Method Of Isolating Nucleic Acid From Specimens In Liquid-Based Cytology Preservatives Containing Formaldehyde
A technology of cytology and preservatives, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, organic chemistry, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as unresolved and insufficiently given
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
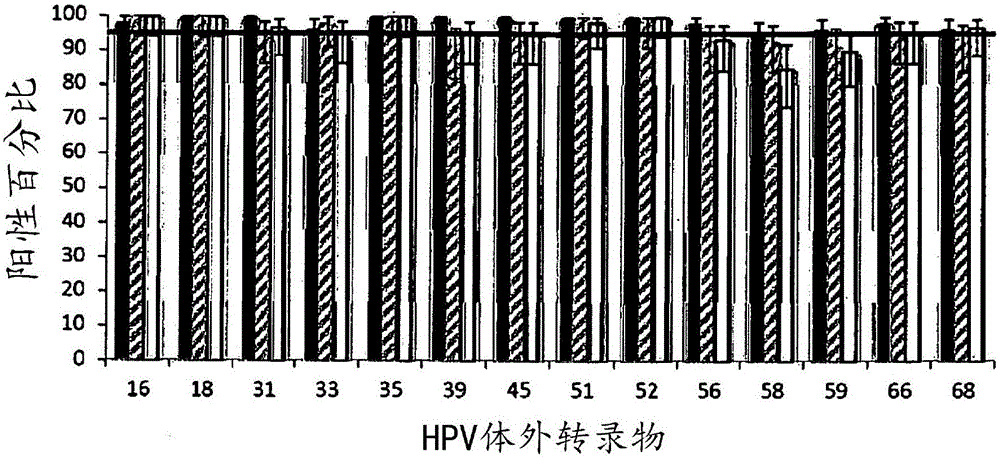
[0080] Example 1 describes the method used to assess the analytical sensitivity of the experimental system by testing an experimental panel comprising in vitro transcripts for each of the 14 high-risk HPV genotypes. The success of nucleic acid processing techniques involving treatment with 2-imidazolidinone and proteinase K at elevated temperature conditions was measured by detection of HPV RNA using a commercially available assay. As described below, the results show that treatment conditions do not affect the amplification and detection of HPV RNA.
[0081] Example 1
[0082] Establishing Analytical Sensitivity of HPV Assays Using Synthetic Transcripts
[0083] Transcripts synthesized in vitro serve as templates for amplification in conventional TMA reactions using HPV gene probe assays were performed. Transcript copy numbers for each of the different HPV types correspond to the limit of detection (LOD) of the APTIMA HPV Gene Probe assay, which has been preserved in ...
example 2
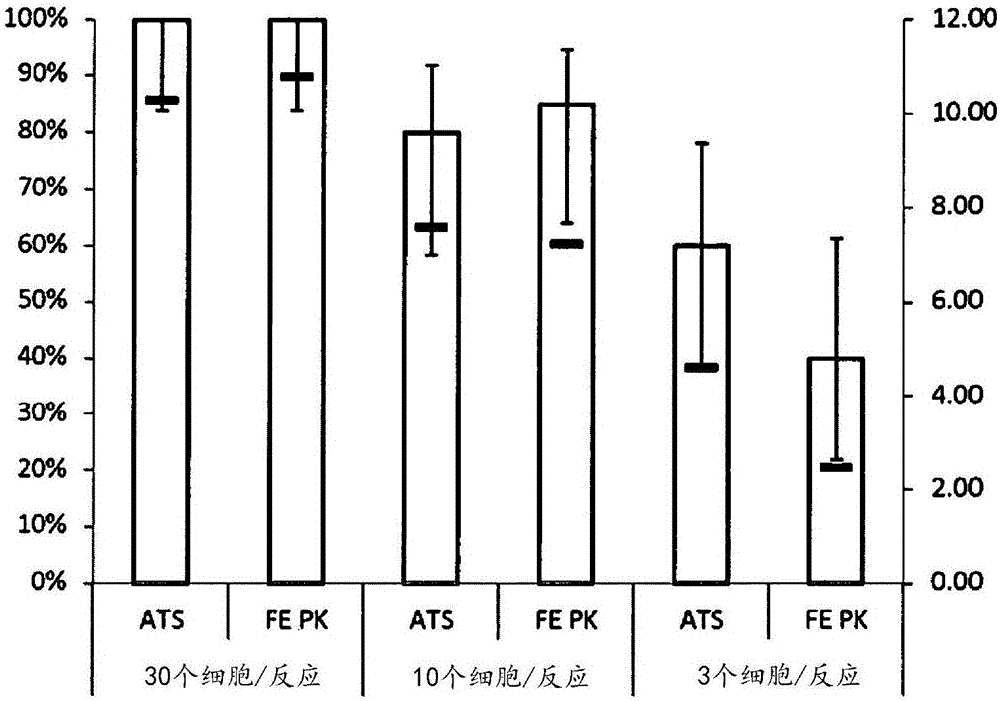
[0086] Example 2 describes a method for evaluating the analytical sensitivity of an HPV assay by testing a panel of HPV-containing human cells. The method was generally as described in Example 1 except: (1) an HPV expressing cell line was used instead of in vitro transcripts; and (2) samples were incubated for extended periods of time in the presence of formaldehyde-containing preservatives.
[0087] Example 2
[0088] Establishing Analytical Sensitivity of HPV Assays Using HPV-Containing Human Cell Lines
[0089] HPV-containing human cell lines were spiked into sample pools of SUREPATH liquid-based cytology preservative, stored at 25°C for 7 days, and then treated with a combination of recovery agent solution and proteinase K at 90°C for 15 minutes, or at 65°C °C were tested in half-log dilutions (3 to 30 cells / reaction) after proteinase K treatment alone for 2 hours. As in Example 1, the combination of recovery agent solution and proteinase K is conveniently provided a...
example 3
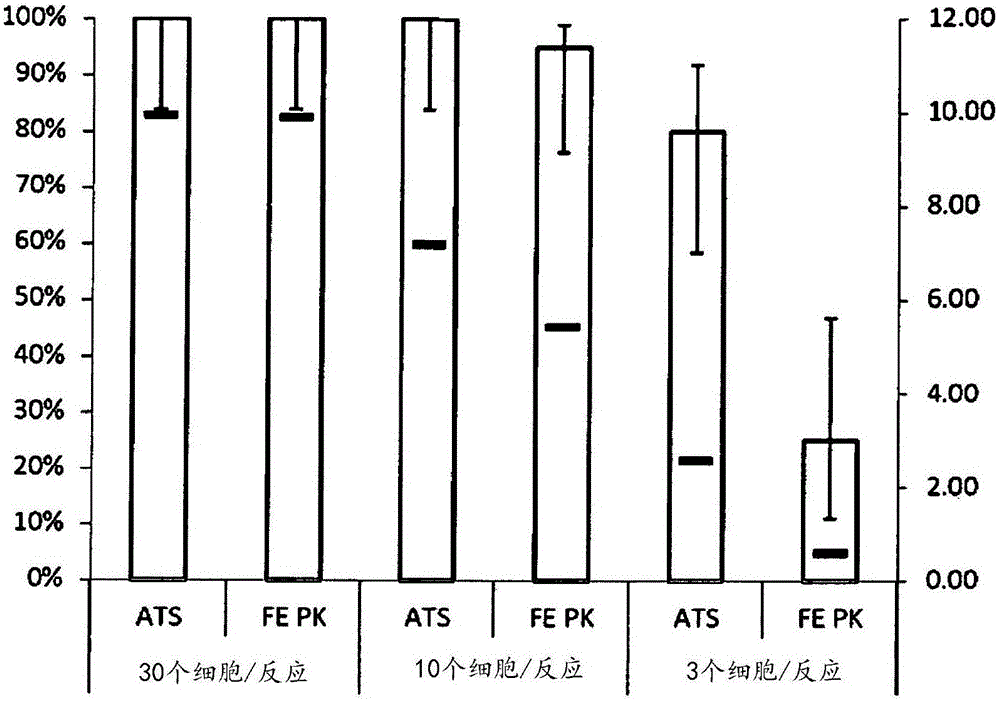
[0091] The method described in Example 3 demonstrates how the combined use of 2-imidazolidinone and proteinase K under elevated temperature conditions improves the recovery of amplifiable nucleic acids from samples stored for long periods of time in liquid-based cytological preservatives containing formaldehyde Rate. As discussed below, the difference in RNA recovery was most pronounced over extended time periods compared to experiments treated with proteinase K alone.
[0092] Example 3
[0093] Enhanced recovery of amplifiable mRNA from cell samples stored in formaldehyde-containing liquid-based cytology preservatives
[0094] To mimic clinical samples, ten pools of residual samples in SUREPATH Liquid-Based Cytology Preservative previously confirmed as HPV-negative using the APTIMA HPV Gene Probe assay were split in half and spiked into either SiHa or HeLa cells. All tubes were stored neat at 25°C for up to 42 days. On each test day, aliquots of each pool were diluted...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com