Method of determining the presence or absence of target nucleic acid in cell sample
A target nucleic acid and cell technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA preparation, etc., can solve problems such as extending running time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0175] According to one embodiment, the method of the present invention comprises the following steps d) and e):
[0176] Step d):
[0177] - contacting the sample containing the released and denatured nucleic acid with one or more target nucleic acid-specific probes under conditions that allow the probes to hybridize to single-stranded target nucleic acid molecules to form double-stranded nucleic acid hybrids;
[0178] Step e):
[0179] - detecting the presence or absence of a double-stranded nucleic acid hybrid.
[0180] Preferably, the method of the present invention comprises the following steps d) and e):
[0181] Step d):
[0182] - subjecting a sample containing released and denatured nucleic acid and magnetic particles for binding cells to one or more target nucleic acids under conditions that allow hybridization of the probes to single-stranded target nucleic acid molecules to form double-stranded nucleic acid hybrids sex probe contact;
[0183] Step e):
[0184...
Embodiment 1
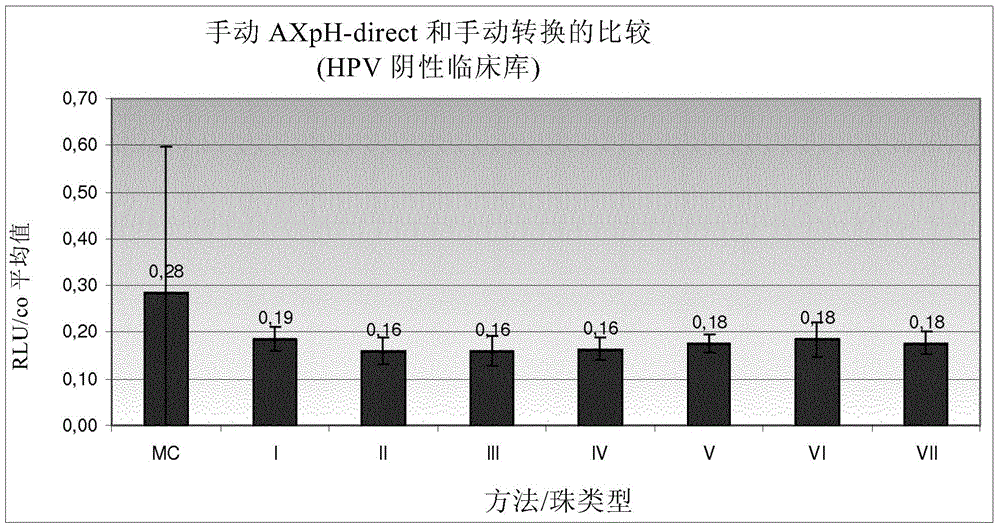
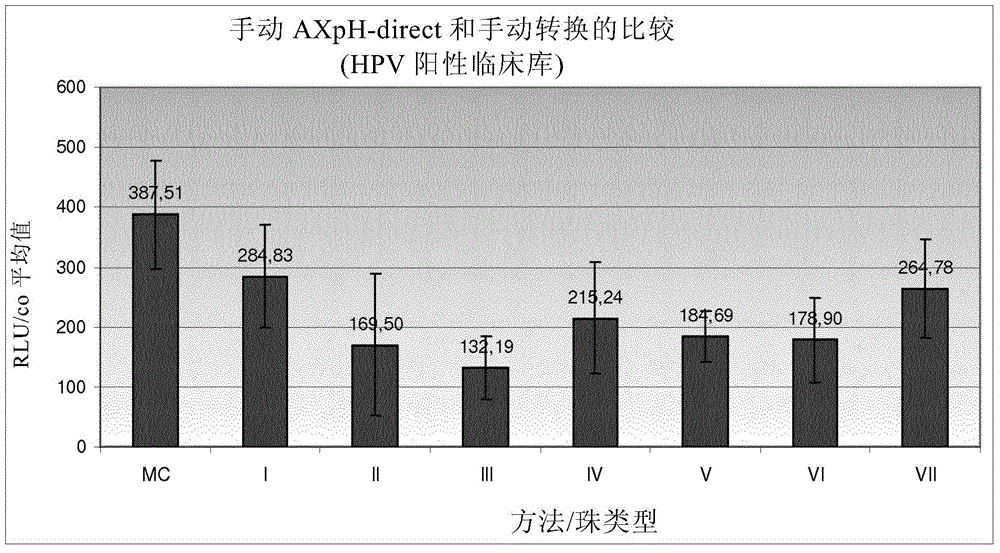
[0380] Example 1: Comparison of manual AXpH-direct and manual conversion
[0381] 1.1) Reference: Sample preparation by manual conversion (MC)
[0382] In MC, which is a standard prior art method, sample preparation is as follows: Samples of HPV-negative clinical pools and HPV-positive clinical pools formulated in culture medium (see below). Obtained by density gradient centrifugation Post-gradient samples, corresponding obtained samples were further processed as described below.
[0383] First, vortex the sample thoroughly. 2.8ml of each sample was transferred to a 15ml centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 800g for 10 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was decanted and the centrifuge tube (opening facing down) was tapped 3 times on a cloth. 200 μl of sample transport medium (Specimen Transport Medium-STM, Digene - containing chaotropic agent) was added to each pellet, ie sample, and vortexed at maximum speed for 15 seconds until all pellets were resuspended...
Embodiment 2
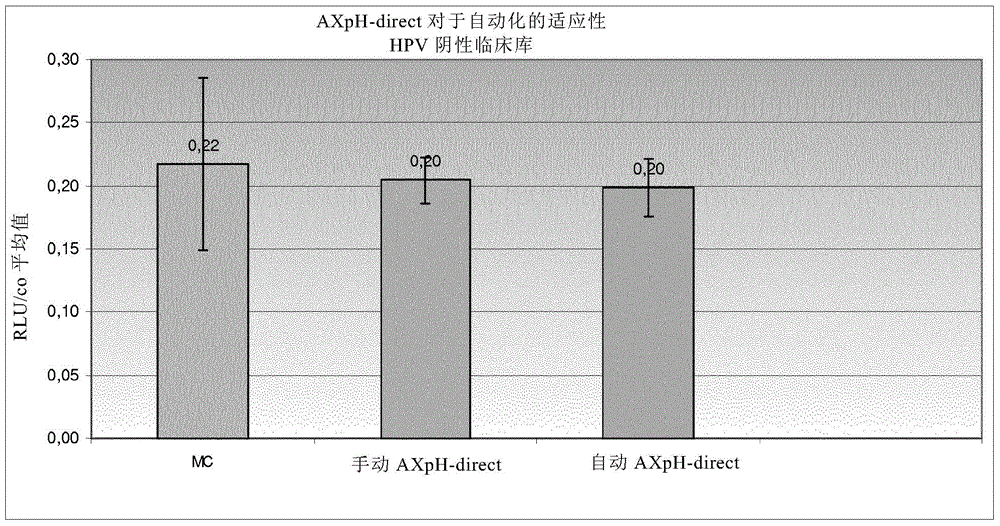
[0400] Example 2: AXpH-direct method for the applicability of automation
[0401] In Example 2, the following samples were processed:
[0402] 1) HPV-negative clinical library in medium (RLU / CO about 0.2),
[0403] 2) SiHa cells in medium (HPV positive; 1 × 10 5 cells / ml),
[0404] 3) HPV-positive clinical pool 1 in medium (RLU / CO approximately 186.4), and
[0405] 4) HPV positive clinical pool 2 in medium (RLU / CO ~530).
[0406] 1.1) Reference: Manual Conversion (MC)
[0407] See Example 1 for the manual conversion (MC) protocol.
[0408] 1.2) Manual AXpH-direct method
[0409] First, vortex the sample thoroughly. Combine 2.8ml of each sample, i.e., with 1.4ml 1.4ml of the original sample mixed with medium, transferred to a 5ml PP-tube. 50 [mu]l of Bead Suspension I (see Example 1) was added. Secure the tube with the cap, carefully invert 10 times, and vortex for 30 seconds. Samples were then incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. After incubation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com