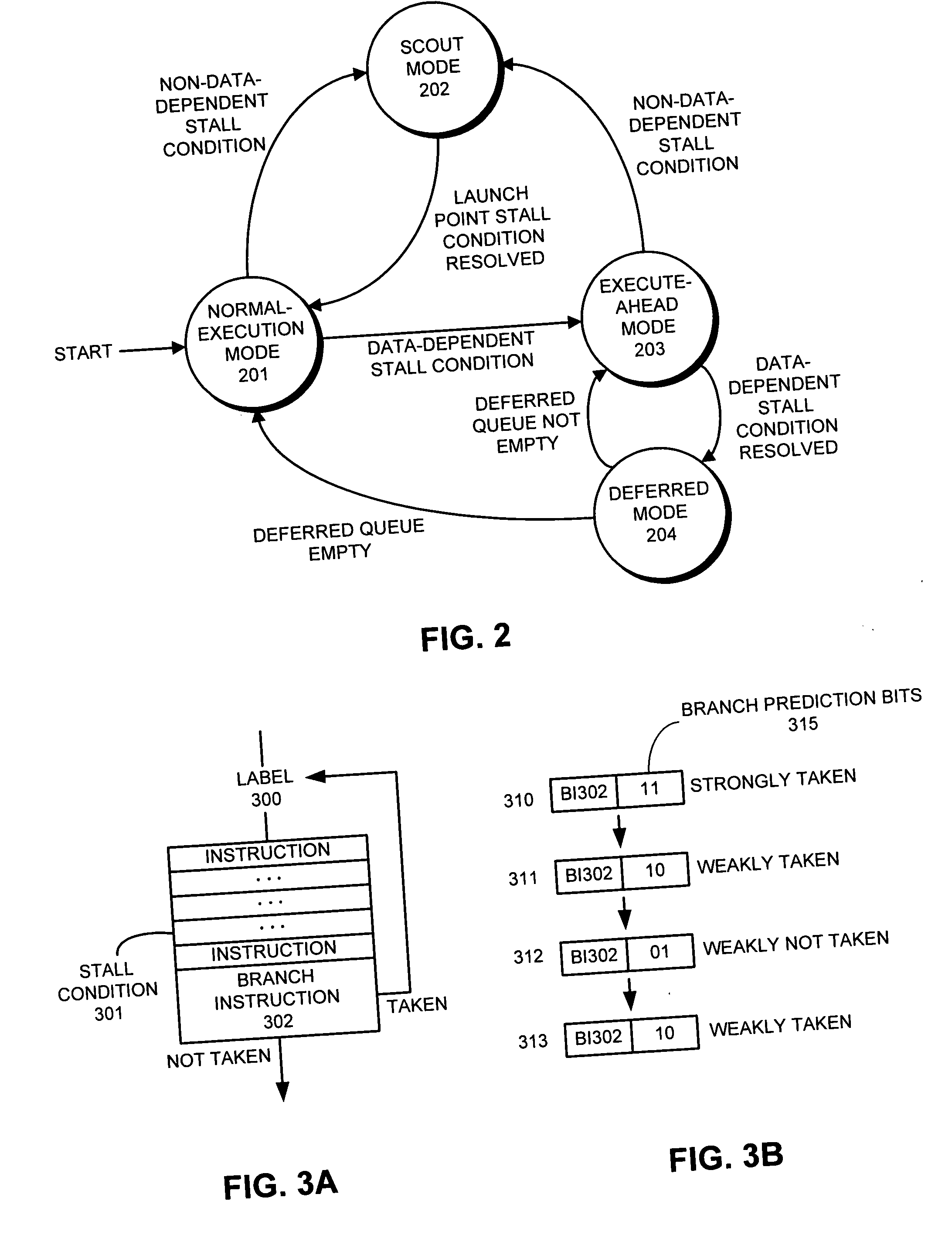
Branch prediction accuracy in a processor that supports speculative execution
InactiveUS20060168432A1Branch prediction accuracy can be increasedDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSpeculative executionProcedure sequence
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system which improves branch prediction accuracy in a processor that supports speculative-execution. During normal-execution mode, the system issues instructions in program order. Upon encountering a launch condition which causes a processor to enter a speculative-execution mode, the system performs a checkpoint and begins executing instructions in a speculative-execution mode. Upon encountering a branch instruction during speculative-execution mode, the system selects the subsequent instruction to be executed based on a current state of a branch predictor and does not update the current state of the branch predictor, thereby preventing the branch predictor from being incorrectly updated twice when re-executing the branch instruction after returning to normal-execution mode.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
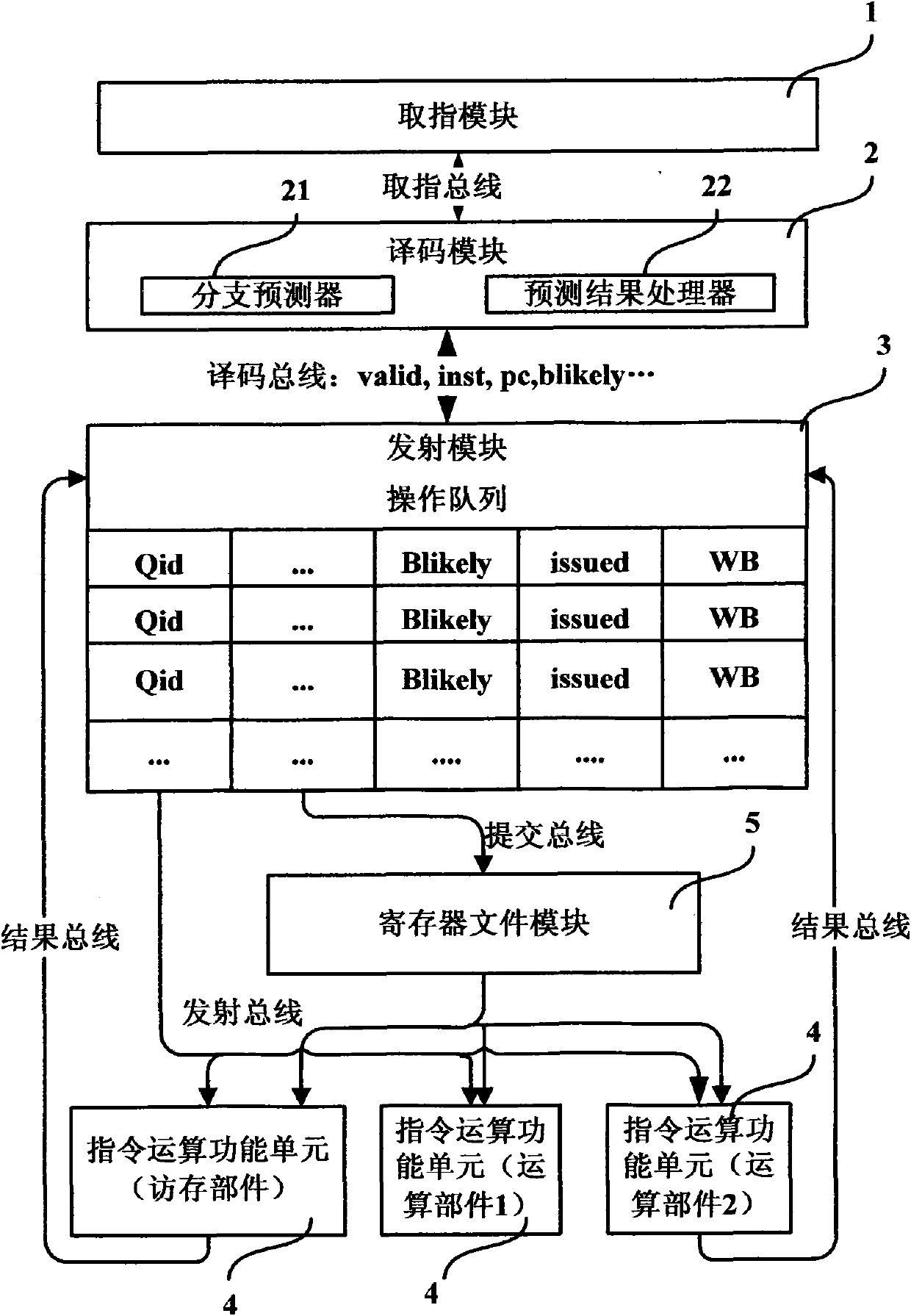
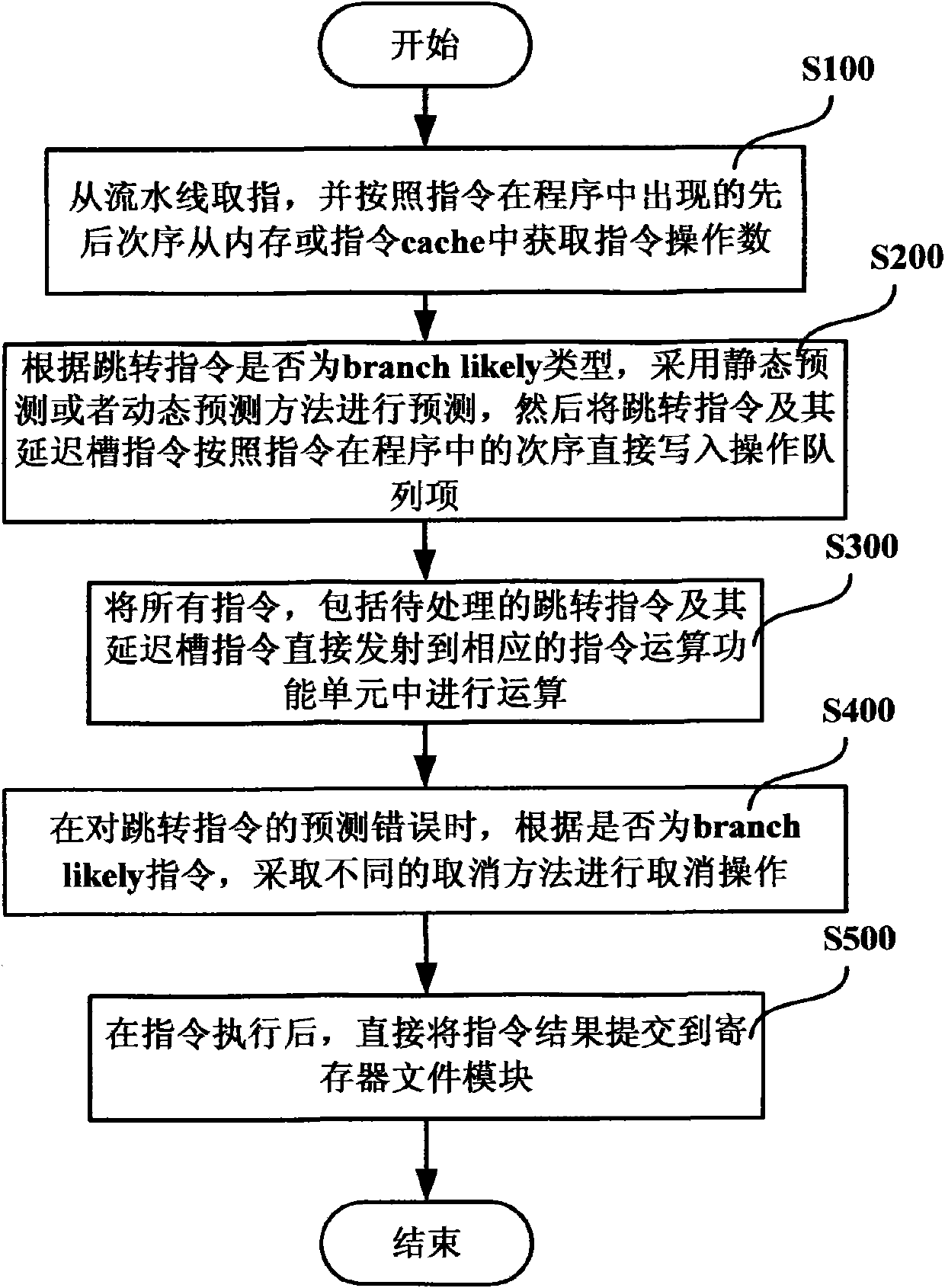
System and method for processing jump instruction of microprocessor in branch prediction way
ActiveCN101770358ASimple branch prediction methodImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionPrecodingProcessing Instruction
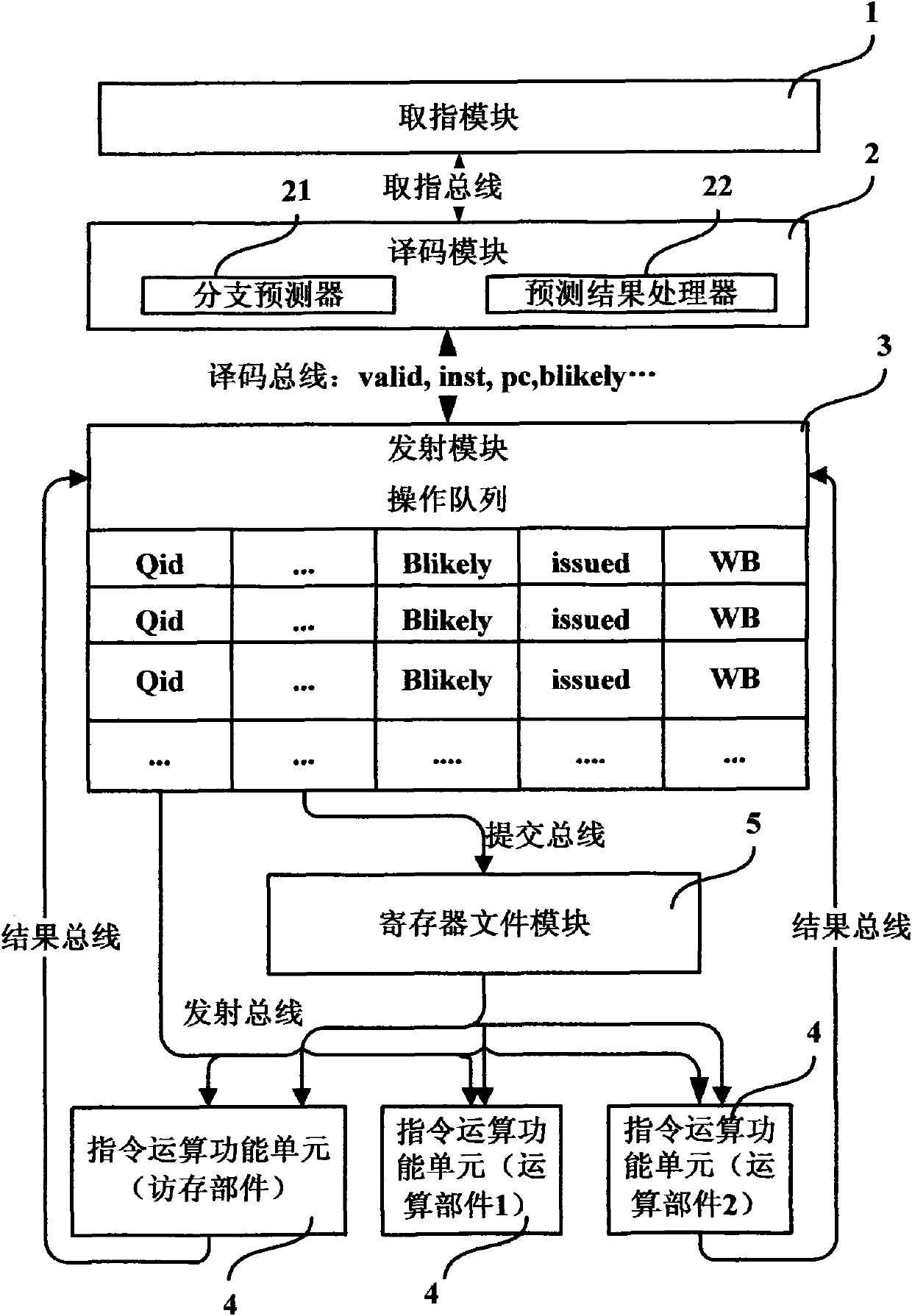
The invention discloses a system and a method for processing a jump instruction of a microprocessor in a branch prediction way. The system comprises a coding module and a transmission module, wherein the coding module comprises a branch predictor used for predicting by adopting a static prediction method when the jump instruction to be processed is in the jump execution type or adopting a dynamicprediction method when the jump instruction to be processed is not in the jump execution type after the coding module judges that an instruction to be processed is the jump instruction and judges thetype of the jump instruction through precoding, and directly writing the jump instruction to be processed and a delay slot instruction thereof in an operational queue in a sequence of the instructions in a program; and the transmission module comprises a prediction result processor used for canceling the instruction executed by error and continue fetching in a correct jump direction when the branch predictor predicts the jump instruction by error after the jump instruction is executed and written back to the transmission module. The system cancels operation by adopting different cancellation methods on the basis that whether the instruction is the jump execution instruction or not when the instruction is cancelled.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
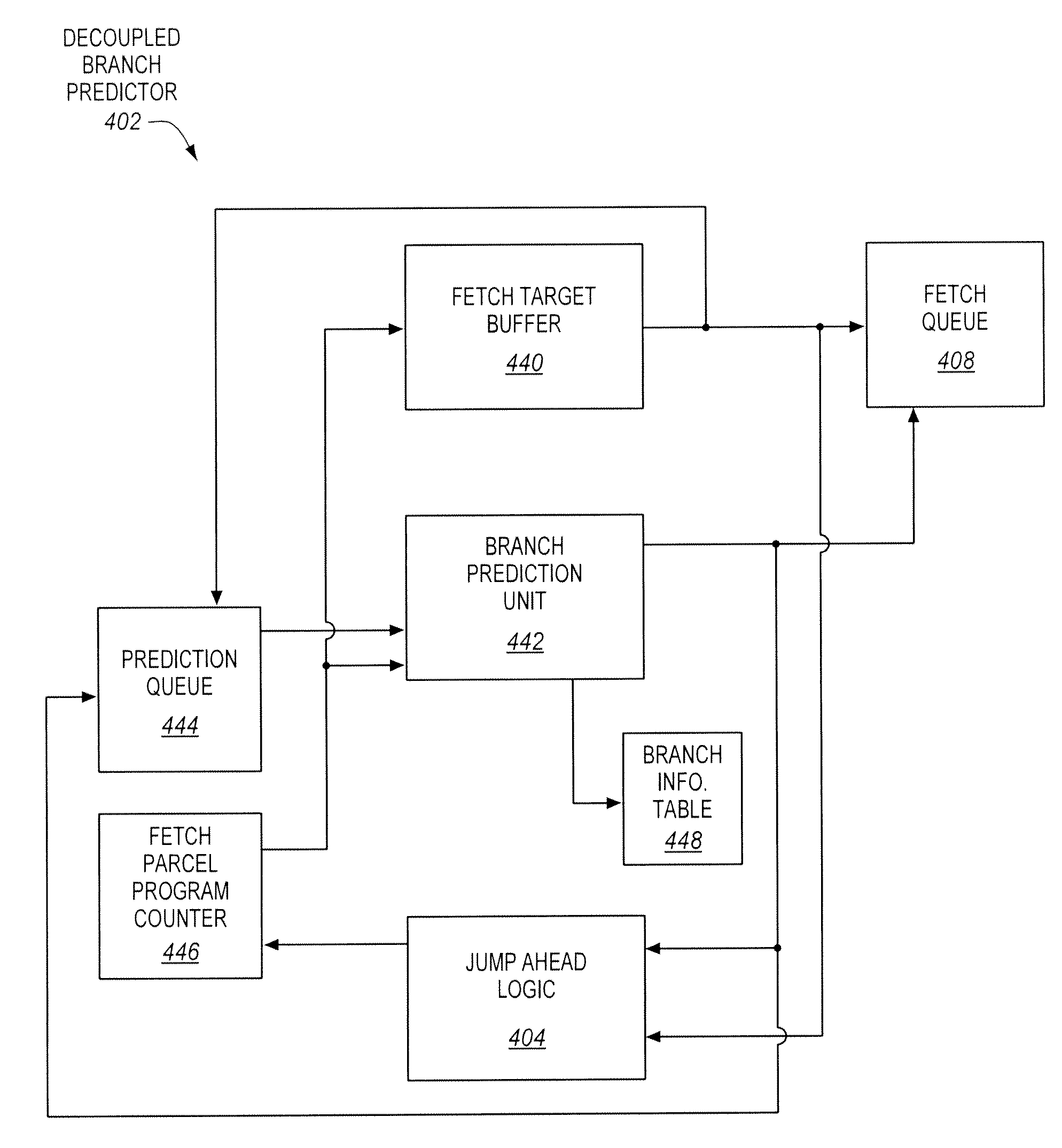
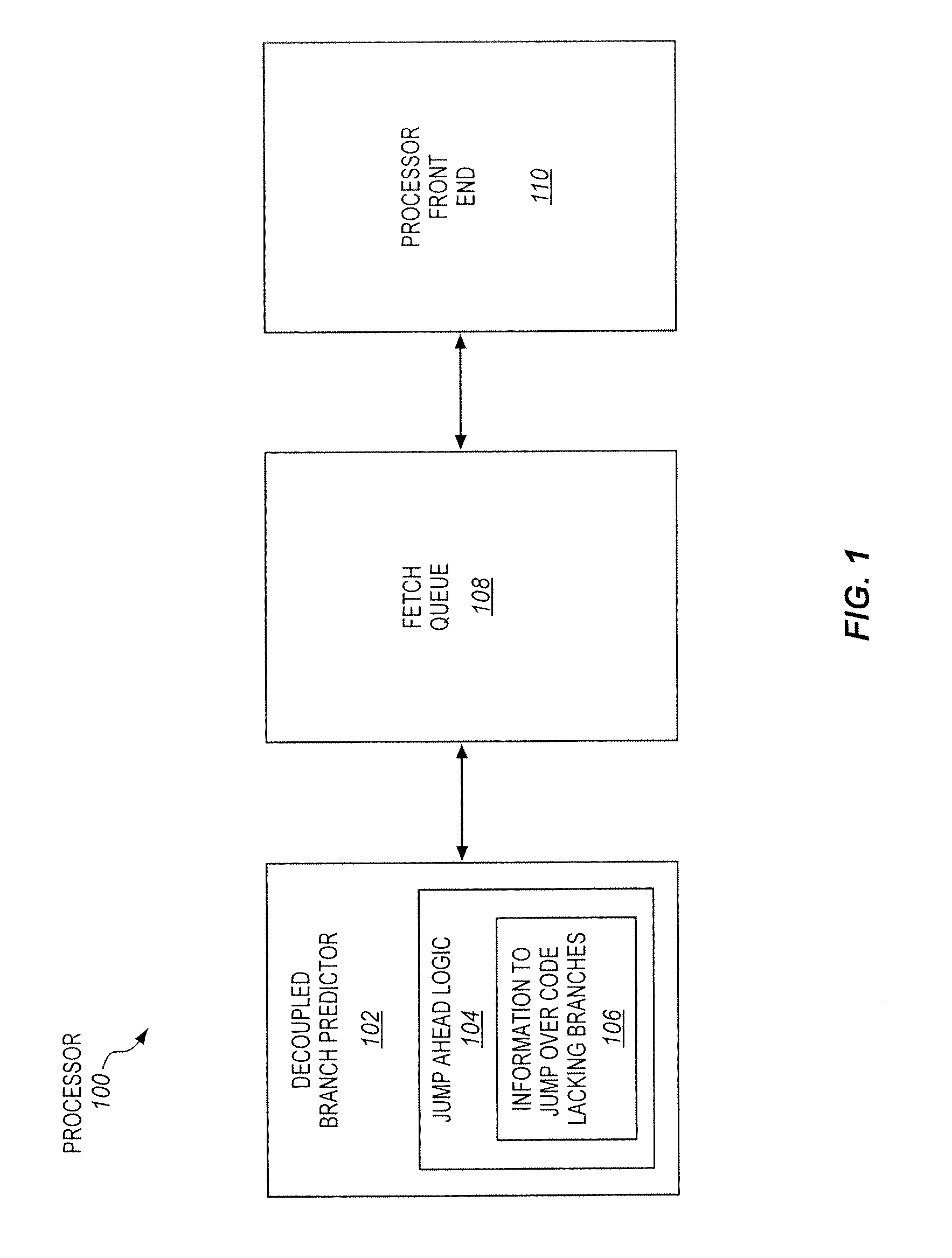
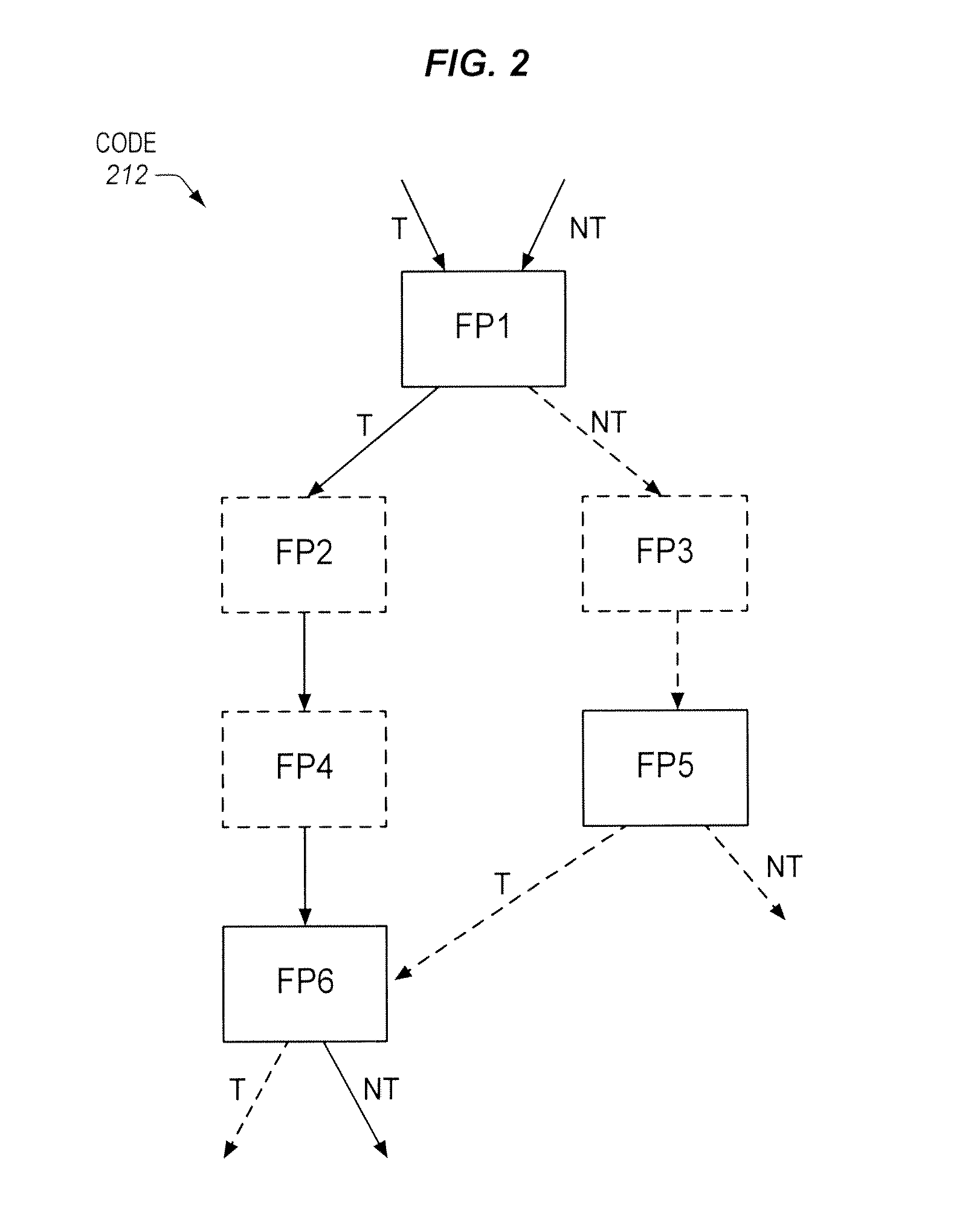
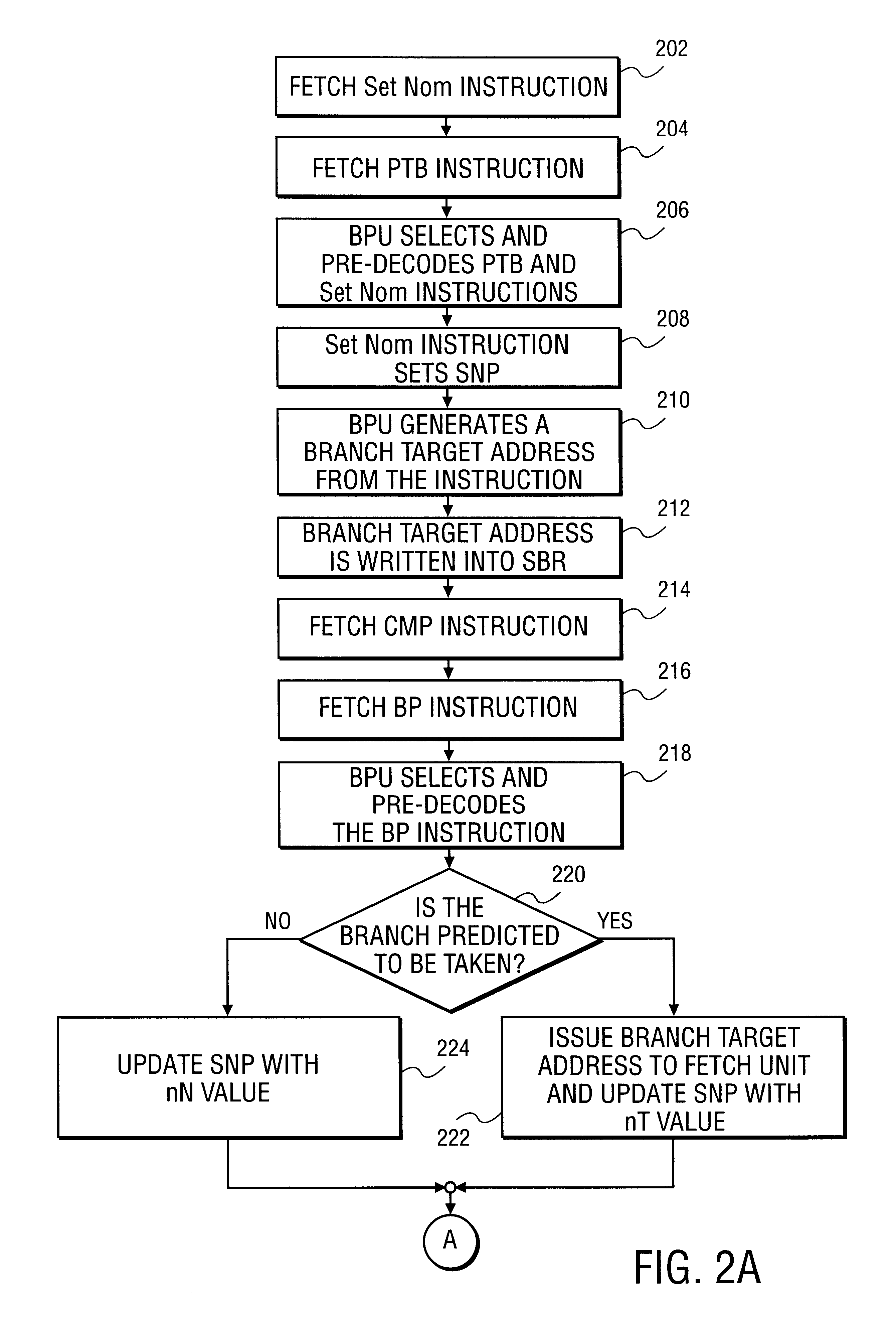
Branch Predictor with Jump Ahead Logic to Jump Over Portions of Program Code Lacking Branches
A processor of an aspect includes front end logic to process parcels of program code. Each of the parcels has multiple instructions. A branch predictor of the processor is coupled with the front end logic. The branch predictor is to predict directions of branch instructions of the program code. The processor includes jump ahead logic to cause the branch predictor to jump over at least one parcel of the program code that does not have a branch instruction between parcels of the program code that each have at least one branch instruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Branch predictor and method used for operating same
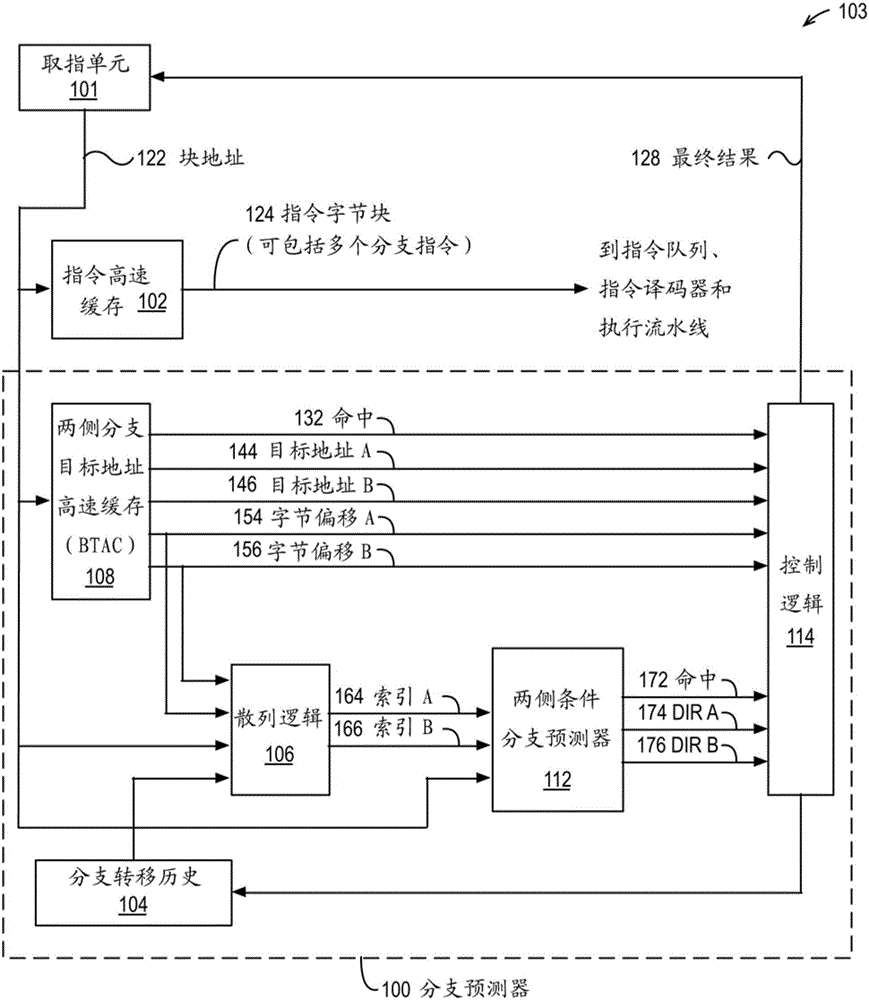
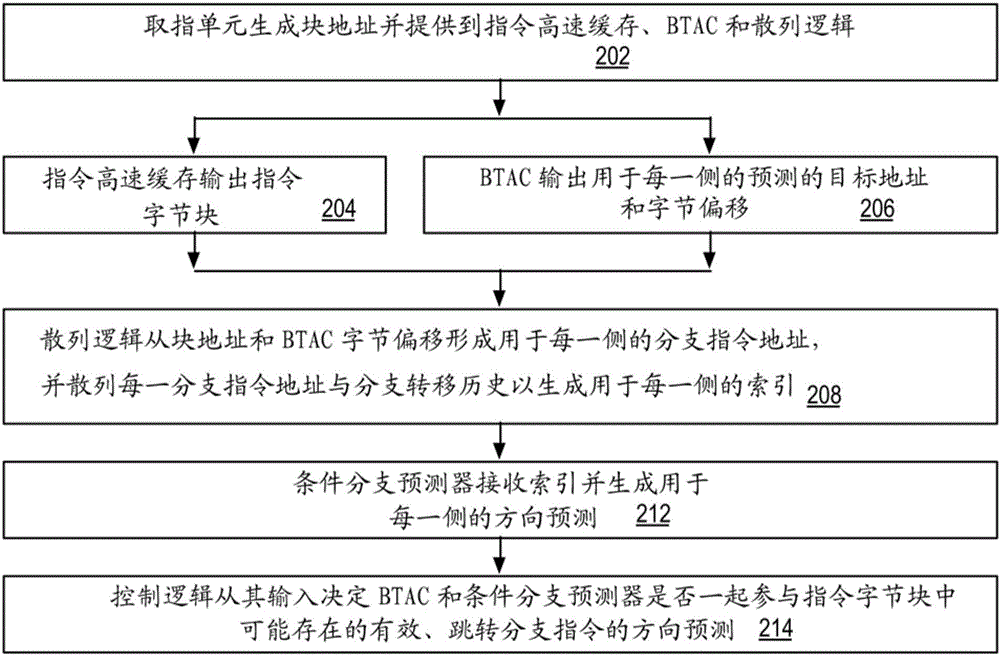
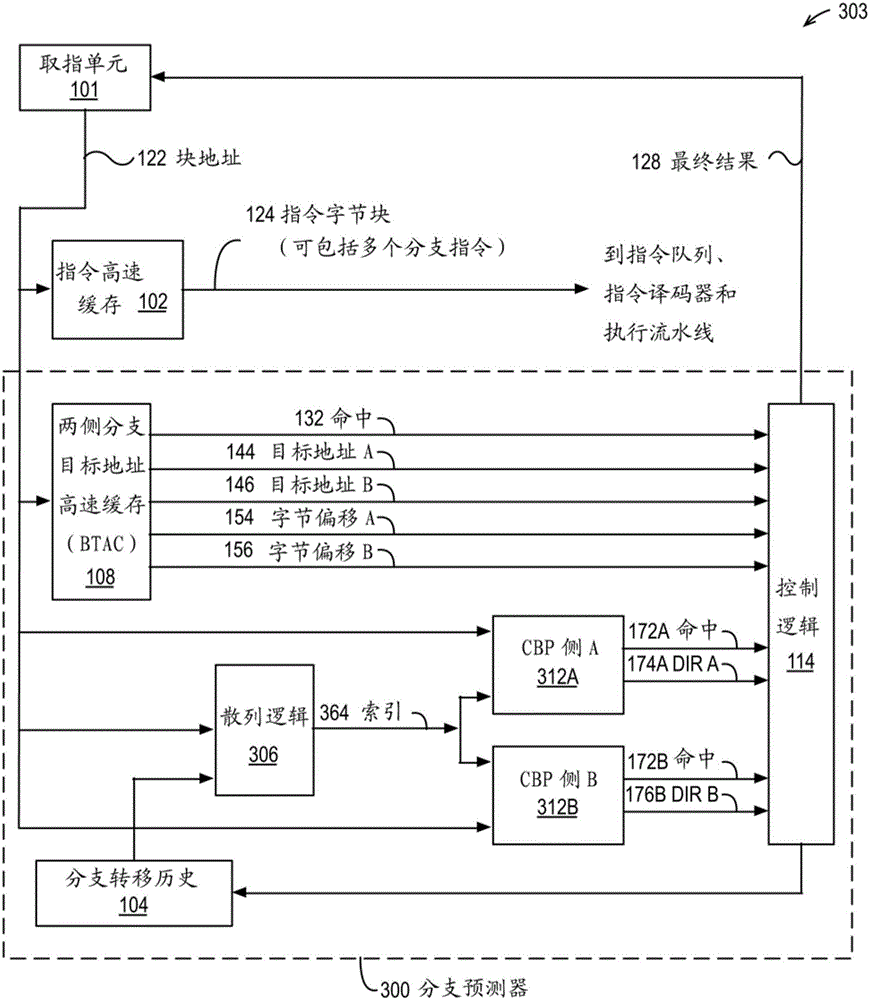
ActiveCN106406823AMemory architecture accessing/allocationConcurrent instruction executionBranch target address cacheByte
The invention provides a branch predictor and a method for operating the same. The branch predictor contains a block address capable of being used for accessing an instruction byte block of an instruction cache and a first / second byte offset in the instruction byte block. Hash logic performs hash operation on a branch pattern and a first / second address formed by the block address and the first / second byte offset to generate a first / second index. A condition branch predictor receives the first / second index and provides a first / second direction prediction of a first / second condition branch instruction in the instruction byte block in response to the first / second index. In an embodiment, a branch target address cache (BTAC) provides the byte offset, and the first / second direction prediction is statically associated with a first / second target address also provided by the BTAC. Instead, the byte offset is a predetermined value, and the first / second direction prediction is dynamically associated with the first / second target address based on the relative size of the byte offset provided by the BTAC.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
System and method for multi-mode branch predictor
The invention relates to a system and a method for a multi-mode branch predictor, which are used for predicting the executions of branches capable of executing commands of a computer. In the embodiment, the branch predictor can comprises a program counting register used for storing a program counting value and a branch history register used for storing a branch history value. In addition, the branch predictor can also comprises a prediction Hash table with a plurality of predicted values, and each predicted value uniquely corresponds to a plurality of storage positions. By utilizing the assemblies, the branch predictor can generate a first predicted value corresponding to the program counting value and a second predicted value corresponding to the logical combination of the program counting value and the branch history value. By utilizing the two predicted values obtained from two different prediction modes, the branch predictor can be better suitable for generating an integral predicted value based on the first predicted value and the second predicted value, and the integral predicted value is more exact than a single predicted value based on a single prediction mode.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS BEIJING R& D
Delaying Branch Prediction Updates Until After a Transaction is Completed
ActiveUS20150347134A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsTransactional memoryBranch predictor
In a branch predictor in a processor capable of executing transactional memory transactions, the branch predictor for speculatively prediction outcome of branch instructions, such as taken / not-taken, target address and target instruction. Branch prediction information is buffered during a transaction, and is only loaded into the branch predictor when the transaction is completed, but discarded if the transaction aborts.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Branch prediction combining static and dynamic prediction techniques
InactiveUS7404070B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsComputerized systemMotion estimation
A computer system comprises a processor that comprises a hardware branch predictor and software instructions executed by the processor. The software instructions comprise conditional branch instructions and separate static branch prediction instructions. The static branch prediction instructions comprise a plurality of groups of static branch prediction bits, each group being configurable to provide prediction information for a separate conditional branch instruction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Instruction loop buffer with tiered power savings
ActiveUS20150293577A1Good power savingSave powerVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingBranch predictorPower saving
Techniques are disclosed relating to power reduction during execution of instruction loops. Multiple different power saving modes may be used by a processor, such as a first power saving mode after only a few loop iterations (e.g., 2-3) and a second, deeper power saving mode after a greater number of loop iterations. The first power saving mode may include keeping a branch predictor and / or other structures active, but the second power saving mode may include reducing power to the branch predictor and / or other structures. An observation mode and an instruction capture mode may also be used by a processor prior to entering a power saving mode for loop execution. Power saving modes may also be achieved during execution of complex loops having multiple backward branches (e.g., nested loops).
Owner:APPLE INC
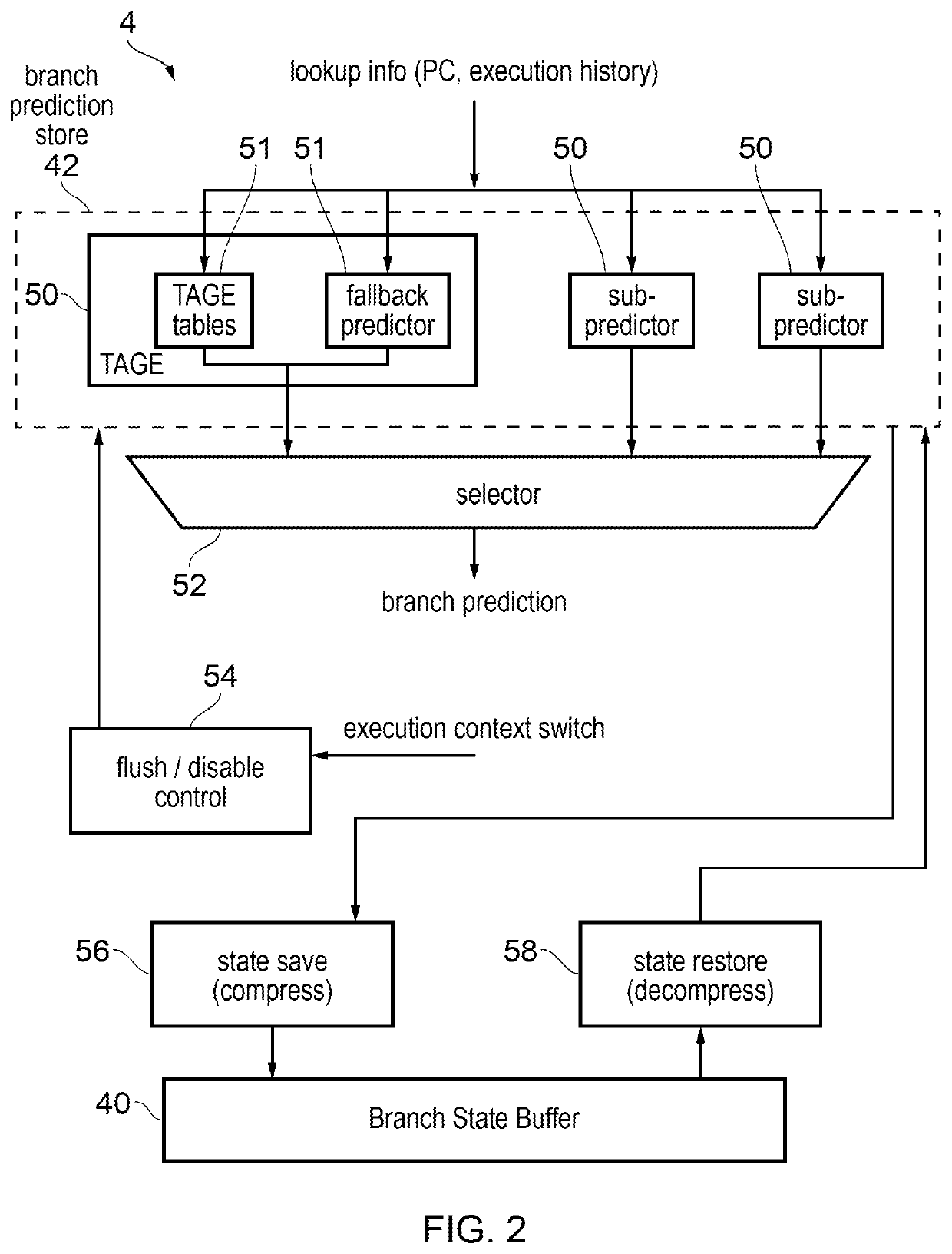
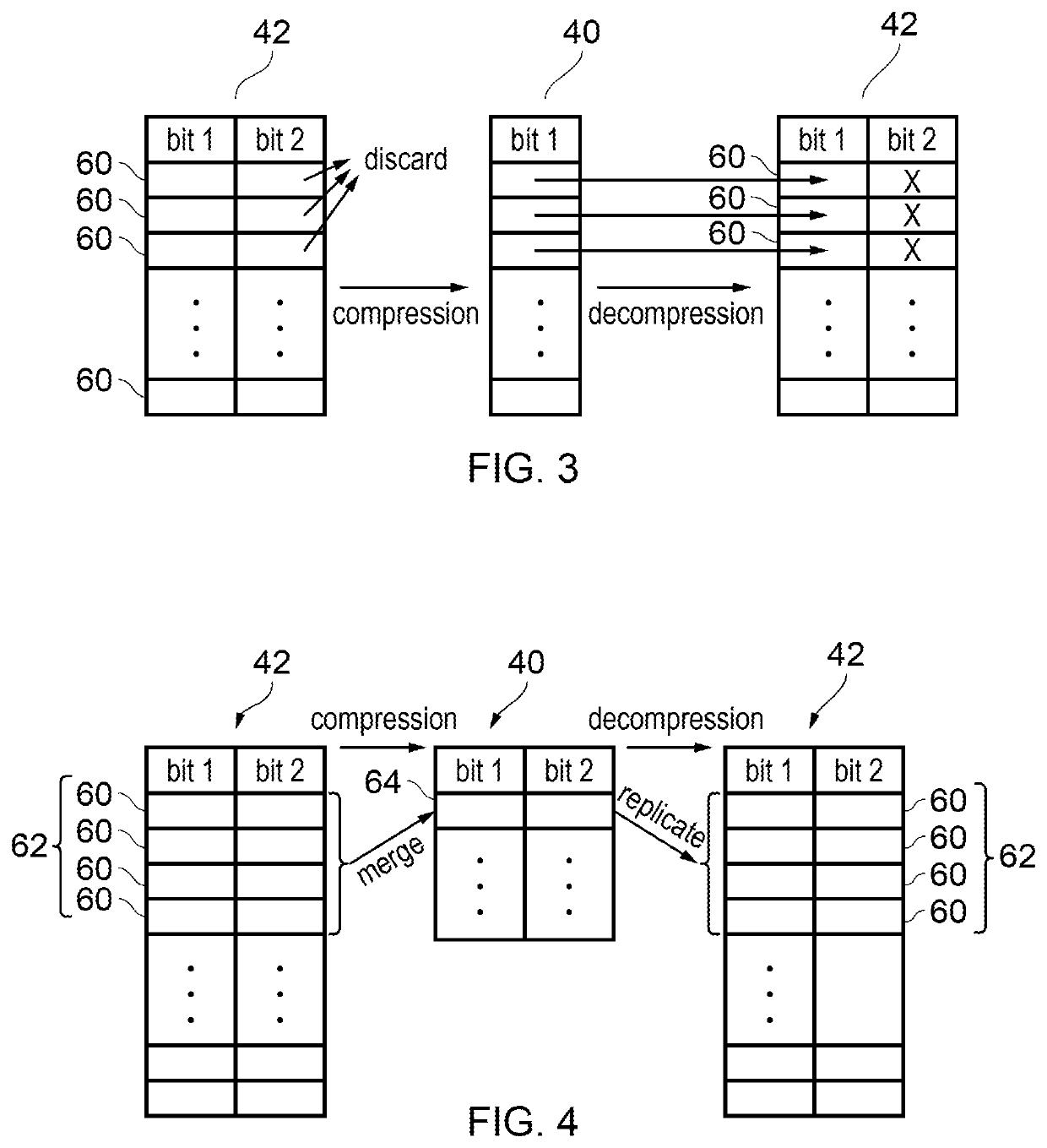
Tage branch predictor with perceptron predictor as fallback predictor
ActiveUS20190361707A1Instruction analysisConcurrent instruction executionTheoretical computer scienceContext switch
A TAGE branch predictor has, as its fallback predictor, a perceptron predictor. This provides a branch predictor which reduces the penalty of context switches and branch prediction state flushes.
Owner:ARM LTD
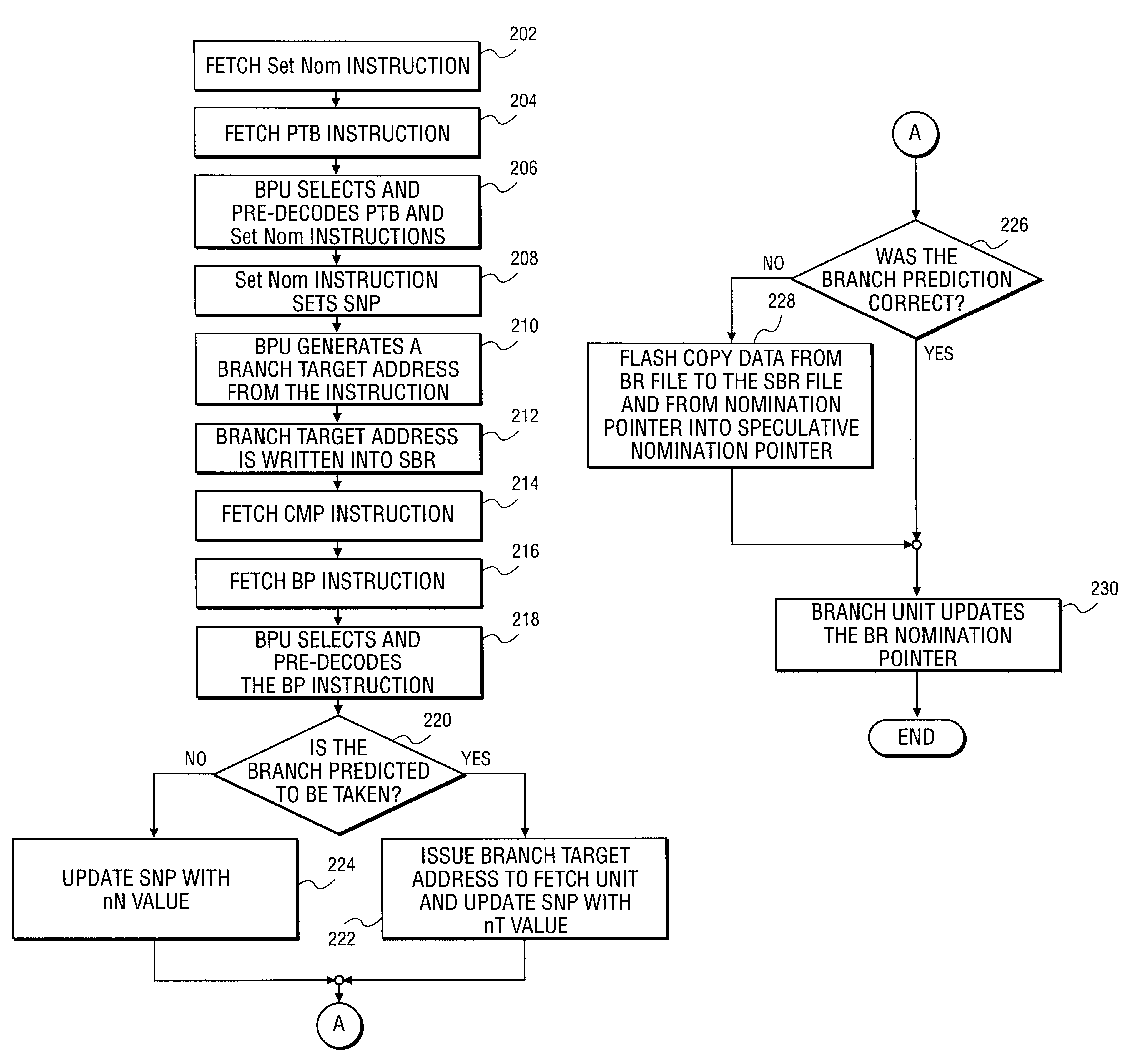
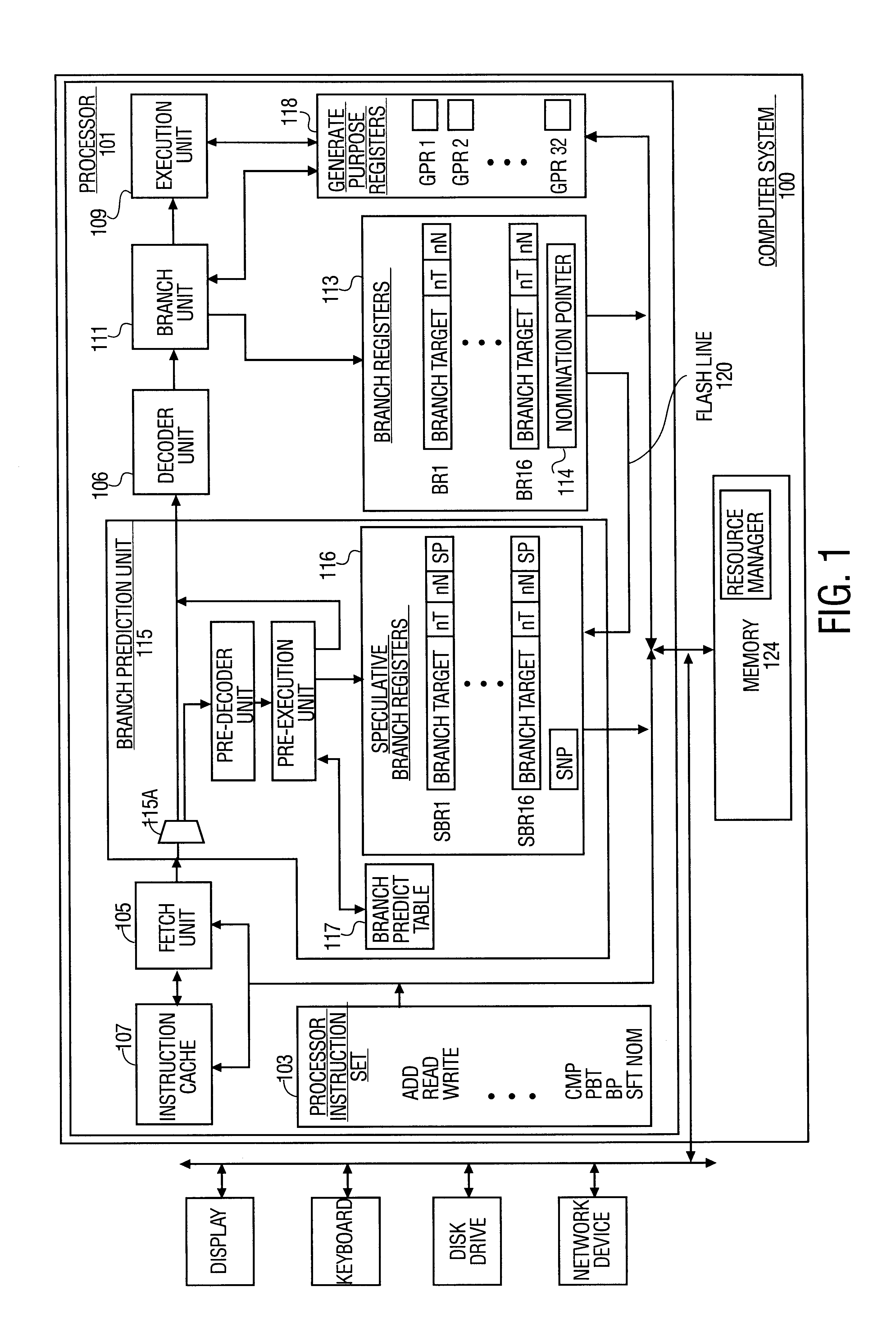
Microprocessor having a branch predictor using speculative branch registers
InactiveUS6871275B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationInstruction memoryMemory hierarchy
A method and apparatus for speculatively providing a branch target address as specified by an impending branch operation. In one embodiment, a branch prediction unit of the present invention is operable to pre-decode and pre-execute branch operations in a pipestage prior to a decoding stage and an execution stage of a pipelined processor. The branch operations of the present invention are performed via multiple instructions separately scheduled and executed, wherein a first instruction of a branch operation specifies a branch target, and a second instruction of a branch operation specifies when a branch of the branch operation is to occur. In an alternative embodiment of the present invention, the branch prediction unit is further operable to pre-fetch instructions from a memory hierarchy into a local instruction memory device in response to the branch prediction unit pre-decoding a first instruction of a branch operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
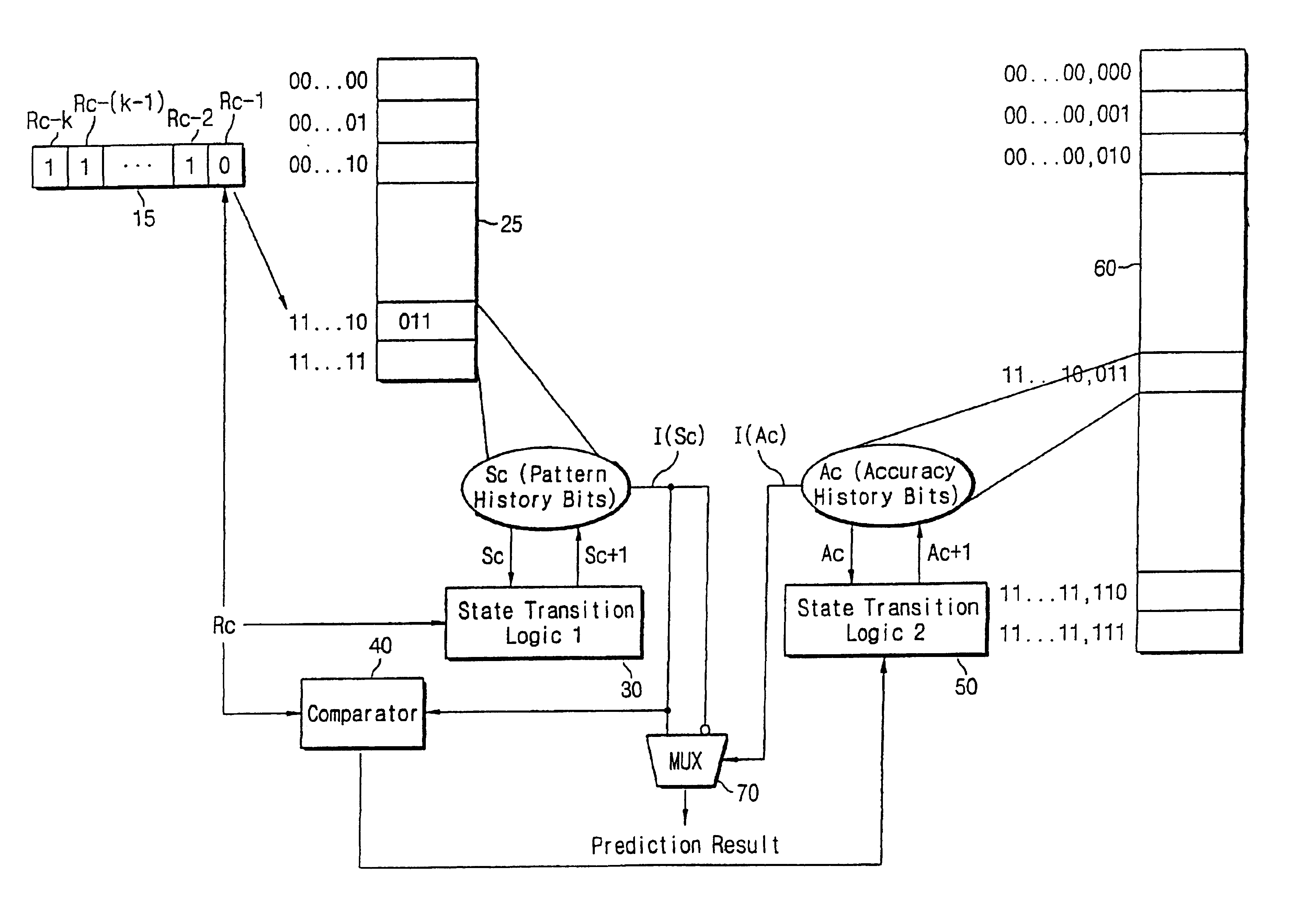
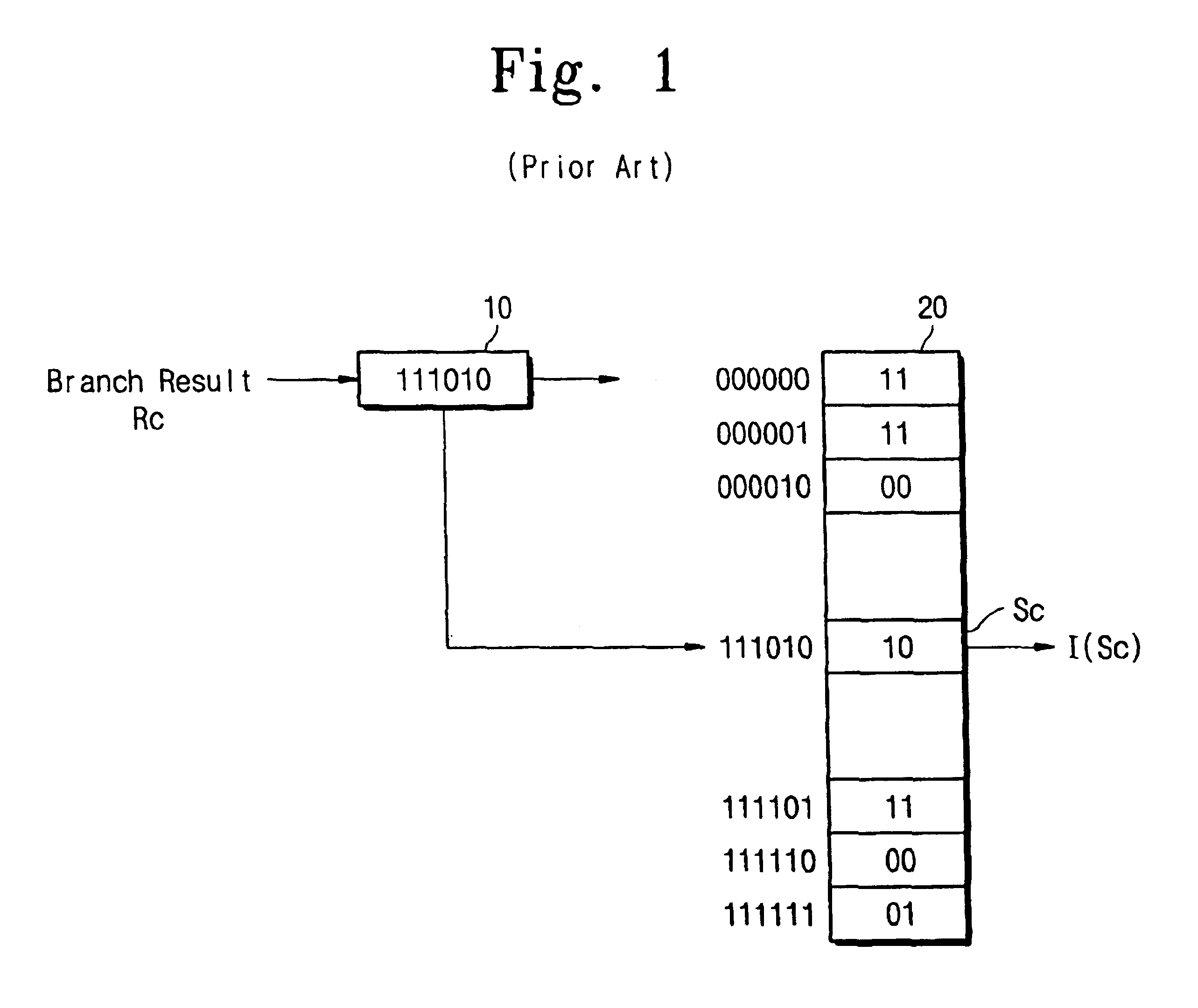
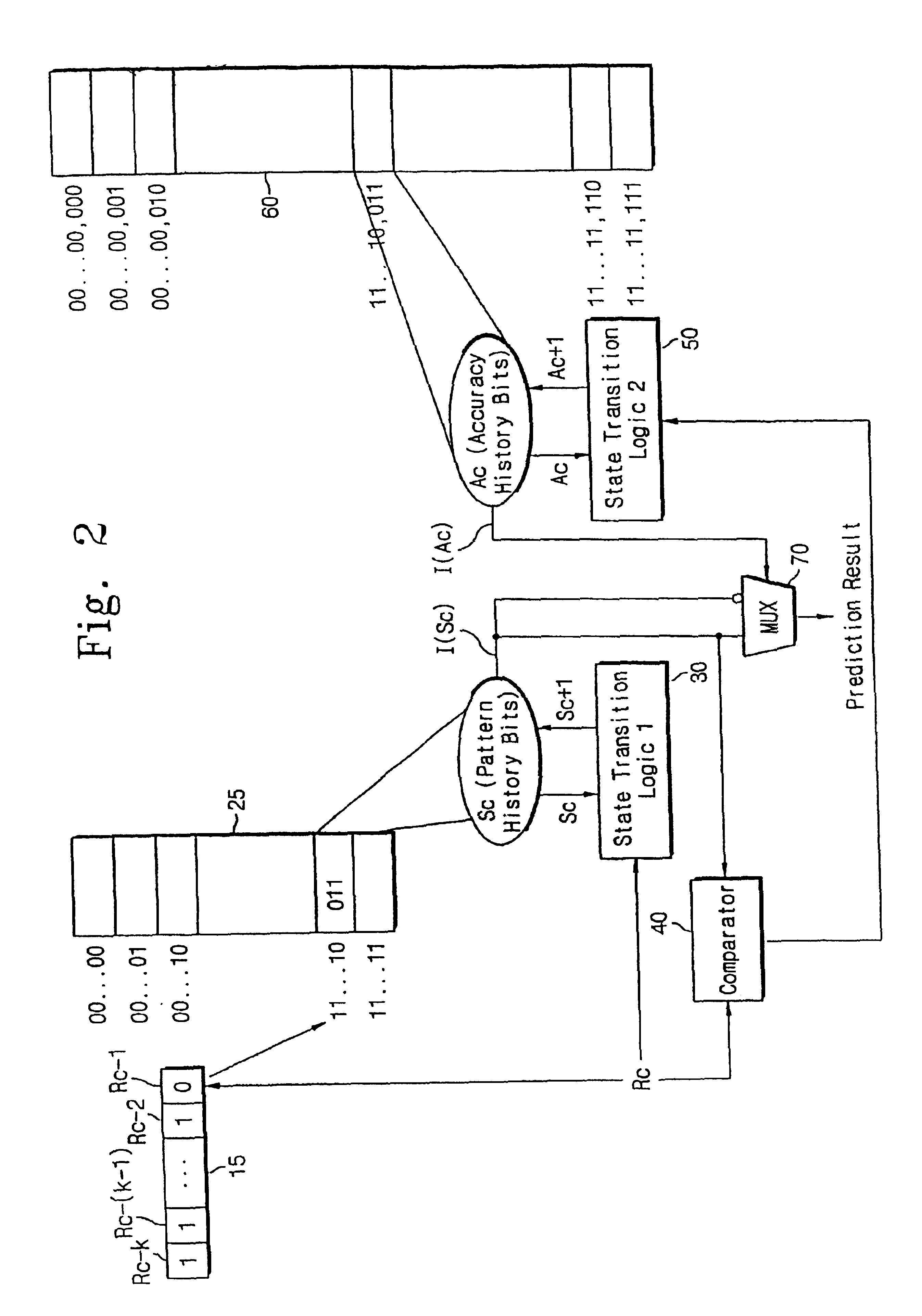
Multi-level pattern history branch predictor using branch prediction accuracy history to mediate the predicted outcome
InactiveUS6918033B1Efficient processingReducing prediction missDigital computer detailsNext instruction address formationMachine learningBranch predictor
A branch predictor outputs either a predicted conditional branch or an inverted predicted conditional branch as a final branch prediction outcome, in response to a predicted accuracy history signal based on one or more accuracy history bits. According to the accuracy history bit, it is determined whether the branch prediction outcome of the branch predictor is correct. If the predicted conditional branch is correct, the branch predictor outputs the predicted conditional branch, and if the predicted conditional branch is not correct, the branch predictor outputs the inverted predicted conditional branch, in response to the predicted accuracy history signal. For performing this process, the branch prediction appends an accuracy history table and a multiplexer to a conventional branch predictor, so that the branch prediction according to the present invention can reduce the misprediction with relatively simple circuitry and low hardware cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
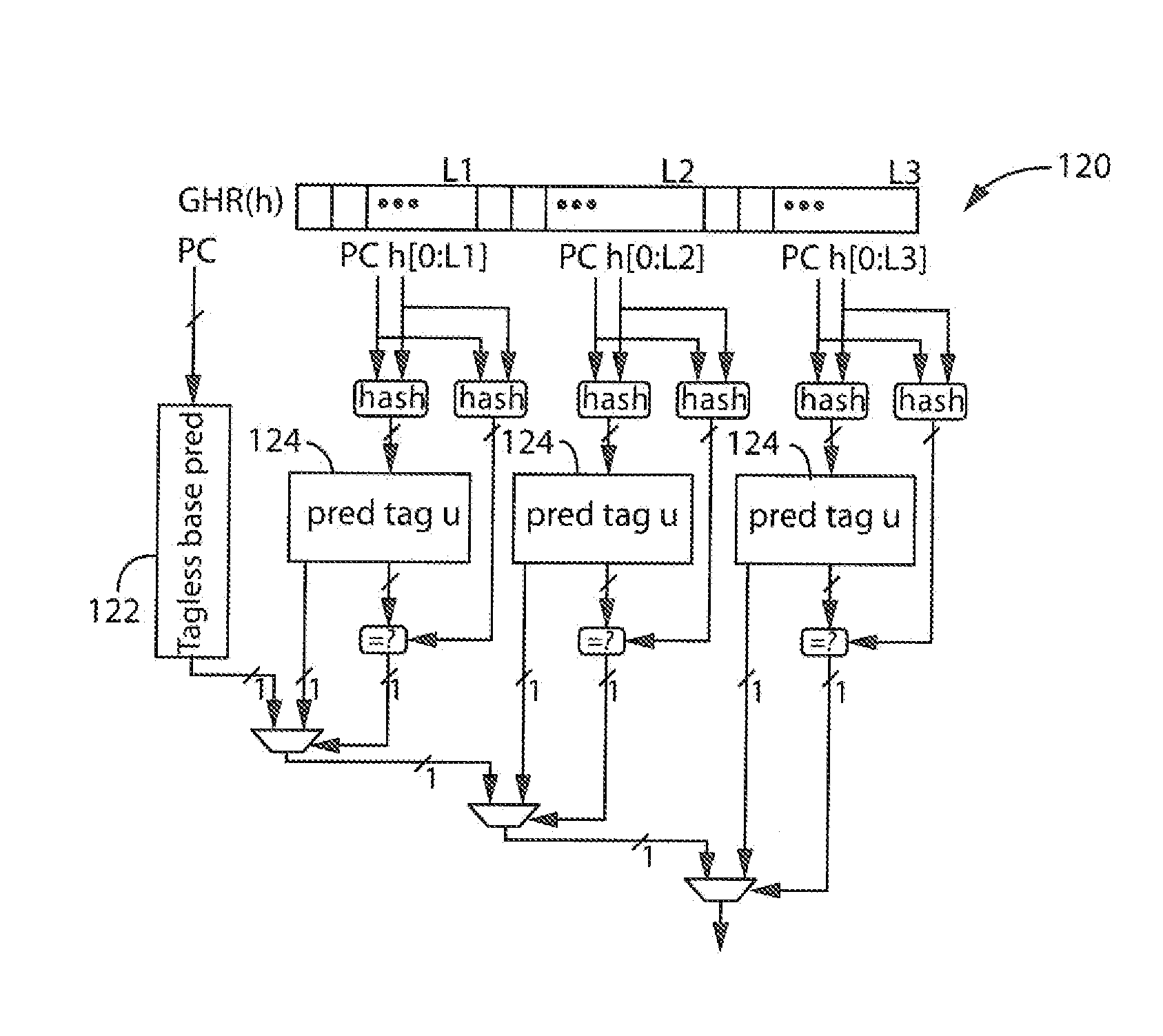
Apparatus and Method for Bias-Free Branch Prediction
ActiveUS20150363203A1Little correlationImprove forecast accuracyInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionBranch correlation
Aspects of the present invention provide an apparatus and method for filtering biased conditional branches in a branch predictor in favor of non-biased conditional branches. Biased conditional branches, which are consistently skewed toward one direction or outcome, are filtered such that an increased number of non-biased conditional branches which resolve in both directions may be considered. As a result, more useful branches may be captured over larger distances, thereby providing correlations deeper in a global history to provide greater prediction accuracy. In addition, by tracking only the latest occurrences of non-biased conditional branches using a recency stack structure, even more distant branch correlations may be made.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
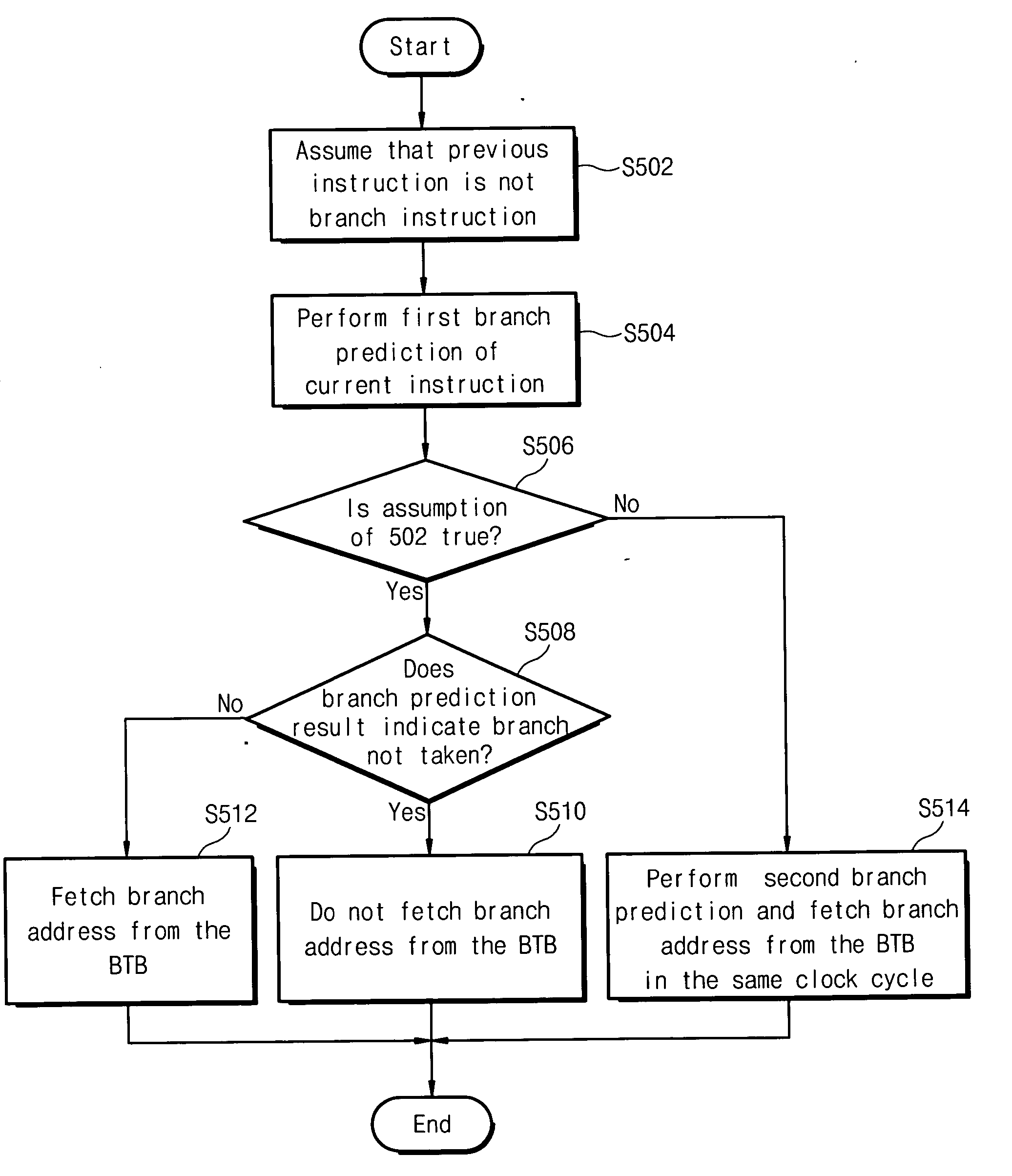
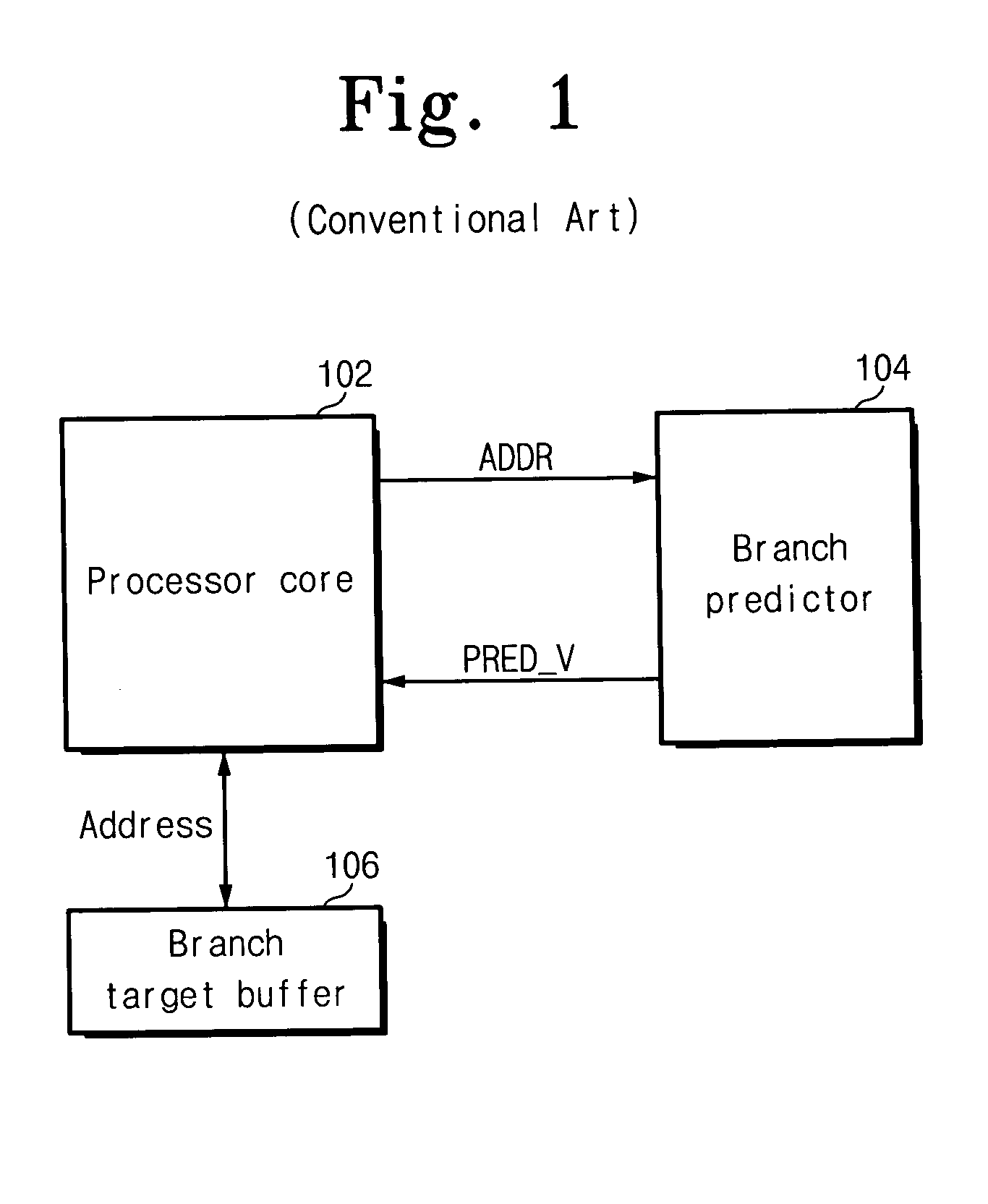
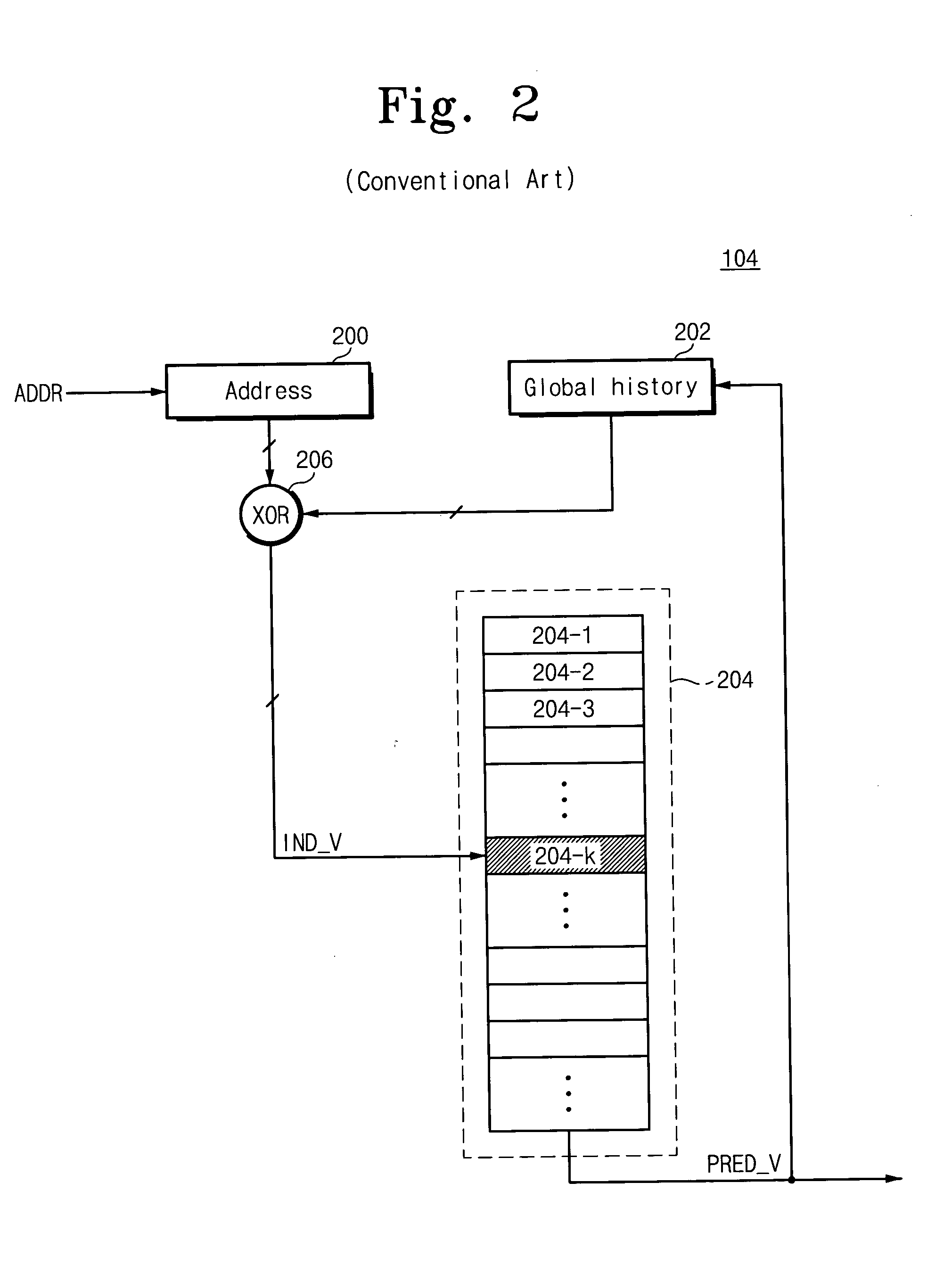
Branch predictor, system and method of branch prediction
ActiveUS20050091479A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionPredictive methodsPrediction system
A method, system and branch predictor for branch prediction. The system includes a processor core for executing instructions, a branch target buffer for fetching a branch address, and a branch predictor for first predicting a branch of a current instruction address and indicating to the processor core when to fetch the branch address from the branch target buffer. A branch predictor, including a branch prediction table for storing a plurality of branch prediction values of previous branch instructions, and a controller for selecting one of the plurality of branch prediction values and outputting the selected one of the plurality of branch prediction values to a processor core, the selected one of the plurality of branch prediction values indicating to the processor core when to fetch a branch address from a branch target buffer. A method of branch prediction, including first outputting a current instruction address from a processor core to a branch predictor, predicting whether a branch occurs based on the received current instruction address and a global history, and second outputting a branch prediction value from the branch predictor to the processor core, the branch prediction value indicating whether the processor core fetches a branch address from a branch target buffer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com