Allocating threads to resources using speculation metrics
A resource allocation and threading technology, applied in the direction of resource allocation, program synchronization, multiprogramming device, etc., can solve problems such as helpless instruction throughput, restricted resources, and incorrectness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] Embodiments of the invention are described below by way of example only. These examples represent the best method currently known to applicants to put the invention into practice, but they are not the only way in which this can be done. The description clarifies the functionality of the example and the sequence of steps used to build and run the example. However, the same or equivalent functions and sequences can be performed by different examples.
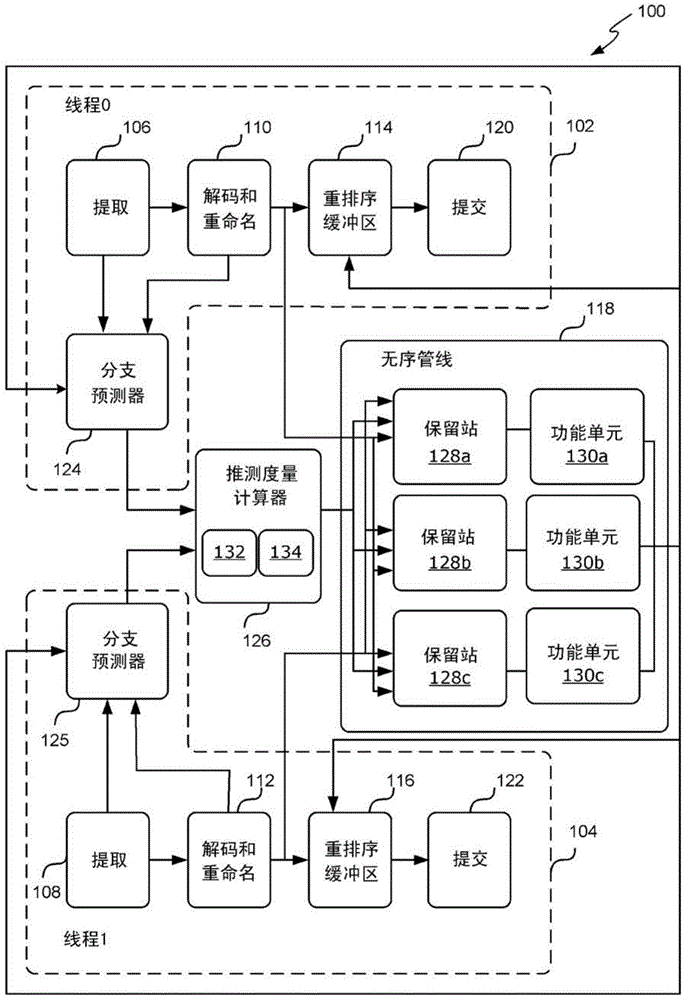
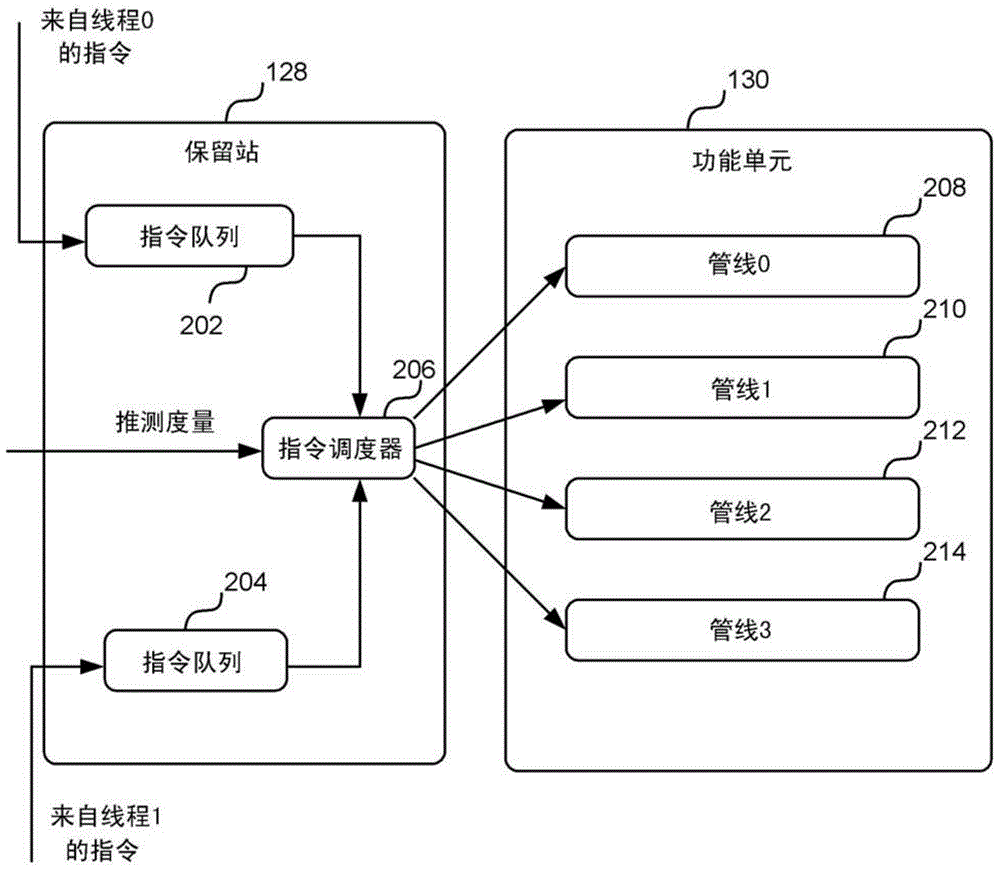
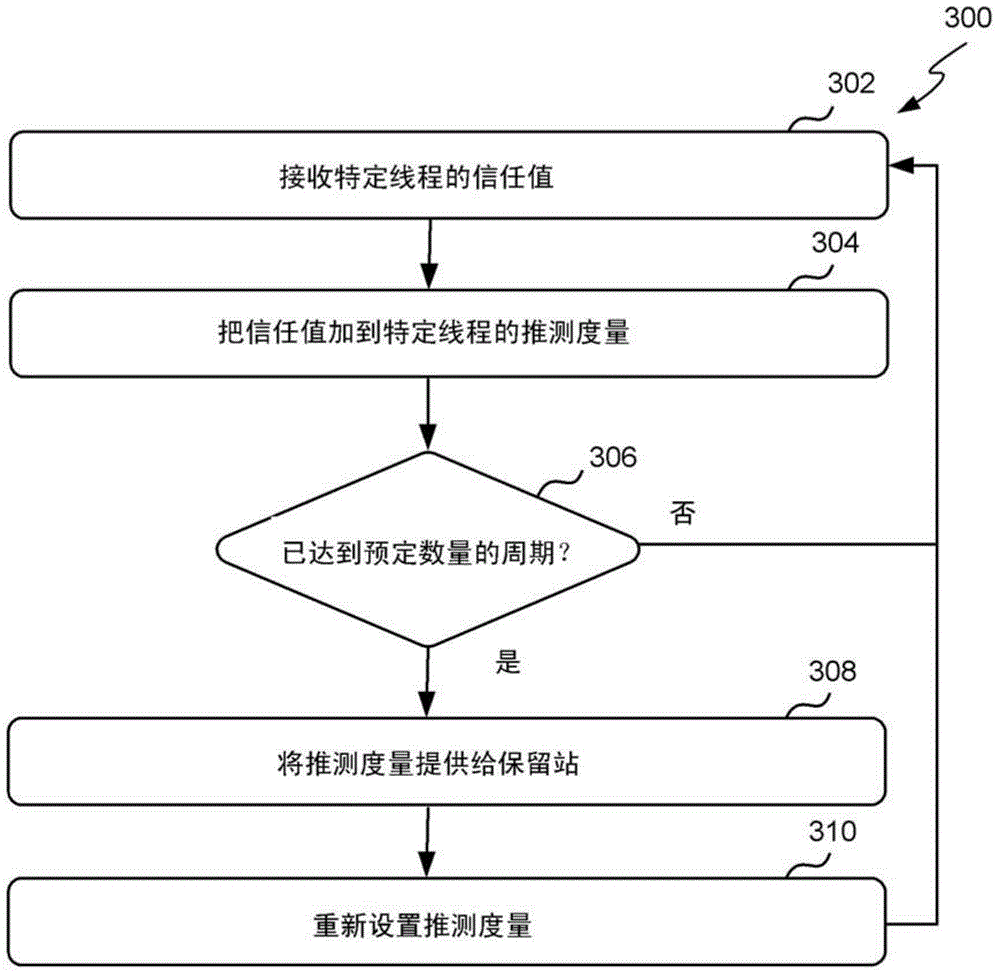
[0025] Embodiments described herein combine the superscalar and multithreading techniques described above to improve parallel processing in processors. In particular, the processors and methods described herein implement branch prediction and multithreading, where resources are assigned to threads based on speculative metrics. Each speculative metric represents how speculative an instruction associated with a particular thread is. The more speculative an instruction is, the more likely that instruction has been incorrect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com