Branch predictor and method used for operating same
A predictor, branching technology, used in instruments, memory systems, machine execution devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] vocabulary
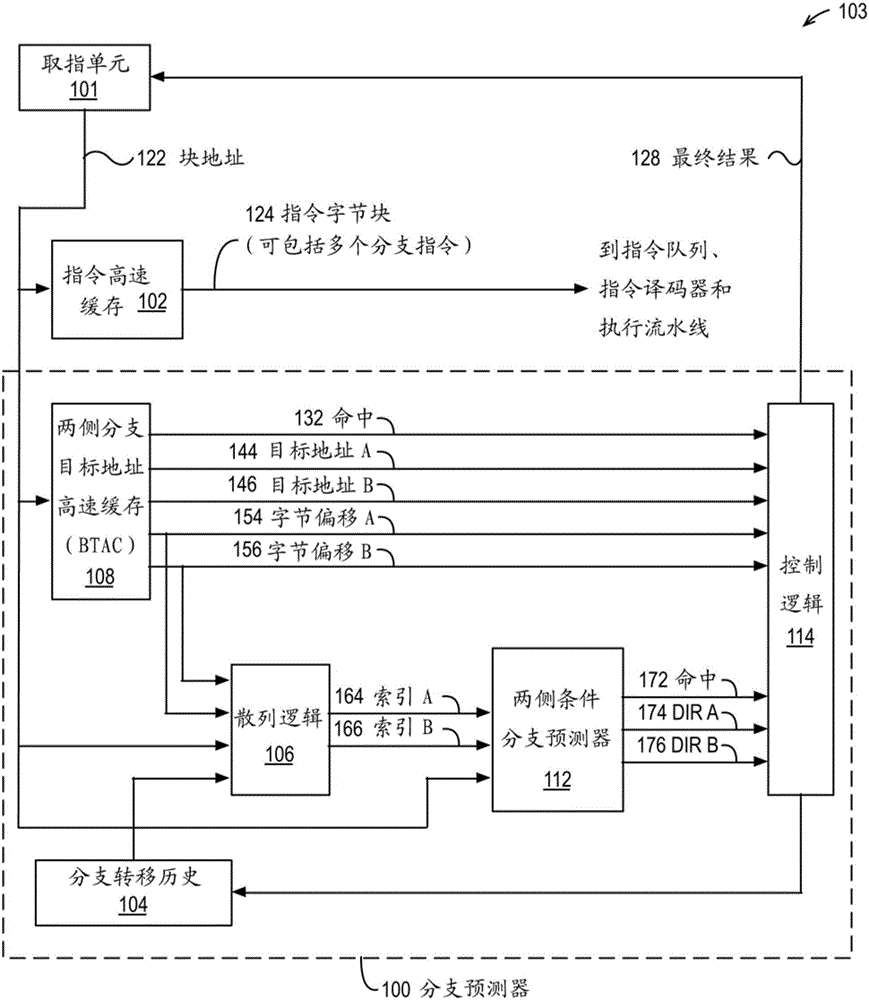
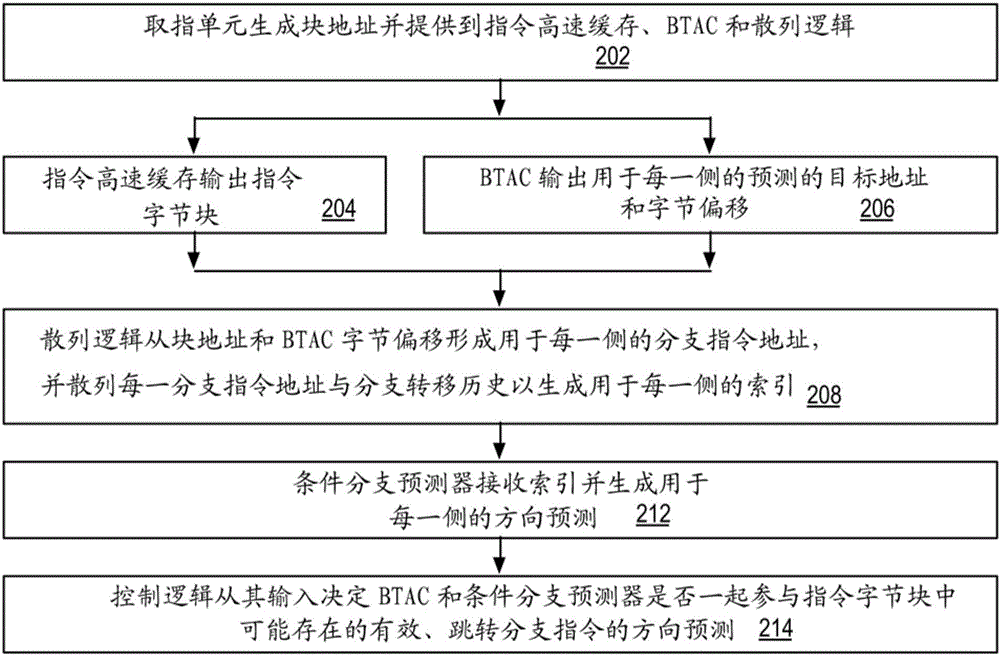
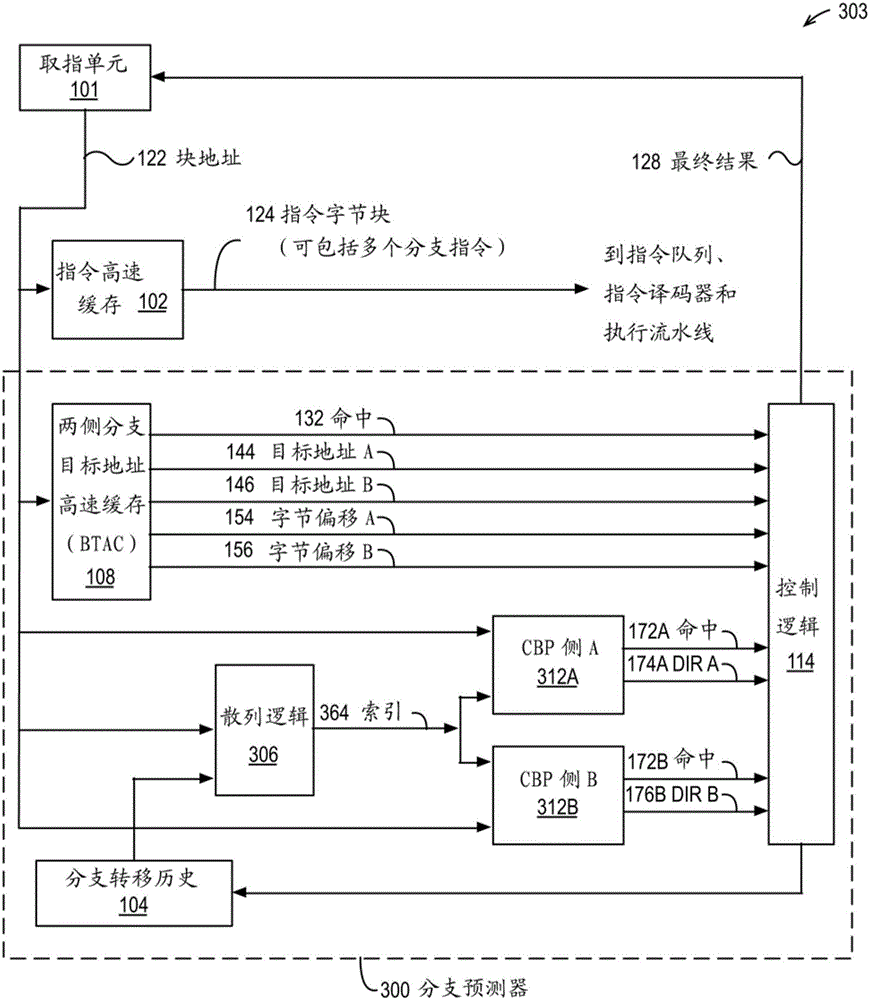
[0012] Hashing two or more entities, such as addresses and branch patterns, refers to performing one or more ANDs on one or more bits of each of two or more entities / Or logical operations to generate a result with fewer bits than the largest of two or more entities. One or more AND / or logic operations may include, but are not limited to: selection of physical pre-positioning; Boolean logic operations including XOR, NAND, AND, OR, NOT, cyclic shift and translation; and Arithmetic operations of, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulo. To illustrate by example, assume a 100-bit branch history, a 32-bit address, and the result is a 10-bit index. Hashing the address and branch transfer history (that is, hashing the address and the branch transfer history) may include bits [9:0] and bit [19:10] of the branch transfer history and bit [9:] of the branch instruction address. 0] XOR.
[0013] The branch predictor in the embodiment uses the conditional bran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com