Patents
Literature
192 results about "Out-of-order execution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
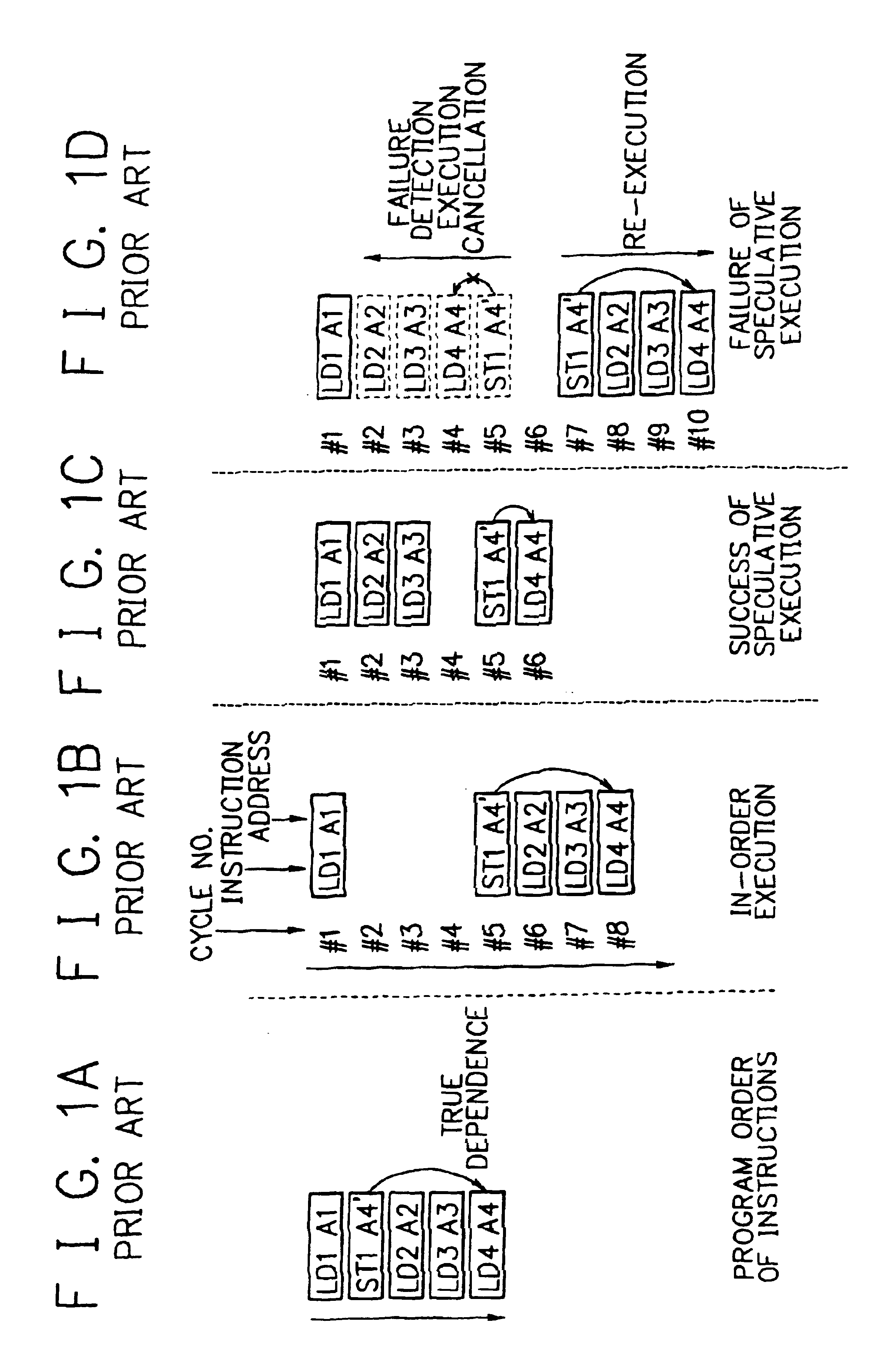
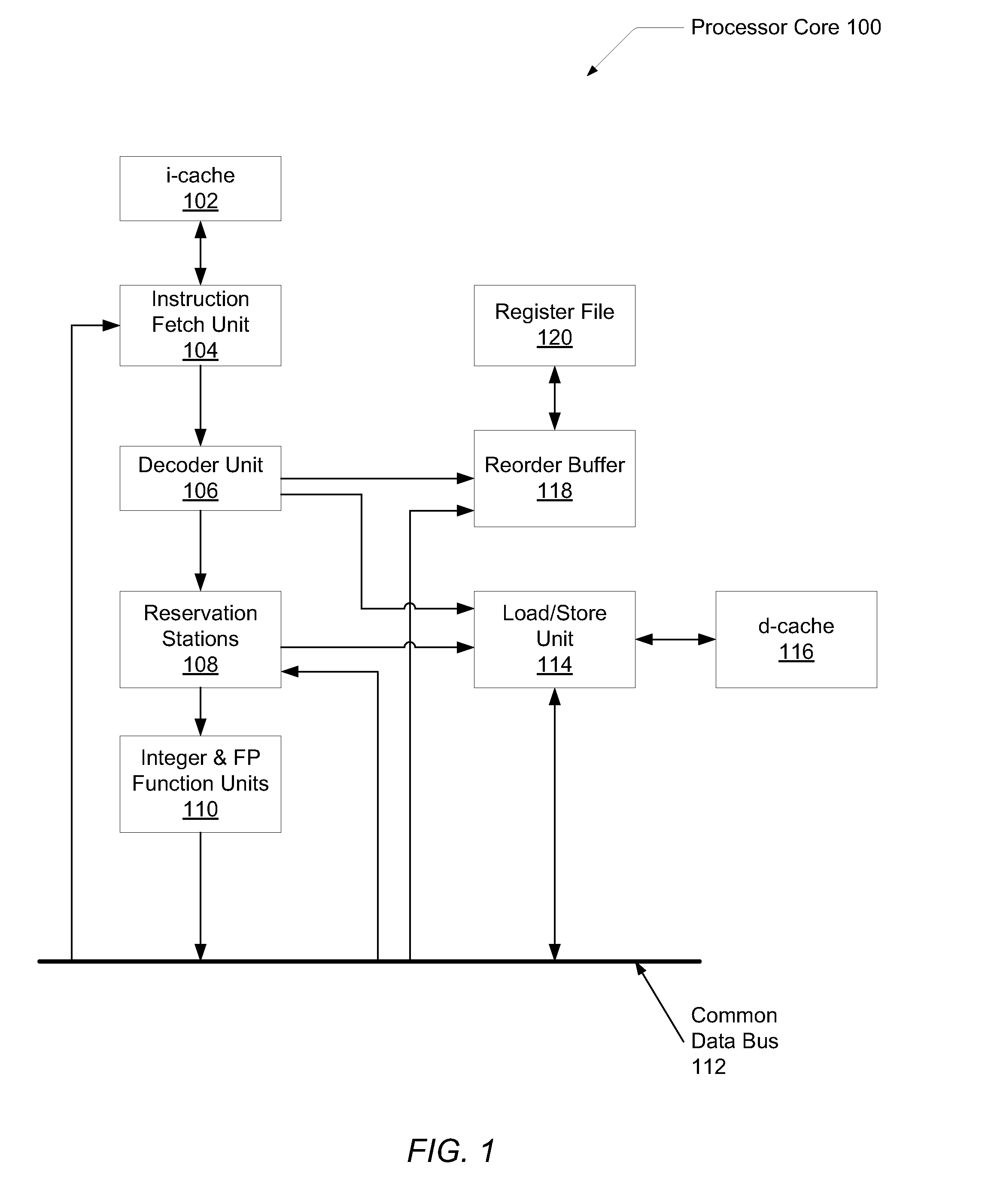
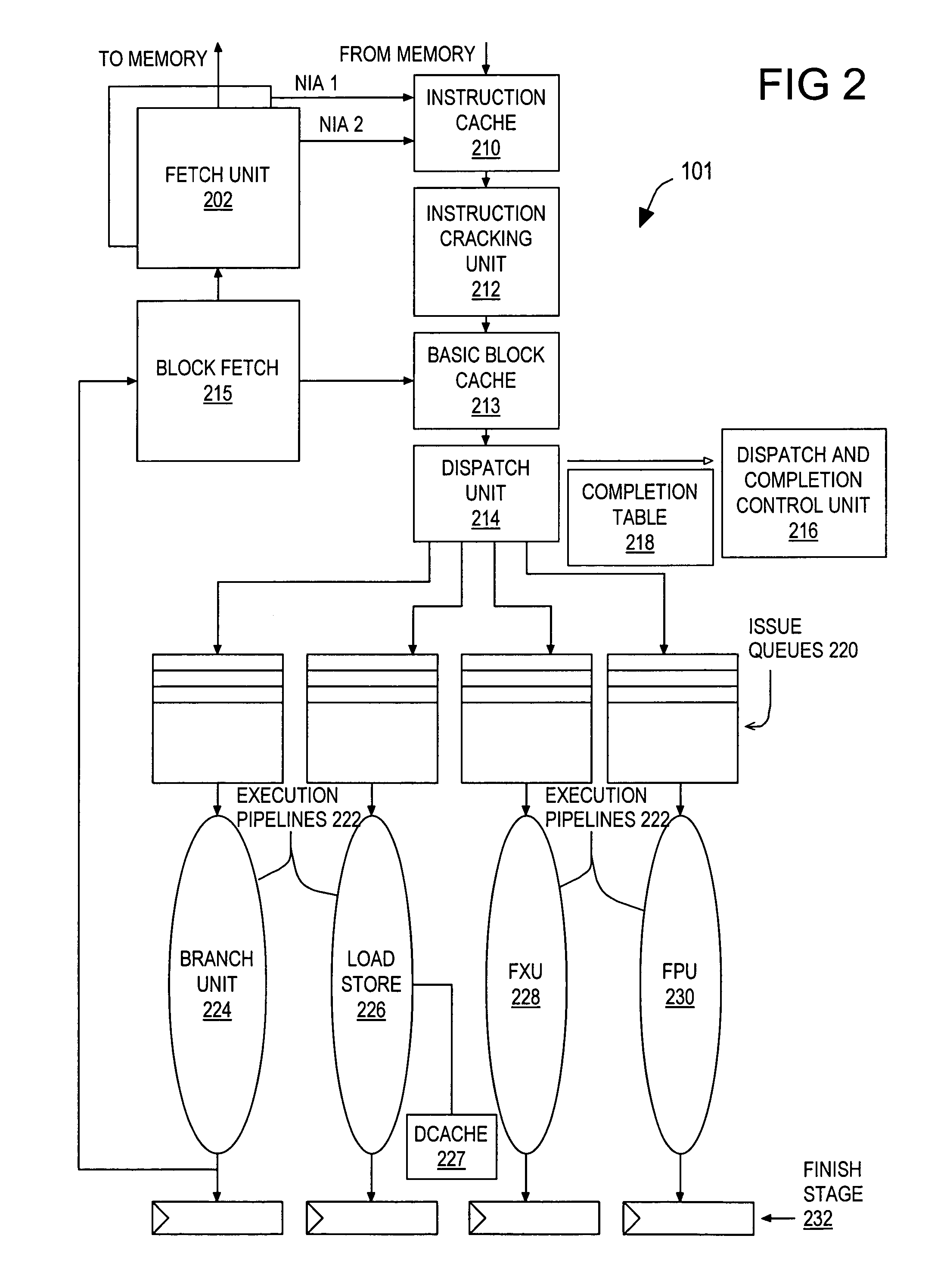
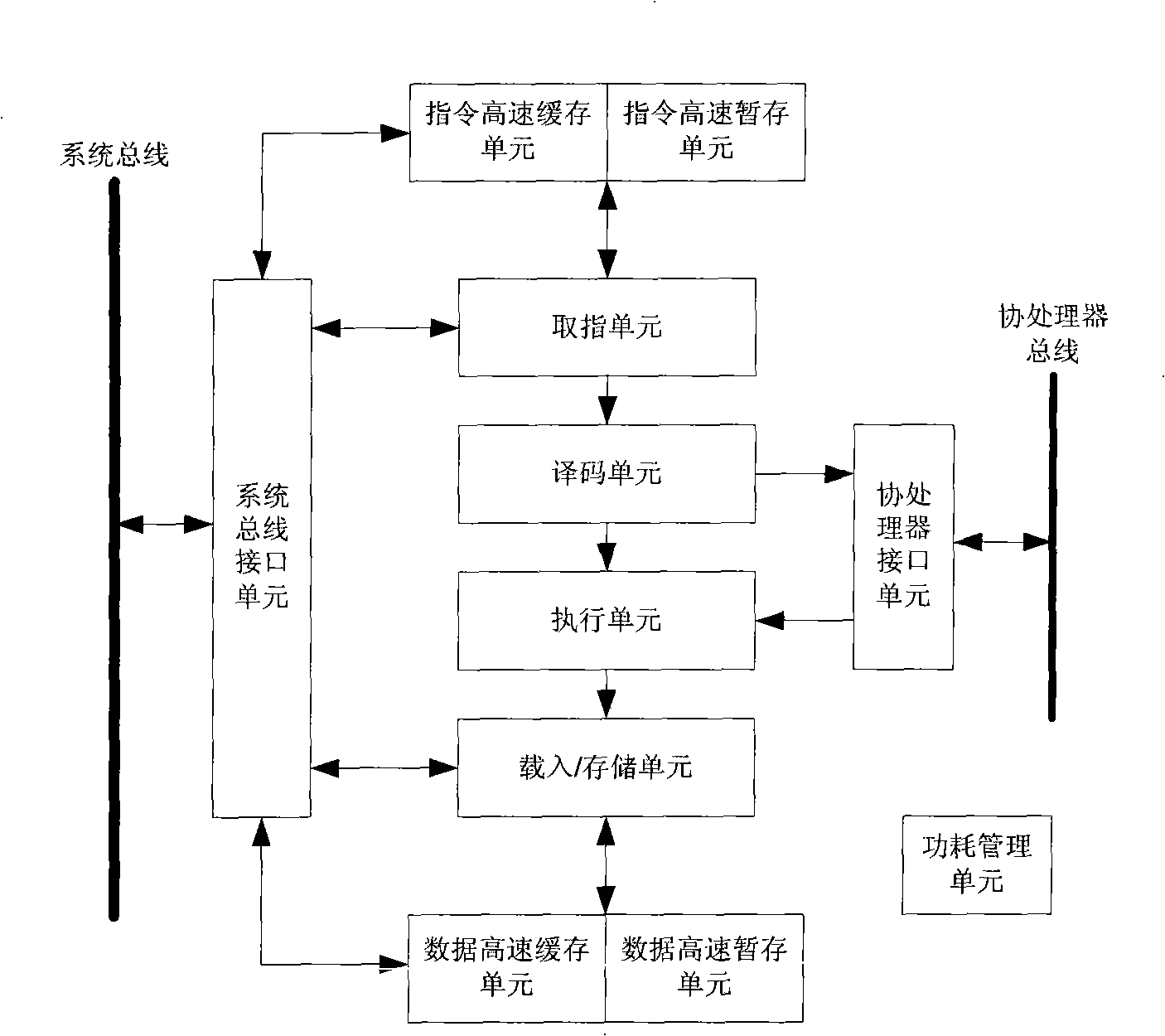
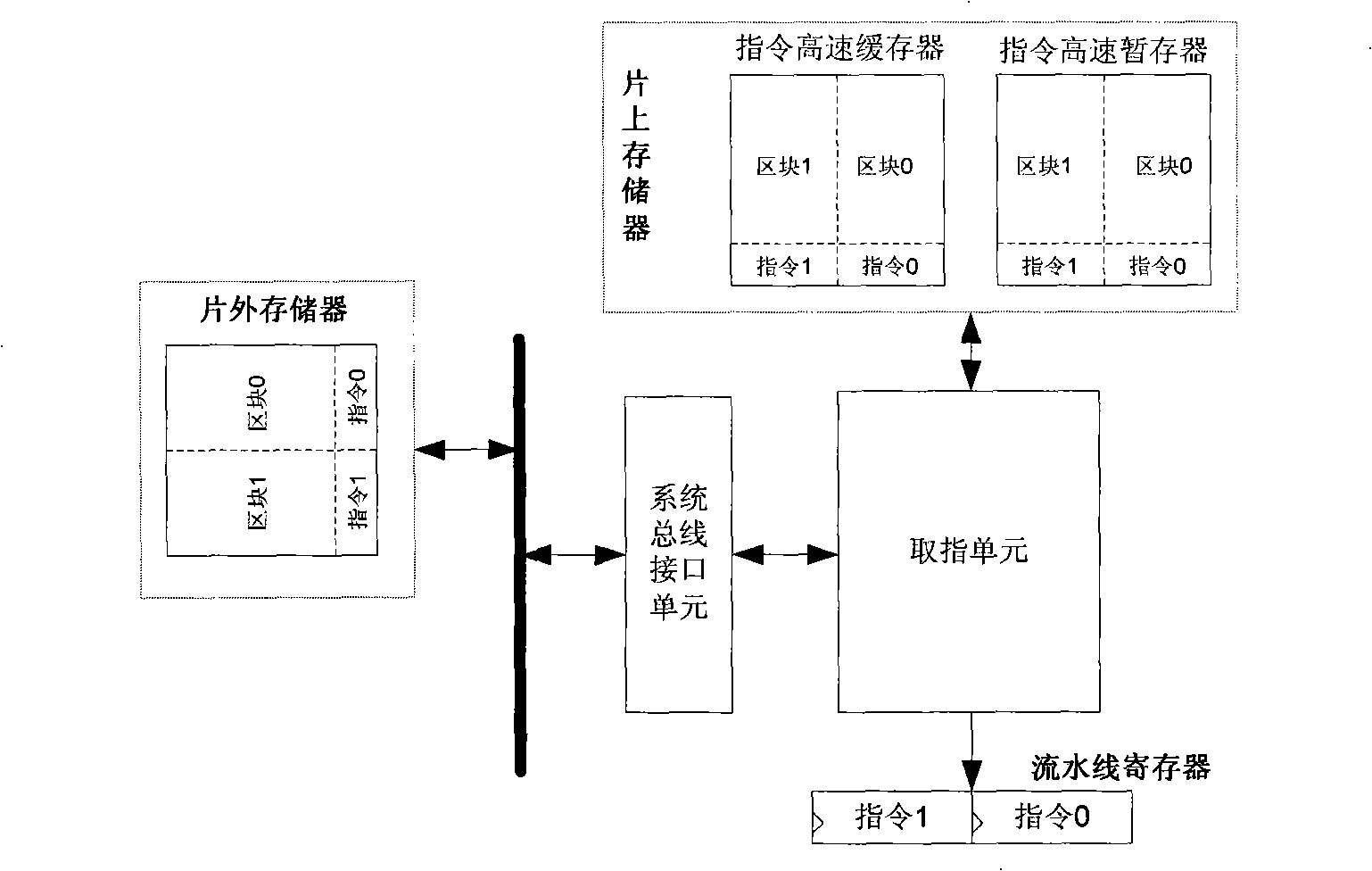
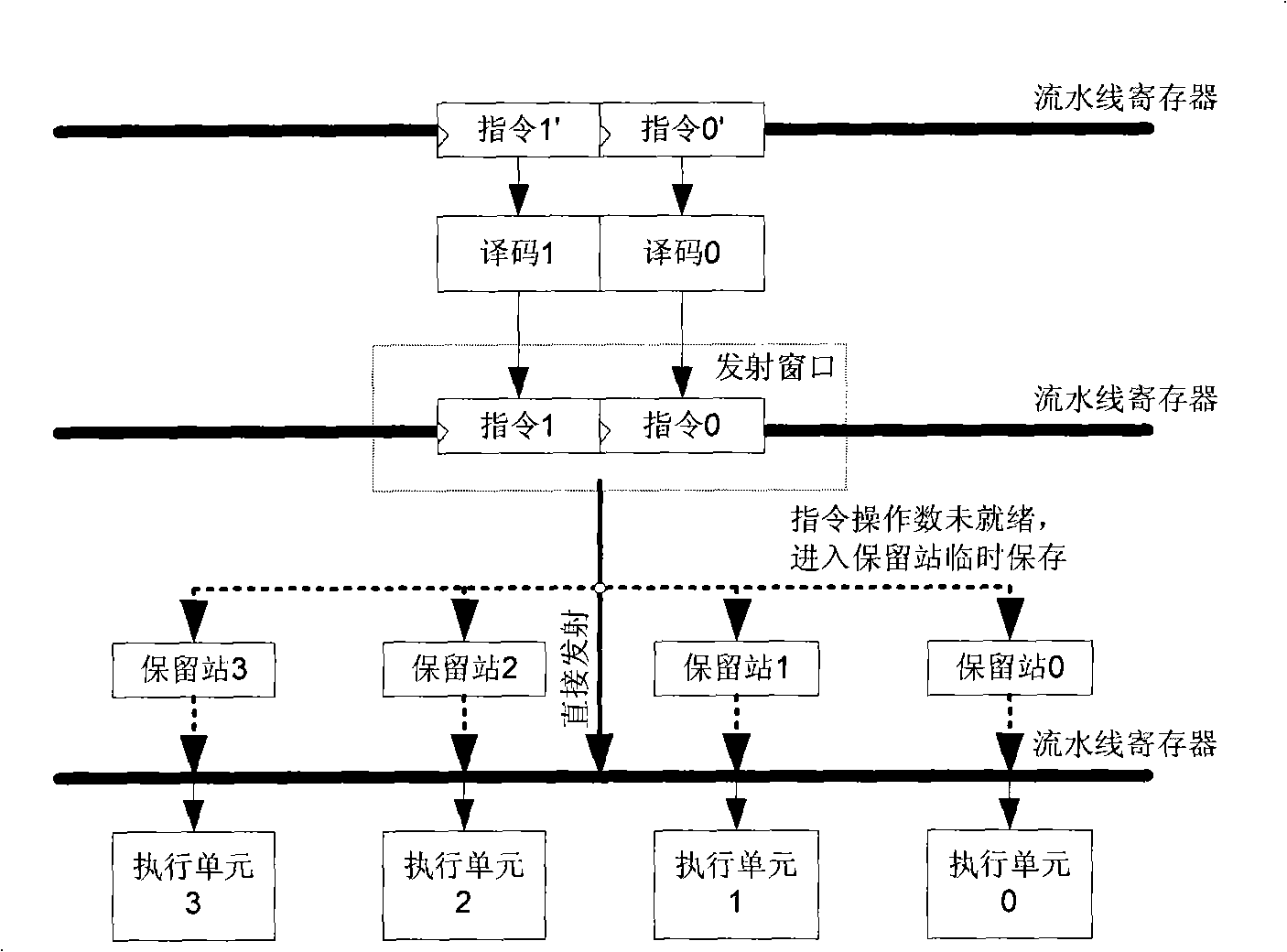
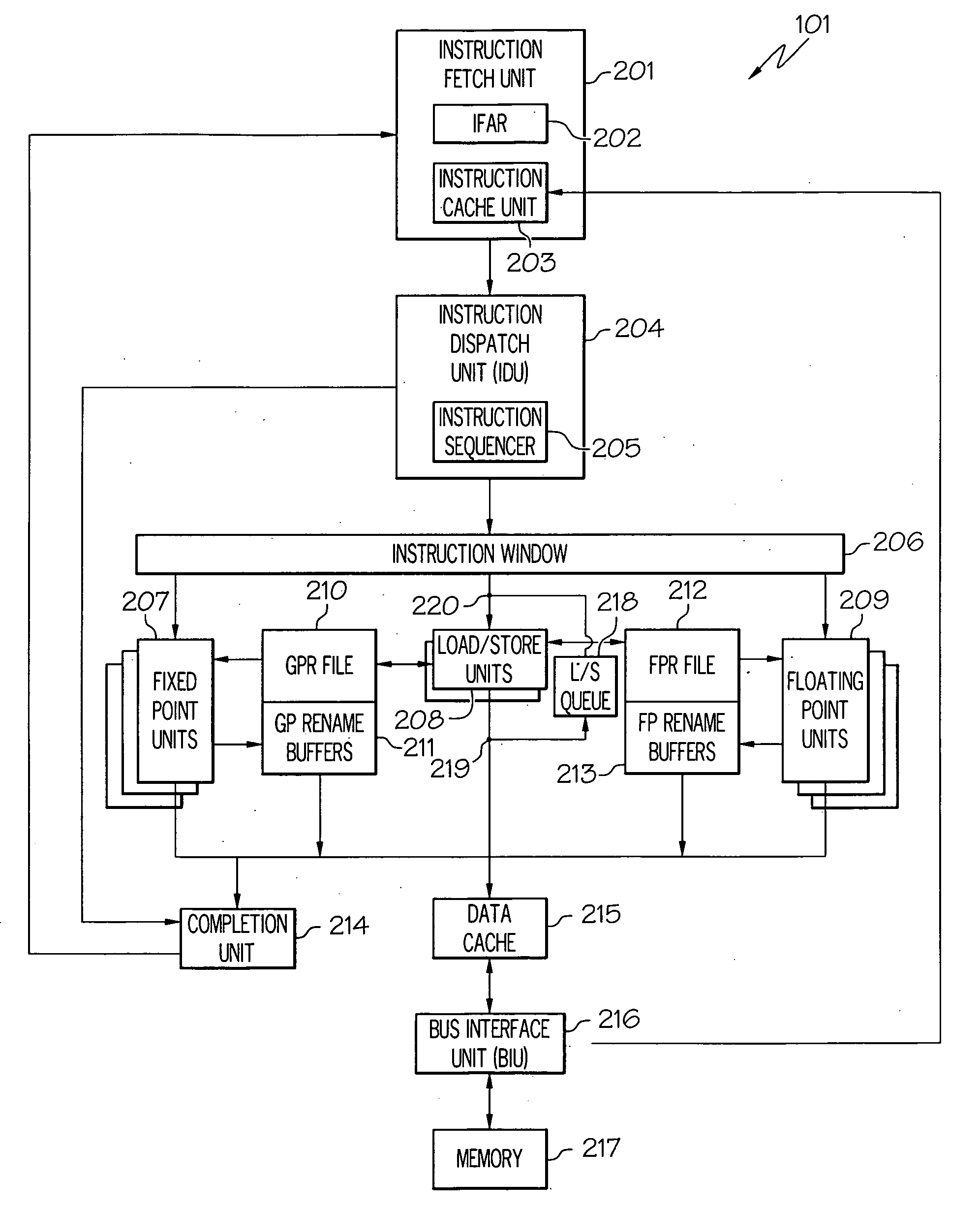
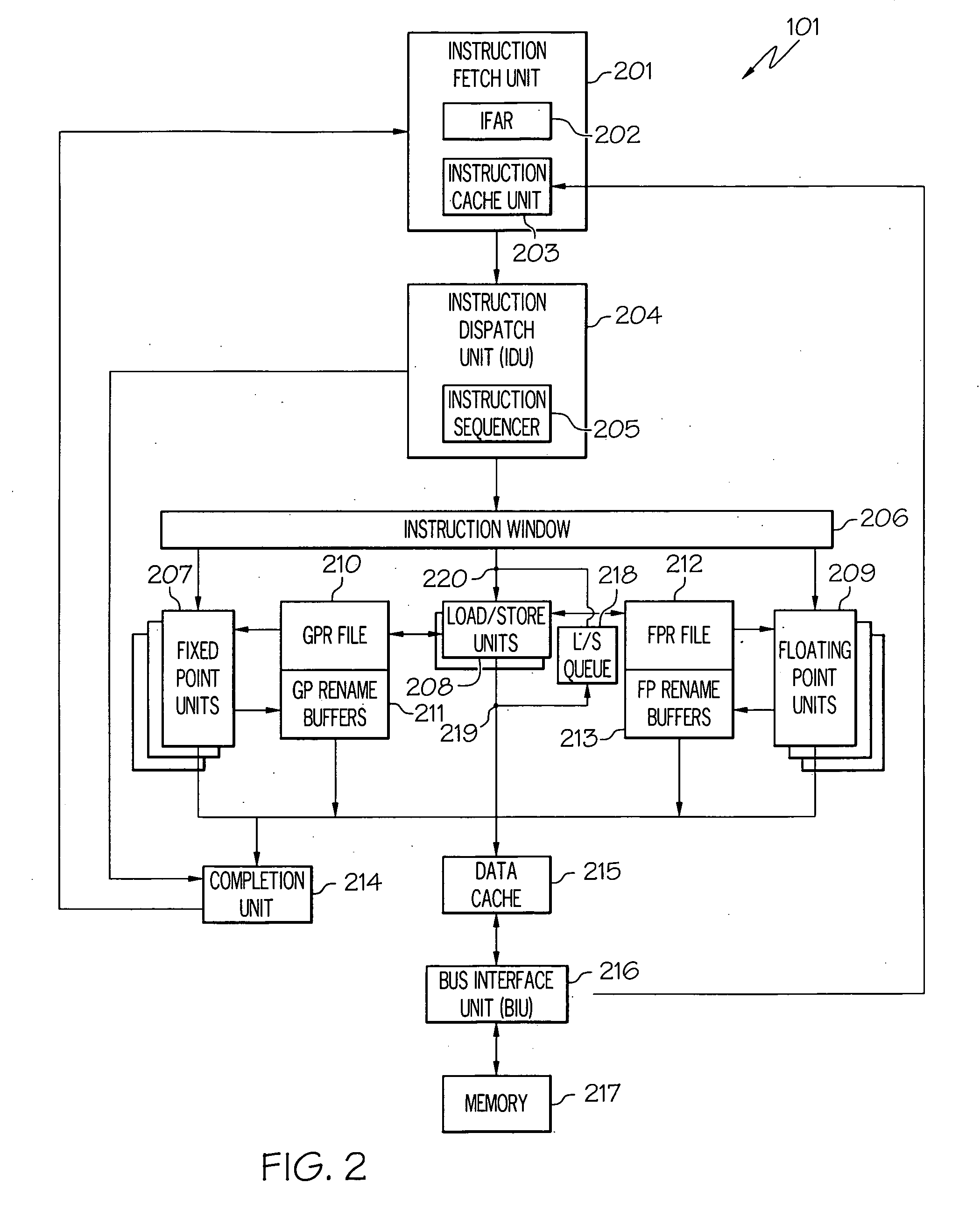
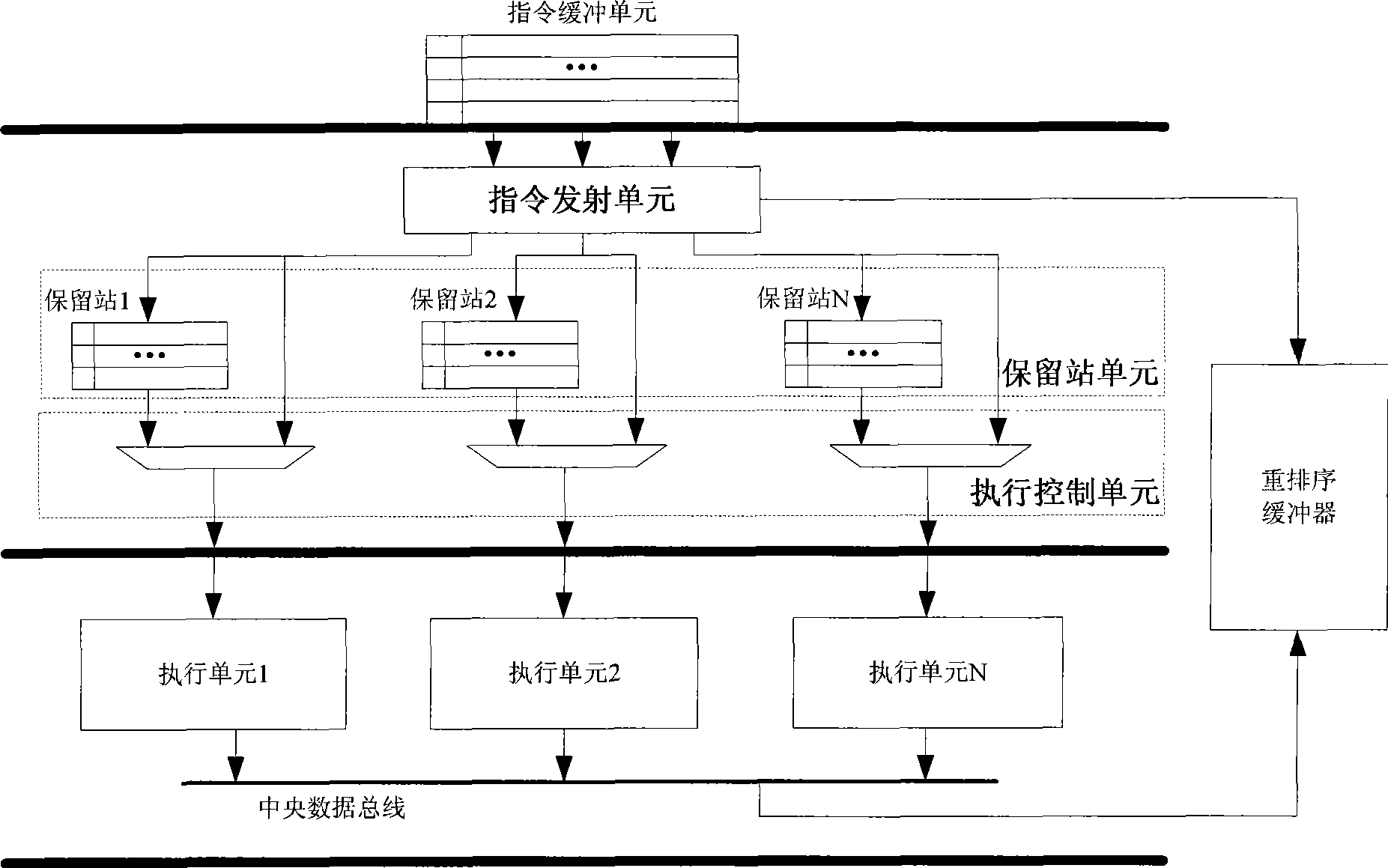
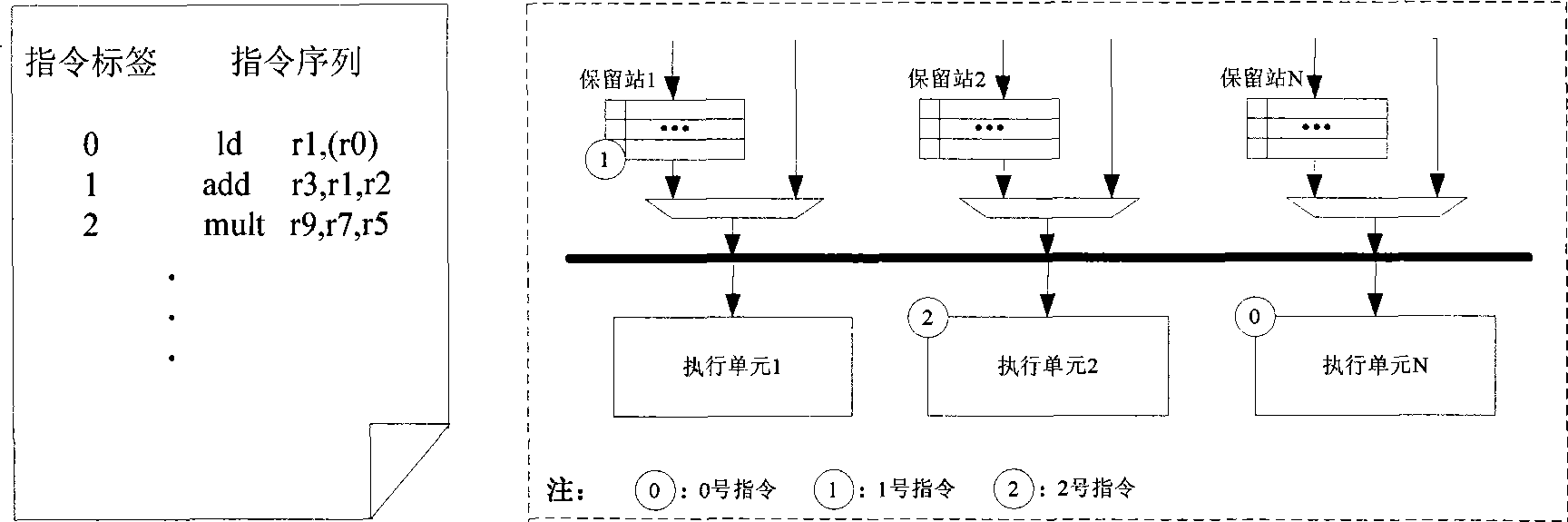
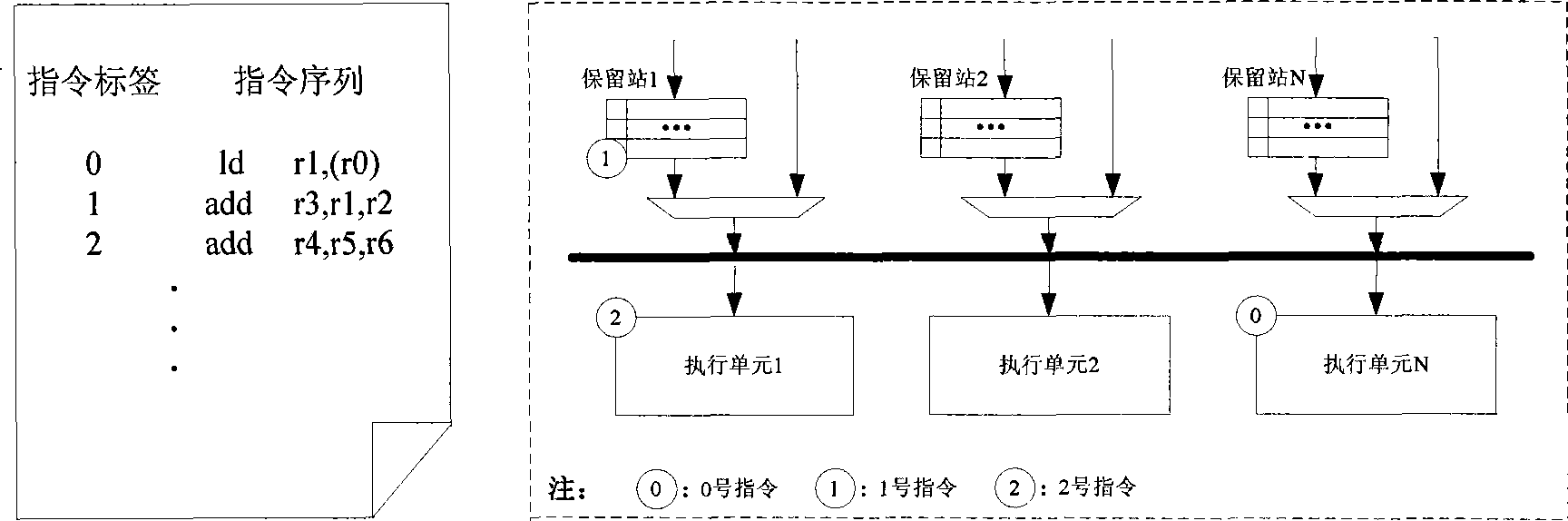
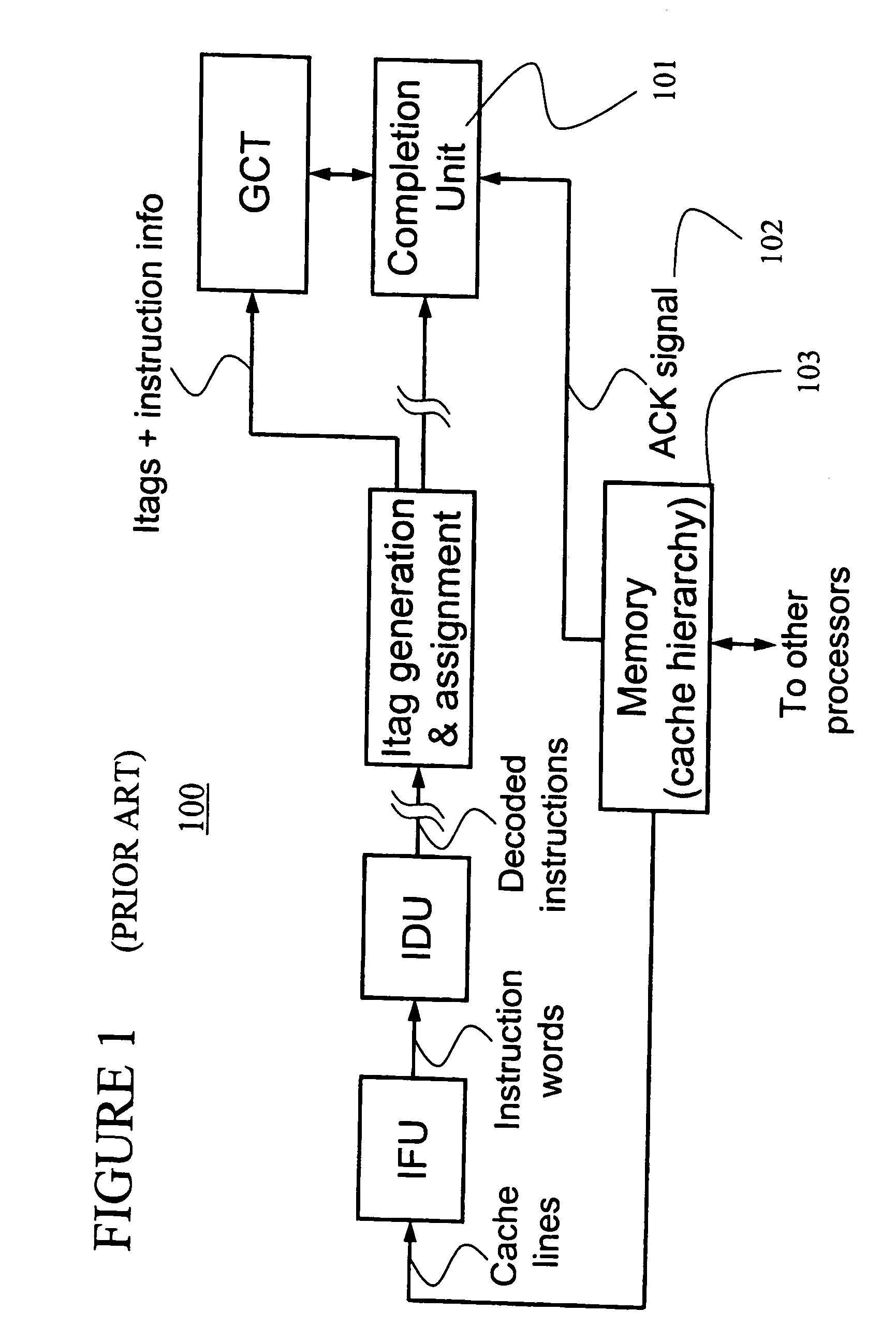
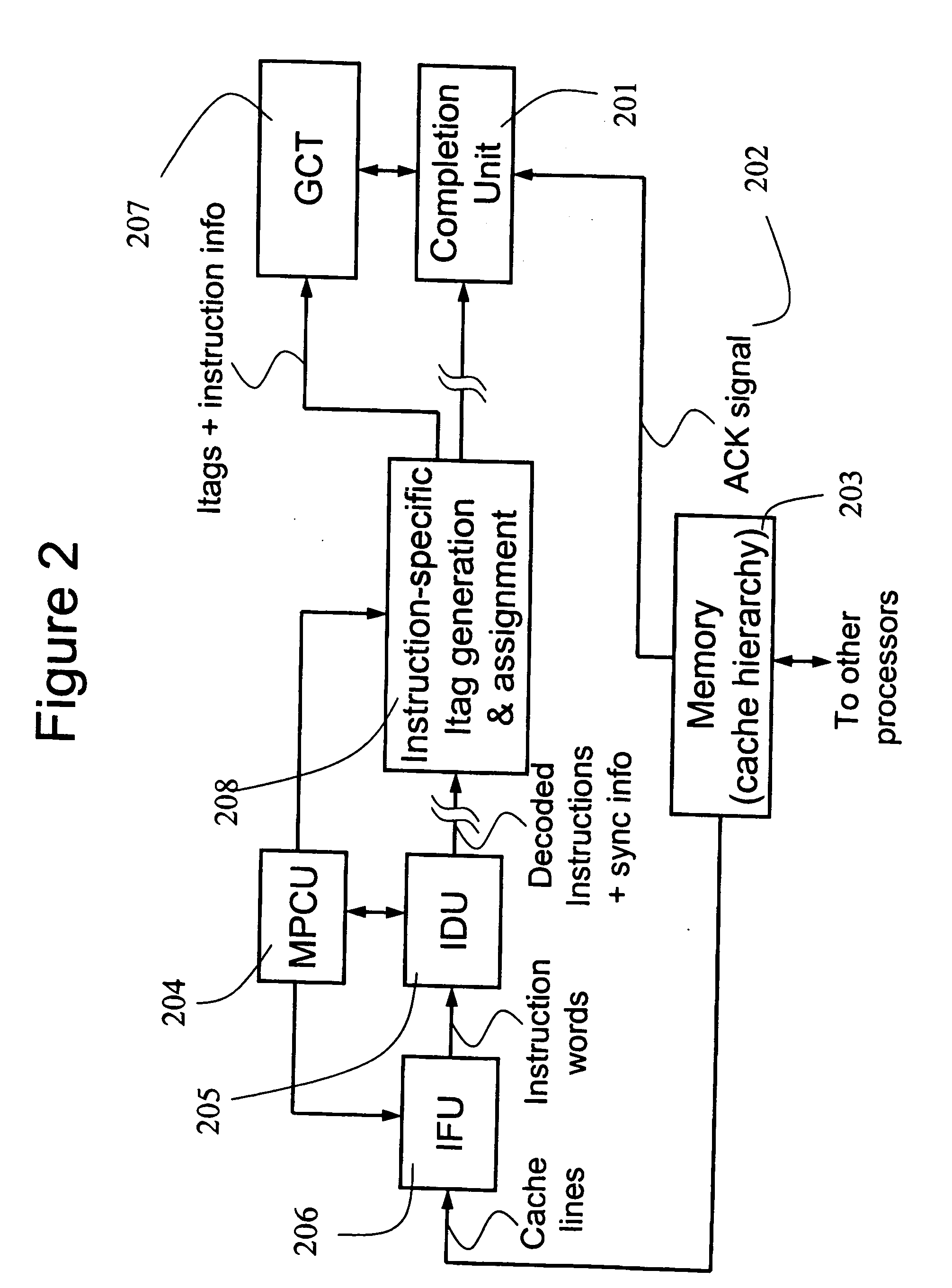
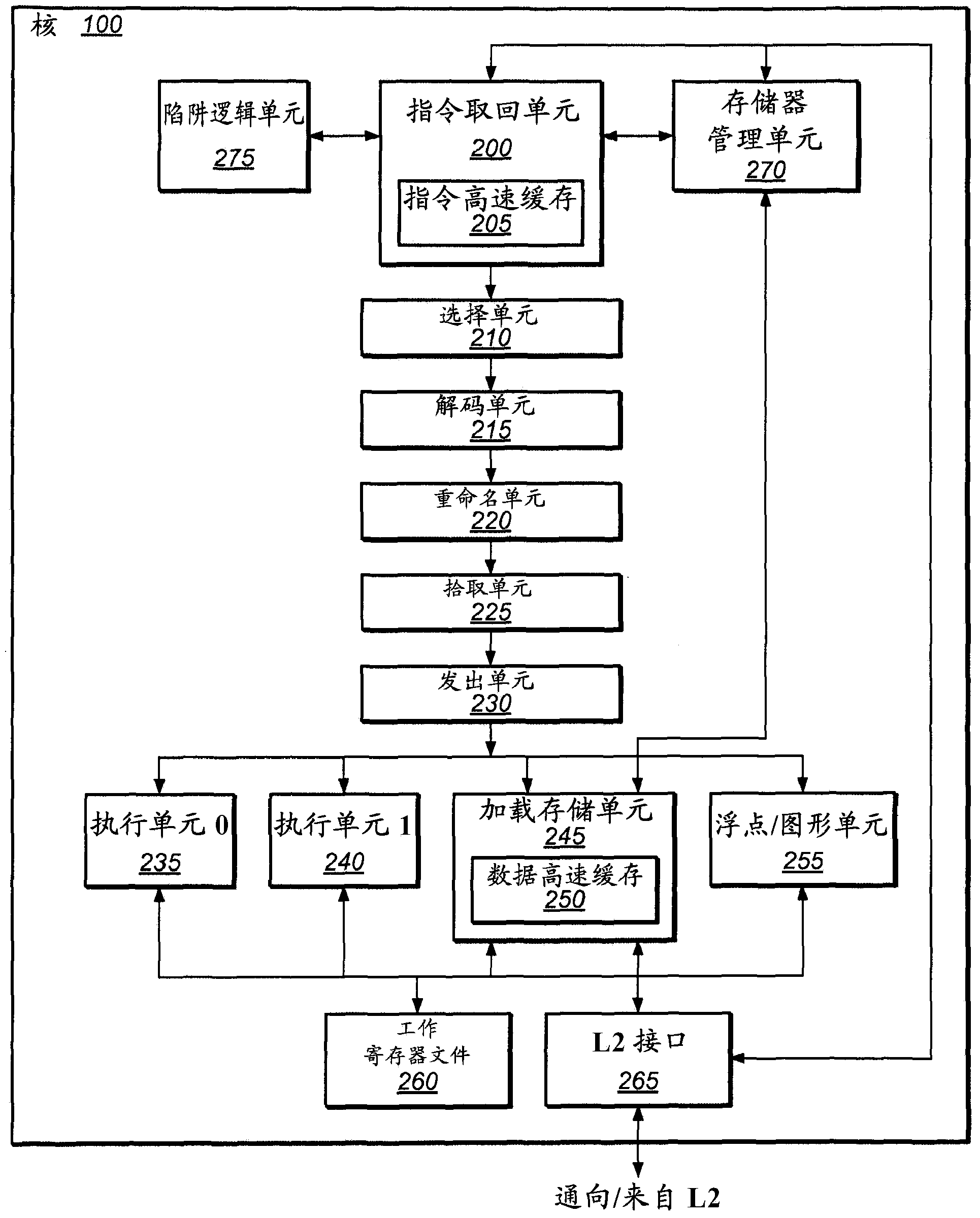
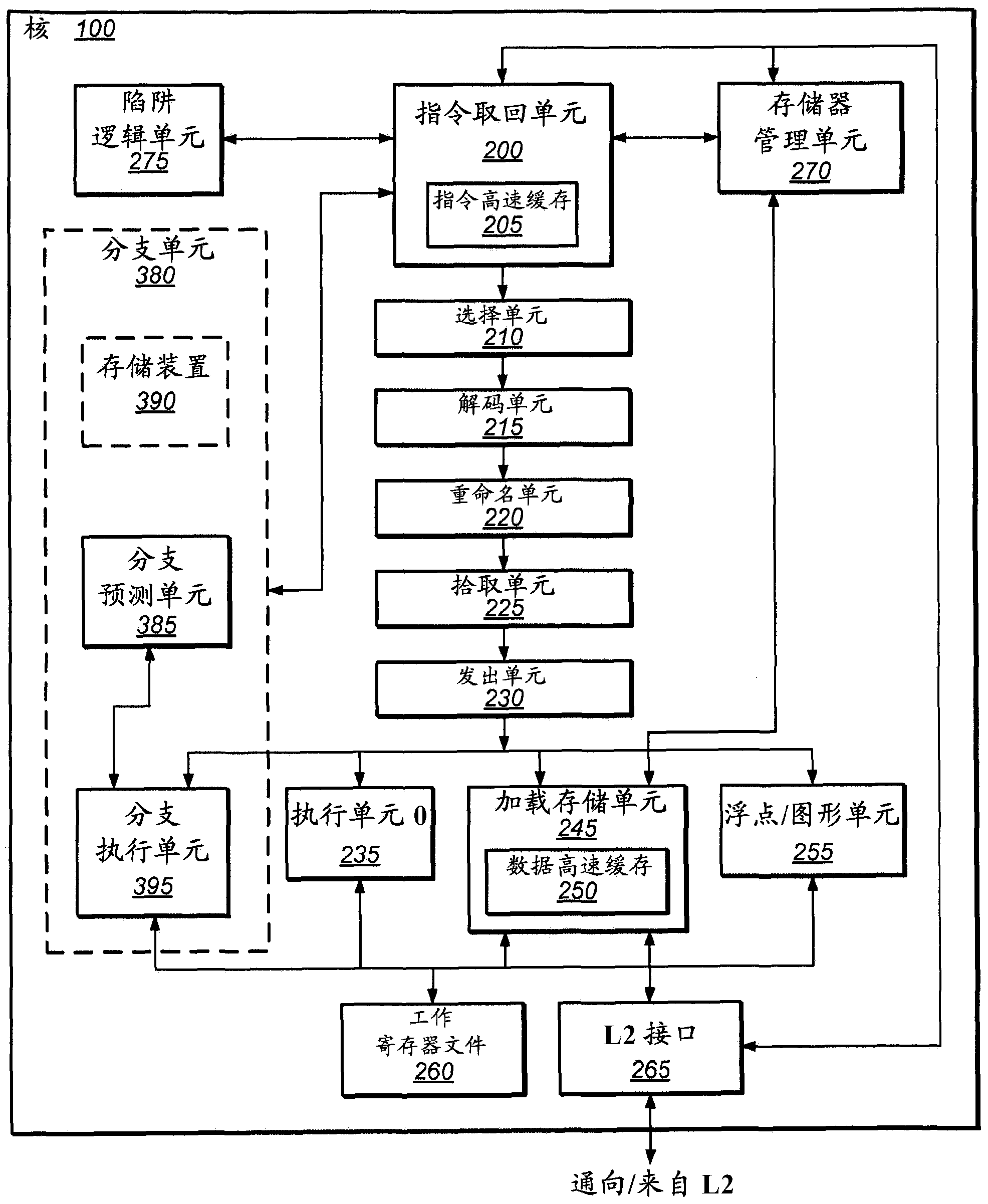
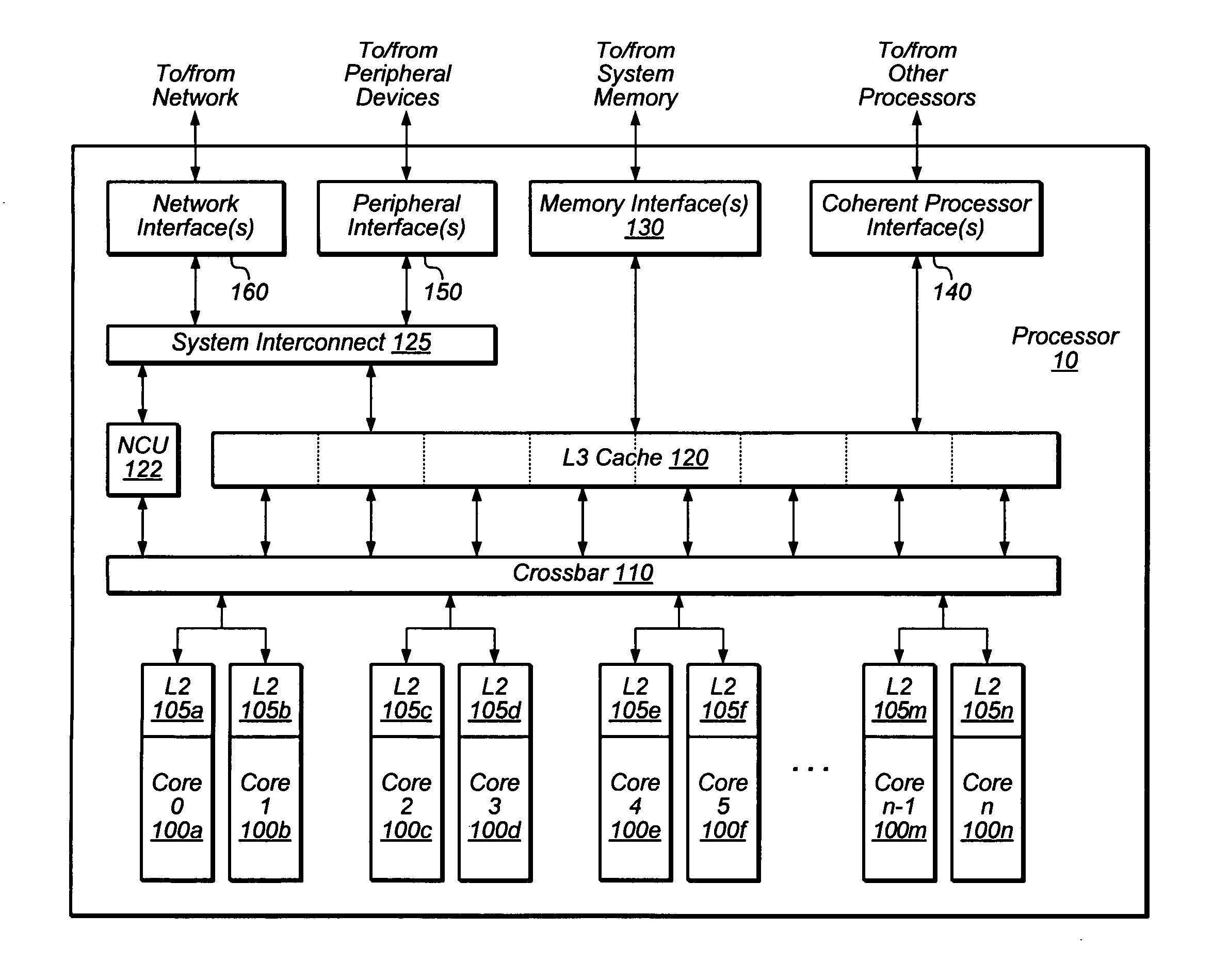
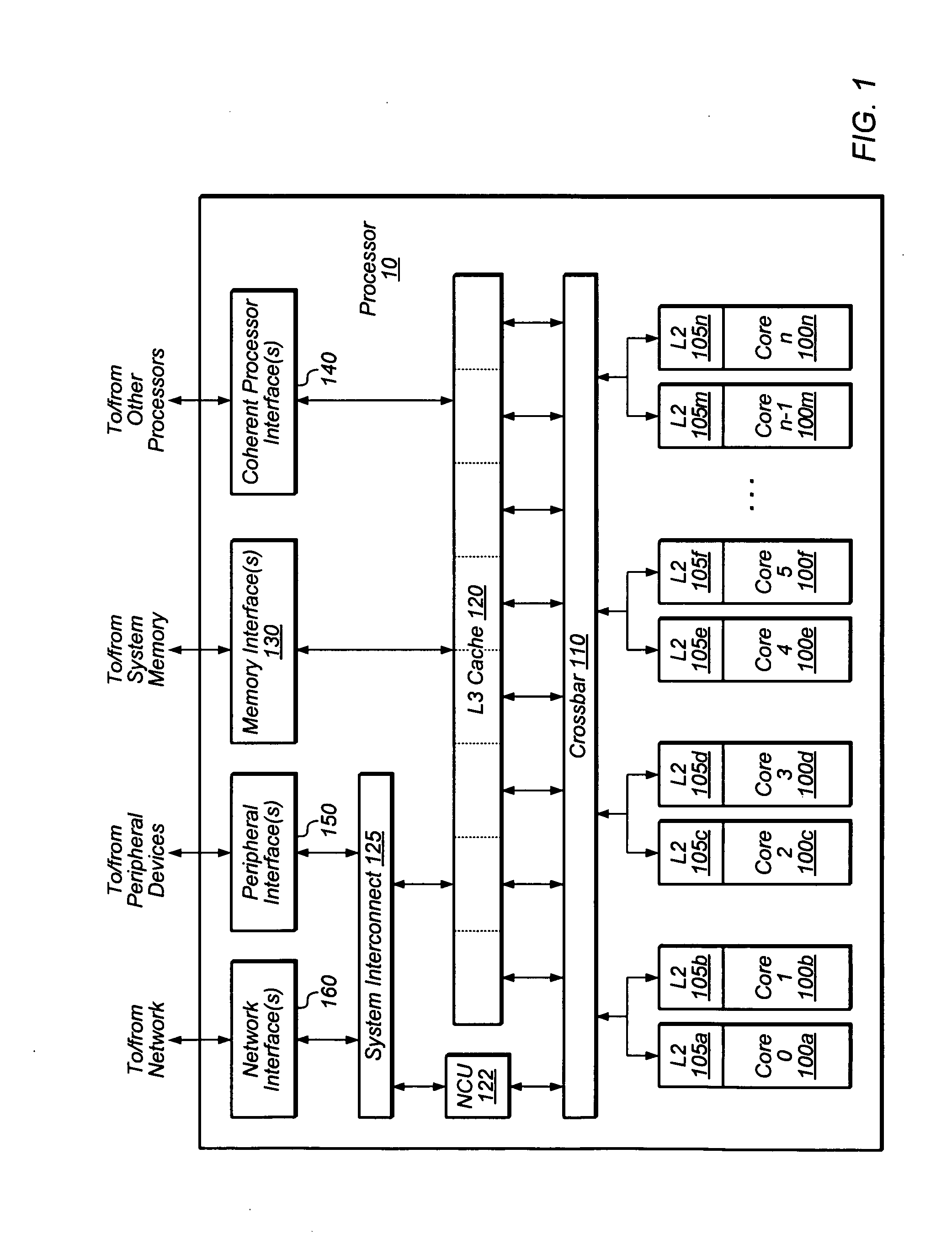
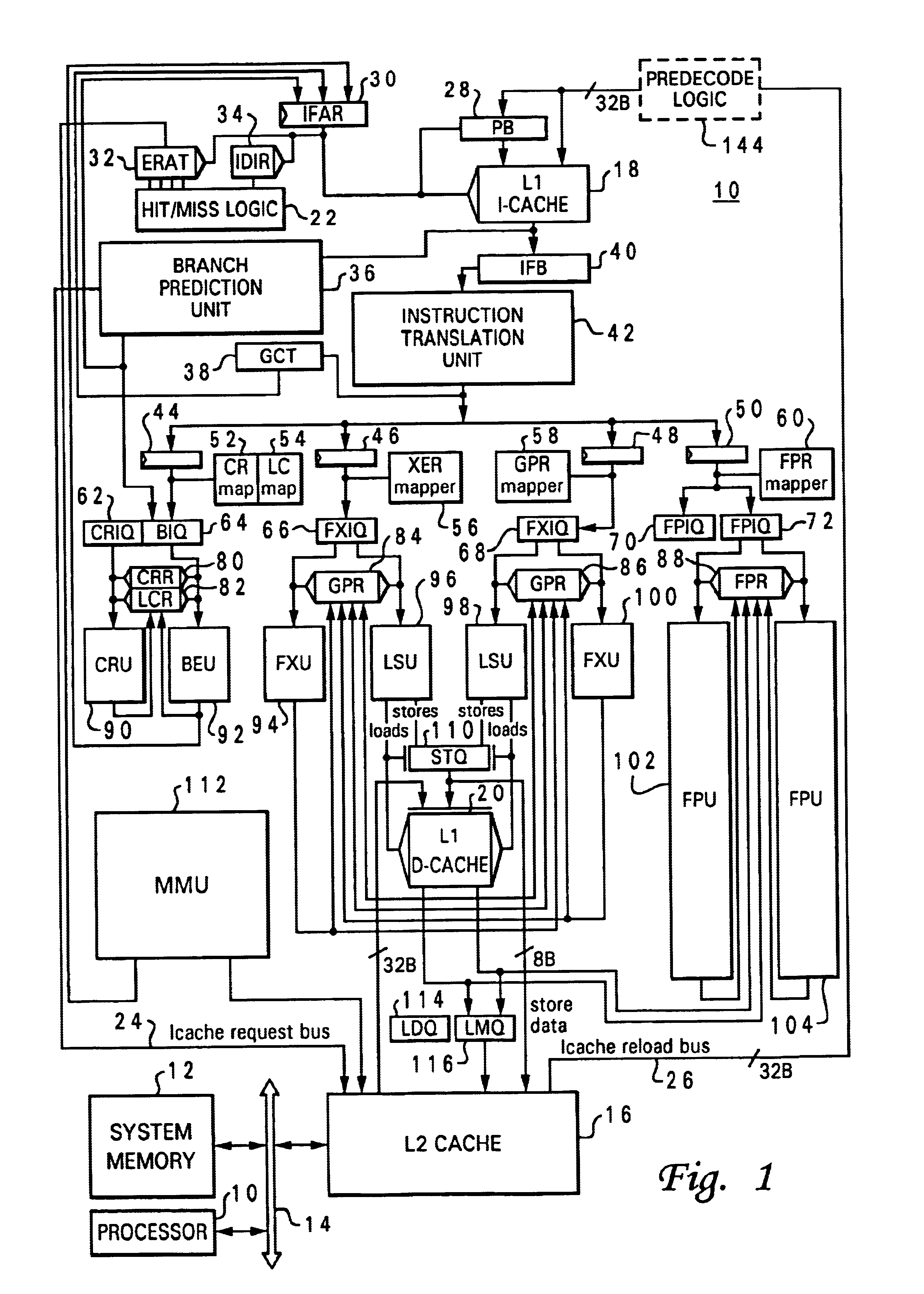
In computer engineering, out-of-order execution (or more formally dynamic execution) is a paradigm used in most high-performance central processing units to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted. In this paradigm, a processor executes instructions in an order governed by the availability of input data and execution units, rather than by their original order in a program. In doing so, the processor can avoid being idle while waiting for the preceding instruction to complete and can, in the meantime, process the next instructions that are able to run immediately and independently.
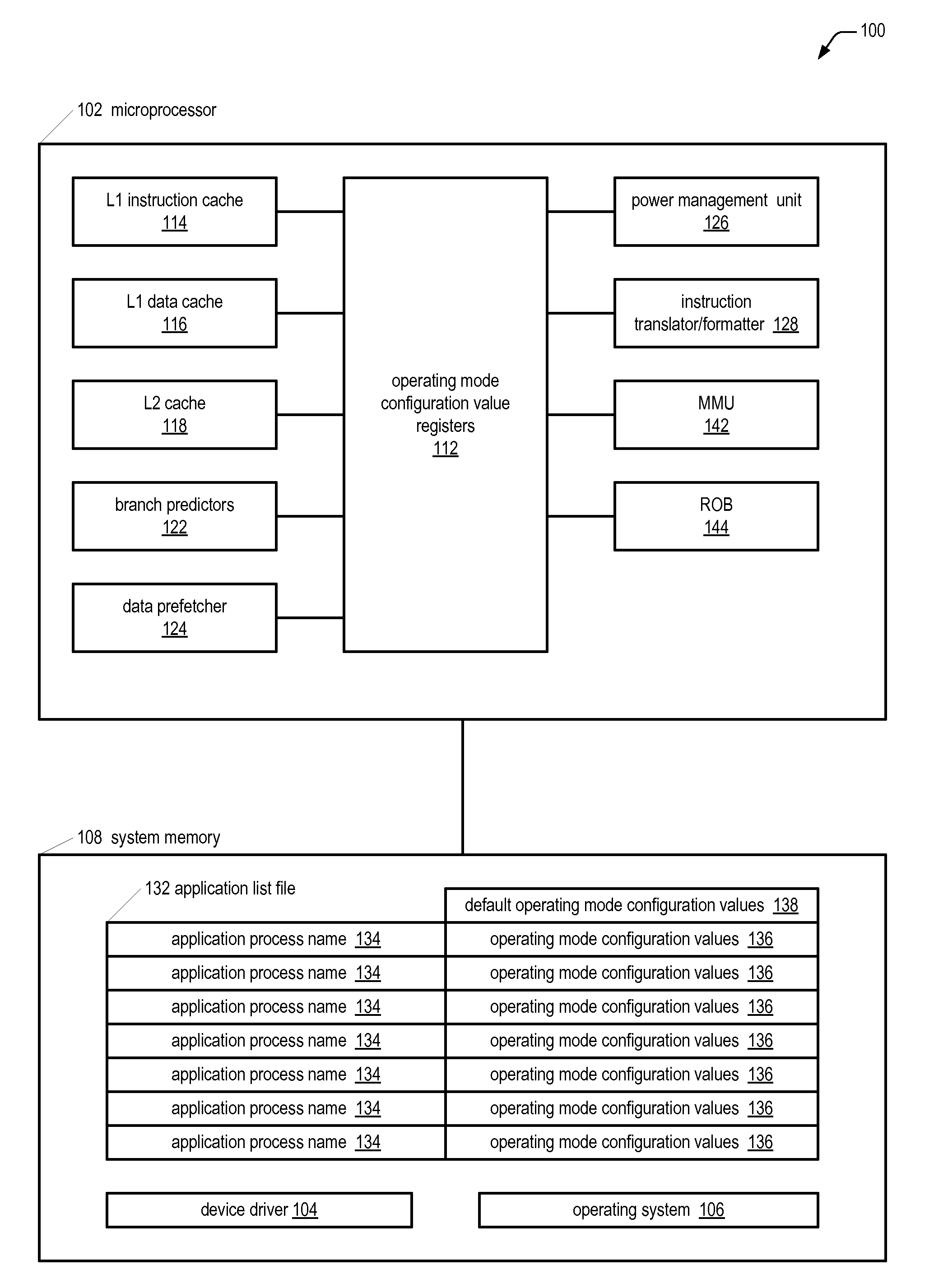
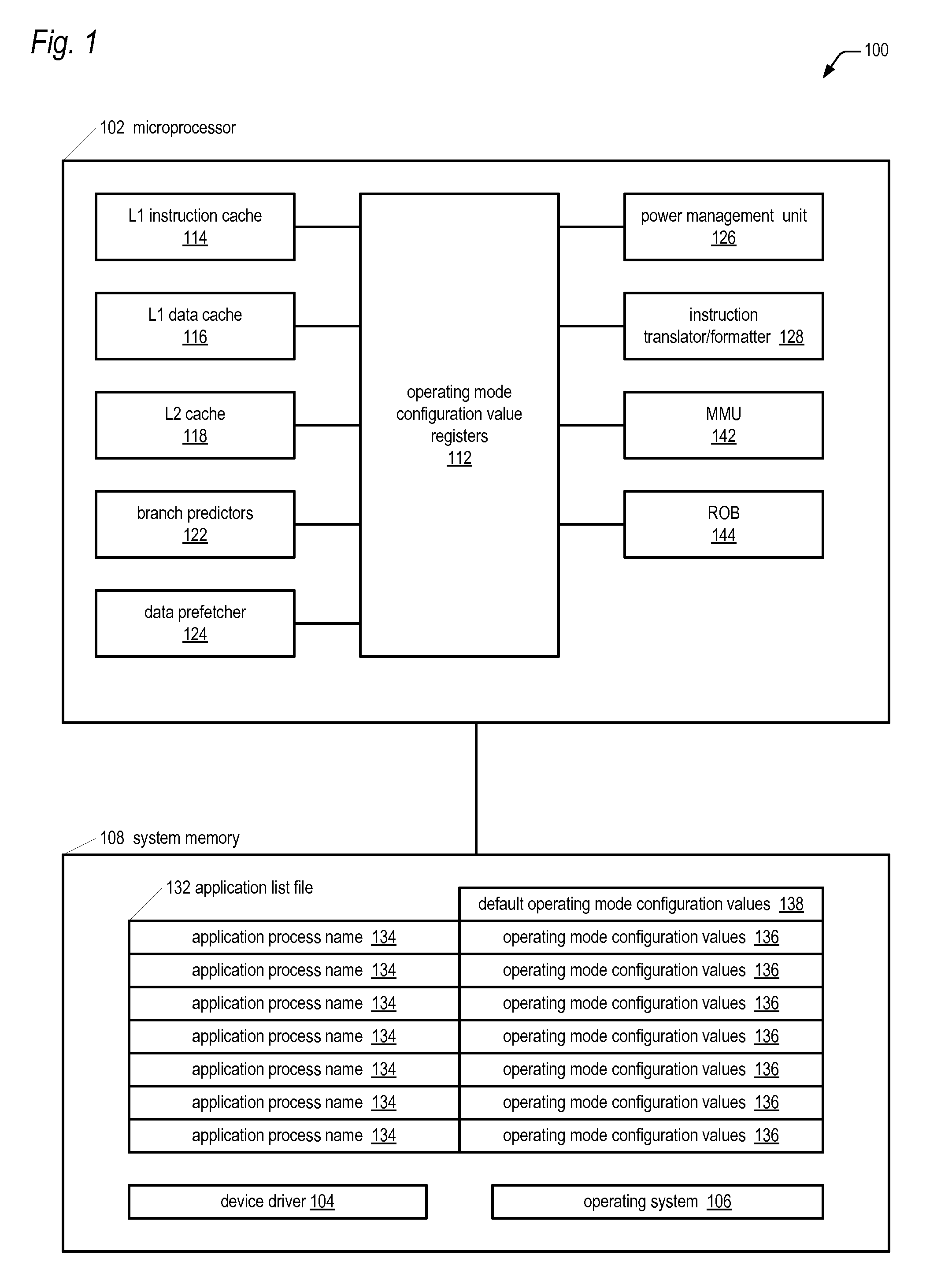
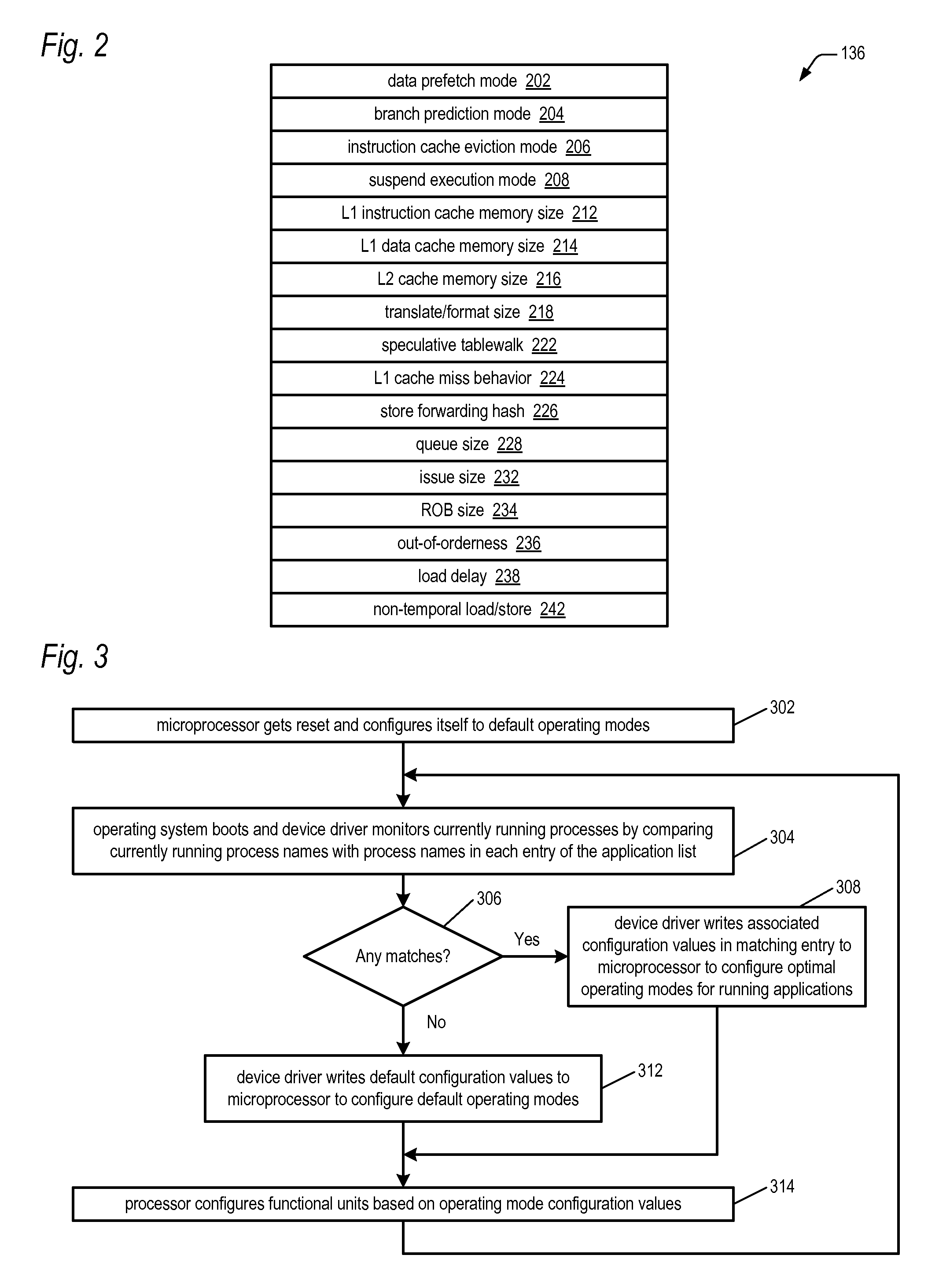
Microprocessor with multiple operating modes dynamically configurable by a device driver based on currently running applications
ActiveUS20100011198A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionRuntime instruction translationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBranch target address cacheApplication software
A computing system includes a microprocessor that receives values for configuring operating modes thereof. A device driver monitors which software applications currently running on the microprocessor are in a predetermined list and responsively dynamically writes the values to the microprocessor to configure its operating modes. Examples of the operating modes the device driver may configure relate to the following: data prefetching; branch prediction; instruction cache eviction; instruction execution suspension; sizes of cache memories, reorder buffer, store / load / fill queues; hashing algorithms related to data forwarding and branch target address cache indexing; number of instruction translation, formatting, and issuing per clock cycle; load delay mechanism; speculative page tablewalks; instruction merging; out-of-order execution extent; caching of non-temporal hinted data; and serial or parallel access of an L2 cache and processor bus in response to an instruction cache miss.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
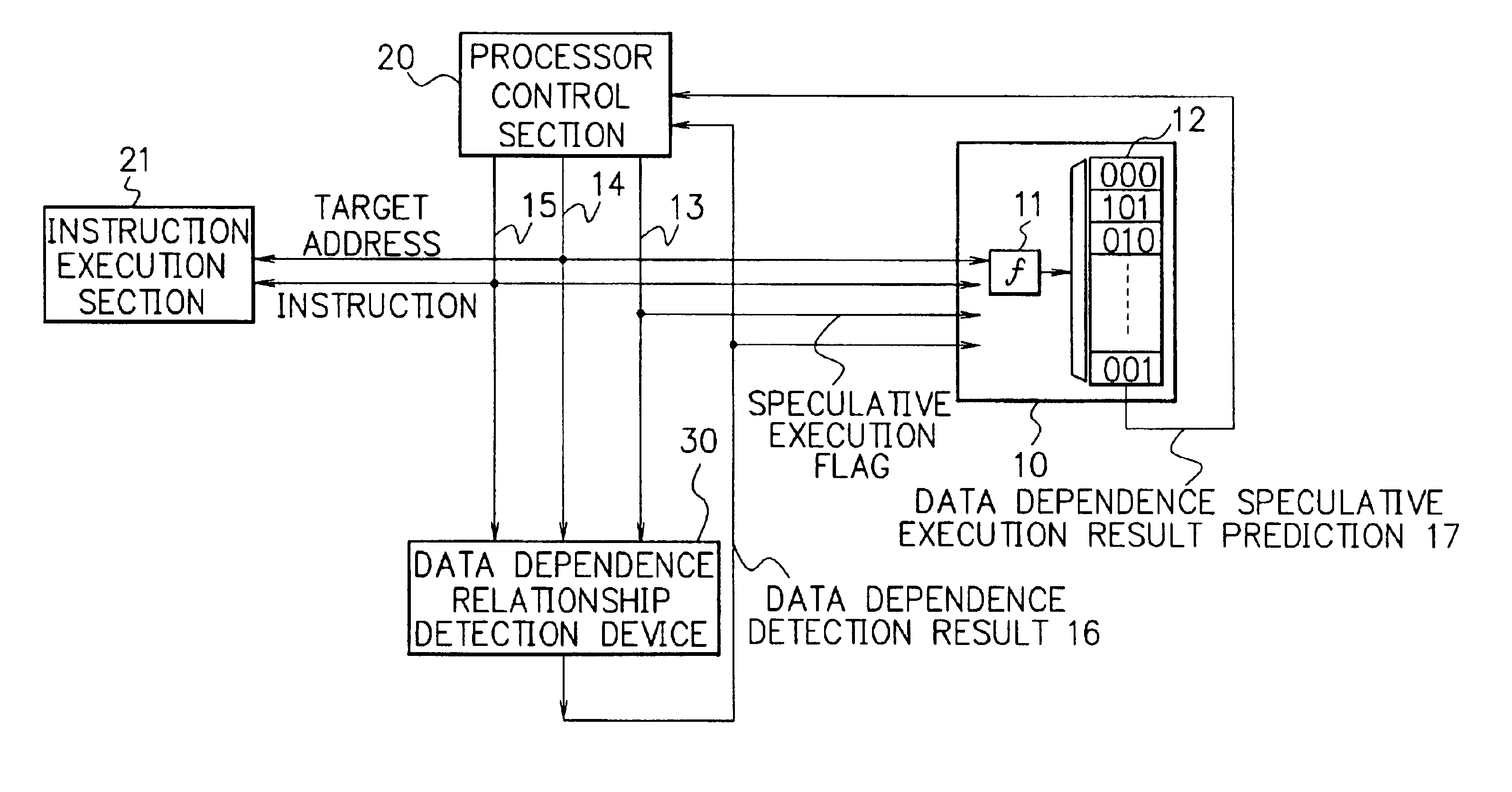
Processor, multiprocessor system and method for speculatively executing memory operations using memory target addresses of the memory operations to index into a speculative execution result history storage means to predict the outcome of the memory operation
InactiveUS6970997B2Low failure rateImprove execution performanceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionMemory addressSpeculative execution
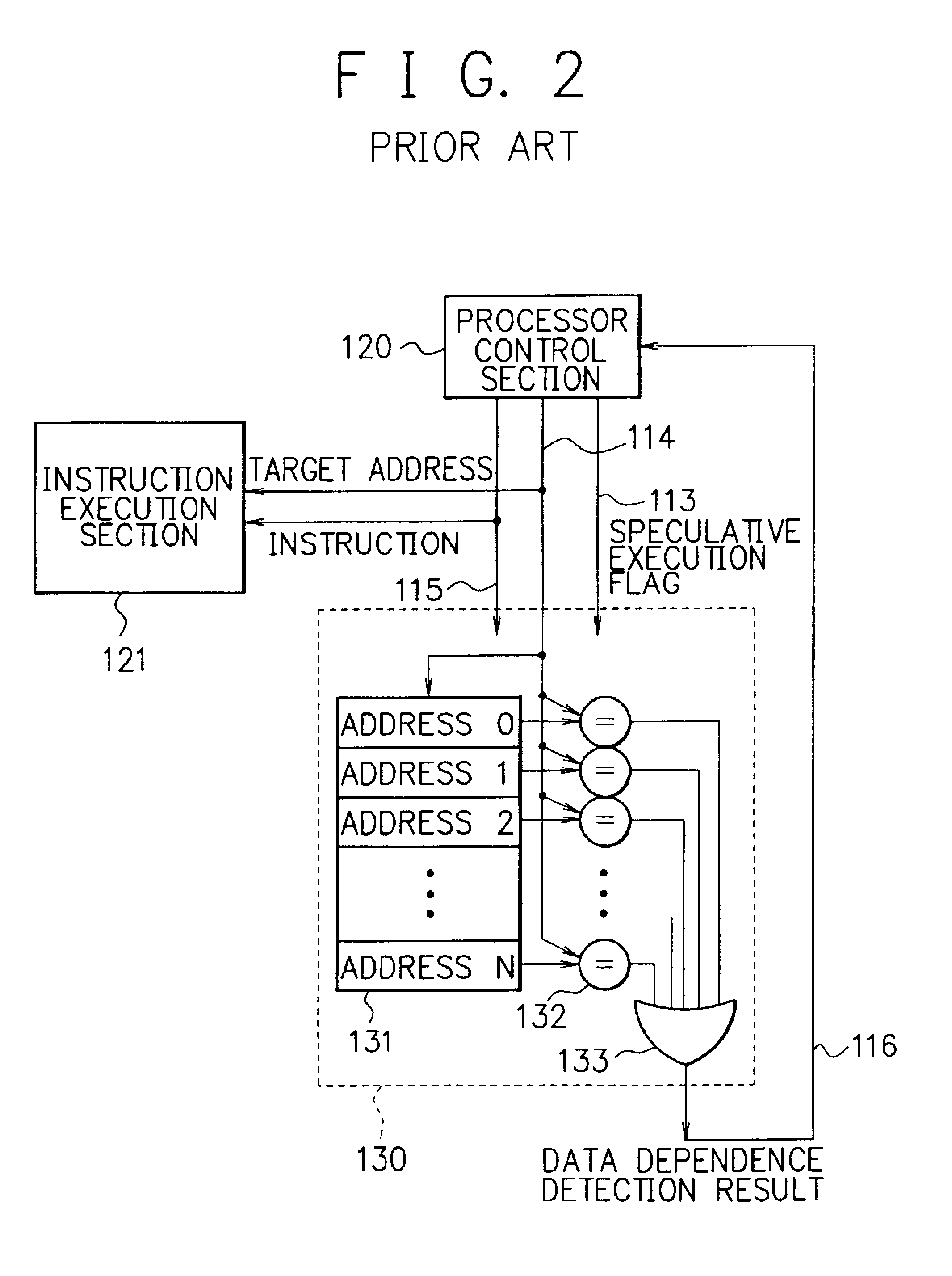
When a processor executes a memory operation instruction by means of data dependence speculative execution, a speculative execution result history table which stores history information concerning success / failure results of the speculative execution of memory operation instructions of the past is referred to and thereby whether the speculative execution will succeed or fail is predicted. In the prediction, the target address of the memory operation instruction is converted by a hash function circuit into an entry number of the speculative execution result history table (allowing the existence of aliases), and an entry of the table designated by the entry number is referred to. If the prediction is “success”, the memory operation instruction is executed in out-of-order execution speculatively (with regard to data dependence relationship between the instructions). If the prediction is “failure”, the speculative execution is canceled and the memory operation instruction is executed later in the program order non-speculatively. Whether the speculative execution of the memory operation instructions has succeeded or failed is judged by detecting the data dependence relationship between the memory operation instructions, and the speculative execution result history table is updated taking the judgment into account.
Owner:NEC CORP
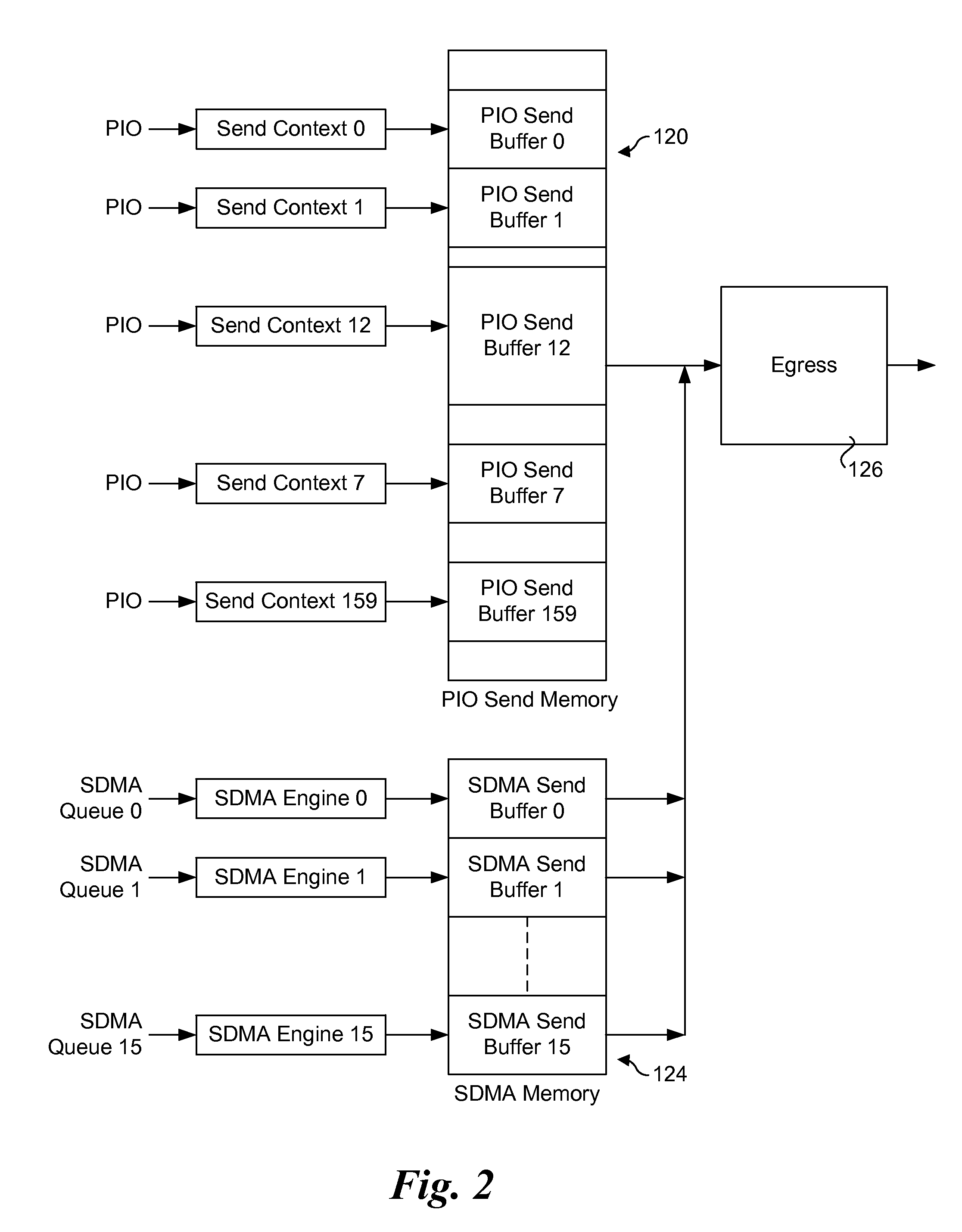
Sending packets using optimized pio write sequences without sfences
ActiveUS20150378737A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationNetwork packetPosted write
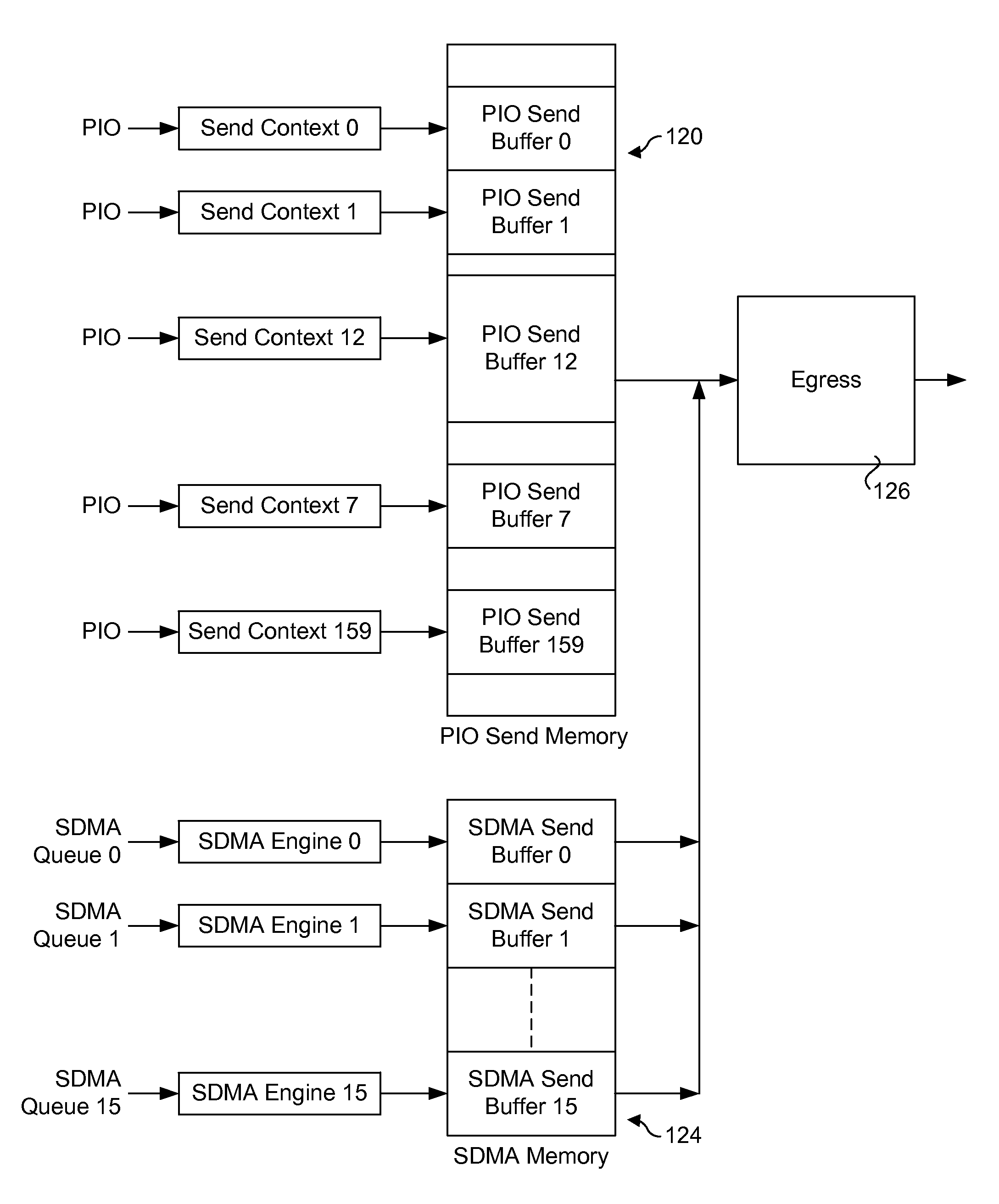
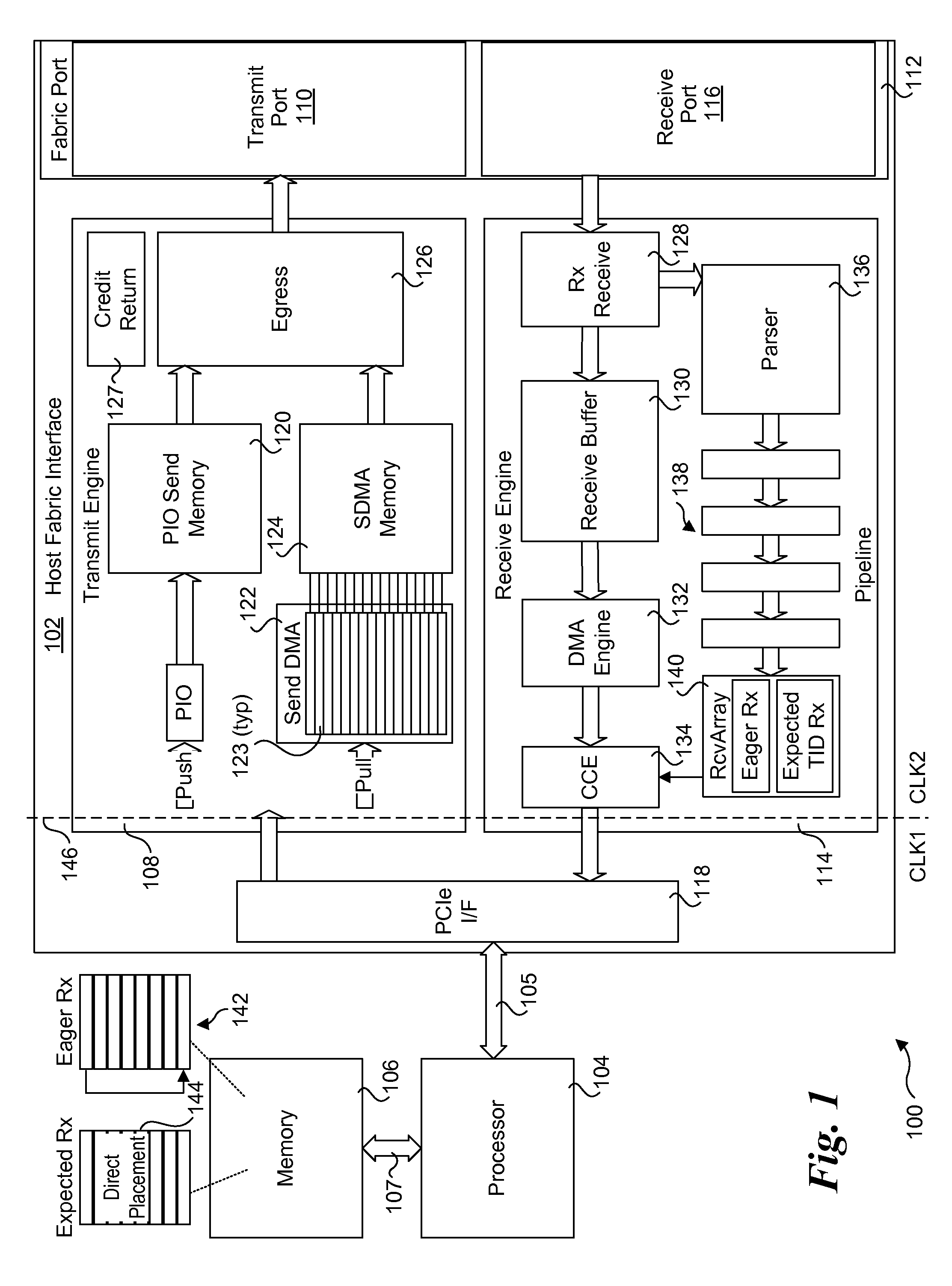
Method and apparatus for sending packets using optimized PIO write sequences without sfences. Sequences of Programmed Input / Output (PIO) write instructions to write packet data to a PIO send memory are received at a processor supporting out of order execution. The PIO write instructions are received in an original order and executed out of order, with each PIO write instruction writing a store unit of data to a store buffer or a store block of data to the store buffer. Logic is provided for the store buffer to detect when store blocks are filled, resulting in the data in those store blocks being drained via PCIe posted writes that are written to send blocks in the PIO send memory at addresses defined by the PIO write instructions. Logic is employed for detecting the fill size of packets and when a packet's send blocks have been filled, enabling the packet data to be eligible for egress.
Owner:INTEL CORP
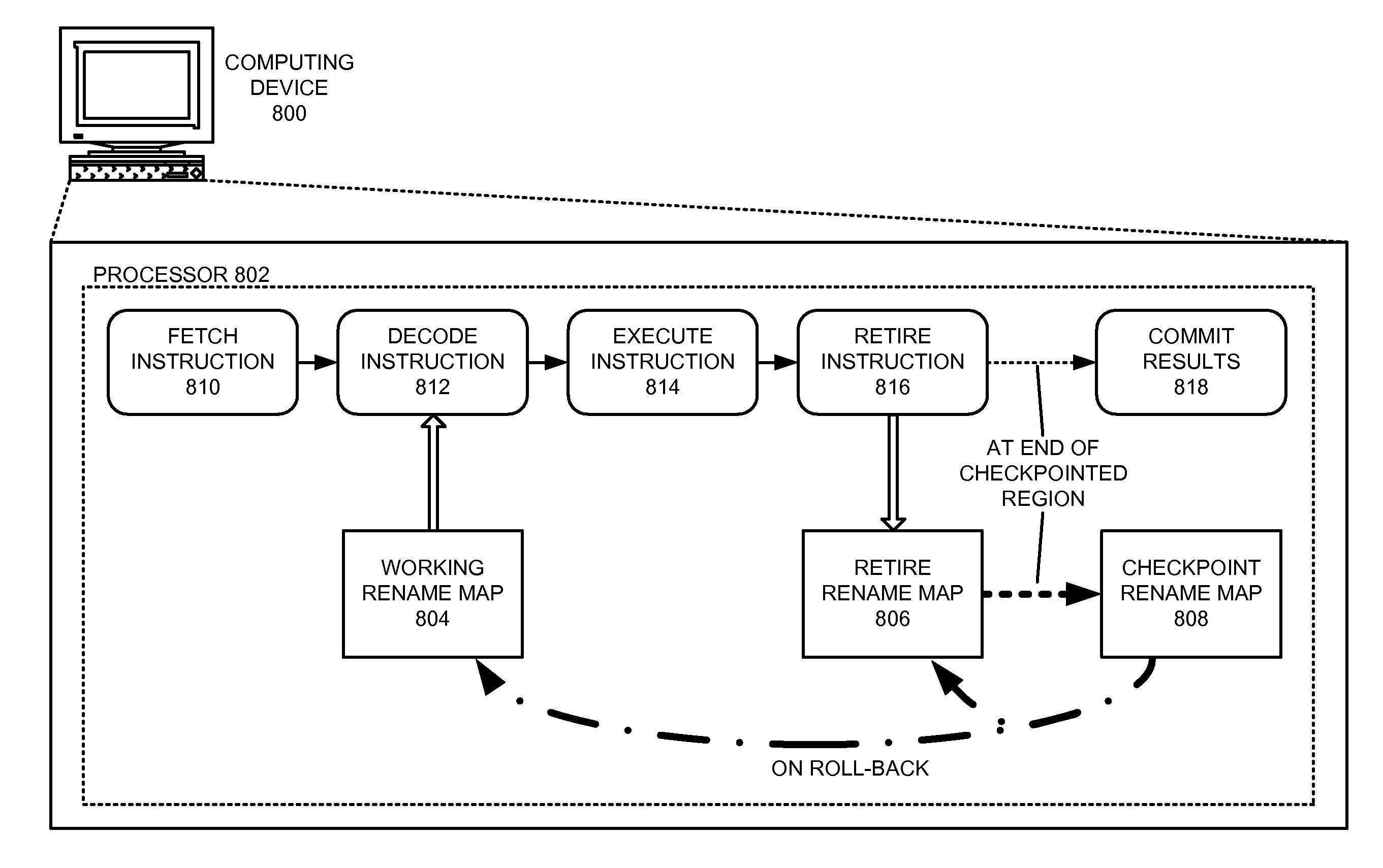
Using register rename maps to facilitate precise exception semantics
ActiveUS20100153690A1Facilitates precise exception semantics for a virtual machineEasy to implementDigital computer detailsMemory systemsSemanticsOut-of-order execution
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates precise exception semantics. The system includes a processor that uses register rename maps to support out-of-order execution, where the register rename maps track mappings between native architectural registers and physical registers for a program executing on the processor. These register rename maps include: 1) a working rename map that maps architectural registers associated with a decoded instruction to corresponding physical registers; 2) a retire rename map that tracks and preserves a set of physical registers that are associated with retired instructions; and 3) a checkpoint rename map that stores a mapping between a set of architectural registers and a set of physical registers for a preceding checkpoint in the program. When the program signals an exception, the processor uses the checkpoint rename map to roll back program execution to the preceding checkpoint.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Wavescalar architecture having a wave order memory
InactiveUS20050166205A1Reduce communication costsMaximizing processor utilizationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram synchronisationTerm memoryLow complexity
A dataflow instruction set architecture and execution model, referred to as WaveScalar, which is designed for scalable, low-complexity / high-performance processors, while efficiently providing traditional memory semantics through a mechanism called wave-ordered memory. Wave-ordered memory enables “real-world” programs, written in any language, to be run on the WaveScalar architecture, as well as any out-of-order execution unit. Because it is software-controlled, wave-ordered memory can be disabled to obtain greater parallelism. Wavescalar also includes a software-controlled tag management system.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
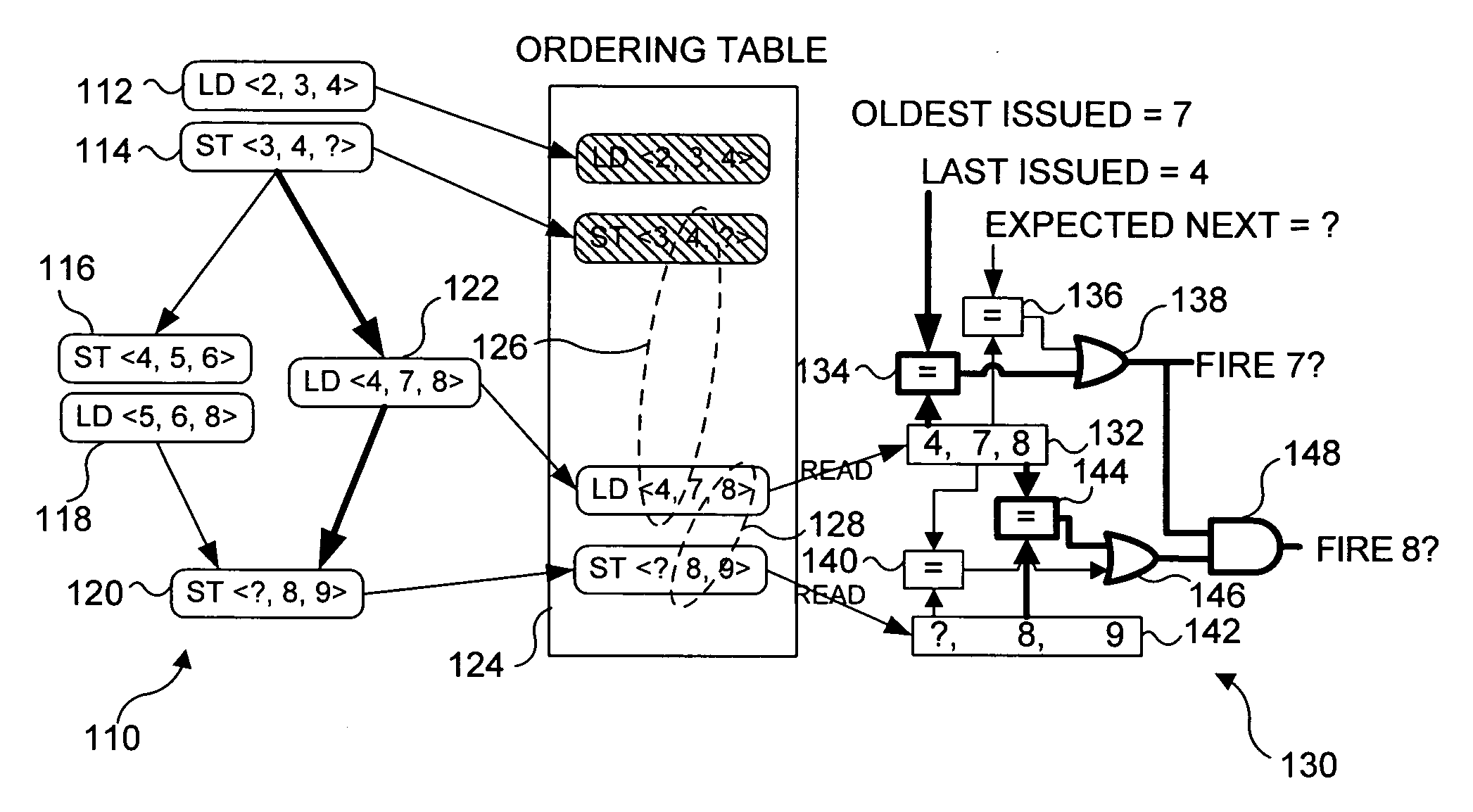
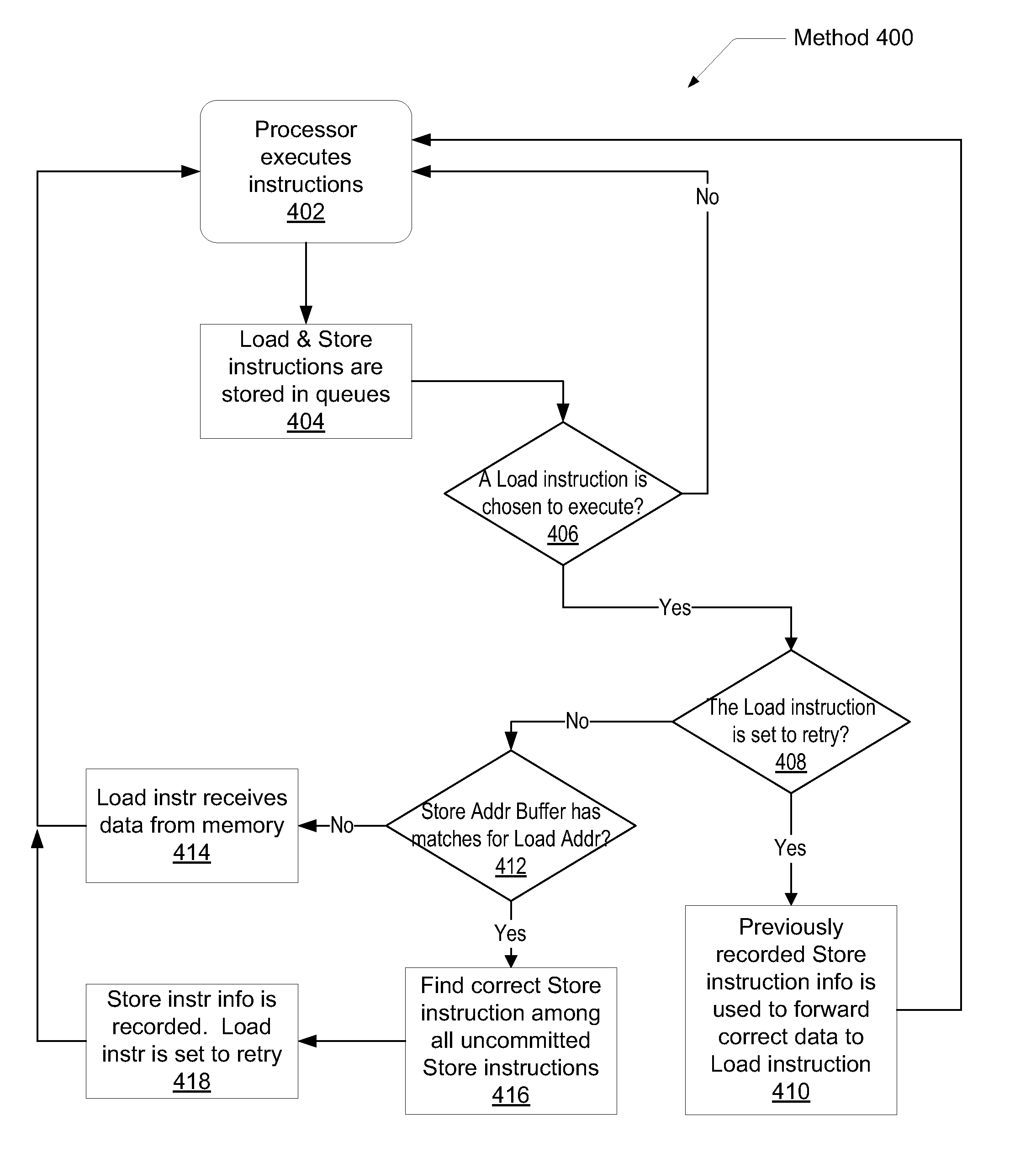
System and method of load-store forwarding
ActiveUS20090037697A1Improve processor performanceImprove performanceDigital computer detailsMemory systemsLoad instructionStore and forward
A system and method for data forwarding from a store instruction to a load instruction during out-of-order execution, when the load instruction address matches against multiple older uncommitted store addresses or if the forwarding fails during the first pass due to any other reason. In a first pass, the youngest store instruction in program order of all store instructions older than a load instruction is found and an indication to the store buffer entry holding information of the youngest store instruction is recorded. In a second pass, the recorded indication is used to index the store buffer and the store bypass data is forwarded to the load instruction. Simultaneously, it is verified if no new store, younger than the previously identified store and older than the load has not been issued due to out-of-order execution.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
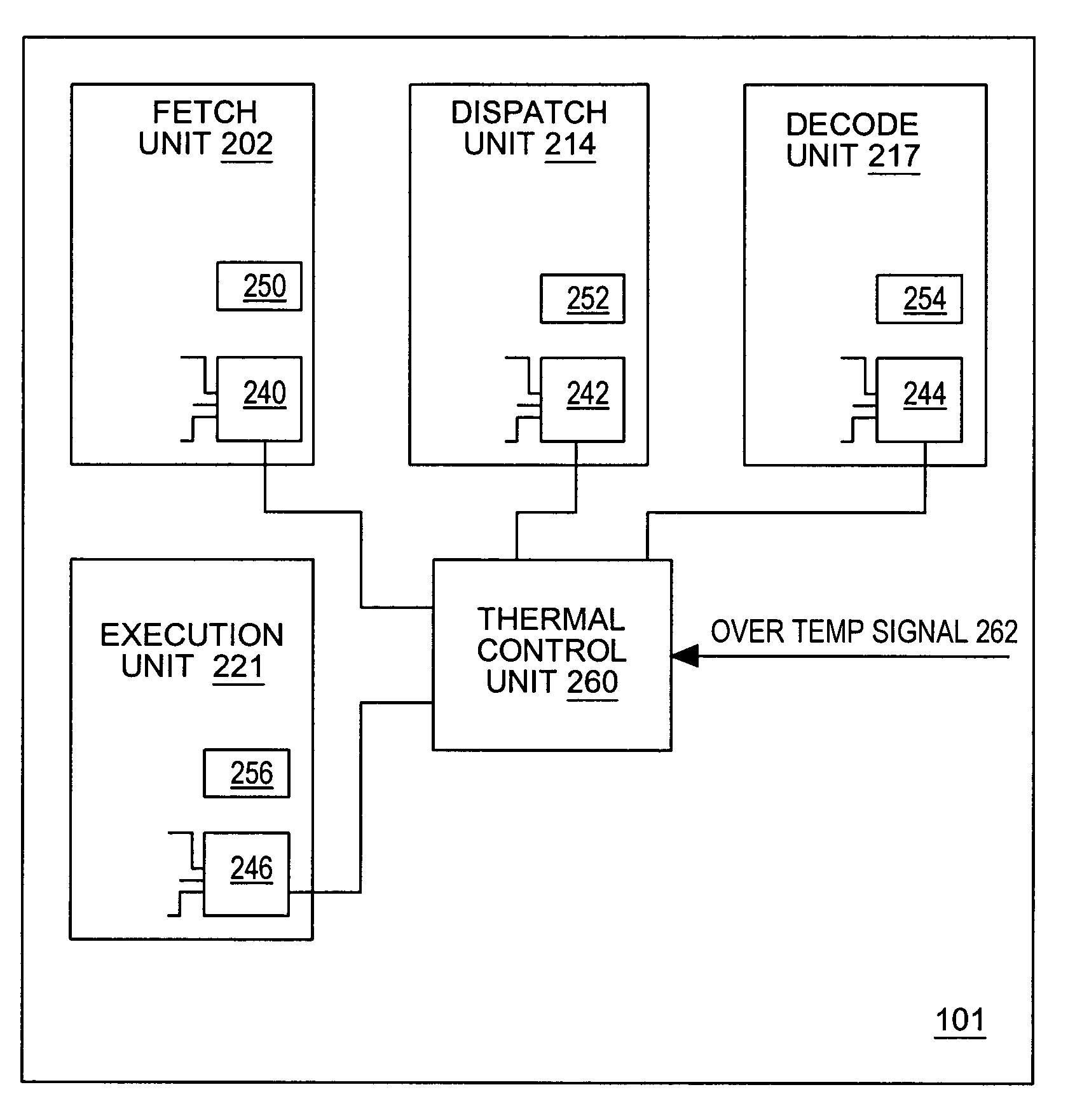
Performance throttling for temperature reduction in a microprocessor
InactiveUS7051221B2Reducing processor activitySlowing processor performanceEnergy efficient ICTInstruction analysisPower savingOut-of-order execution
A microprocessor includes a functional block having dynamic power savings circuitry, a functional block control circuit, and a thermal control unit. The functional block control circuits are capable of altering performance characteristics of their associated functional blocks automatically upon detecting an over temperature condition. The thermal control unit receives an over-temperature signal indicating a processor temperature exceeding a threshold and invokes the one or more of the functional block control units in response to the signal. The functional block control units respond to signals from the thermal control unit by reducing processor activity, slowing processor performance, or both. The reduced activity that results causes the dynamic power saving circuitry to engage. The functional block control units can throttle performance by numerous means including reducing the exploitable parallelism within the processor, suspending out-of-order execution, reducing effective resource size, and the like.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance low-power-consumption embedded processor based on command dual-transmission
ActiveCN101526895AImprove parallel processing capabilitiesAchieve leapfrog developmentConcurrent instruction executionPower supply for data processingAssembly lineExecution control
The invention provides a high-performance low-power-consumption embedded processor based on command dual-transmission, comprising a command fetching unit, a two-way decoding unit, a transmitting unit, a command dispatch execution control unit, a command executing unit and a loading / storing unit; wherein the command fetching unit is used for pre-fetching two commands in a single clock cycle and sending the commands into an assembly line; the two-way decoding unit is used for parallelly decoding the two commands in the single clock cycle; the transmitting unit is used for parallelly transmitting the two commands in the single clock cycle; the command dispatch execution control unit is used for dynamically adjusting the command dispatch according to the computing load and controlling execution according to an out-of-order execution mechanism; the command executing unit is used for computing the results of the commands; and the loading / storing unit is used for ensuring that when the commands are absent, sequent commands can successfully occupy the assembly line and visit the data memory on the disc and the data memory outside the disc. The invention can improve the performance of the embedded processor and reduce the cost under the precondition of low power consumption.
Owner:C SKY MICROSYST CO LTD
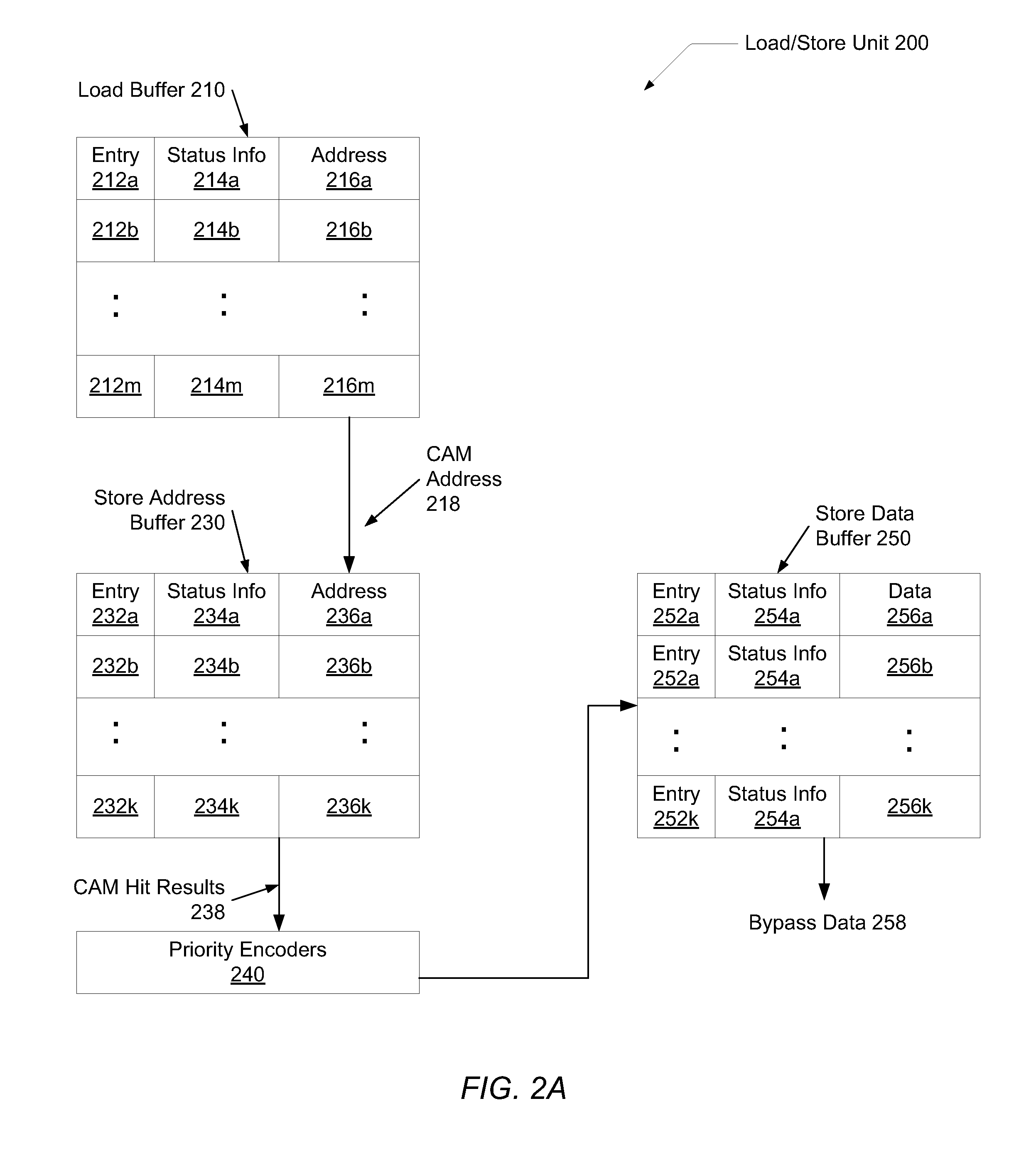
Unordered load/store queue
ActiveUS20090013135A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcedure sequenceStore instruction
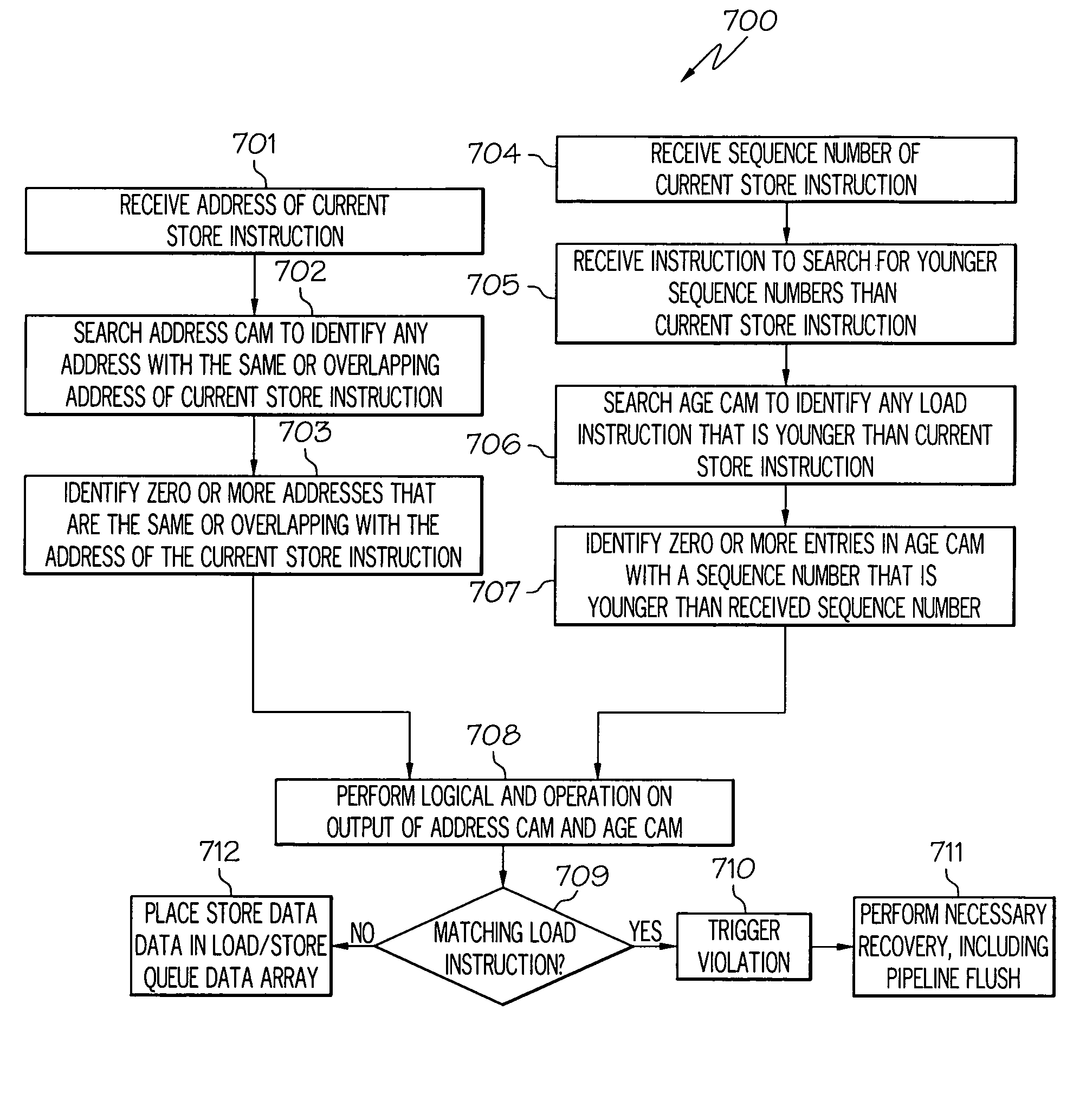
A method and processor for providing full load / store queue functionality to an unordered load / store queue for a processor with out-of-order execution. Load and store instructions are inserted in a load / store queue in execution order. Each entry in the load / store queue includes an identification corresponding to a program order. Conflict detection in such an unordered load / store queue may be performed by searching a first CAM for all addresses that are the same or overlap with the address of the load or store instruction to be executed. A further search may be performed in a second CAM to identify those entries that are associated with younger or older instructions with respect to the sequence number of the load or store instruction to be executed. The output results of the Address CAM and Age CAM are logically ANDed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
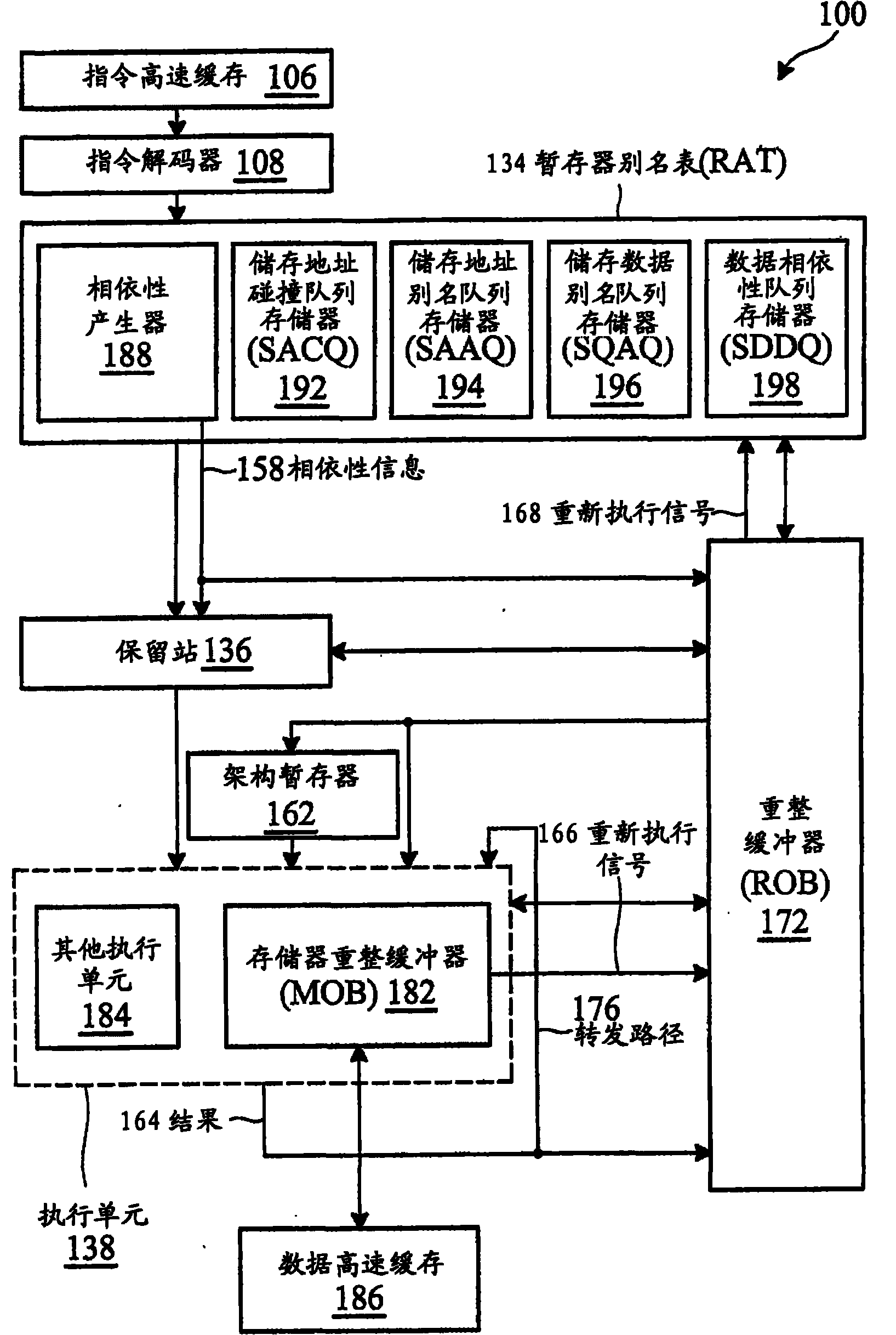
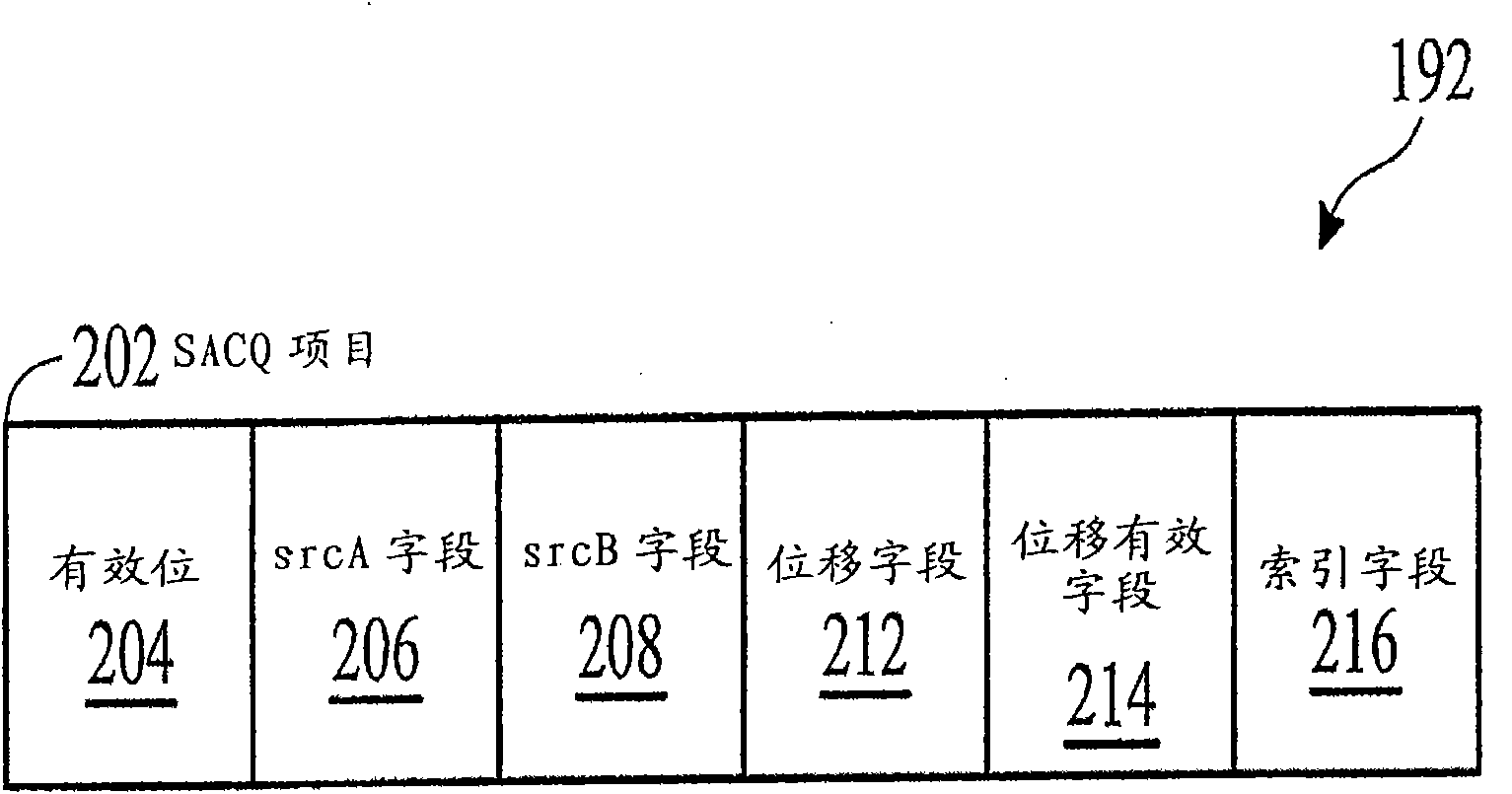
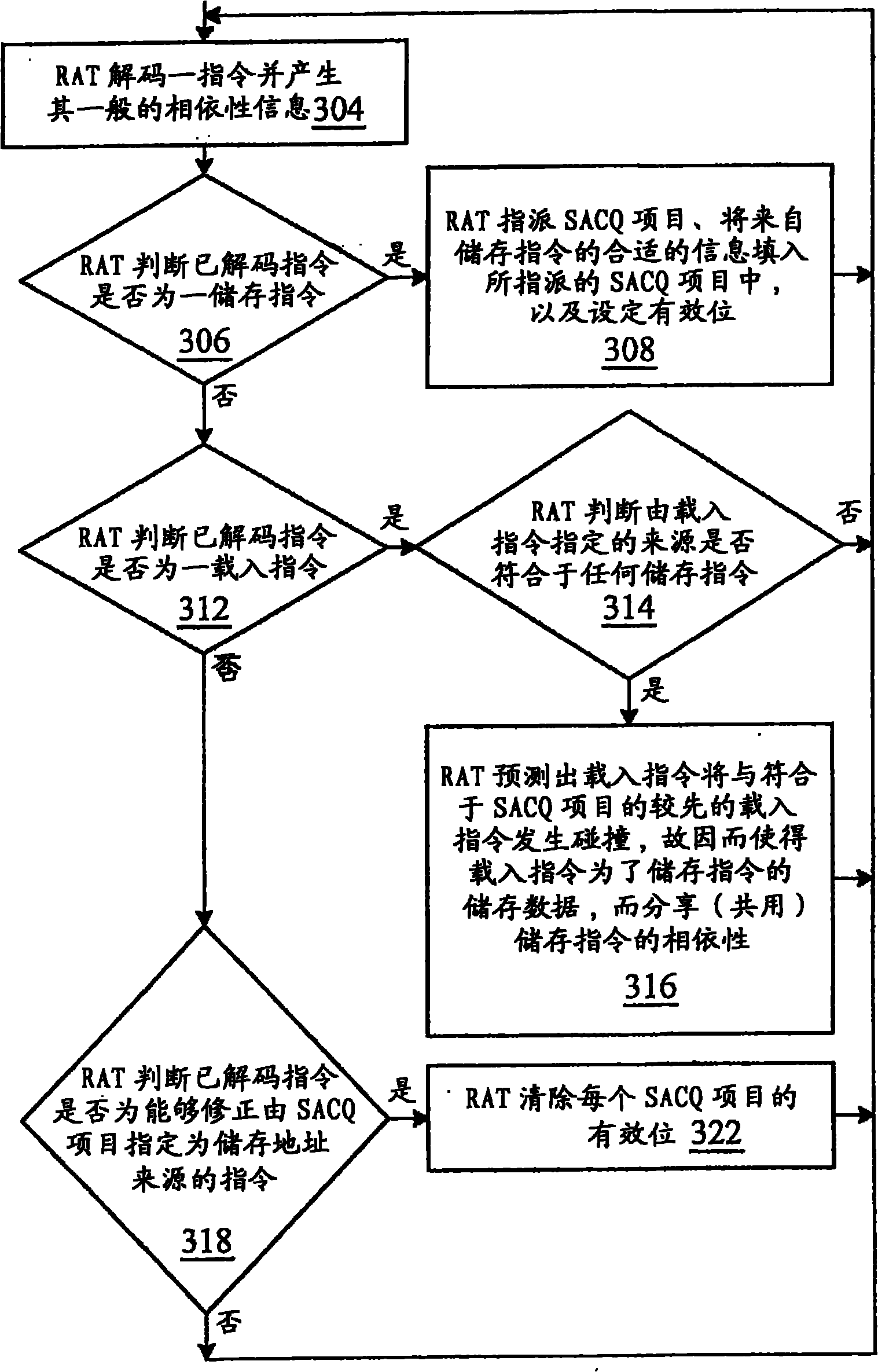
Out-of-order execution control device of built-in processor
InactiveCN101477454AImprove performanceSimplify Bypass LogicConcurrent instruction executionReservation stationProcessor register
The invention relates to a device of an embedded processor, which can control the out-of-order execution. The device comprises a transmit unit, a reservation station register unit and an execution control unit. The transmit unit is used for storing a decoded instruction on a pipeline register, and sending an instruction in a single-clock-cycle manner; the reservation station register unit is used for temporarily storing an instruction for generating for generating a pause when the sent instruction generates a pause because of the related conflict of write / read data, and conducting the bypass monitoring on operands; the execution control unit is used for monitoring the working condition of each execution unit in a real time manner, and dynamically distributing the instruction in the reservation station register unit or the current transmitted instruction according to the information returned by each execution unit. The invention has the advantages of simple design, easy realization and remarkable promotion of the performance of the embedded processor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device and method for testing a device through resolution of data into atomic operations
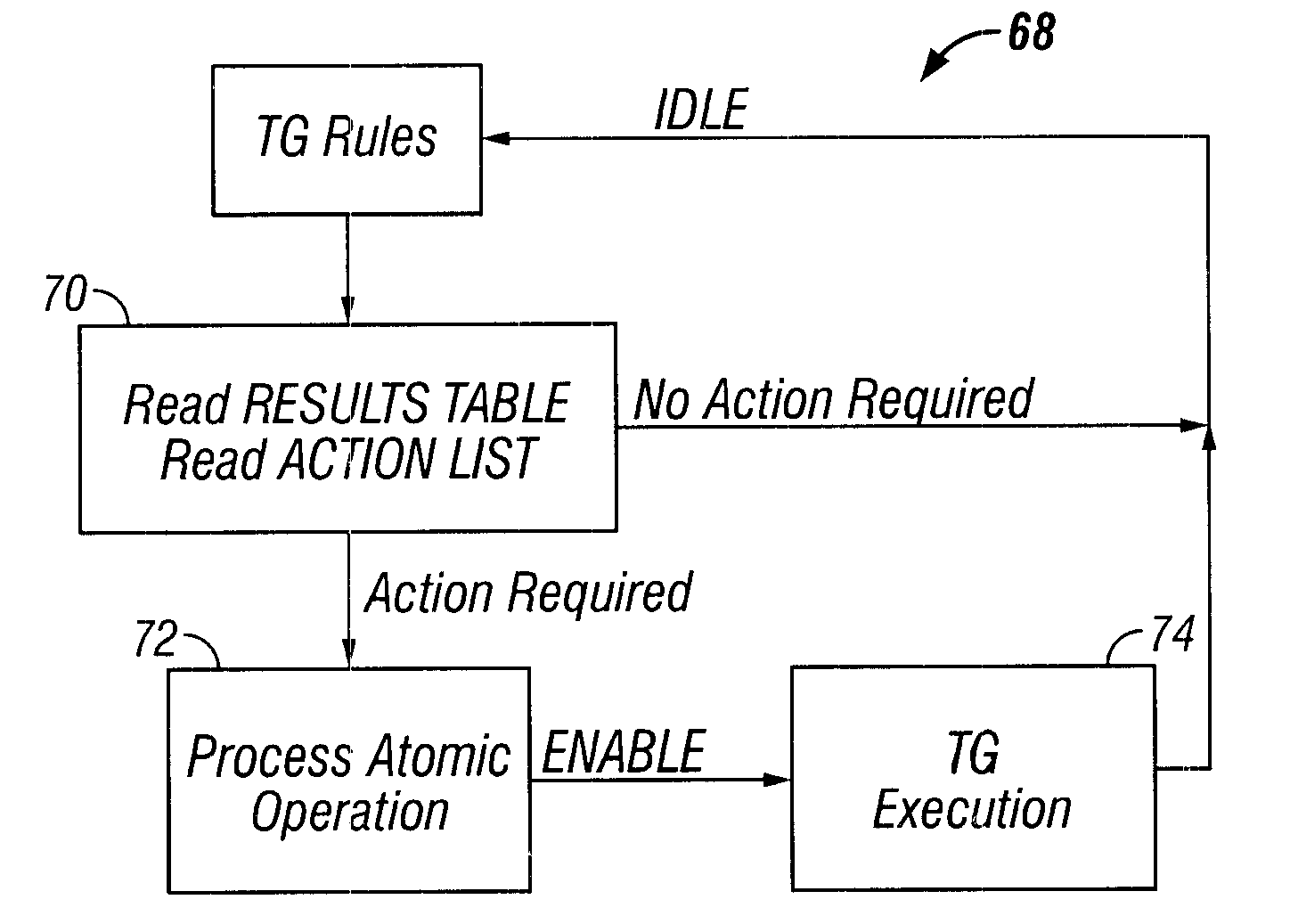
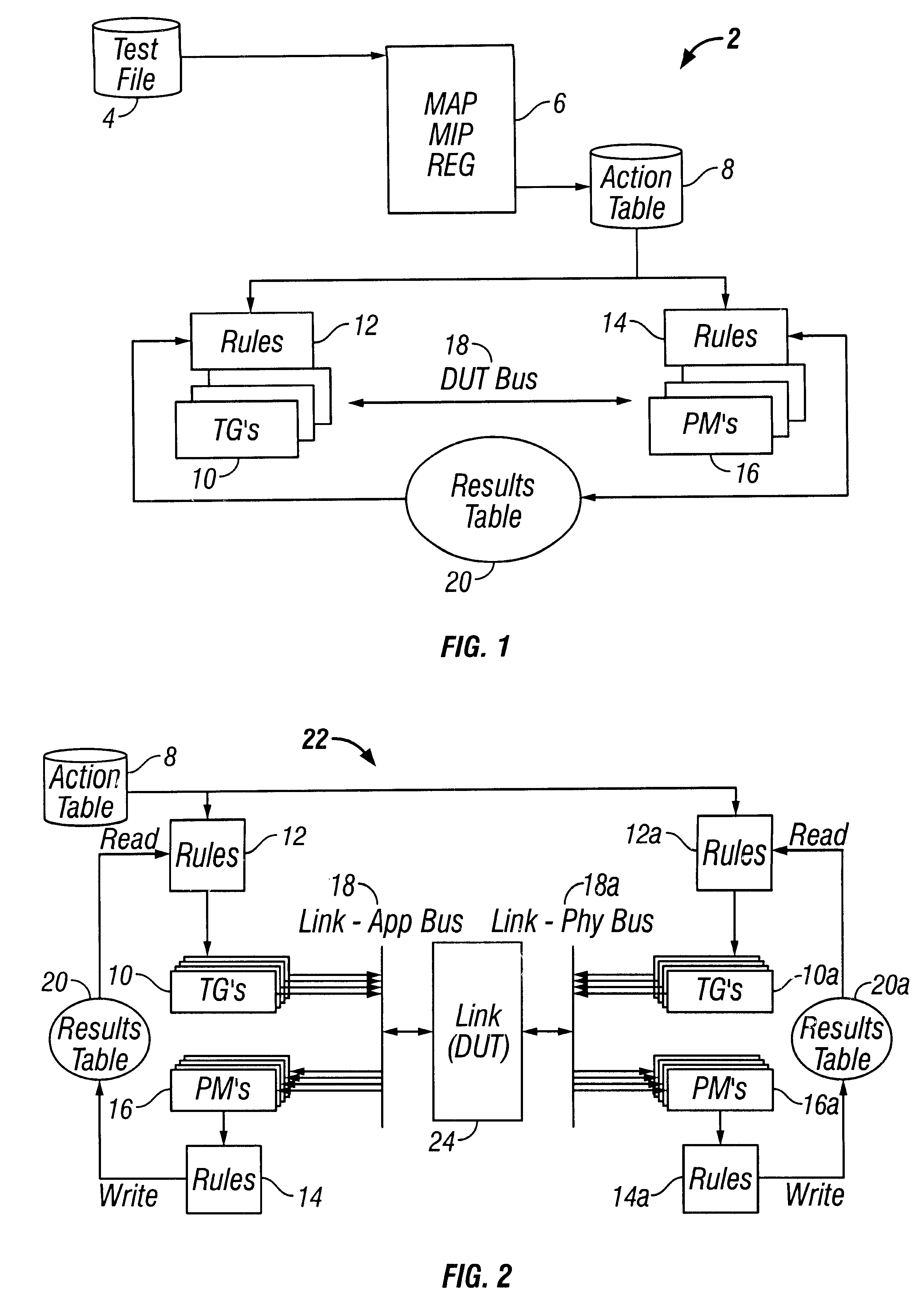
InactiveUS6457152B1Improve throughputElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionClosed loopVerilog
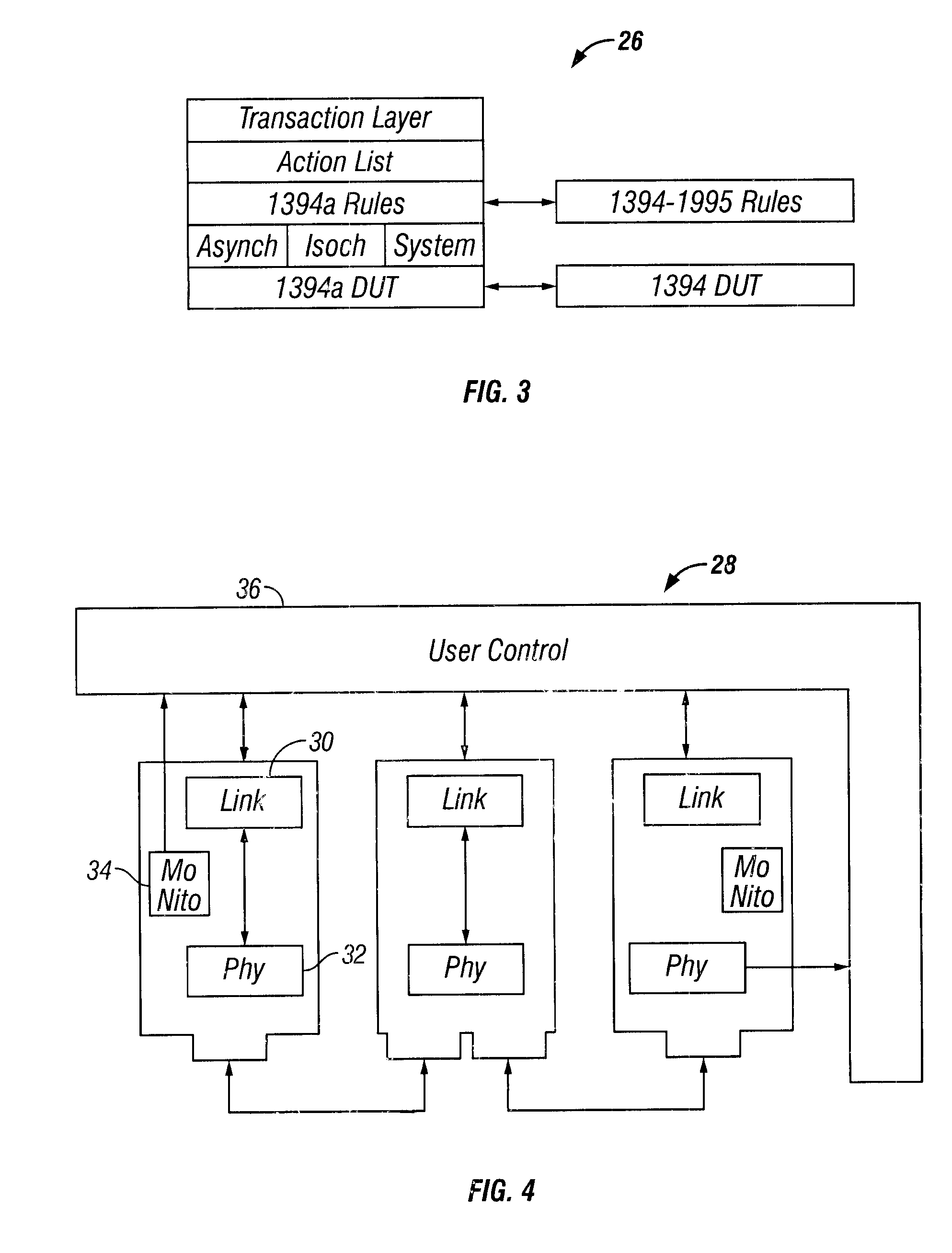
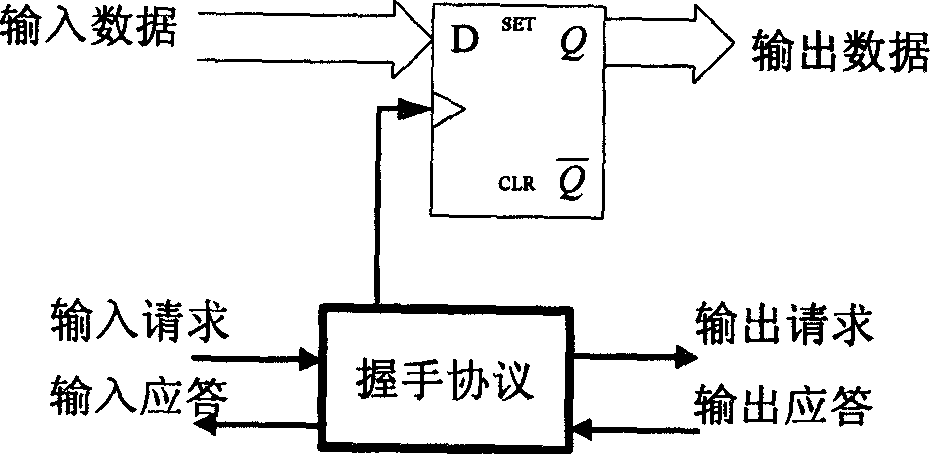
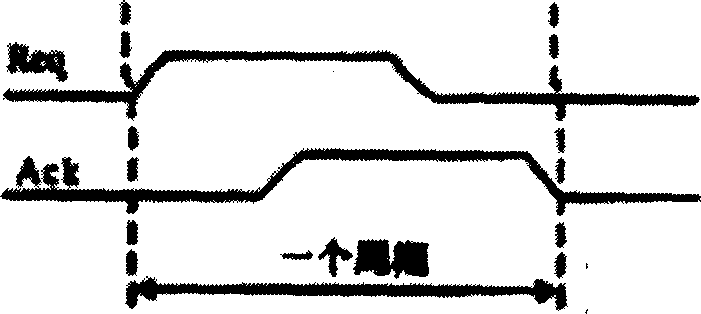
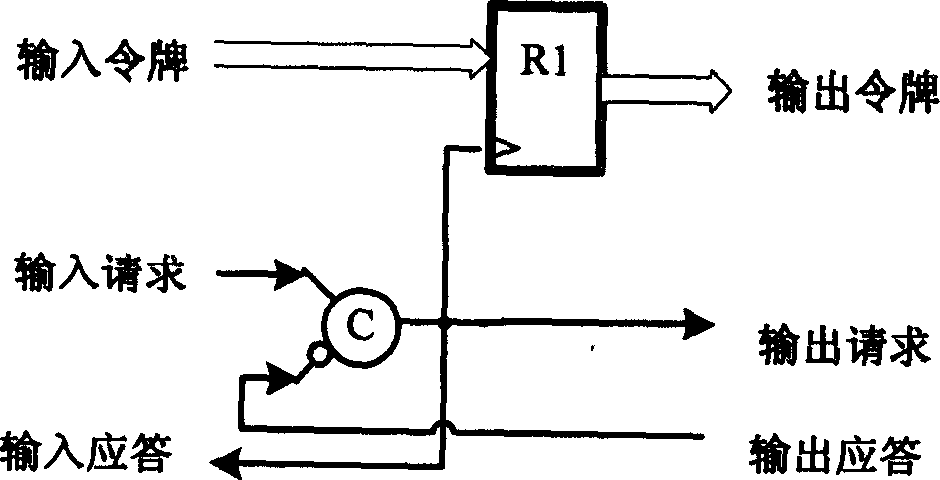
A method of testing a device includes monitoring an output of the device, wherein the output is generated by the device in response to an applied test command; and resolving the output into atomic operations, wherein the atomic operations are substantially the smallest constituent operations which are substantially independent of the device. The method is used to provide a simple, comprehensive test environment that effectively tests 1394a and 1394-1995 designs, for example, in Verilog. The test environment contains rules which completely characterize the behavior of different 1394 bus protocols as defined by the IEEE specifications. The test environment provides portability between different devices under test and between different protocols, automated closed-loop reconciliation of test commands and protocol requirements, topology independence, and out-of-order execution of instructions or relative sequencing. The test environment further allows failure injection, and separate and independent design of the device and a test system.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
AES encrypted circuit structure for data stream executed in desequencing
InactiveCN1761185AEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesData streamComputer architecture
Structure of Rijindael encrypted circuit of executing in desequencing belongs to cipher IC in area of resisting analytical attack of difference power consumption. Circuit structure integrated in a chip contains the input part and the output part to accomplish expansion and expansion loop of cryptographic-key including channel switch unit, registers of initial cryptographic-key, AK temporary storage unit of arithmetic unit for expansion of cryptographic-key, and matching check unit. Circle transforming loop for converting circled cryptographic-key includes switch unit for circled updating channel, AddKey arithmetic unit, EU arithmetic unit, AK temporary storage unit and relevant check unit. Using bit-by-bit hybrid operation, row shift operation, circled iterated operation etc for circled cryptographic-key and information of state obtains cipher text, which is output through output part. The invention lowers 66úÑ difference power consumption so as to raise difficulty of attack.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
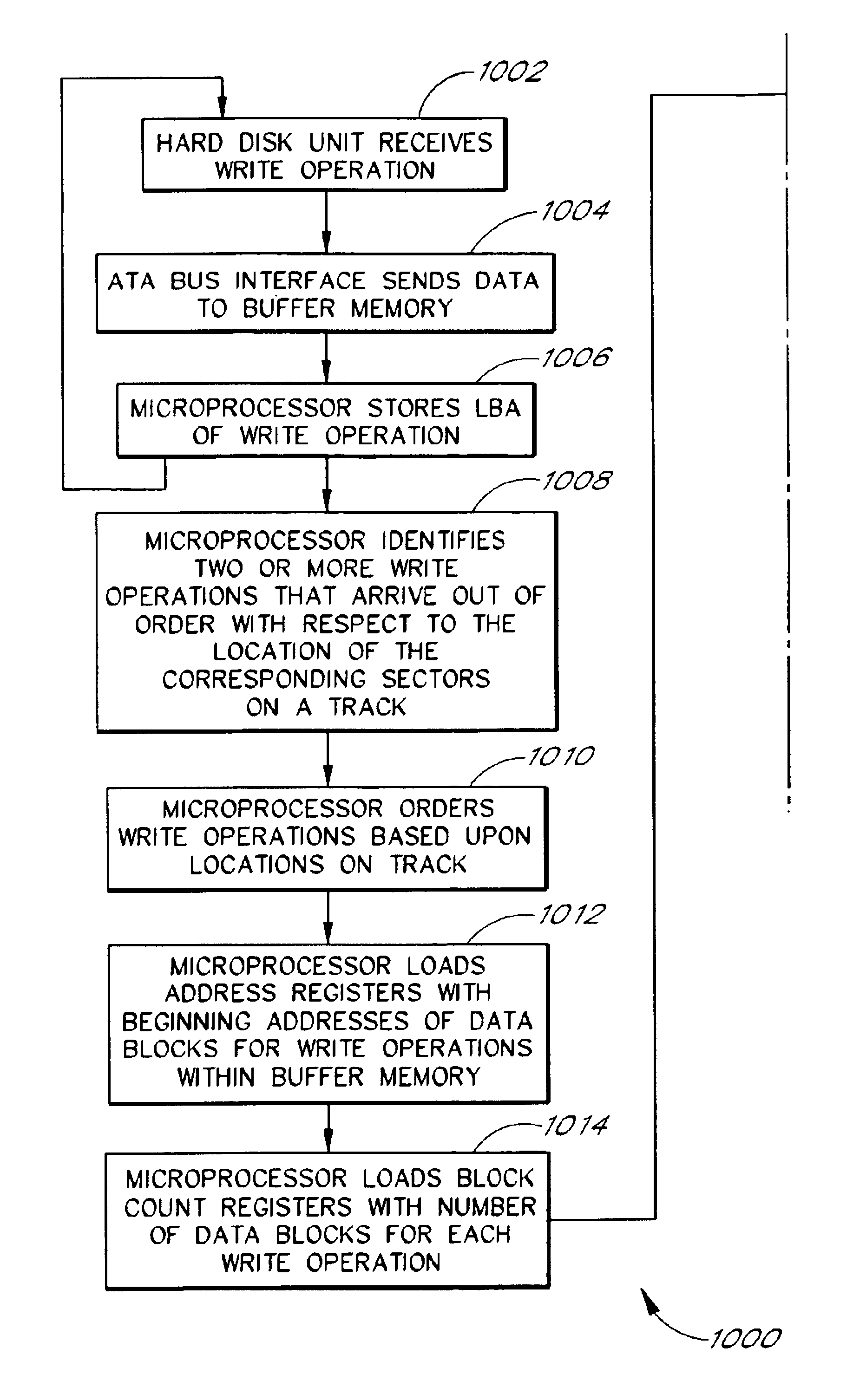
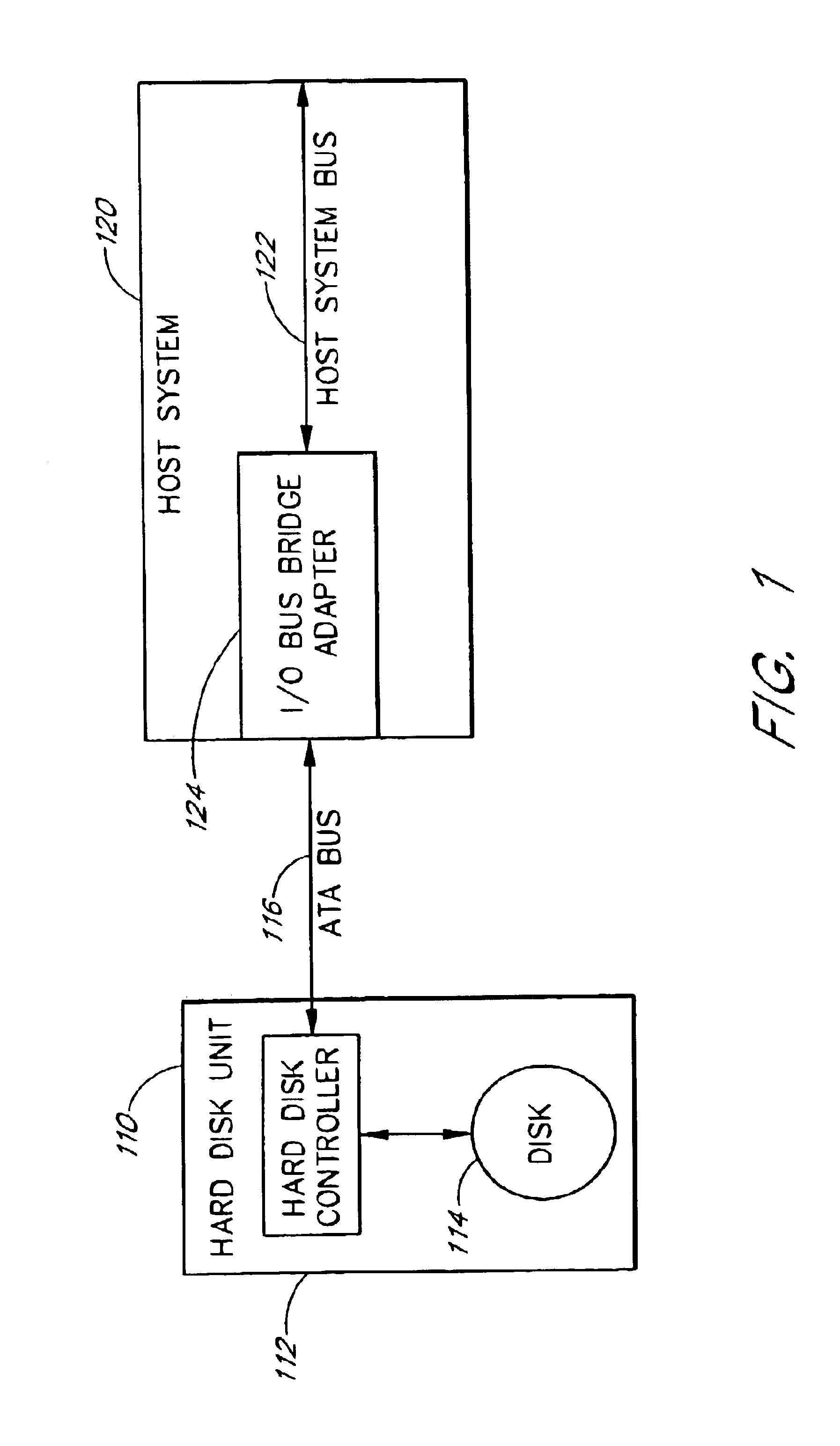
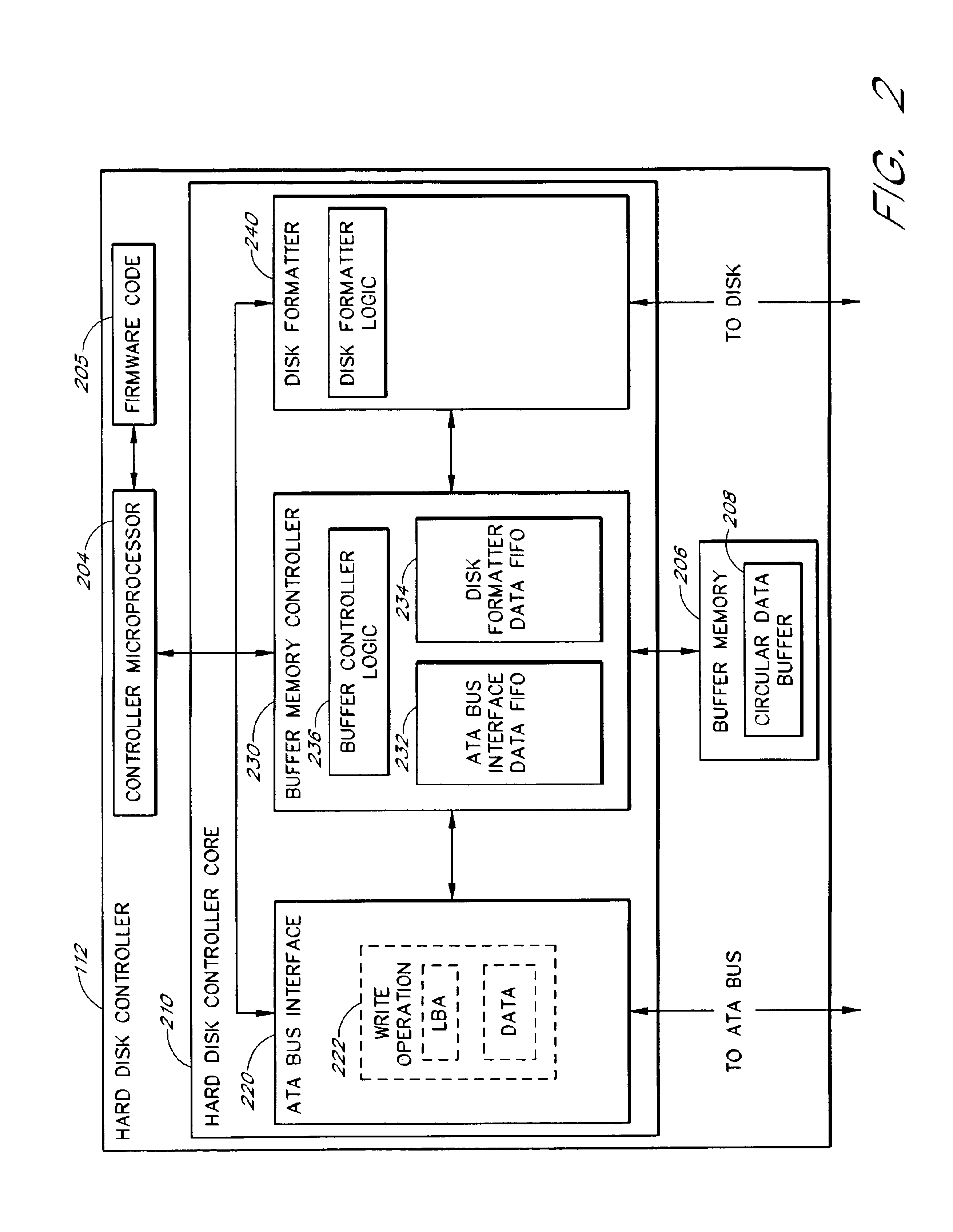
Disk controller configured to perform out of order execution of write operations
InactiveUS6826650B1Input/output to record carriersRecord information storageMemory addressDisk controller
A hard disk unit includes a disk, controller microprocessor, host bus interface, buffer memory, buffer memory controller and disk formatter. The bus interface receives write operations, and the corresponding write operation data is stored in the buffer memory. The buffer memory controller also includes a set of address registers and a set of block count registers. The microprocessor loads the address registers with the buffer memory addresses of data of multiple write operations and loads the block count registers with the size of the corresponding data. The microprocessor then issues a single command to the buffer memory controller to transfer the data from the buffer memory to the disk formatter. The address registers and block count registers enable the data of multiple write operations to be transferred and written to a disk in an order other than the order in which the write operations were received at the bus interface.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
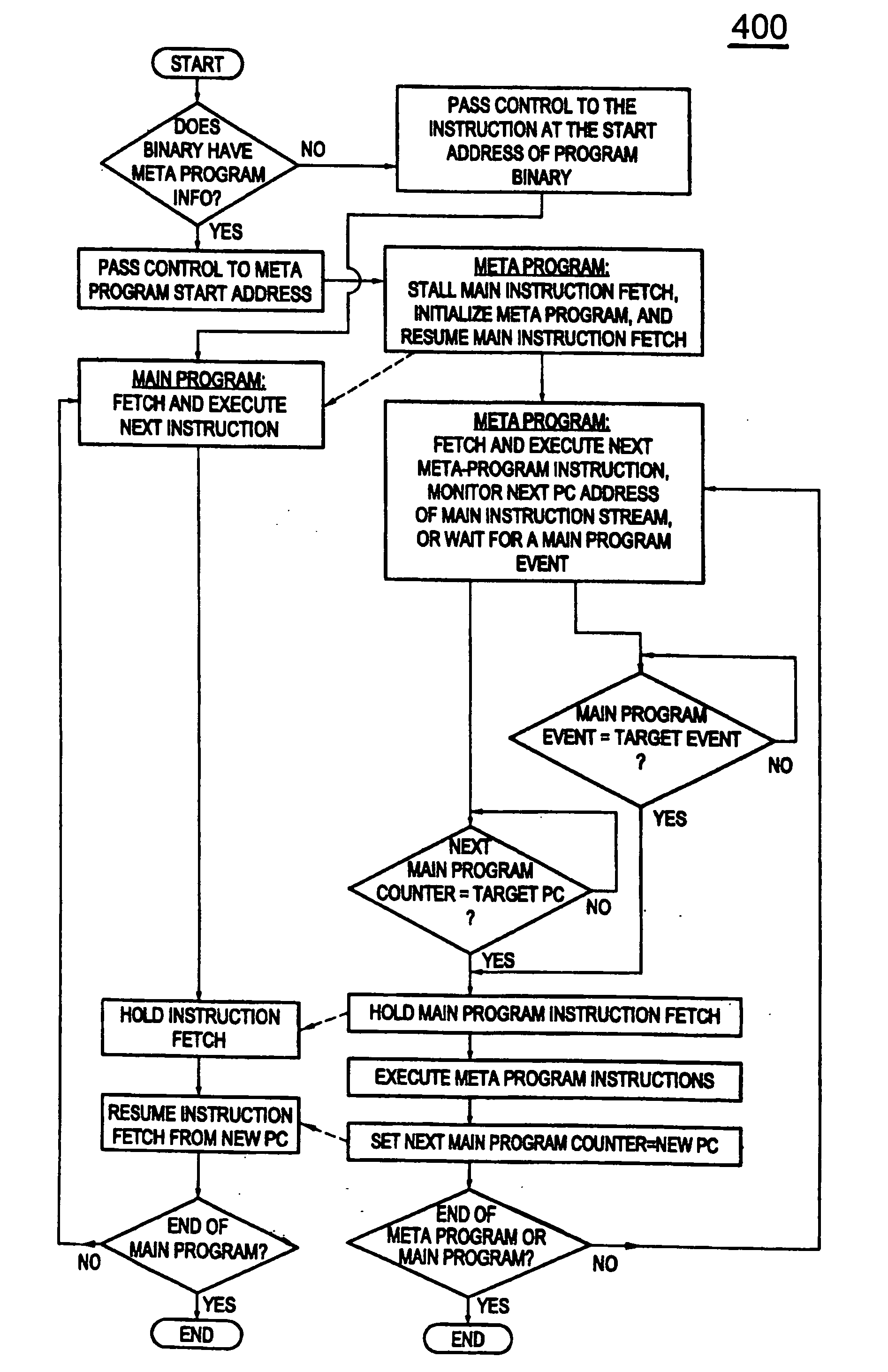
Method and apparatus for fast synchronization and out-of-order execution of instructions in a meta-program based computing system
InactiveUS20080028196A1Simple and efficient and fast methodDigital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingOut-of-order executionComputer architecture
Owner:IBM CORP
Unordered load/store queue
A method and processor for providing full load / store queue functionality to an unordered load / store queue for a processor with out-of-order execution. Load and store instructions are inserted in a load / store queue in execution order. Each entry in the load / store queue includes an identification corresponding to a program order. Conflict detection in such an unordered load / store queue may be performed by searching a first CAM for all addresses that are the same or overlap with the address of the load or store instruction to be executed. A further search may be performed in a second CAM to identify those entries that are associated with younger or older instructions with respect to the sequence number of the load or store instruction to be executed. The output results of the Address CAM and Age CAM are logically ANDed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
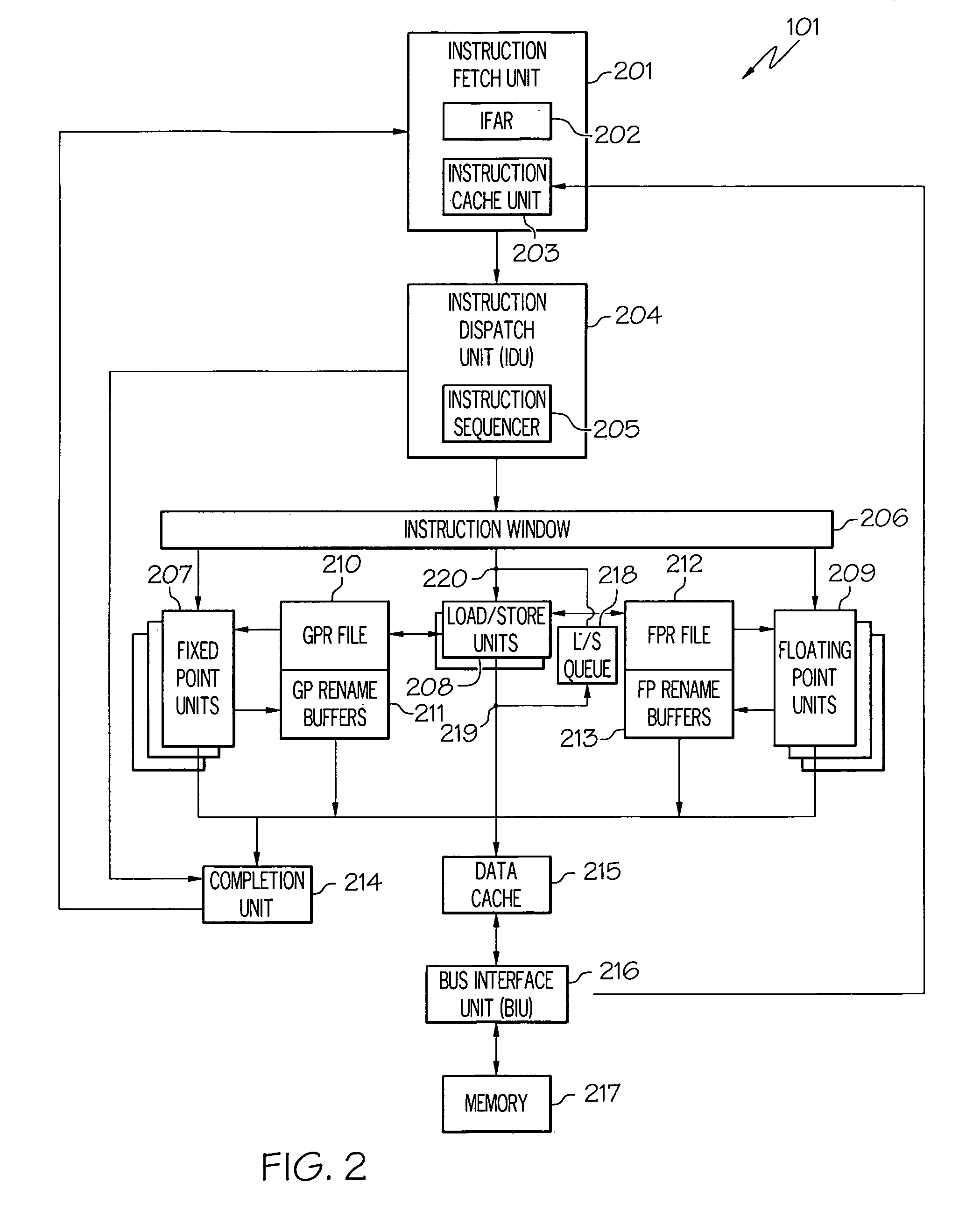
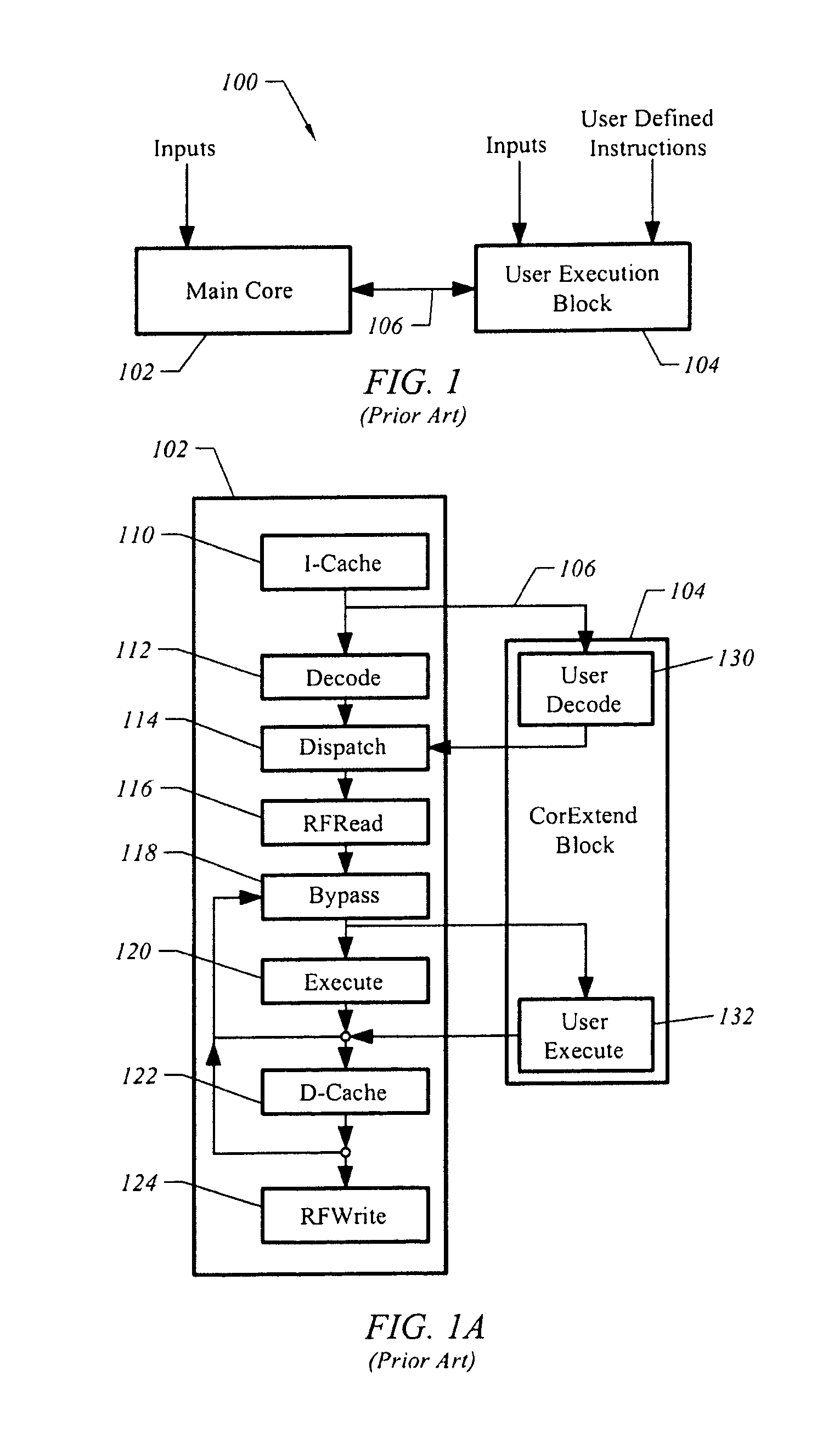
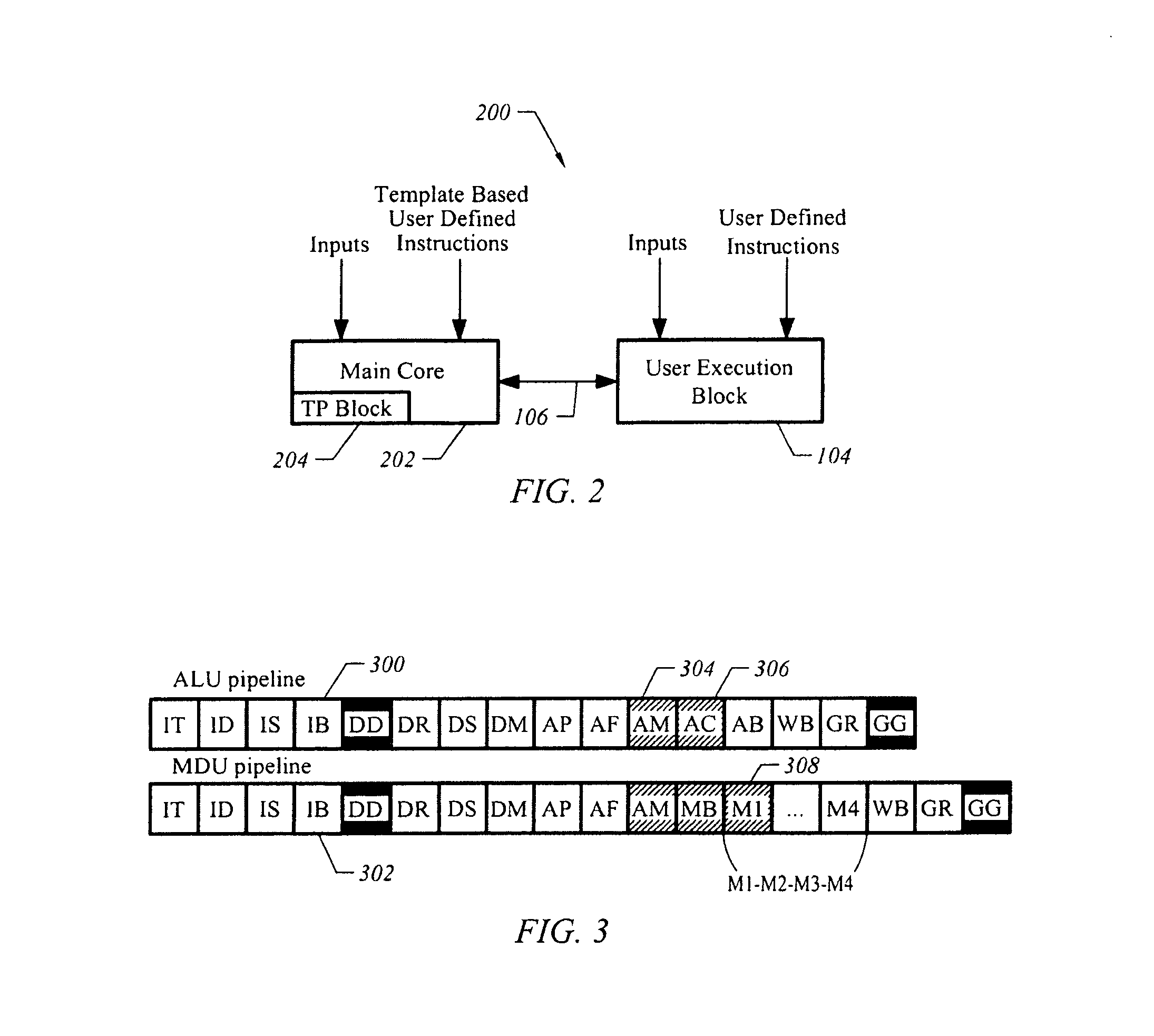
Apparatus and method for processing template based user defined instructions
A system implemented in hardware includes a main processing core decoding instructions for out of order execution. The instructions include template based user defined instructions. A user execution block executes the template based user defined instructions. An interface is positioned between the main processing core and the user execution block. A computer readable medium includes executable instructions to describe a processing core supporting execution of a proprietary instruction set and decoding of customized instructions that adhere to a specified pattern. The specified pattern includes a source, a destination and a latency period. A user execution block is connected to the processing core to execute the customized instructions.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
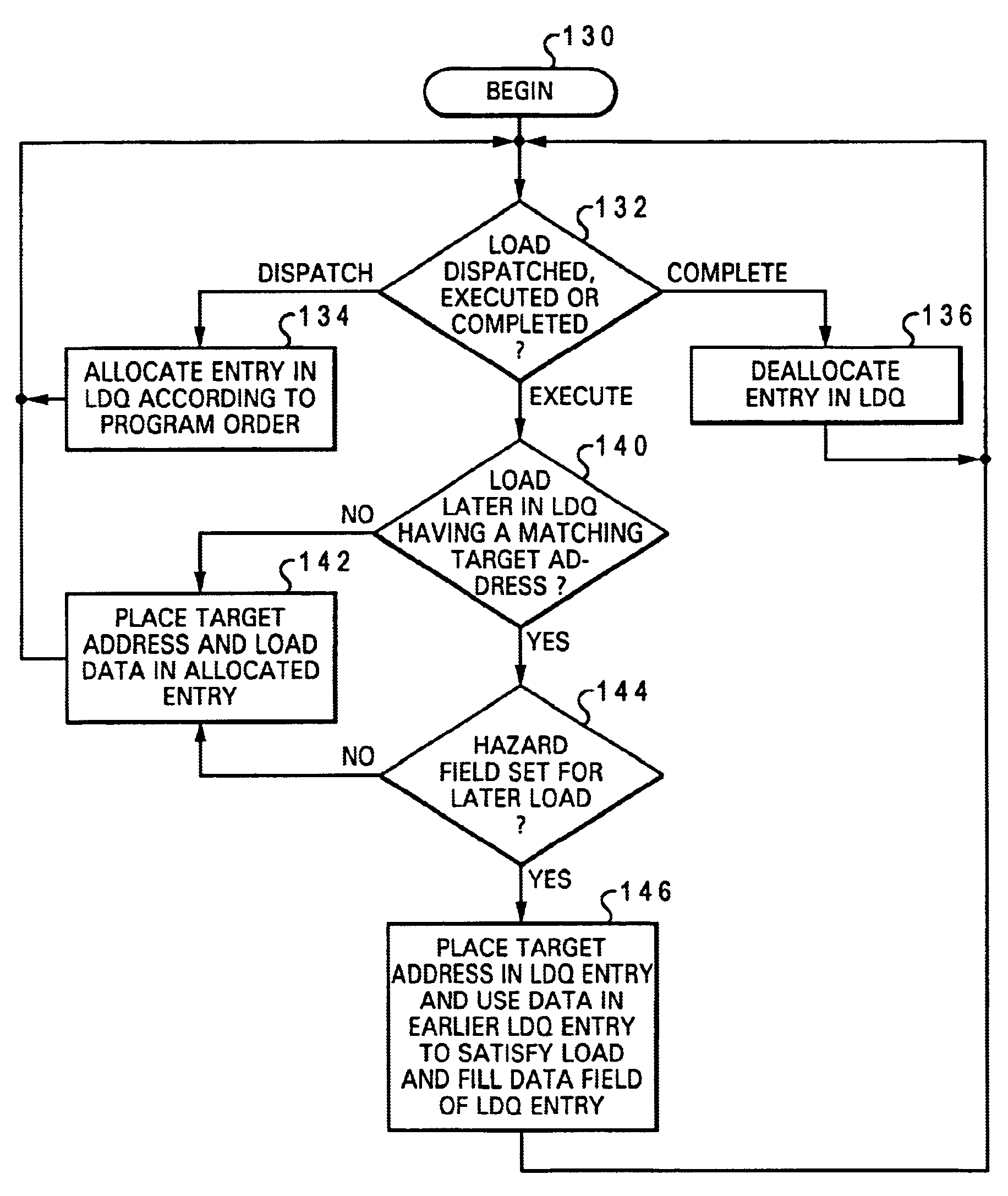
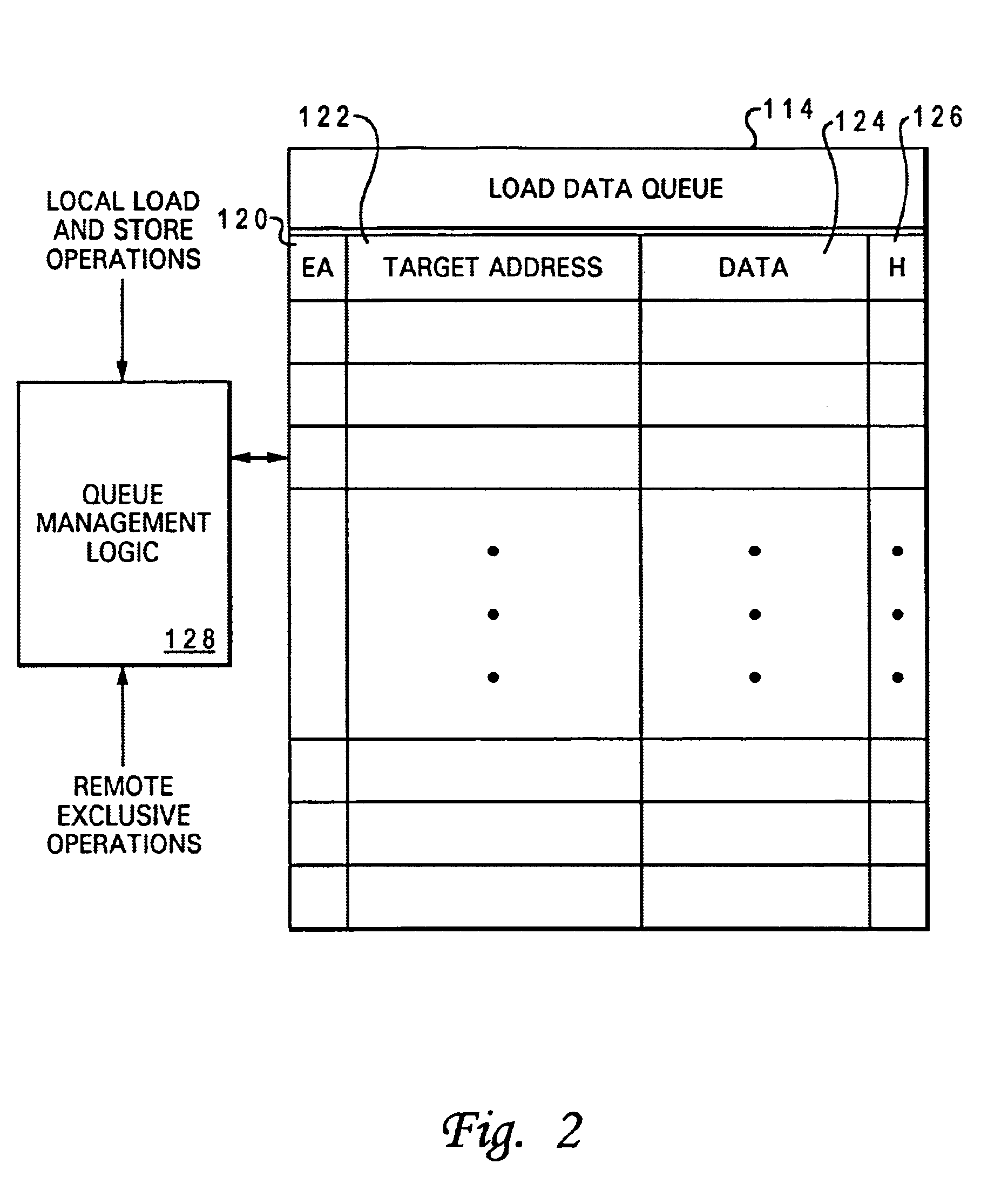
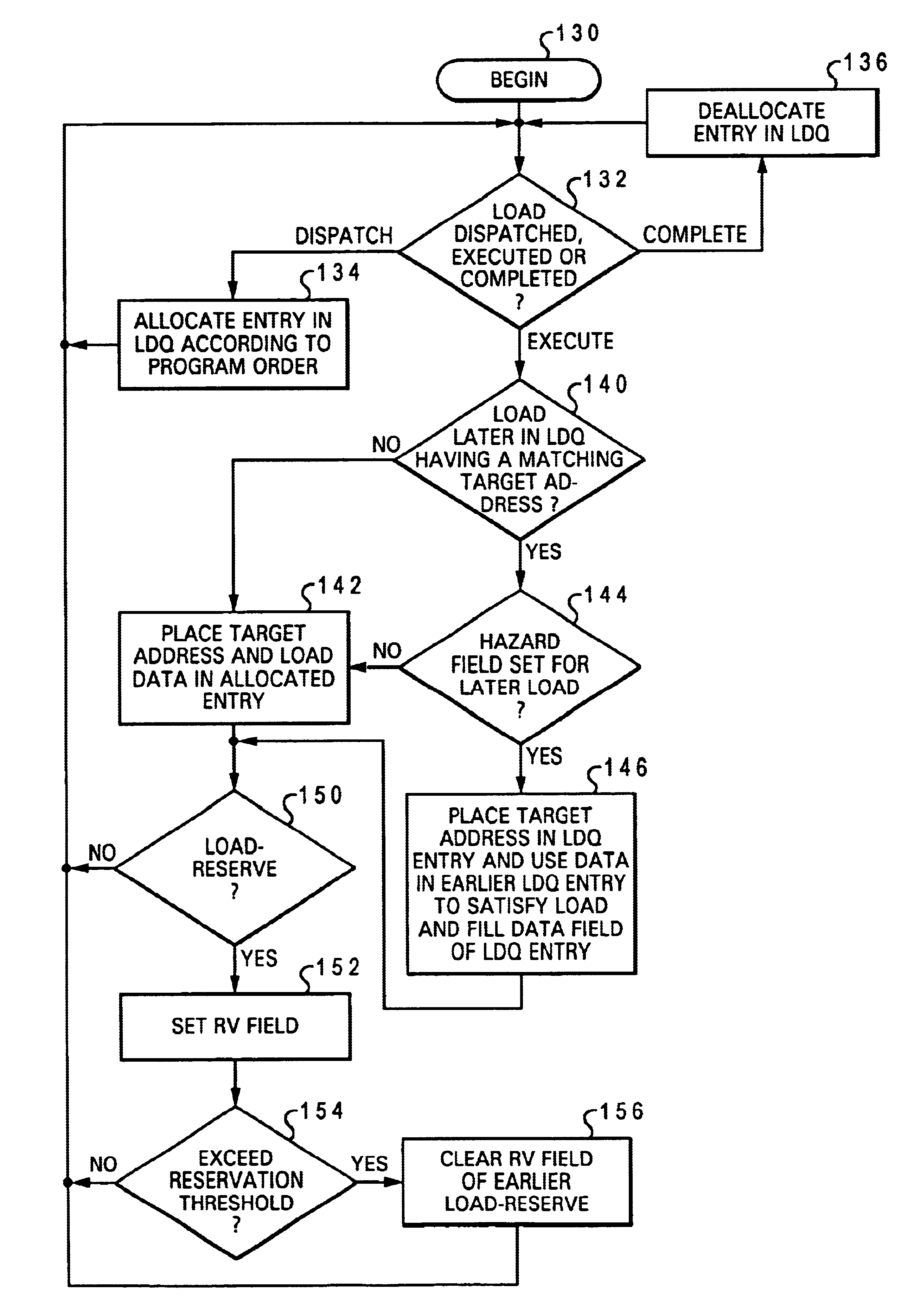
Processor and method of executing load instructions out-of-order having reduced hazard penalty
InactiveUS6868491B1Reduce performance lossLower performance requirementsRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsLoad instructionProcessor register
A processor having a reduced data hazard penalty includes a register set, at least one execution unit that executes load instructions to transfer data into the register set, and a load queue. The load queue contains at least one entry, and each occupied entry in the load queue stores load data retrieved by an executed load instruction in association with a target address of the executed load instruction. The load queue has associated queue management logic that, in response to execution by the execution unit of a load instruction, determines by reference to the load queue whether a data hazard exists for the load instruction. If so, the queue management logic outputs load data from the load queue to the register set in accordance with the load instruction, thus eliminating the need to flush and re-execute the load instruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
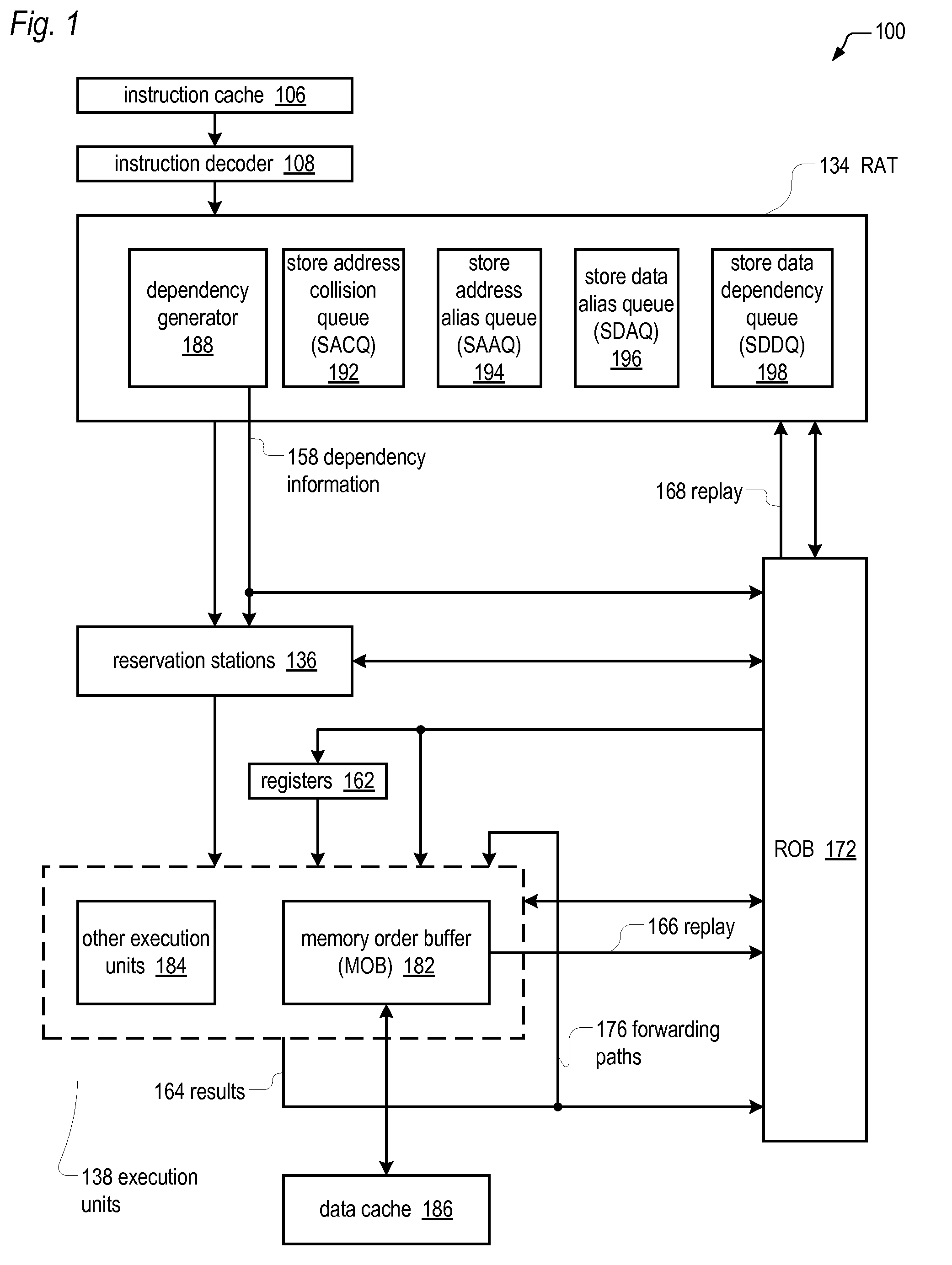
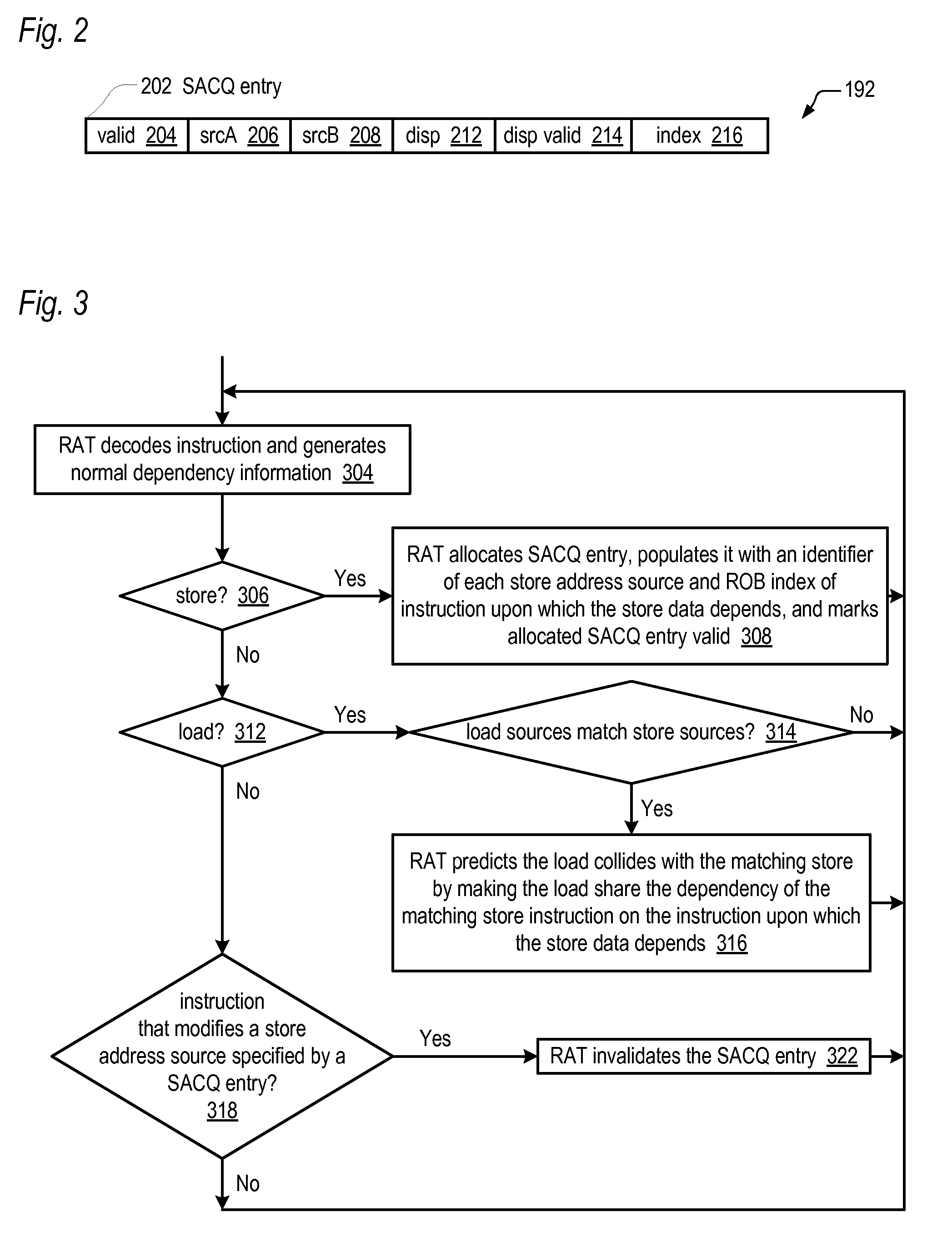
Out-of-order execution microprocessor with reduced store collision load replay reduction
InactiveUS20100306509A1Reduce the possibilityDigital computer detailsMemory systemsLoad instructionStorage violation
An out-of-order execution microprocessor for reducing the likelihood of having to replay a load instruction due to a store collision. The microprocessor includes a queue of entries, each entry configured to hold an instruction pointer of a load instruction and to hold information useable to identify a store instruction that caused the load instruction to be replayed on a first instance of the load instruction. A register alias table (RAT) encounters instructions in program order and generates dependencies used to determine when the instructions may execute out of program order. The RAT encounters the load instruction on a second instance, determines that the load instruction second instance instruction pointer matches the instruction pointer of an entry of the queue, and causes the load instruction on the second instance to have a dependency on the store instruction identified by the information in the matching entry.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
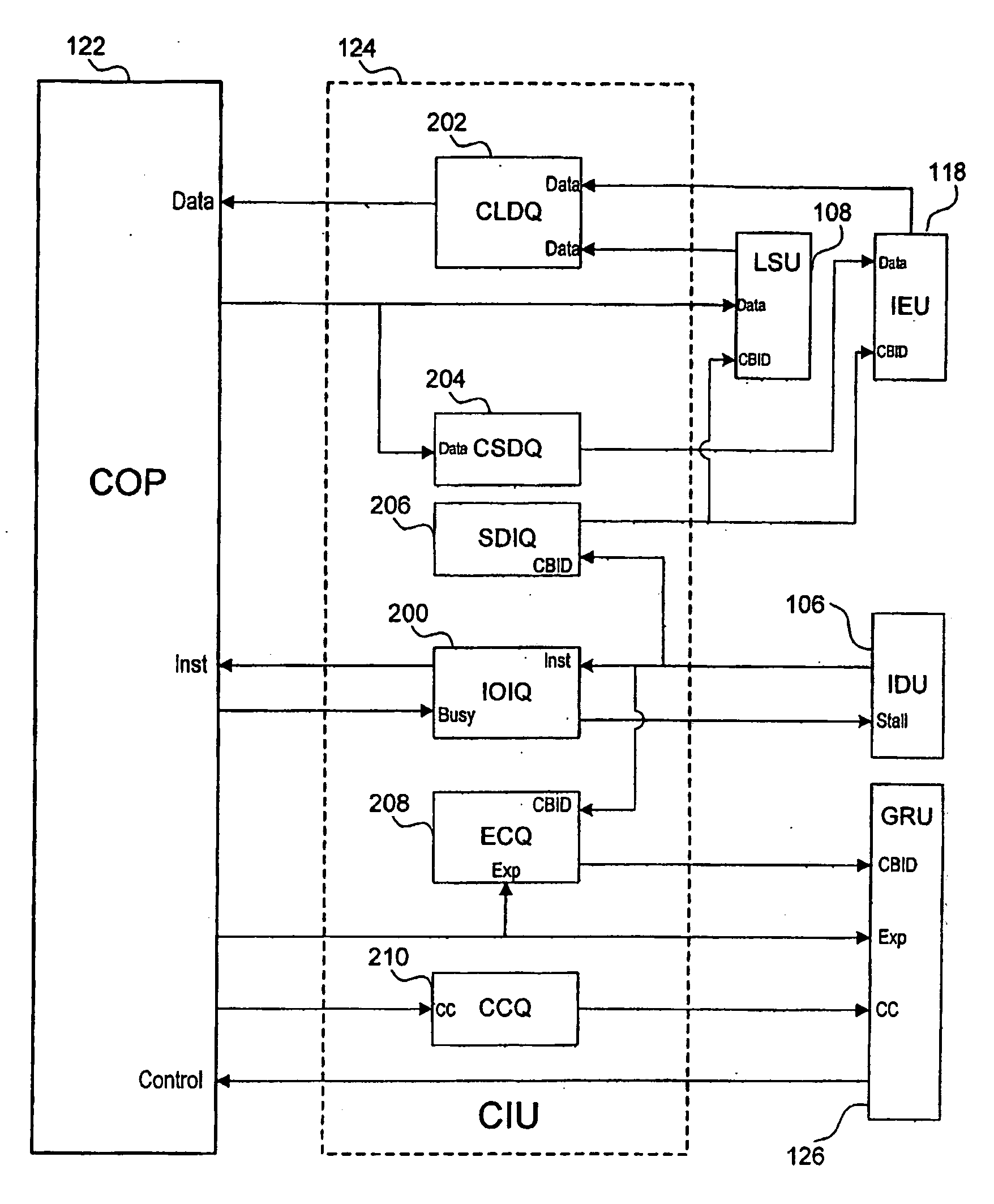
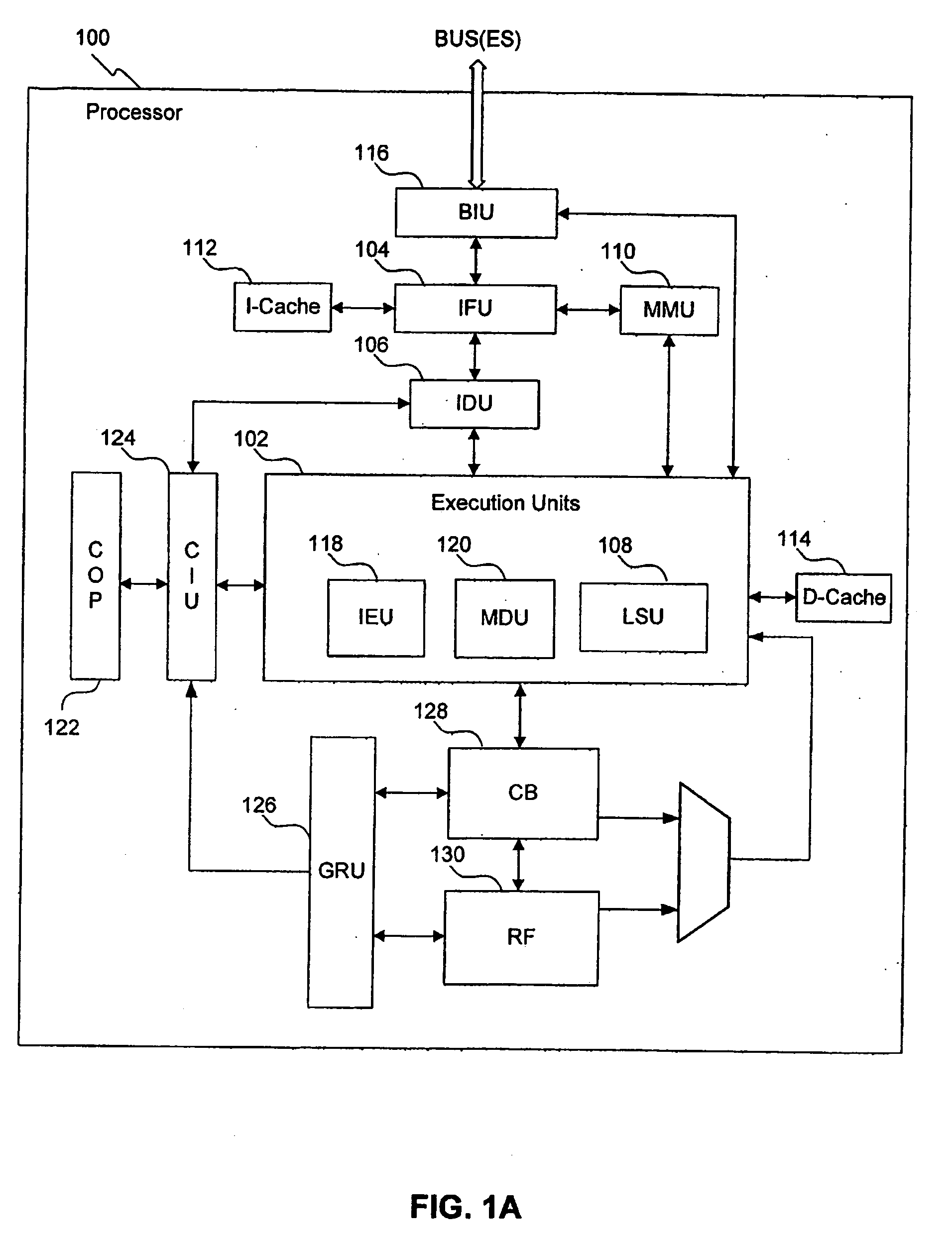
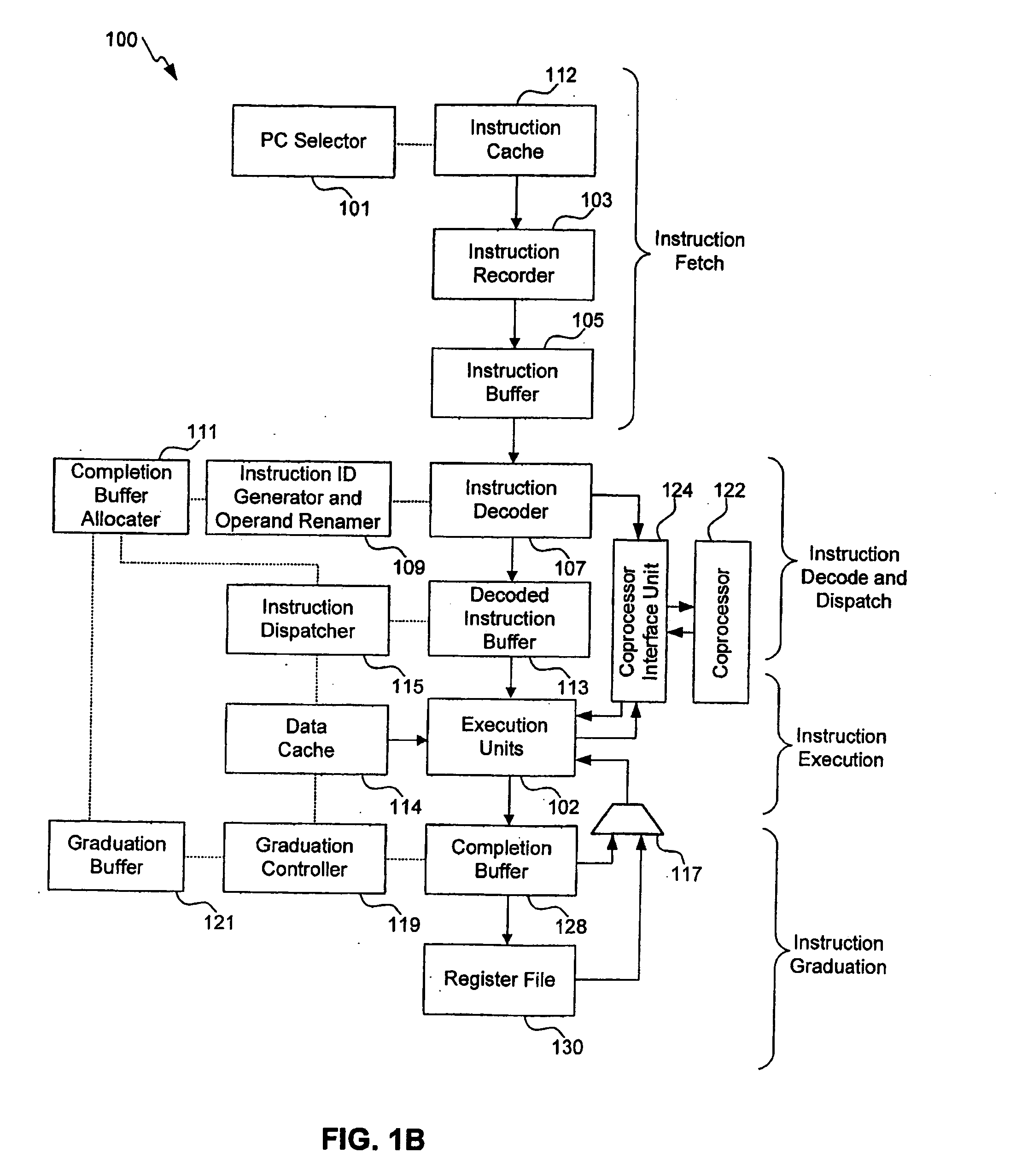
Out-of-order processor having an in-order coprocessor, and applications thereof
ActiveUS20080059771A1Runtime instruction translationGeneral purpose stored program computerCoprocessorScheduling instructions
An in-order coprocessor is interfaced to an out-of-order execution pipeline. In an embodiment, the interfacing is achieved using a coprocessor interface unit that includes an in-order instruction queue, a coprocessor load data queue, and a coprocessor store data queue. Instructions are written into the in-order instruction queue by an instruction dispatch unit. Instructions exit the in-order instruction queue and enter the coprocessor. In the coprocessor, the instructions operate on data read from the coprocessor load data queue. Data is written back, for example, to memory or a register file by inserting the data into the out-of-order execution pipeline, either directly or via the coprocessor store data queue, which writes back the data.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
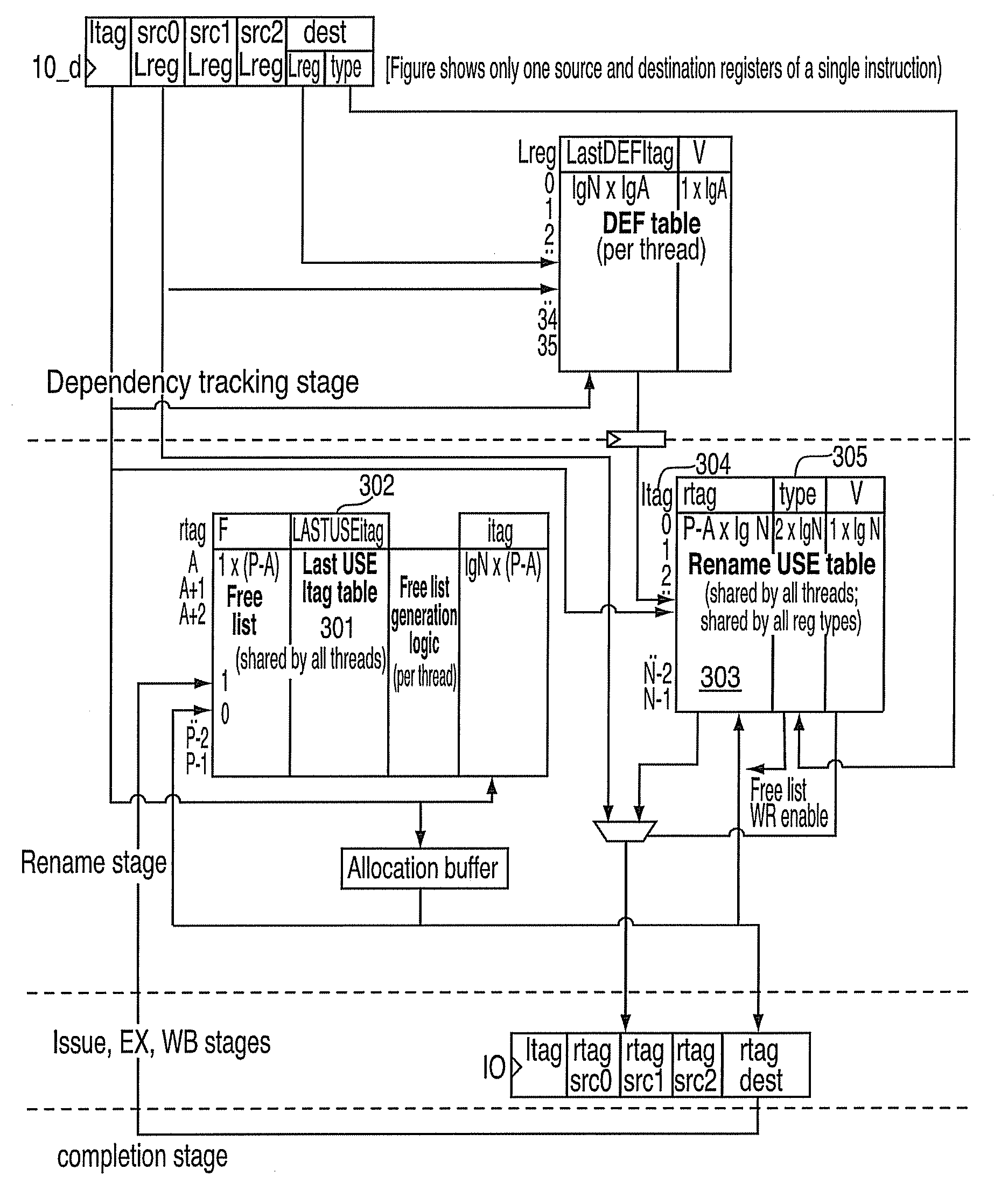
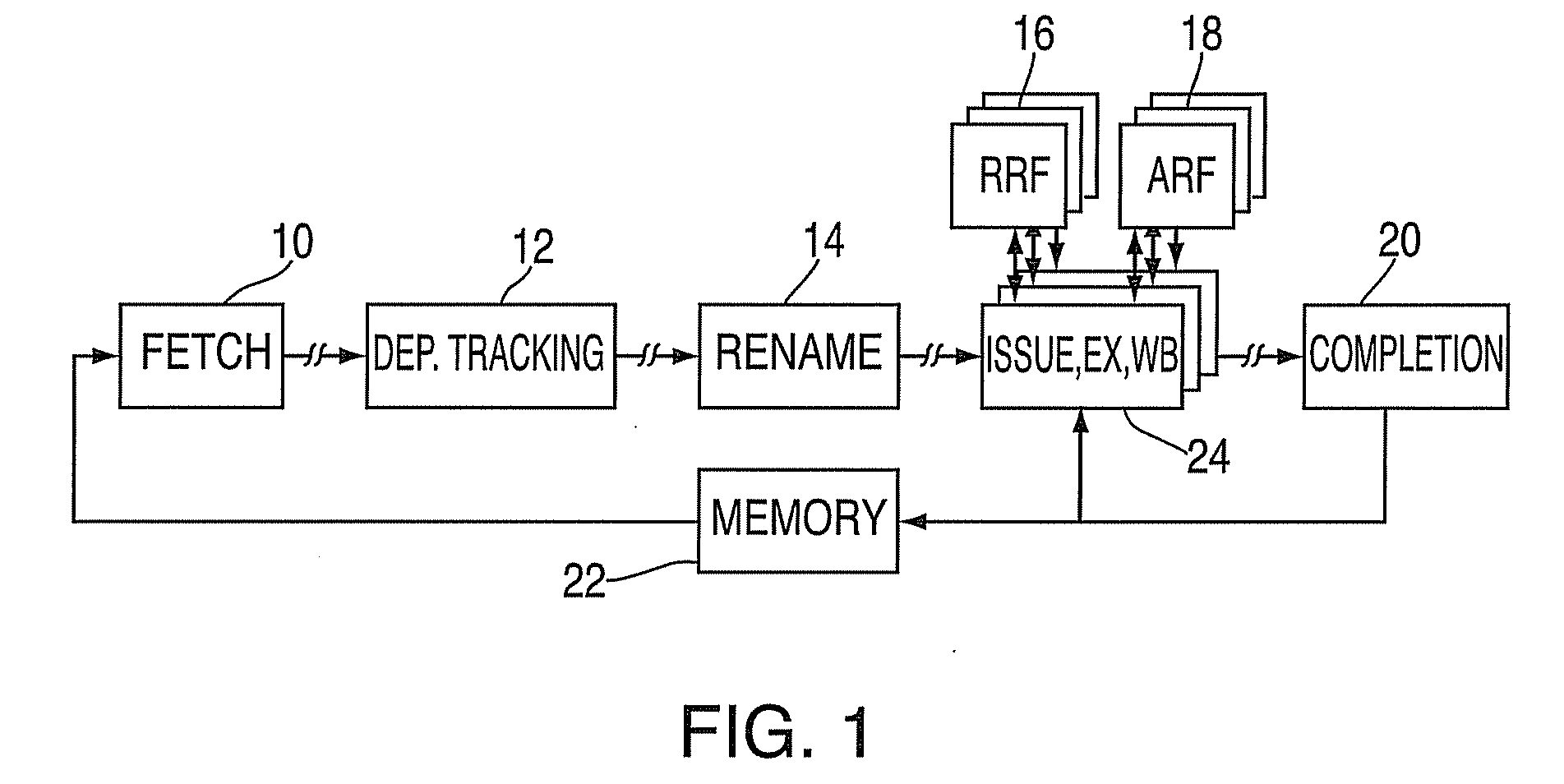
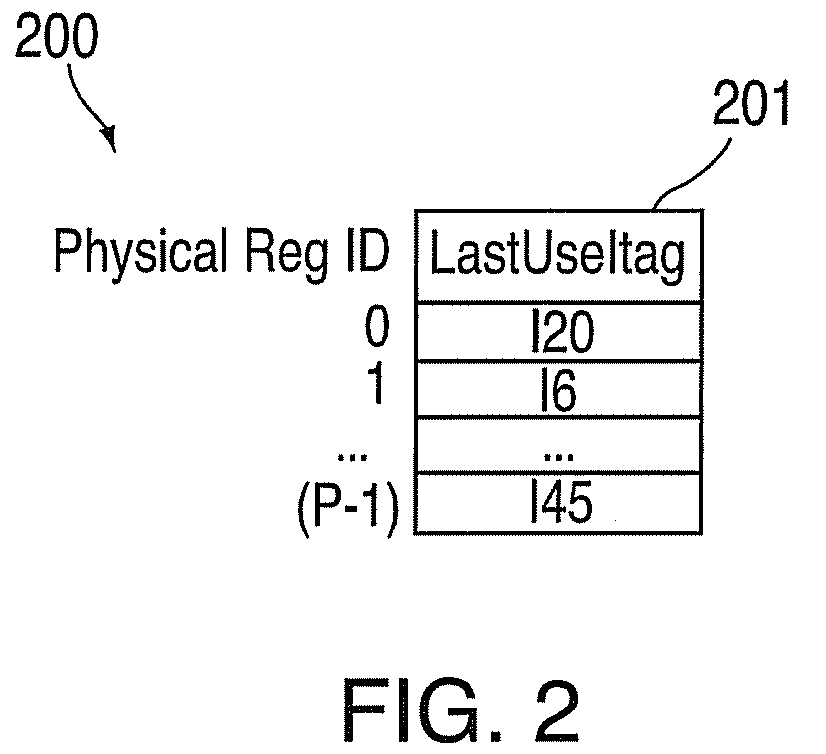
Method And Apparatus For Register Renaming Using Multiple Physical Register Files And Avoiding Associative Search
A method for implementing a register renaming scheme for a digital data processor using a plurality of physical register files for supporting out-of-order execution of a plurality of instructions from one or more threads, the method comprising: using a DEF table to store the instruction dependencies between the plurality of instructions using the instruction tags, the DEF table being indexed by a logical register name and including one entry per logical register; using a rename USE table indexed by the instruction tags to store logical-to-physical register mapping information shared by multiple sets of different types of non-architected copies of logical registers used by multiple threads; using a last USE table to transfer data of the multiple sets of different types of non-architected copies of logical registers into the first set of architected registered files, the last USE table being indexed by a physical register name in the second set of rename registered files; and performing the register renaming scheme at the instruction dispatch or wake-up / issue time.
Owner:IBM CORP
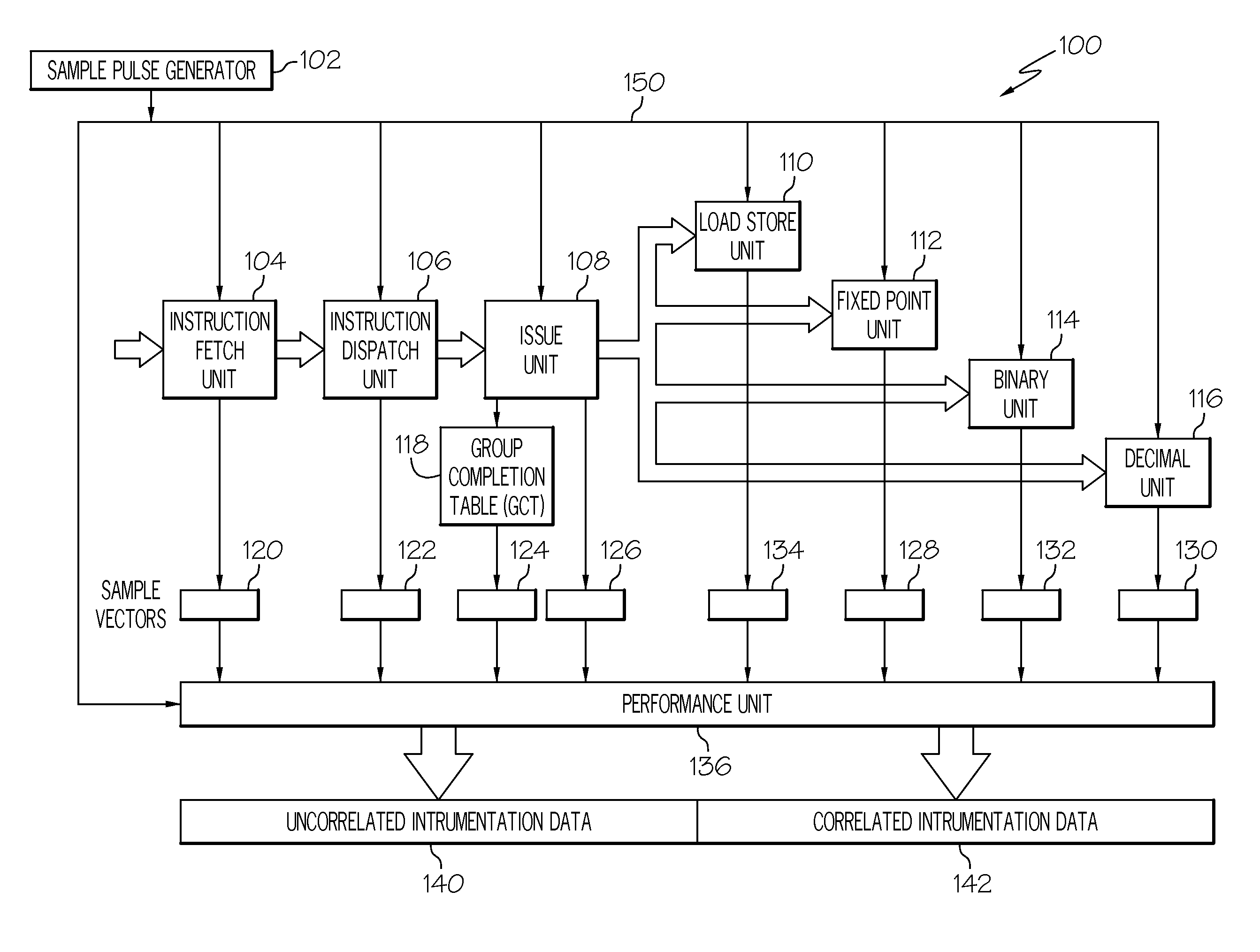
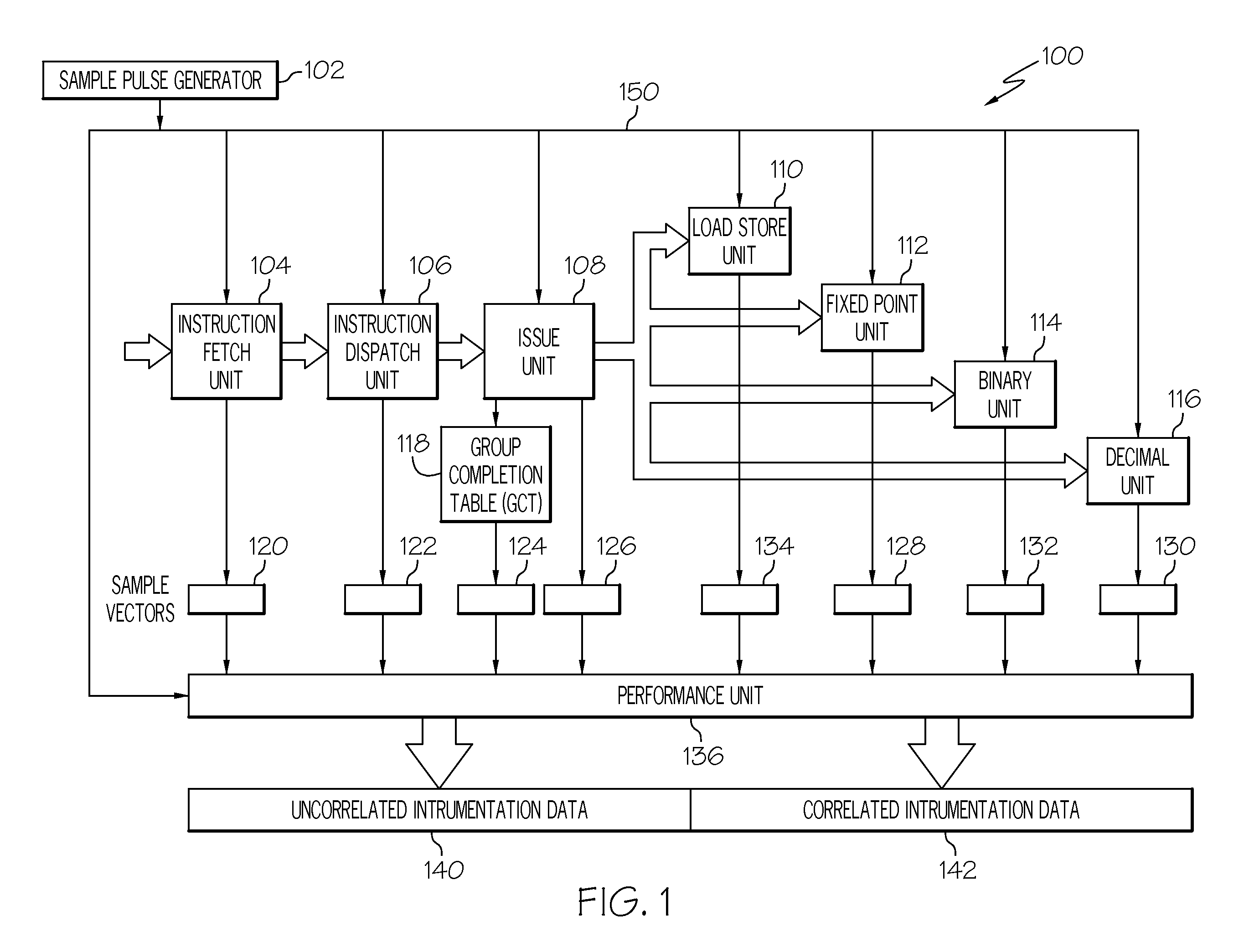
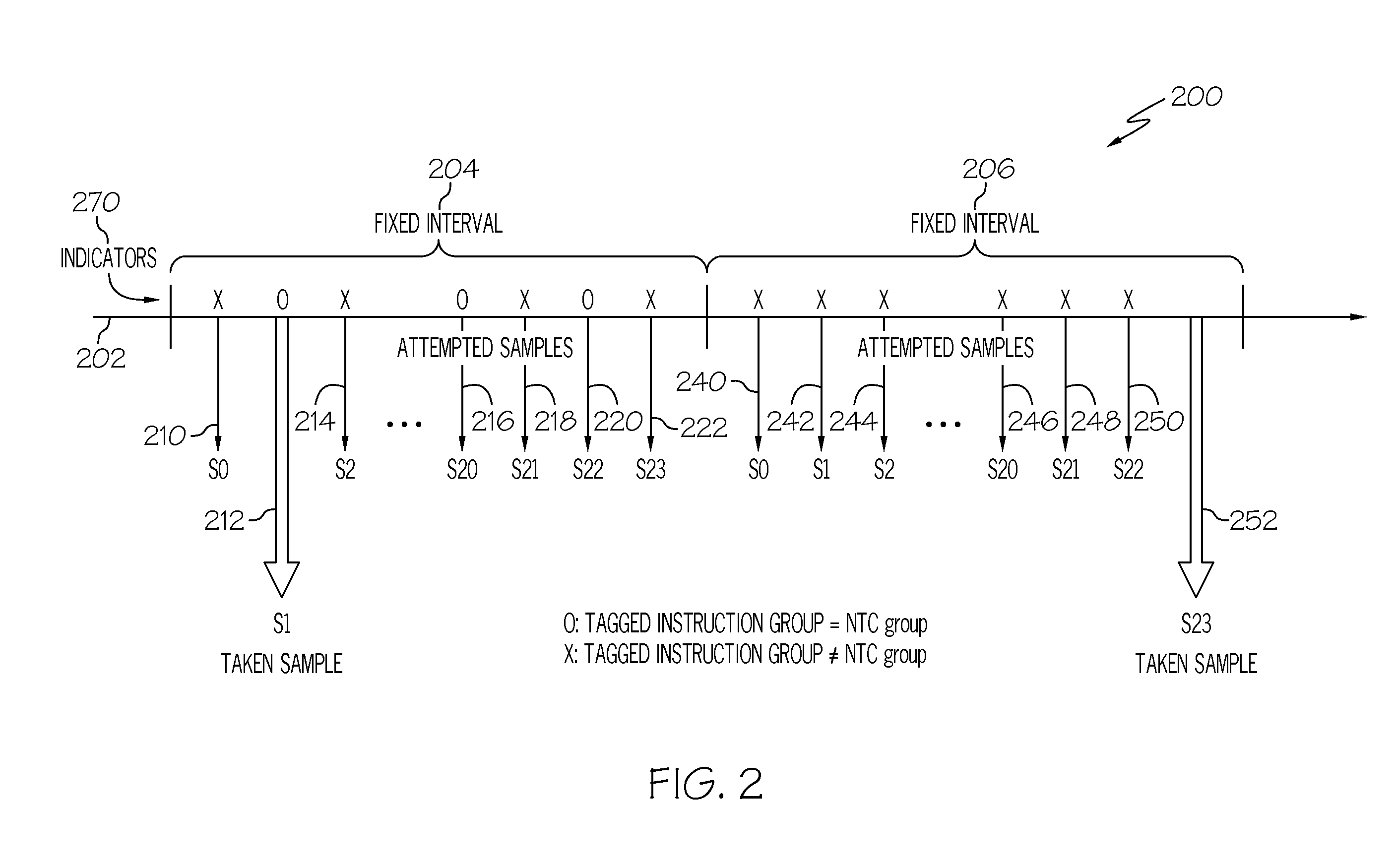
Collecting computer processor instrumentation data
InactiveUS20110154298A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessing InstructionSoftware engineering
A system and method for collecting instrumentation data in a processor with a pipelined instruction execution stages arranged in an out-of-order execution architecture. One instruction group in a Global Completion Table is marked as a tagged group. Instrumentation data is stored for processing stages processing instructions associated with the tagged group. Sample signal pulses trigger a determination of whether the tagged group is the next-to-complete instruction group. When the sample pulse occurs at a time when the tagged group is the next-to-complete group, the instrumentation data is written as an output. Instrumentation data present during sample pulses that occur when the tagged group is not the next-to-complete group is optionally discarded. Sample pulses are generated at a rate equal to the desired sample rate times the number of groups in the global completion table to better ensure occurrence of a next-to-complete tagged group.
Owner:IBM CORP
Suppression of control transfer instructions on incorrect speculative execution paths
Techniques are disclosed relating to a processor that is configured to execute control transfer instructions (CTIs). In some embodiments, the processor includes a mechanism that suppresses results of mispredicted younger CTIs on a speculative execution path. This mechanism permits the branch predictor to maintain its fidelity, and eliminates spurious flushes of the pipeline. In one embodiment, a misprediction bit is be used to indicate that a misprediction has occurred, and younger CTIs than the CTI that was mispredicted are suppressed. In some embodiments, the processor may be configured to execute instruction streams from multiple threads. Each thread may include a misprediction indication. CTIs in each thread may execute in program order with respect to other CTIs of the thread, while instructions other than CTIs may execute out of program order.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dynamic tag allocation in a multithreaded out-of-order processor
ActiveUS20100333098A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsInstruction distributionProcedure sequence
Various techniques for dynamically allocating instruction tags and using those tags are disclosed. These techniques may apply to processors supporting out-of-order execution and to architectures that supports multiple threads. A group of instructions may be assigned a tag value from a pool of available tag values. A tag value may be usable to determine the program order of a group of instructions relative to other instructions in a thread. After the group of instructions has been (or is about to be) committed, the tag value may be freed so that it can be re-used on a second group of instructions. Tag values are dynamically allocated between threads; accordingly, a particular tag value or range of tag values is not dedicated to a particular thread.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for non-speculative fetch and execution of control-dependent blocks
InactiveUS20160055004A1Conditional code generationRuntime instruction translationSpeculative executionRegister bank
An apparatus and method are described for non-speculative execution of conditional instructions. For example, one embodiment of a processor comprises: a register set including a first register to store a set of one or more condition bits; non-speculative execution logic to execute a first instruction to identify a first target instruction strand in response to a first conditional value read from the set of condition bits, the first instruction to wait until the first conditional value becomes known before causing the first target instruction strand to be fetched and executed, the non-speculative execution logic to execute a second instruction to identify an end of the first target instruction strand and responsively identify a new current instruction pointer for instructions which follow the second instruction; and out-of-order execution logic to fetch and execute the instructions which follow the second instruction prior to the execution of the second instruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Out-of-order execution microprocessor and operating method therefor
An out-of-order execution microprocessor for reducing load instruction replay likelihood due to store collisions includes: a first queue memory including a plurality of items; a second queue memory including a plurality of items; and a buffer alternative name list which is coupled on first and second queue memories for generating a plurality of dependency according to a plurality of instructions which are arranged according to order and determining when the instructions are in out-of-order execution. The buffer alternative name list is used for assigning an item in the first queue memory, filling an instruction pointer of the load instruction in the assigned item, assigning an item in the second queue memory, filling a dependency in the assigned item, and making the subsequently executed load instruction share the dependency. The dependency is used for identifying an instruction upon which the store instruction depends for its data in the assigned item in the second queen memory.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
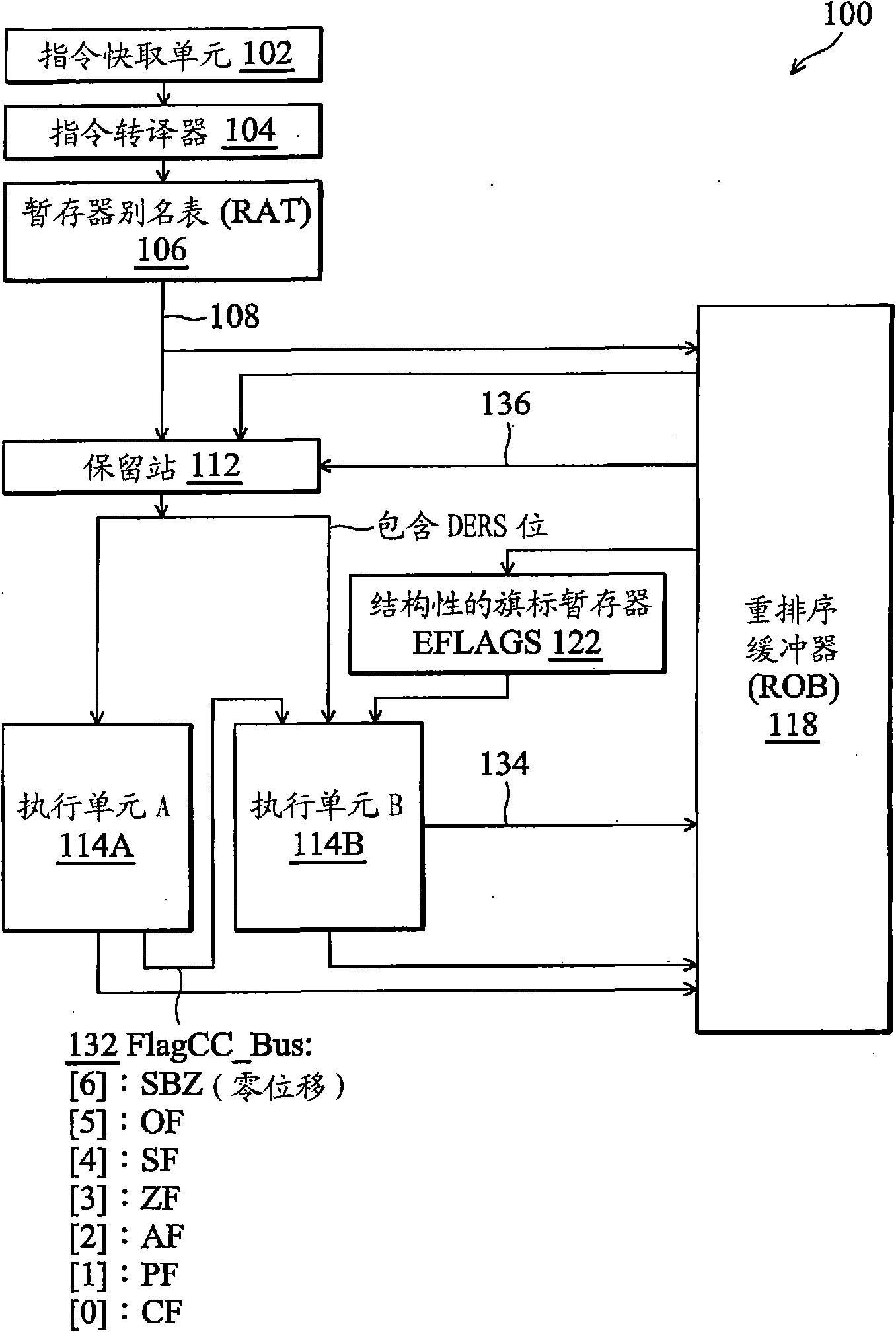
Out-of-order execution micro-processor and method of executing the related command
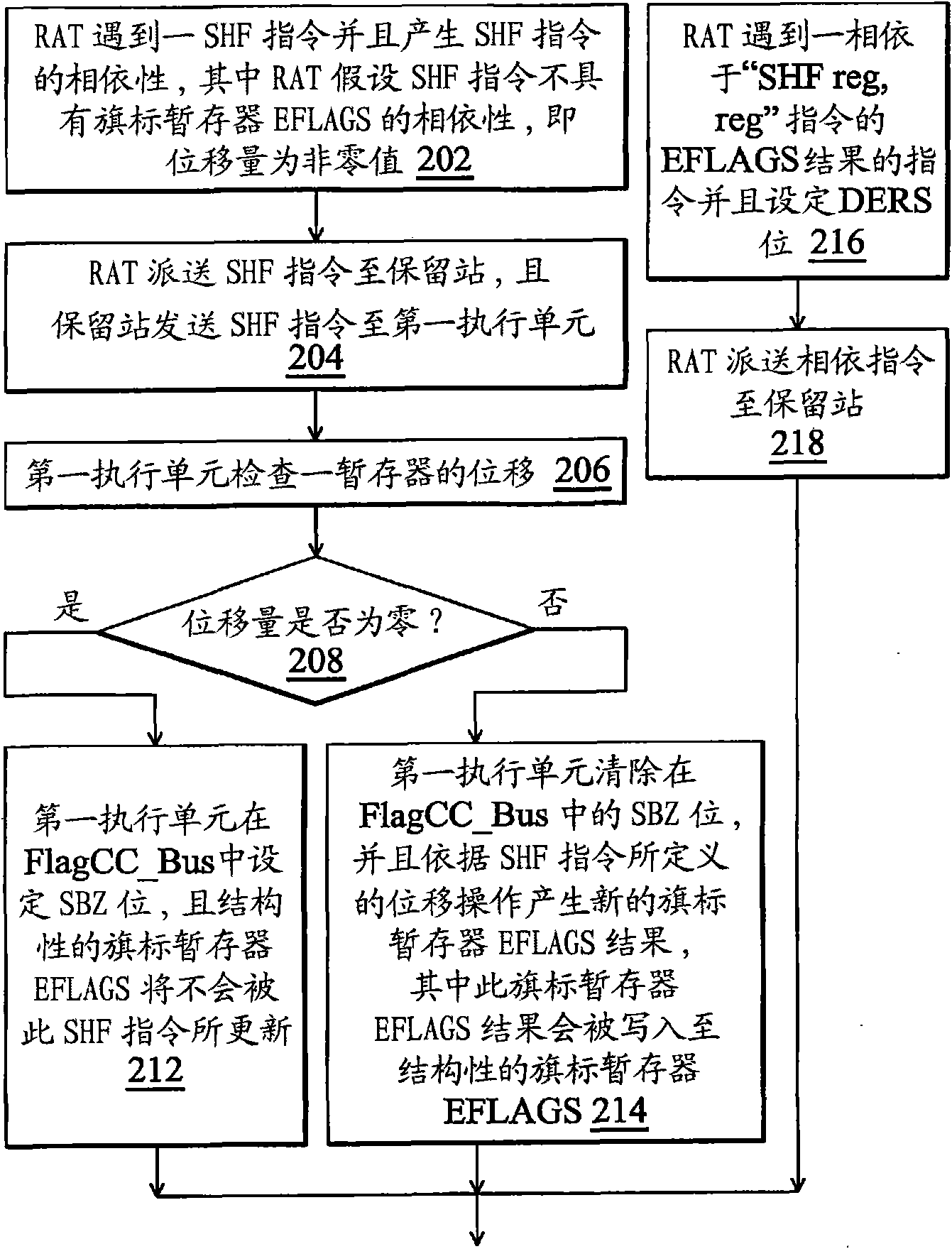
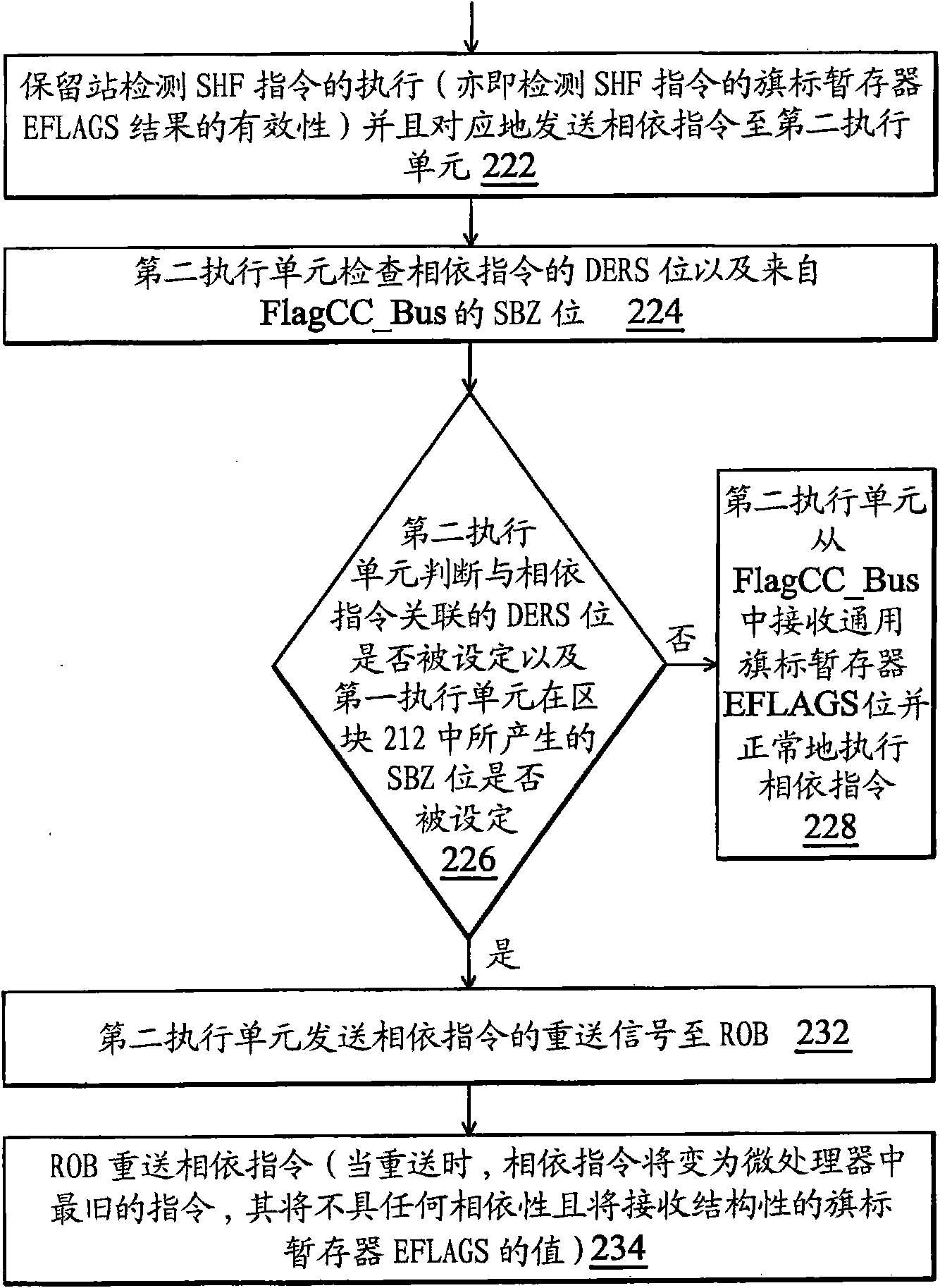
The invention provides an out-of-order execution micro-processor, comprising a temporary memory surname watch for generating a first indication for indicating whether one command depends on a condition code result of a shift command or not. A micro-processor also comprises a first execution unit for executing the shift command and generating a second indication and the second indication indicateswhether one shift amount of the shift command is zero or not. The micro-processor also comprises a second execution unit for receiving the first indication and the second indication and generating a return signal, thus when the first indication indicates that the command depends on the condition code result of the shift command and the second indication indicates that the shift amount of the shift command is zero, the command is returned.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
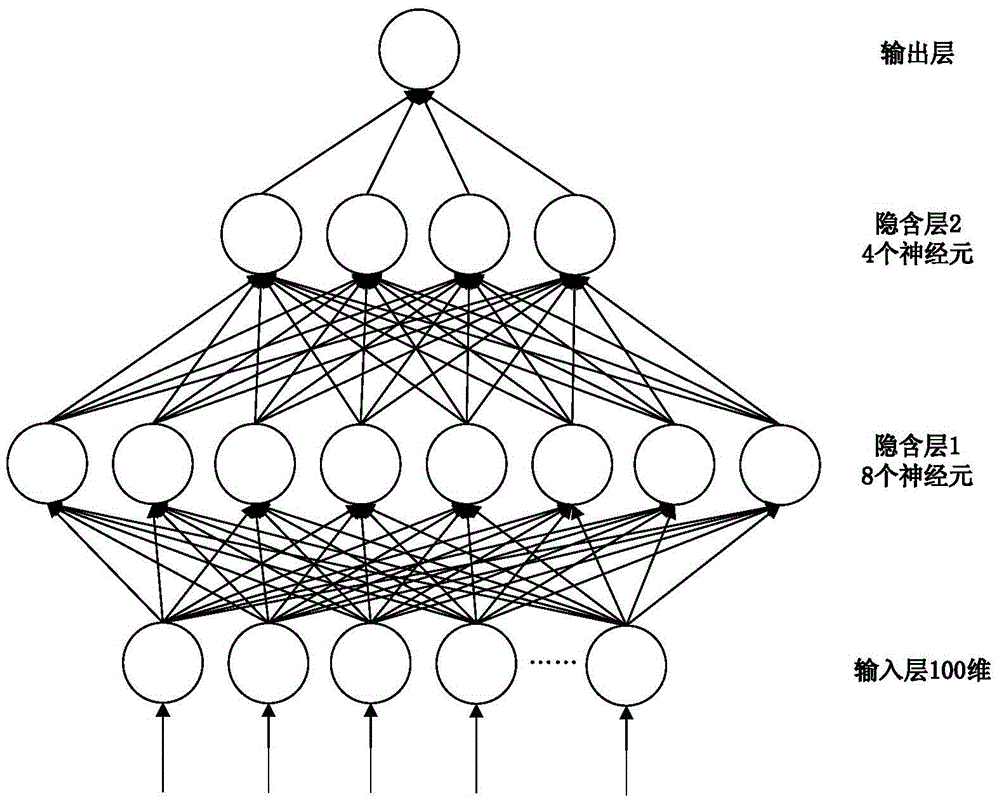
Artificial neural network-based out-of-order processor Cache memory access performance evaluation method
ActiveCN105653790AAccurately capture the full simulation processHigh speedNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkStack distance
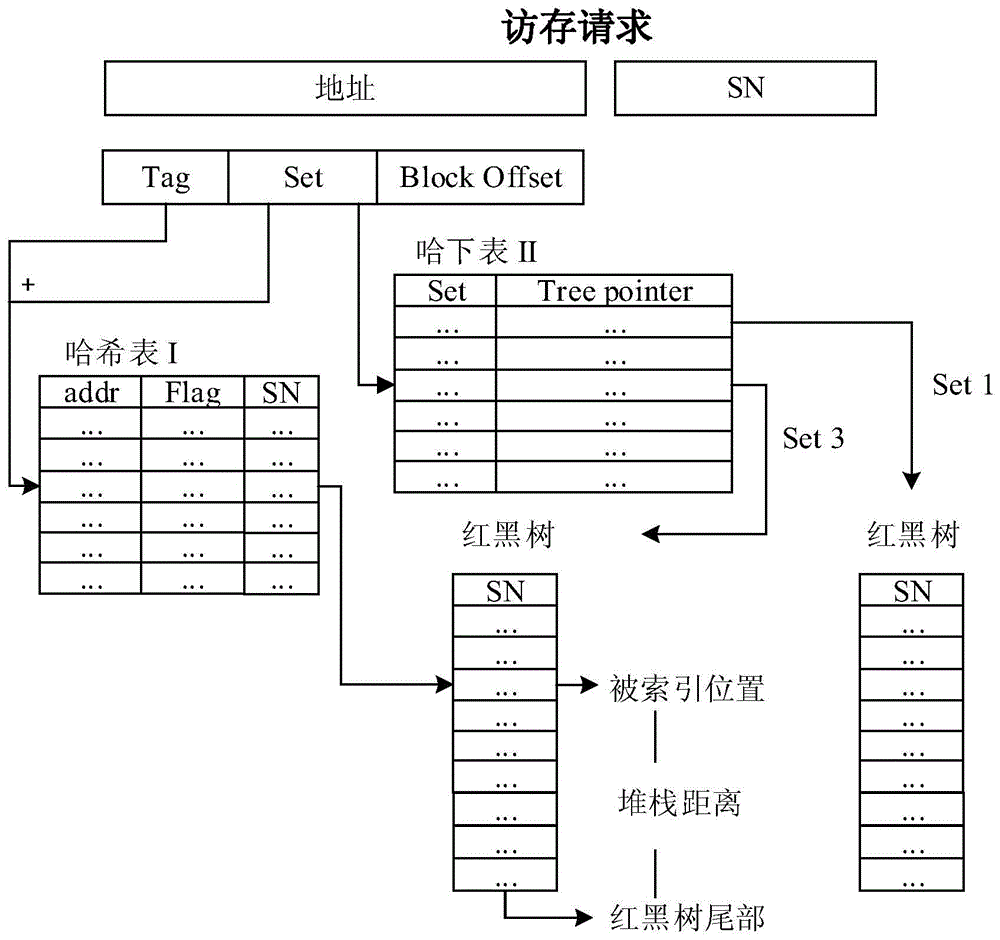
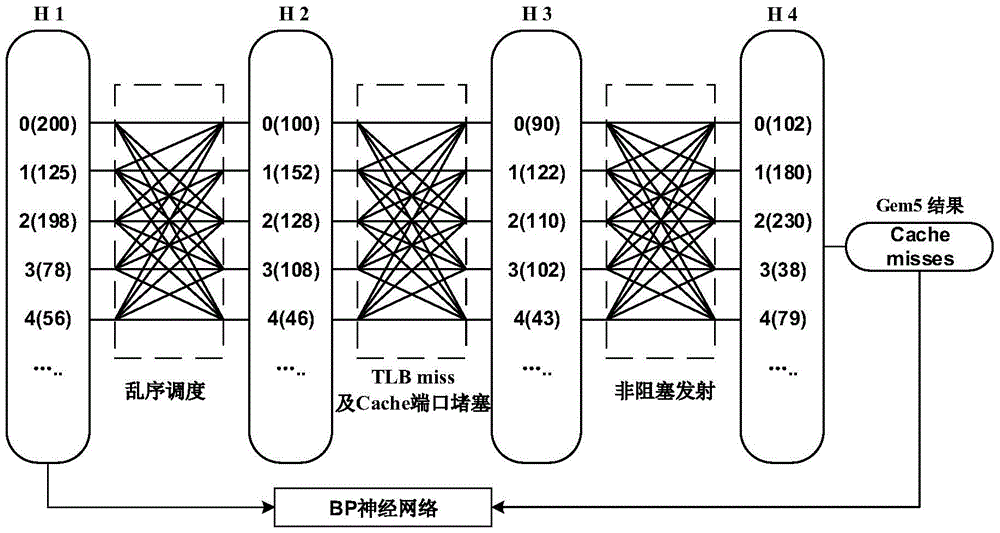
The invention discloses an artificial neural network-based out-of-order processor Cache memory access performance evaluation method, and aims at solving the problem that the memory access instructions are executed out of order so that the stacking distance distribution extracted by utilizing a binary execution tool during the prediction of LRU-Cache memory access behaviors is low in precision. The method comprises the following steps: combining a read-black tree and a hash table; designing a Cache group association architecture-based stacking distance extraction algorithm; respectively calculating a memory access sequence and the stacking distance distribution executed out of order; fitting the stacking distance distribution executed according to the memory access sequence and a memory access missing number by utilizing a BP neural network; and importing the stacking distance distributed extracted on the basis of the binary execution tool into the trained neural network so as to predict the Cache memory access behaviors with high precision. According to the method disclosed in the invention, the artificial neural network is adopted, so that the problem that the stacking distance distribution extracted by utilizing the binary execution tool during the prediction of the Cache memory access behaviors is low in precision is effectively solved.
Owner:RES INST OF SOUTHEAST UNIV IN SUZHOU
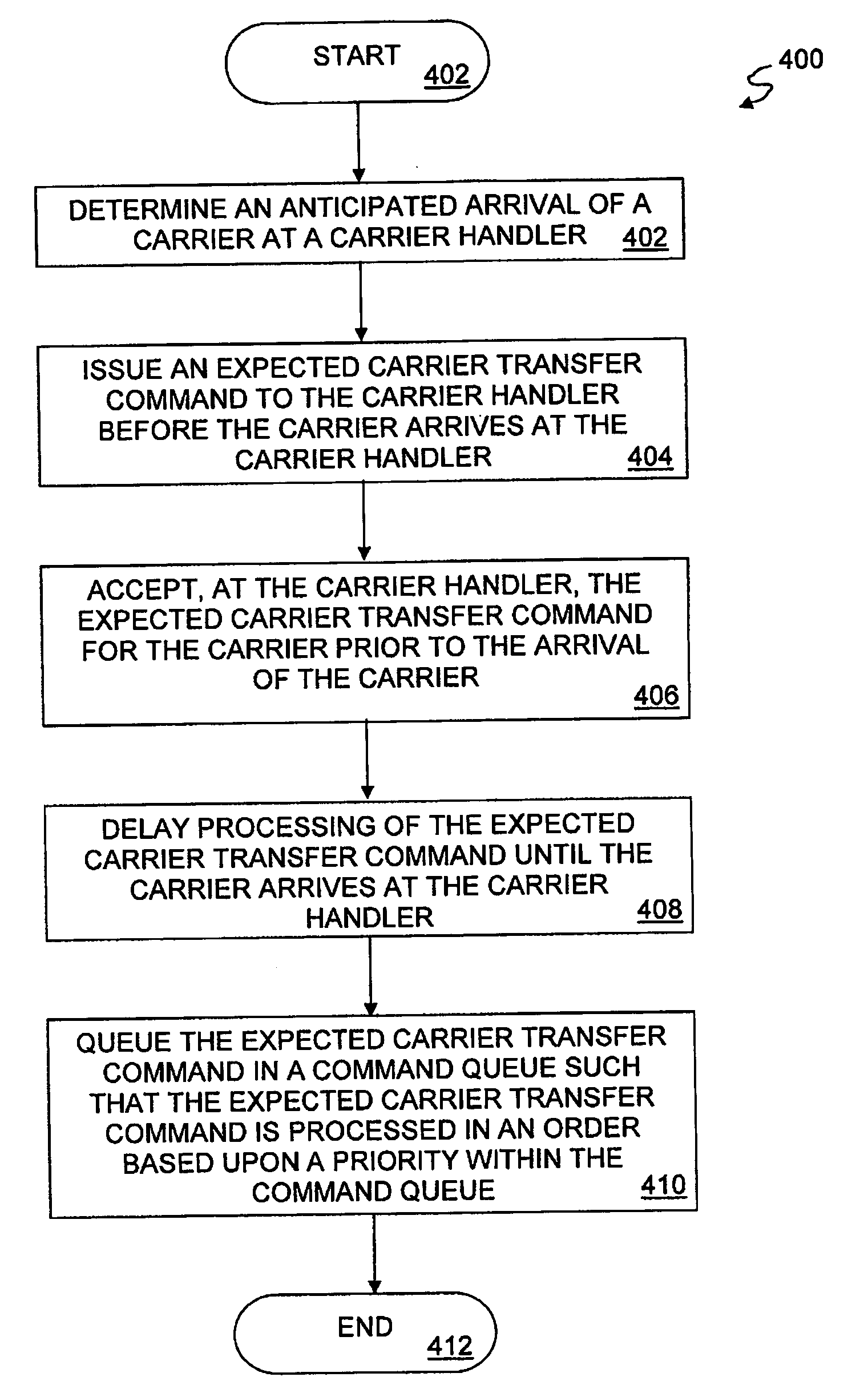
Methods and apparatus for enhanced operation of substrate carrier handlers
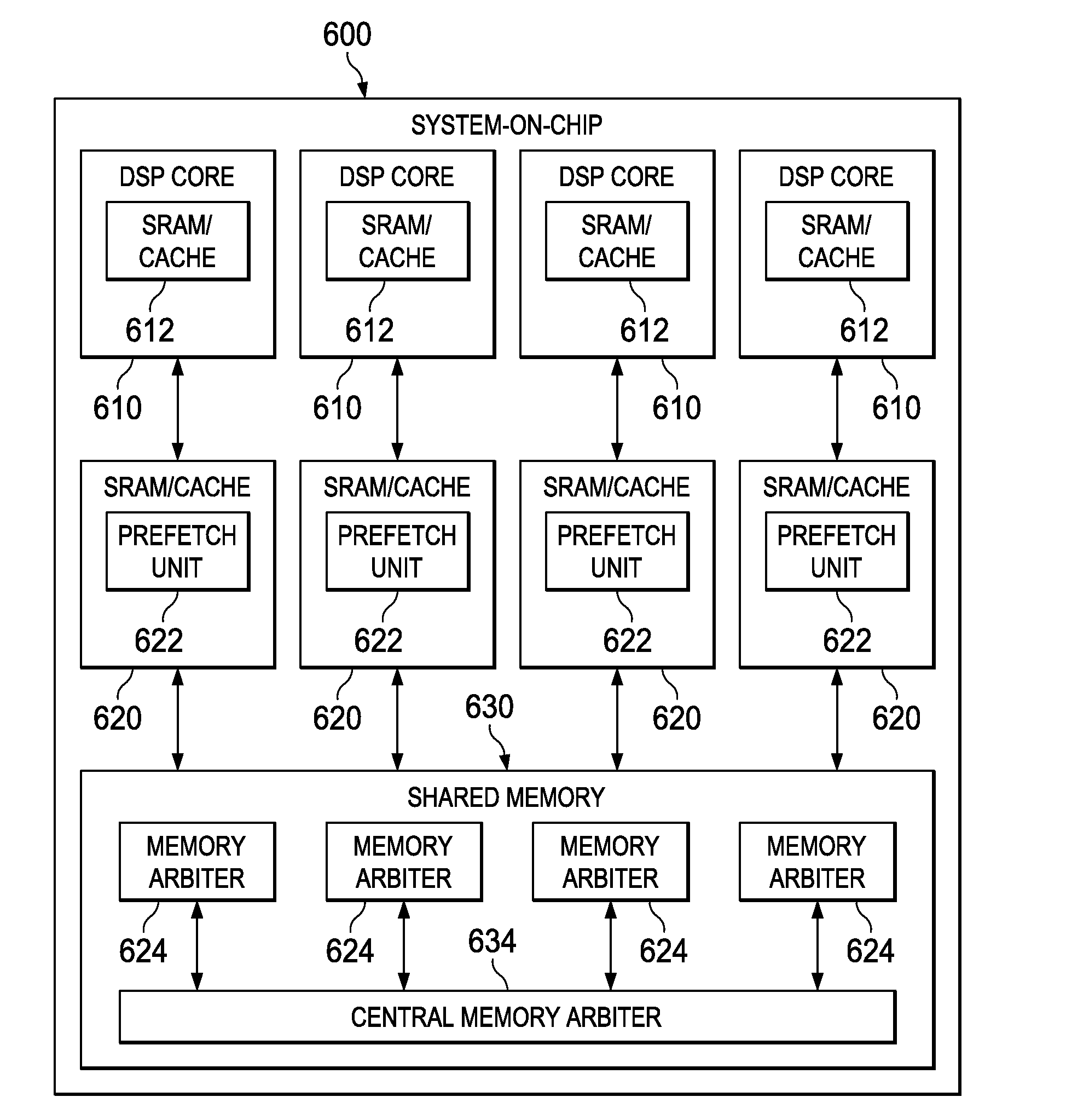
InactiveUS20050209721A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsTransport systemEngineering
A carrier handler is provided that may be adapted to (1) accept transfer commands for carriers before the carriers arrive within the domain of the carrier handler; (2) accept termination commands that result in prior commands being cancelled or aborted independent of the state of the prior commands; (3) select queued commands for out-of-order execution to take advantage of earliest arriving transport system carrier supports suitable for use with the selected commands and / or based upon the anticipated time needed to execute the commands; (4) remove empty carriers from an associated tool to improve port availability; (5) continue to operate even after transfers involving storage locations fail by removing the failed locations from a usable locations list; (6) verify the integrity of carrier and transfer destination status data with sensors prior to attempting a transfer; and (7) calibrate carrier handoffs with a transport system using a calibration carrier equipped with sensors.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Processor and method having a load reorder queue that supports reservations
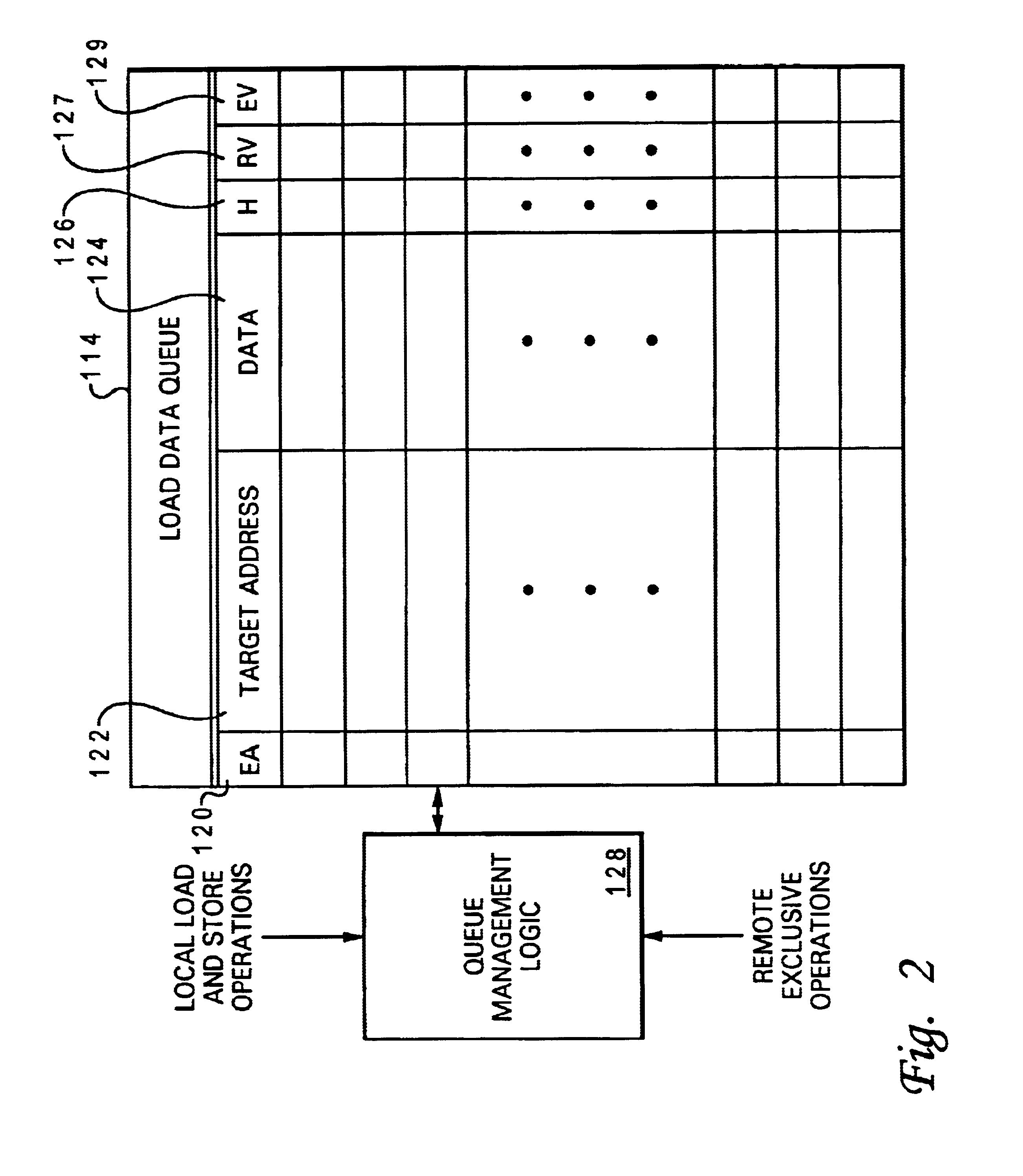
InactiveUS6725358B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationLoad instructionProcessor register
A processor includes a register set, at least one execution unit that executes load instructions to transfer data into the register set, a load queue and associated queue management logic. The load queue contains a plurality of entries that each include a reservation valid field, and each of the plurality of entries is associated with a respective one of a corresponding plurality of load instructions that includes at least one load-reserve instruction. In response to execution of the load-reserve instruction, the queue management logic detects whether a data hazard exists by reference to the load queue, and if so, initiates correction of the data hazard. In addition, the queue management logic records a reservation for the load-reserve instruction by setting the reservation valid field of an entry in the load queue associated with the load-reserve instruction. Thus, the load queue, which is utilized to detect and correct data hazards resulting from out-of-order execution of load instructions, is also advantageously utilized to manage reservations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hazard Detection and Elimination for Coherent Endpoint Allowing Out-of-Order Execution
ActiveUS20140115267A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShared memoryReceipt
A coherence maintenance address queue tracks each memory access from receipt until the memory reports the access complete. The address of each new access is compared against the address of all entries in the queue. This check is made when the access is ready to transmit to the memory. If there is no address match, then the current access does not conflict with any pending access. If there is an address match, the current access is stalled. The multi-core shared memory controller would then typically proceed to another access waiting a slot to the endpoint memory. Stored addresses in the coherence maintenance address queue are retired when the endpoint memory reports completion of the operation. At this point the access is no longer a hazard to following operations.
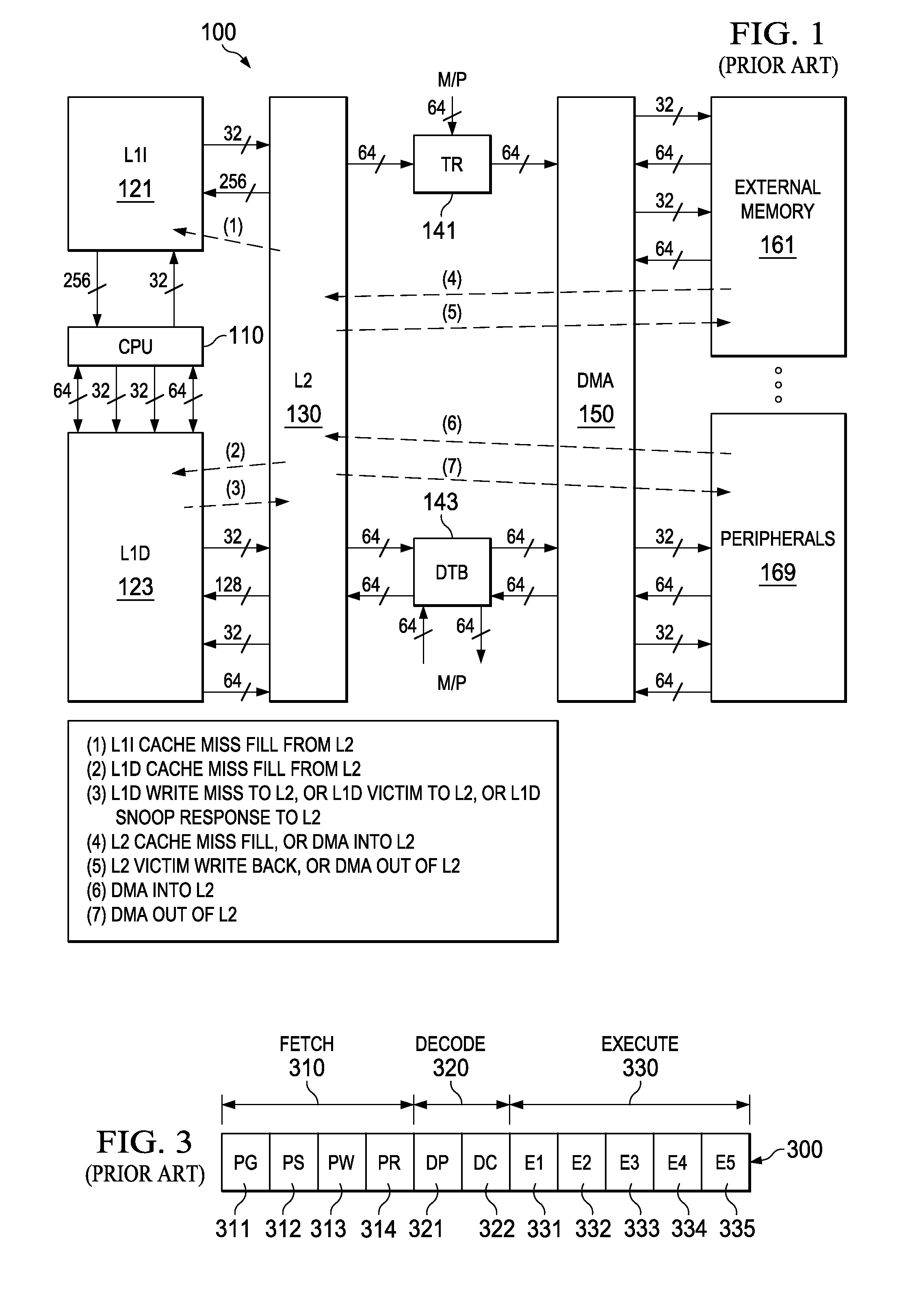
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com