Sidelobe Compression Method of Scanning Beam Based on Optical Waveguide Array Electro-optic Scanner
An electro-optic scanner and scanning beam technology, applied in the laser field, can solve problems such as unequal pitch design, infeasibility, large array element pitch design, etc., to achieve the effect of improving quality and avoiding processing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] 1. Technical principles
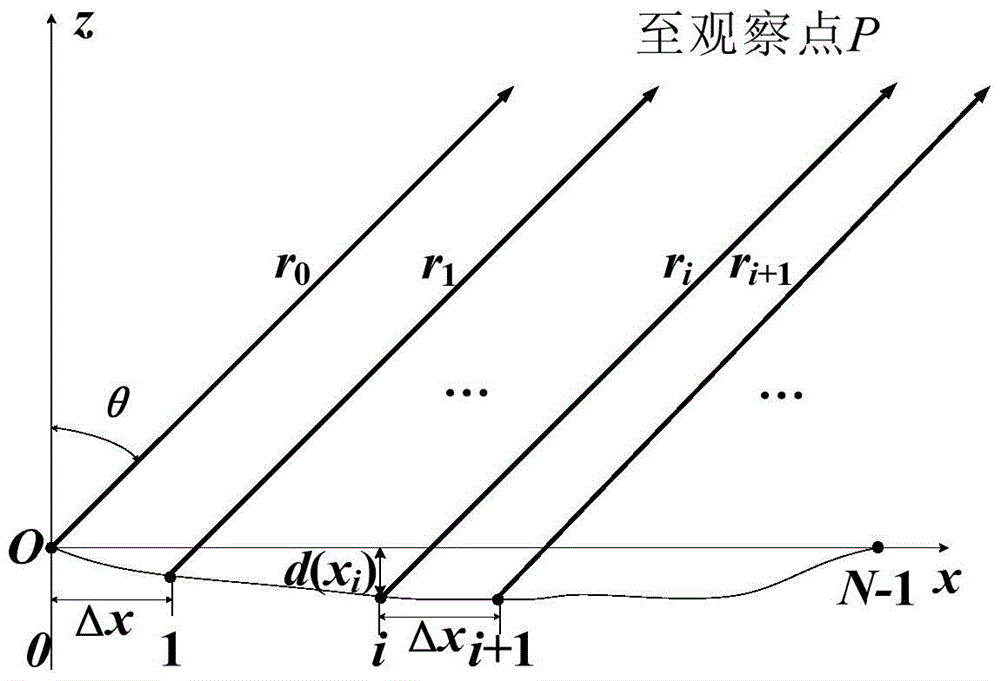
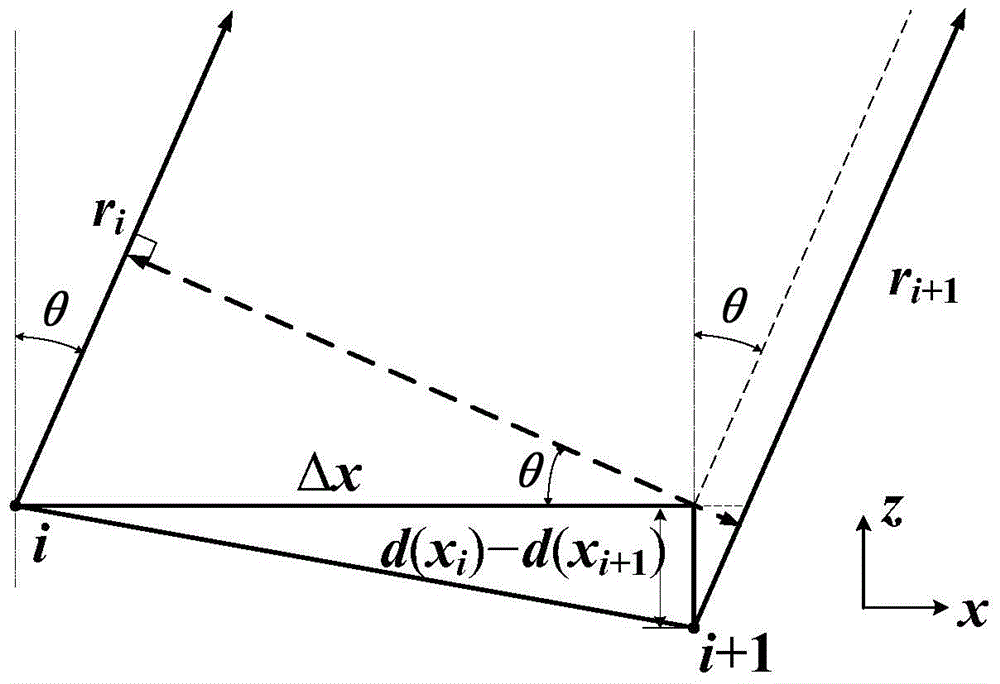
[0024] For an optical waveguide array with an uneven end face, the spatial diffraction geometric model is as follows figure 1 As shown, the output surface composed of N array elements is an arbitrary non-flat surface, and the end surface function d(x i ), defined as the position that deviates from the x-axis along the z-axis direction based on the x-axis. For a point P in the far field, its deflection angle relative to the z-axis direction is θ, and the optical field intensity E of the wavelength λ emitted by the i-th waveguide layer i (θ) is
[0025]
[0026] where A i is the optical field amplitude of the i-th array element, is the phase of the beam after passing through the waveguide, r i is the distance from the i-th array element to point P, f i (θ) is the tilt factor, θ is r i Angle with the z-axis.
[0027] The total optical field at point P is regarded as the total optical field superposition of all N array elements to point...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com