Optical Modules and Optical Transmitters
An optical module and optical waveguide technology, applied in optics, instruments, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the size of the module and increasing the size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] Embodiments of the optical module and the optical transmitter will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
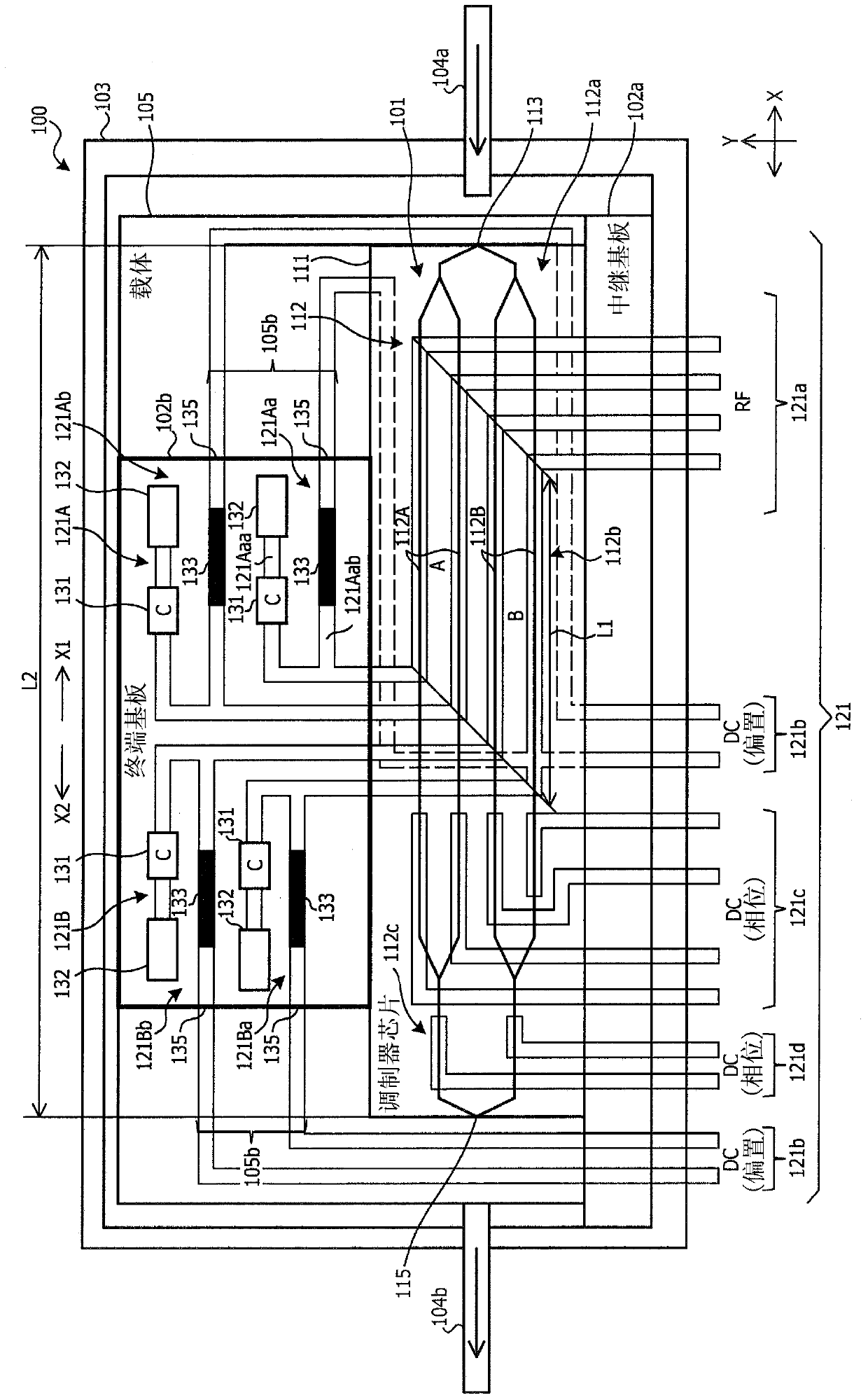
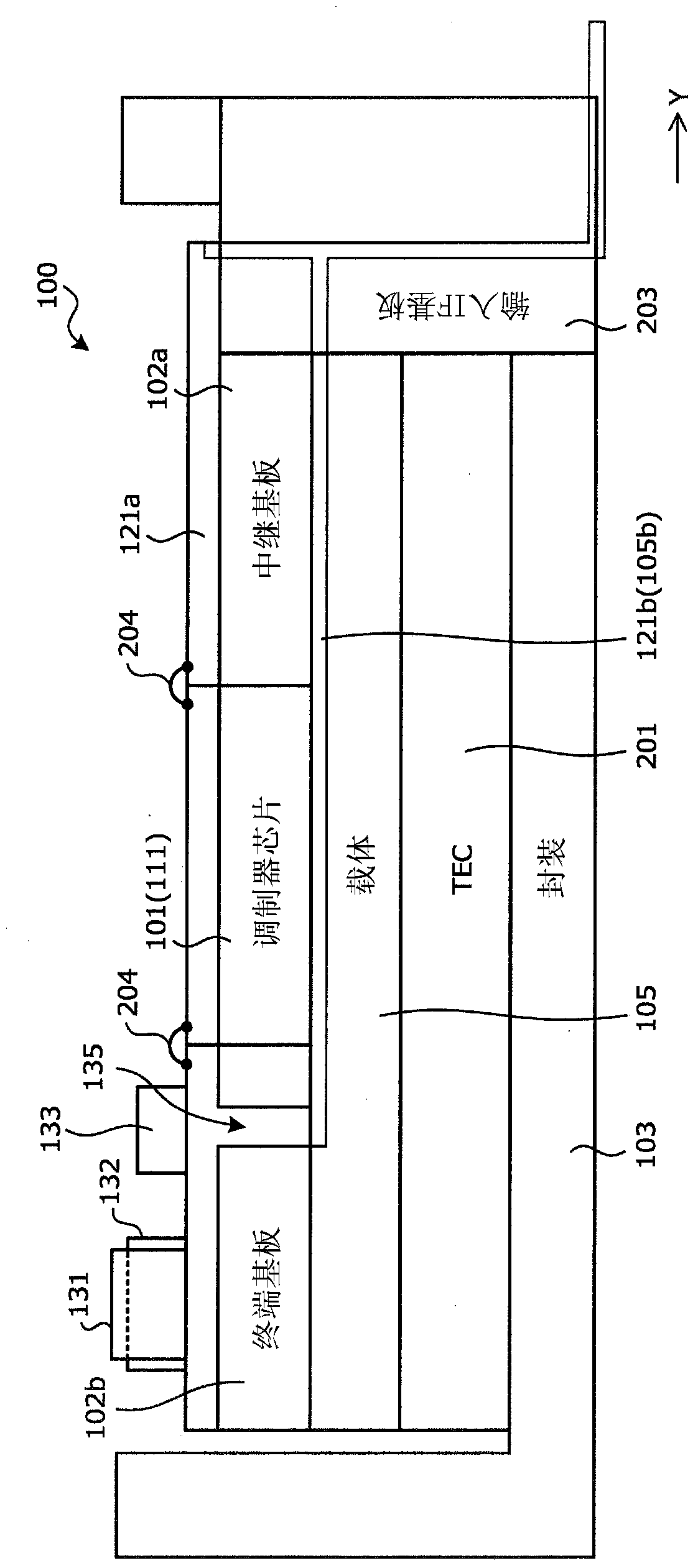
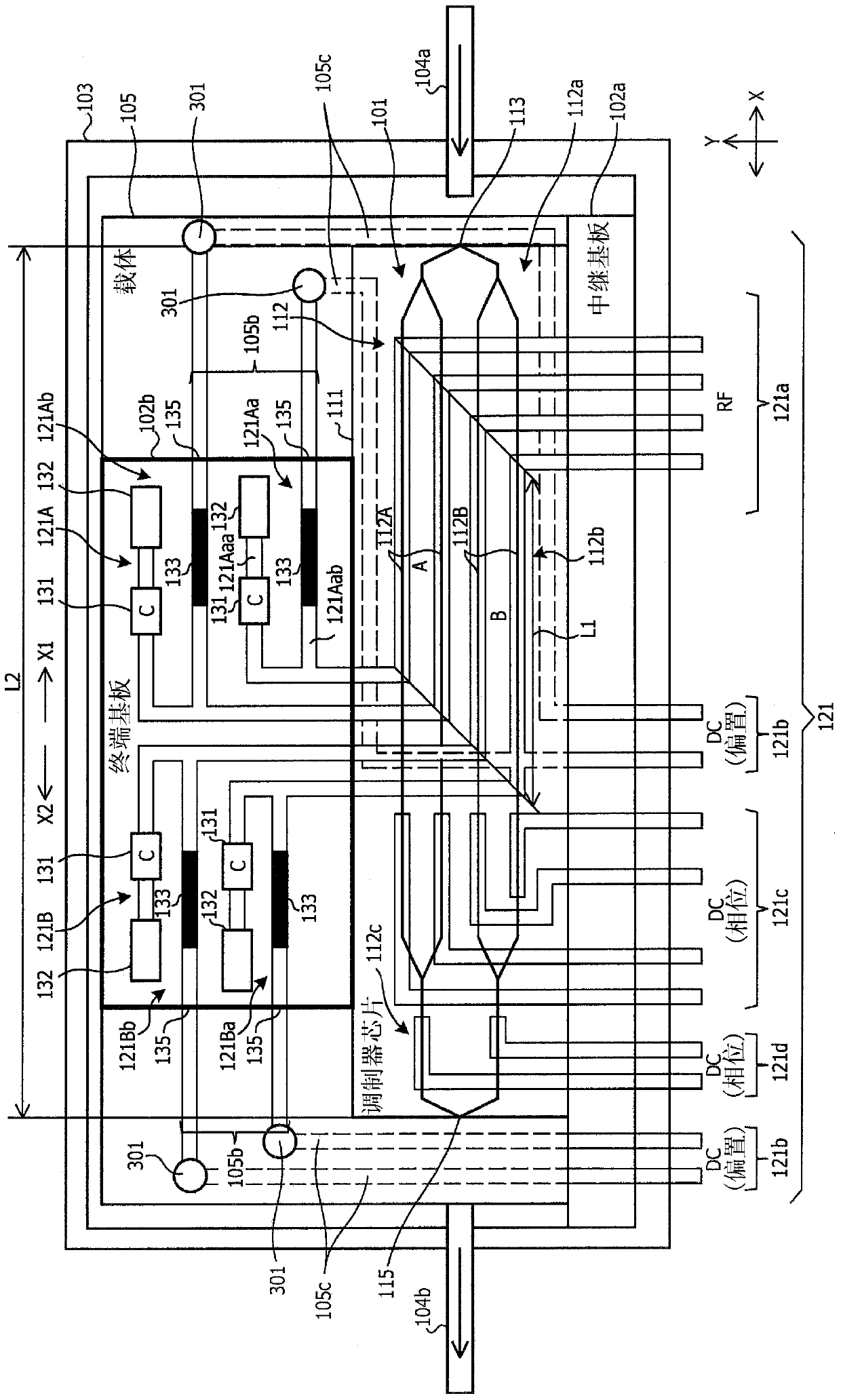
[0024] figure 1 is a top view of the optical module according to the first embodiment, figure 2 is a side sectional view of the optical module according to the first embodiment. This optical module 100 is a construction example of a QPSK optical modulator, including a Mach-Zehnder modulator unit (modulator chip) 101, an electrode substrate 102, and a housing (packaging) for accommodating the Mach-Zehnder modulator unit 101 and the electrode substrate 102 103 , input / output optical fiber 104 ( 104 a , 104 b ), carrier (substrate) 105 . A plurality of terminals (RF terminals and DC terminals, which will be described later) are formed on the electrode substrate 102 .
[0025] On the carrier 105 in the housing 103 the waveguide substrate 111 of the Mach-Zehnder modulator unit (modulator chip) 101 is arranged. On the carrier 105 , the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com