Apparatus and method for efficiently updating branch target address cache
A branch target address, branch instruction technology, applied in machine execution device, memory address/allocation/relocation, concurrent instruction execution, etc., can solve problems such as dead knots, dead knots, errors in microprocessing, and achieve increased efficiency and reduced area. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
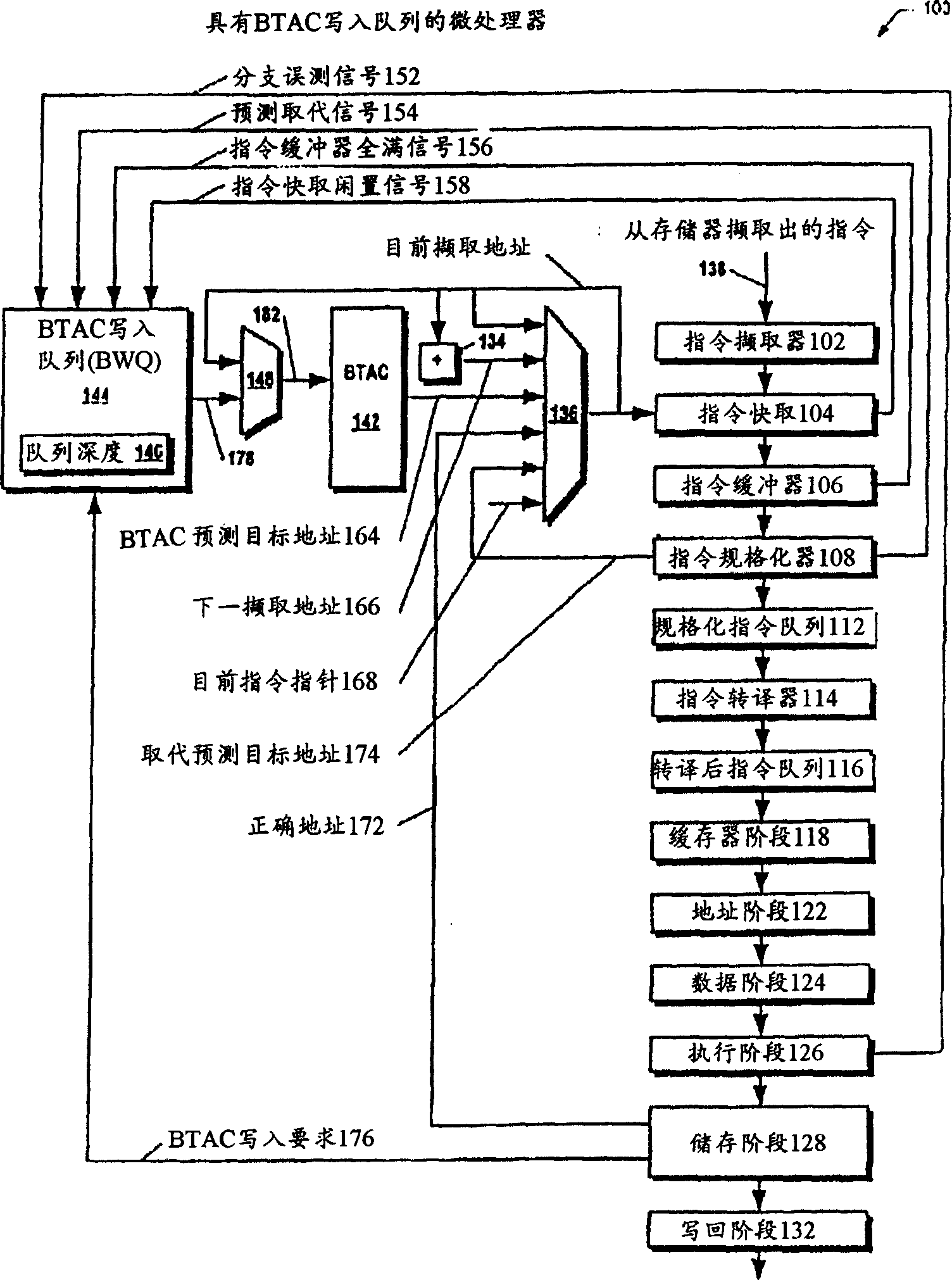
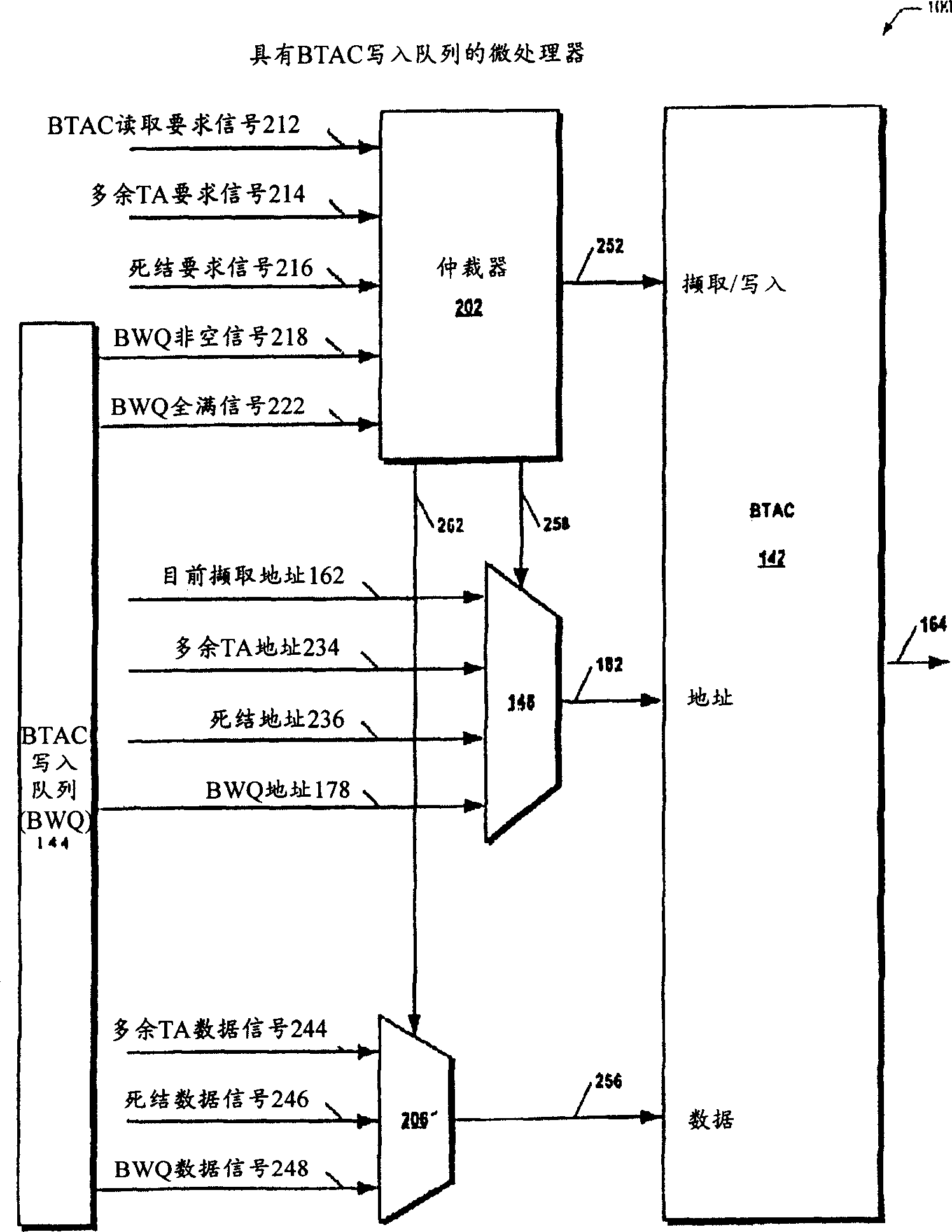
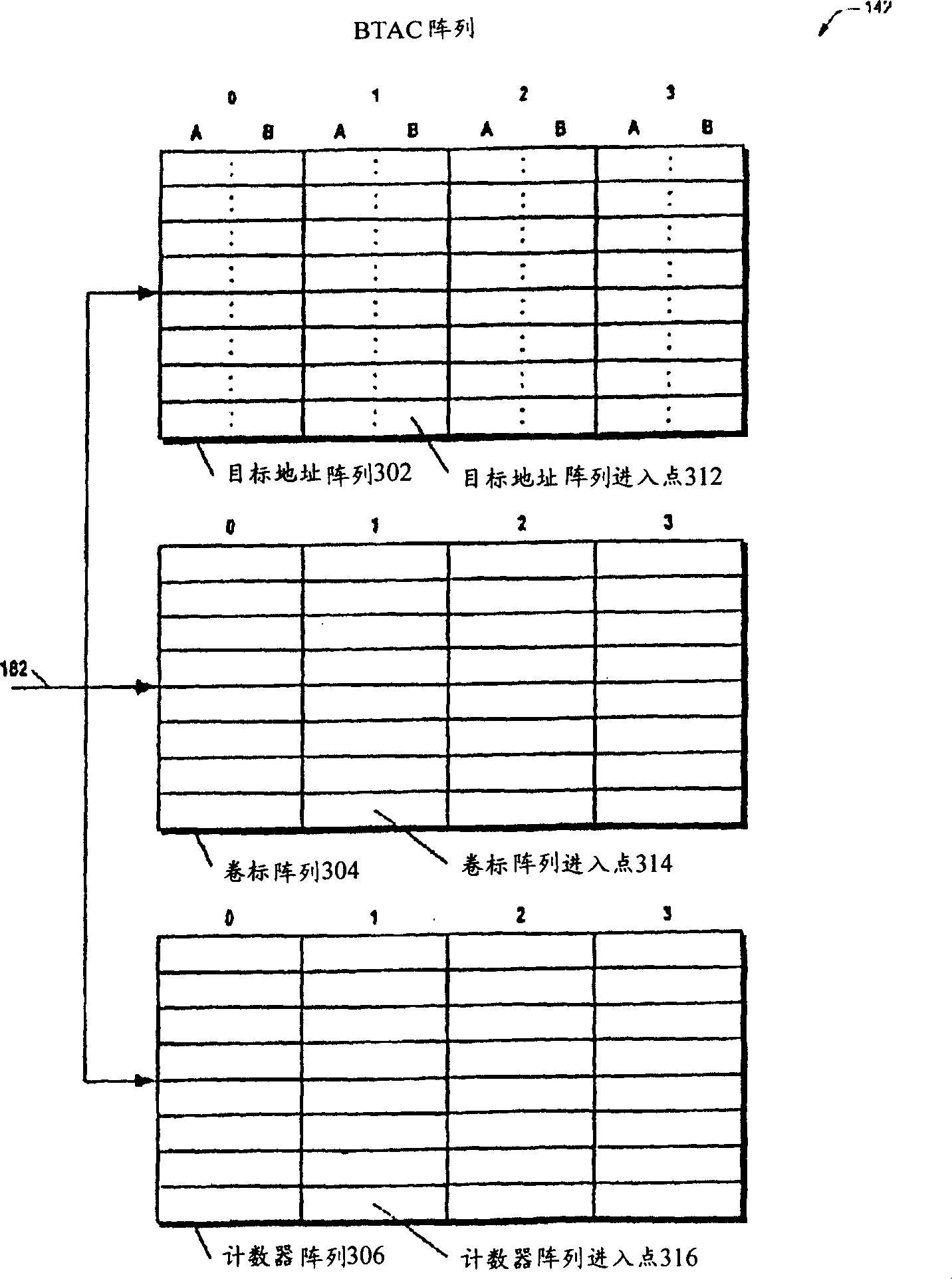
[0079] now refer to figure 1 , shows a block diagram of a microprocessor 100 according to the present invention. The microprocessor 100 includes a pipeline microprocessor.
[0080] The microprocessor 100 includes an instruction fetcher 102 . Instruction fetcher 102 fetches instructions 138 from a memory (eg, system memory) coupled to the microprocessor 100 . In one embodiment, the instruction fetcher 102 fetches instructions from memory in a granularity of cache lines. In one embodiment, the instructions are variable-length instructions. That is, all instructions in the instruction set of the microprocessor 100 have different lengths. In one embodiment, the microprocessor 100 includes a microprocessor whose instruction set is substantially compatible with the variable instruction length x86 architecture instruction set.
[0081] The microprocessor 100 also includes an instruction cache 104 coupled to the instruction fetcher 102 . The instruction cache 104 receives the ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com