Data transmission method and device
A data transmission method and equipment technology, applied in digital transmission systems, transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems affecting decoding performance, difference in signal-to-noise ratio, and different demodulation performance, and improve data decoding performance. , reducing the difference, the effect of interference equalization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
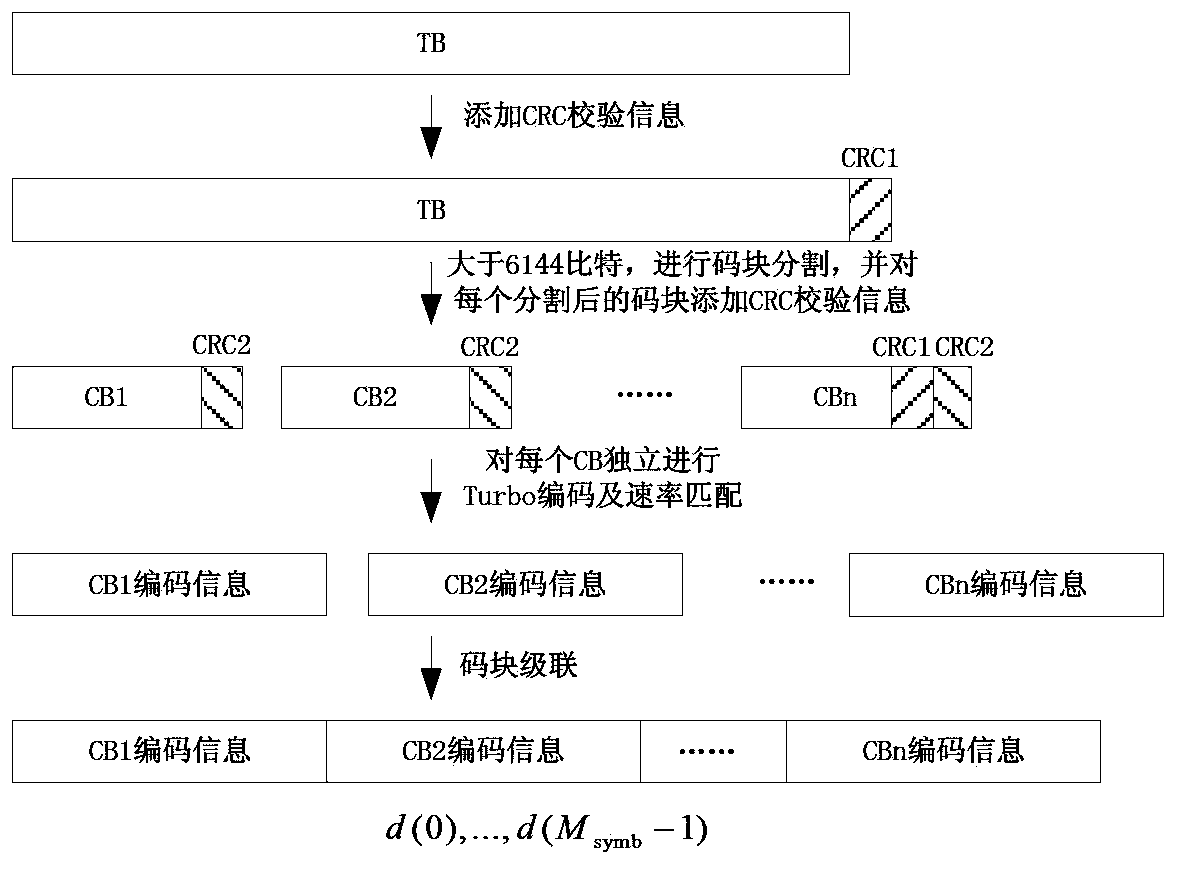
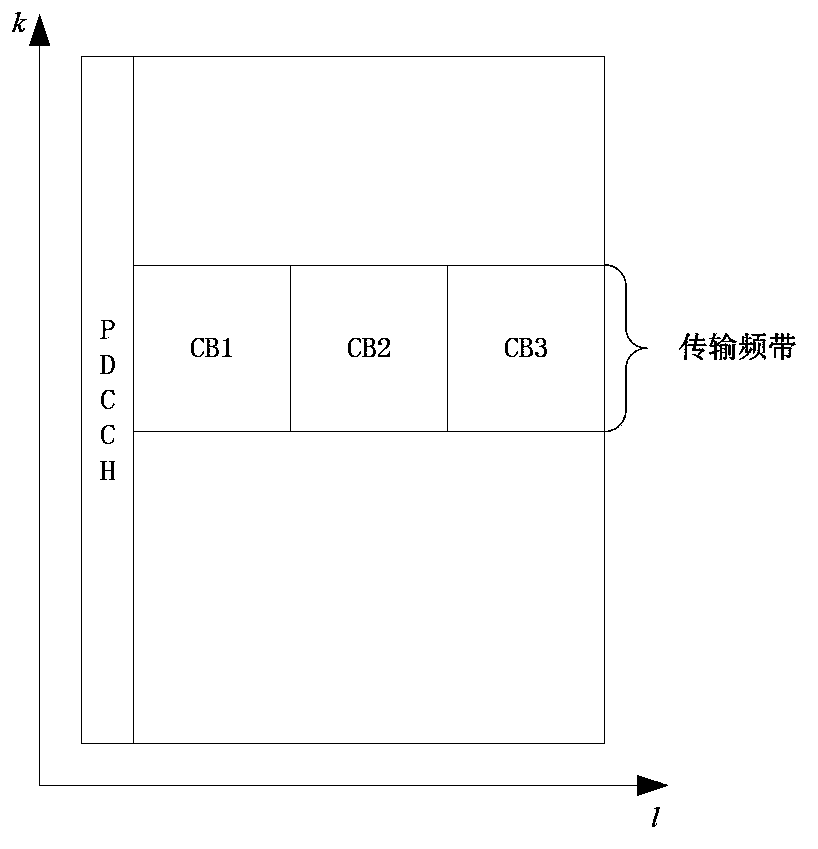
[0117] In this embodiment, one TB is divided into 3 CBs, and the lengths of coded information corresponding to all CBs are equal.
[0118] Step 1: After the sender adds CRC information to the TB to be transmitted, if the TB is larger than 6144 bits, divide the TB into three CBs: CB1, CB2, and CB3, and add CRC information after each CB; Each CB performs turbo encoding and rate matching respectively to obtain the encoding information of each CB;
[0119] Step 2: The sending end interleaves and concatenates the information bit segments contained in the coding information of each CB to obtain the coding information of the TB, such as Figure 8b shown;
[0120] Step 3: The sending end modulates the coded information of the TB, and sends the modulated data;
[0121] Specifically, in step 2, the sending end interleaves and concatenates the information bit segments contained in the coded information of each CB as follows:
[0122] Assume Where L is the length of the coded informa...
Embodiment 2
[0126] In this embodiment, one TB is divided into three CBs, and all CBs have the same length.
[0127] Step 1: The receiving end receives the data corresponding to the TB sent by the sending end, and demodulates the received data to obtain the encoding information of the TB;
[0128] Step 2: The receiving end de-concatenates the coding information of the TB to obtain the coding information of multiple CBs, wherein the coding information of the TB is obtained by interleaving and concatenating information bit segments contained in the coding information of each CB, as shown in Figure 8b shown;
[0129] Step 3: The receiving end performs de-rate matching and decoding processing on each CB.
[0130] Specifically, in step 2, the coding information of the TB is obtained by interleaving and concatenating the information bit segments contained in the coding information of each CB, and the specific method is as follows:
[0131] Assume Where L is the length of the coded informati...
Embodiment 3
[0135] In this embodiment, one TB is divided into three CBs, and there are two kinds of encoded information lengths corresponding to the CBs, CB1 corresponds to a shorter encoded information length, and CB2 and CB3 correspond to longer encoded information lengths.
[0136] Step 1: After the sender adds CRC information to the TB to be transmitted, if the TB is larger than 6144 bits, divide the TB into three CBs: CB1, CB2, and CB3, and add CRC information after each CB; Each CB performs turbo encoding and rate matching respectively to obtain the encoding information of each CB;
[0137] Step 2: The sending end interleaves and concatenates the information bit segments contained in the coding information of each CB to obtain the coding information of the TB, such as Figure 8b shown;
[0138] Step 3: The sending end modulates the coded information of the TB, and sends the modulated data;
[0139] Specifically, in step 2, the sending end interleaves and concatenates the informati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com