A cost-effective CDN system and a method for file pre-push and fragment caching
A cost-effective, high-quality file technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve the problems of reducing node storage space, eliminating unpopular files, and unable to cache files, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing back-to-source bandwidth and storage space, improving resource utilization, and improving service performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
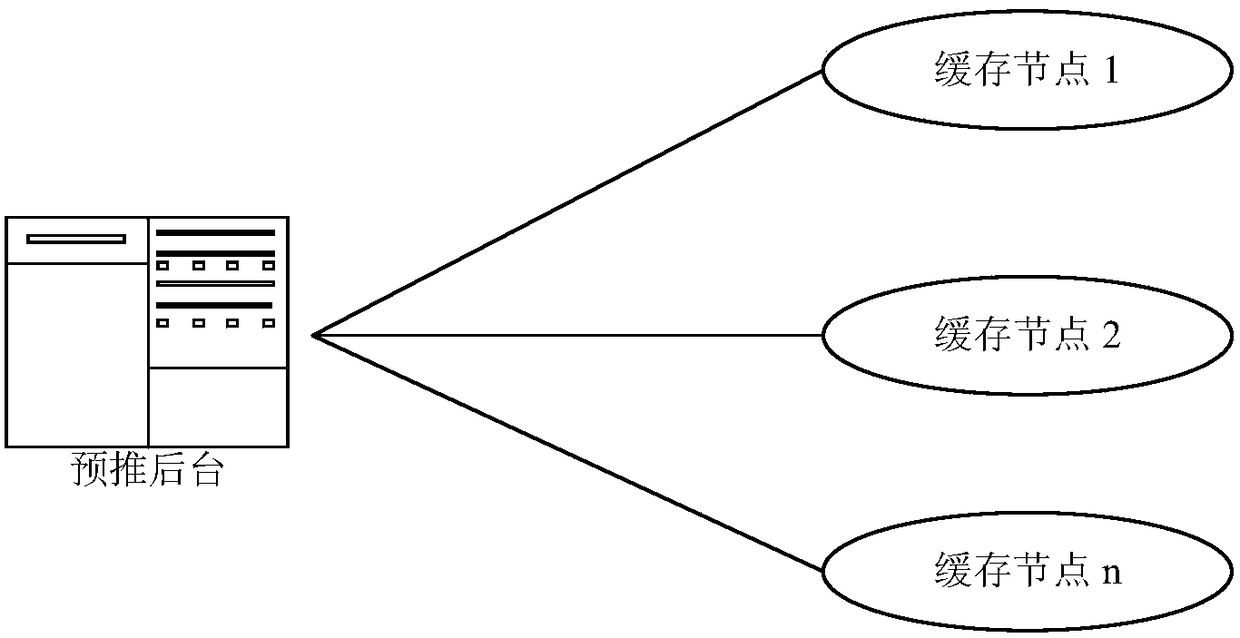
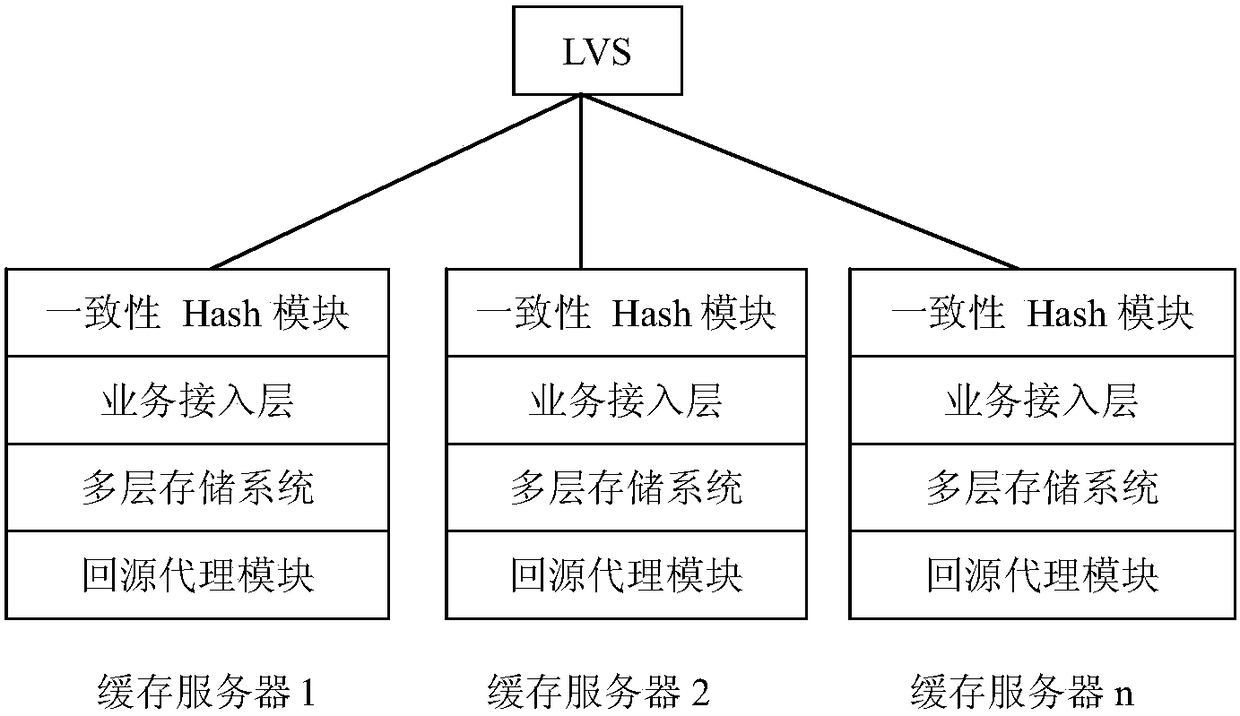
[0066] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a cost-effective CDN system, including:
[0067] File pre-push background: used to record the client’s file pre-push request, and also used to convert the file pre-push request and send it to one or more cache nodes;
[0068] Cache node: including a Linux virtual server and multiple cache servers, multiple cache servers are respectively connected with the Linux virtual server data;
[0069] Linux virtual server: used to select a cache server, and also used to forward the file pre-push request sent by the file pre-push background to the selected cache server;
[0070] Cache server: including a consistency Hash module, a multi-layer storage system and a return-to-source proxy module; The permanent Hash algorithm determines the address and disk number of the cache server storing the pre-push files; the multi-tier storage system is used for scheduling and storing files; the back-to-source proxy...
Embodiment 2
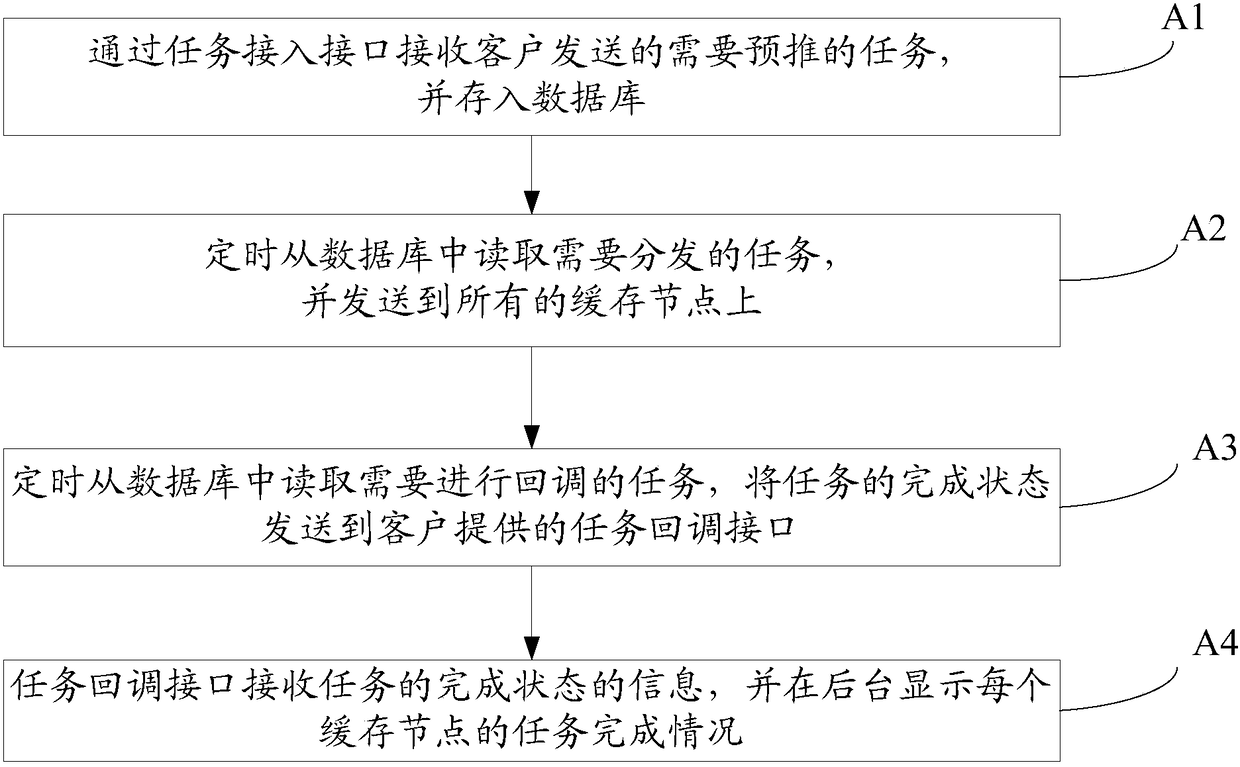
[0125] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for pre-pushing files using the cost-effective CDN system provided in Embodiment 1, including the following steps:
[0126] C1, the file pre-push background sends the file pre-push request to the Linux virtual server;
[0127] C2, the Linux virtual server forwards the file pre-push request to a cache server in the node;
[0128] C3, the cache server uses a consistent Hash algorithm to determine the address and disk number of the local cache server storing the pre-push file according to the file pre-push request URL;
[0129] C4. According to the file pre-push request, call the file pull program to pull the pre-push file back from the upper-level source and load it into the local cache server.
[0130] Such as Figure 9 As shown, in C4 of the embodiment of the present invention, the calling file pulling program to pull back the pre-push file from the upper-level source and load it in...
Embodiment 3
[0149] When a user accesses a file, if the file does not exist in the local cache service, it will be transferred to the local back-to-source proxy server to process the current request. If it is a small file, you can directly go back to the source. If it is a large file, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for processing the back-to-source request by using the cost-effective CDN system described in Embodiment 1, including the following steps:
[0150] E1, determine whether the size information of the file has been stored in the cache server, if yes, then go to E3, otherwise, continue;
[0151] E2, use HTTP HEAD to request back to the source, return the response header, capture the Content-Length field in the response header, and determine the file size;
[0152] E3, according to the set fragment size, construct multiple fragments for the file;
[0153] E4. Determine whether the fragment exists in the local cache server. If it exists, take it out directl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com