Microprocessor and execution method thereof
A technology of microprocessors and execution units, applied in the field of non-sequential microprocessors, which can solve problems such as adverse effects of branch instructions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
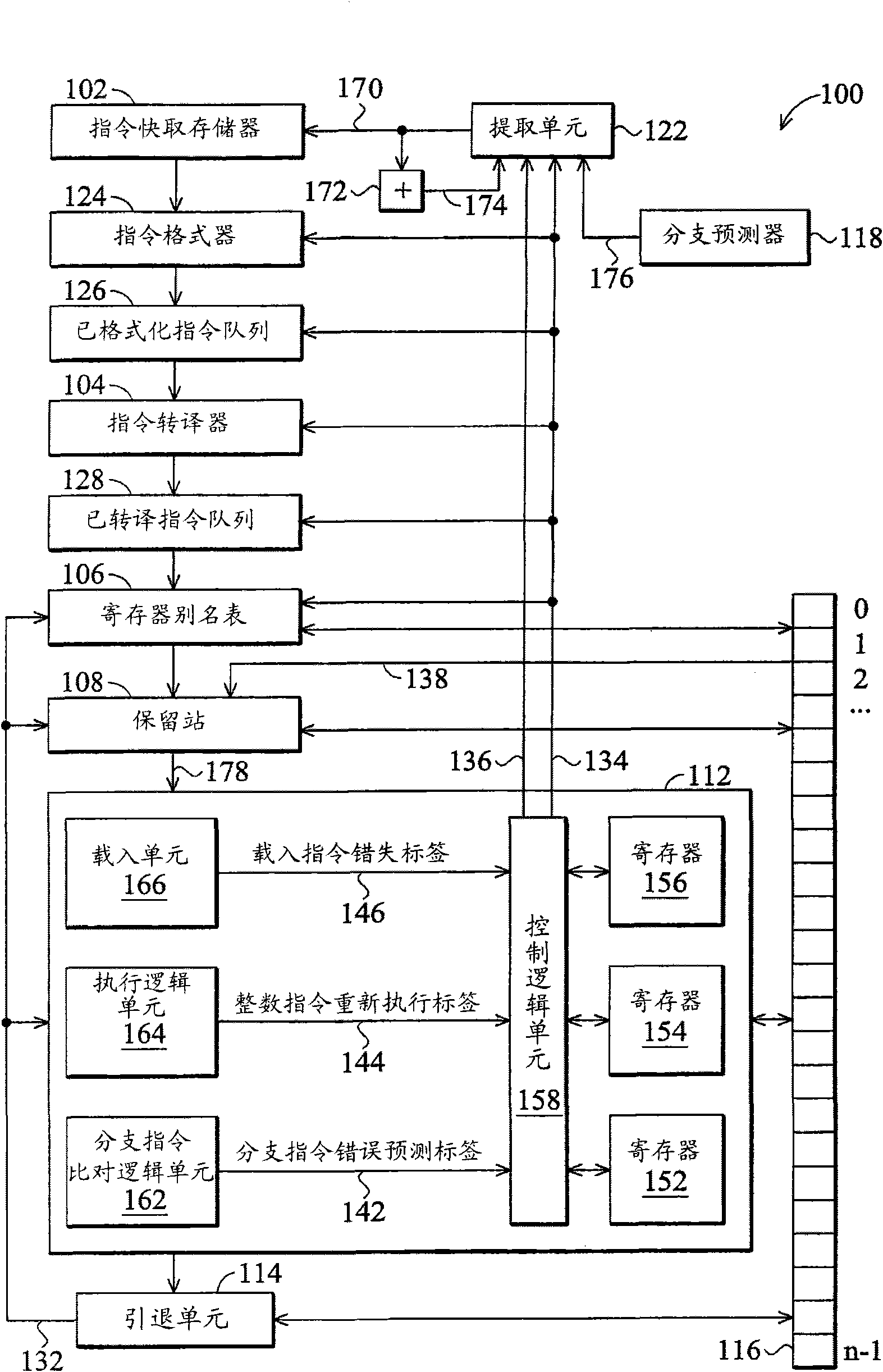
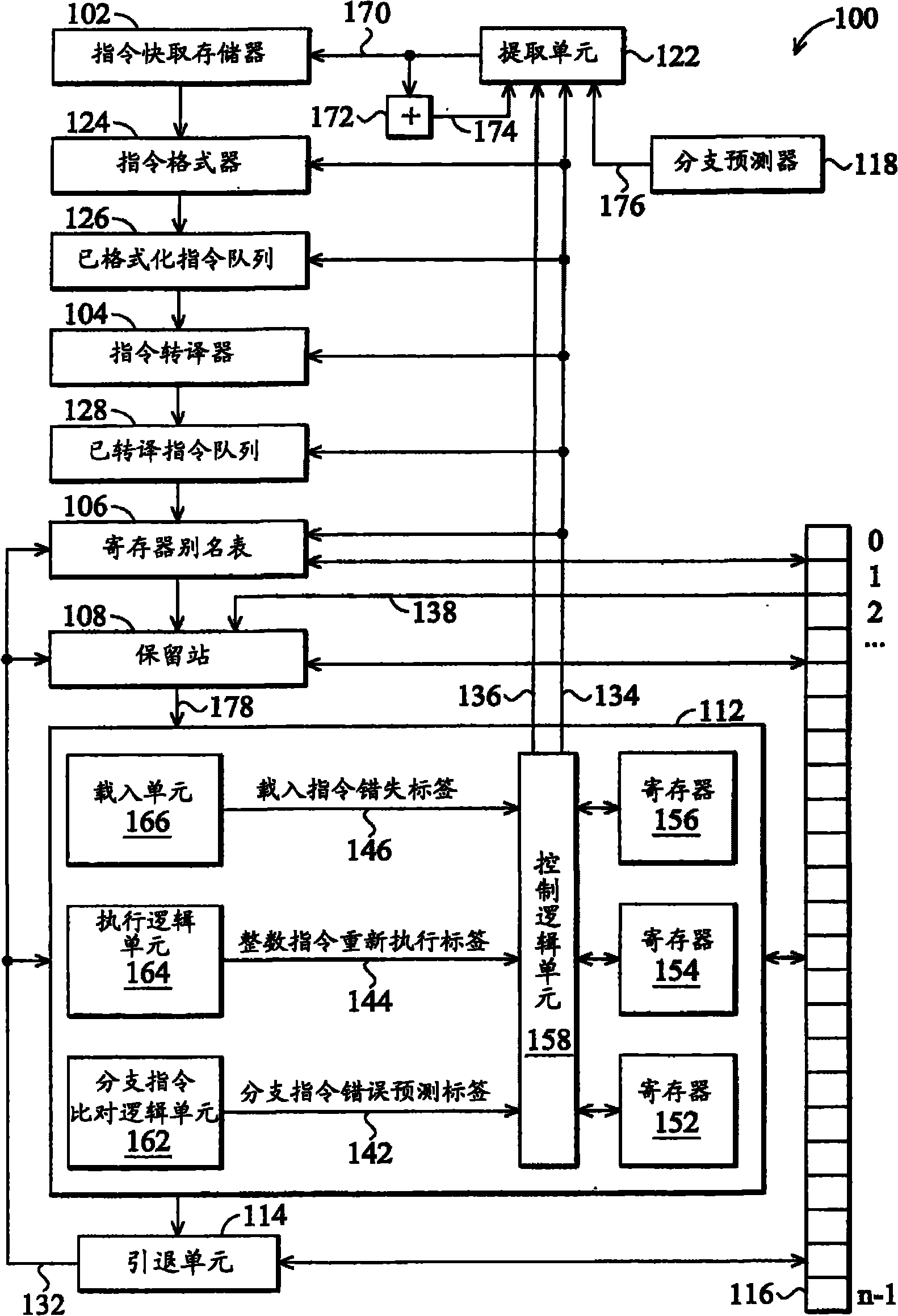
[0028] figure 1 is a block diagram of the microprocessor 100 of the present invention. The microprocessor 100 includes a pipeline composed of multiple stages or functional units. The pipeline includes an instruction fetch unit 122, an instruction cache 102, an instruction formatter ( instruction formatter) 124, formatted instruction queue (formatted instruction queue) 126, instruction translator (instruction translator) 104, translated instruction queue (translated instruction queue) 128, register alias table (register alias table) 106, reservation station (reservation station) ) 108, an execution unit 112, and a retirement unit 114. The microprocessor 100 also includes a branch predictor 118 coupled to the fetch unit 122 . The microprocessor 100 also includes a reorder buffer 116 coupled to the register alias table 106 , the reservation station 108 , the execution unit 112 and the retirement unit 114 .
[0029] The execution unit 112 includes a load unit 166 , an execution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com