Boundary Node Identification Method for Distributed Wireless Sensor Networks
A wireless sensor and distributed technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, network planning, etc., can solve the problems of low recognition accuracy of boundary nodes, high algorithm complexity, poor robustness, etc., to reduce algorithm complexity and running time , low complexity, and the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
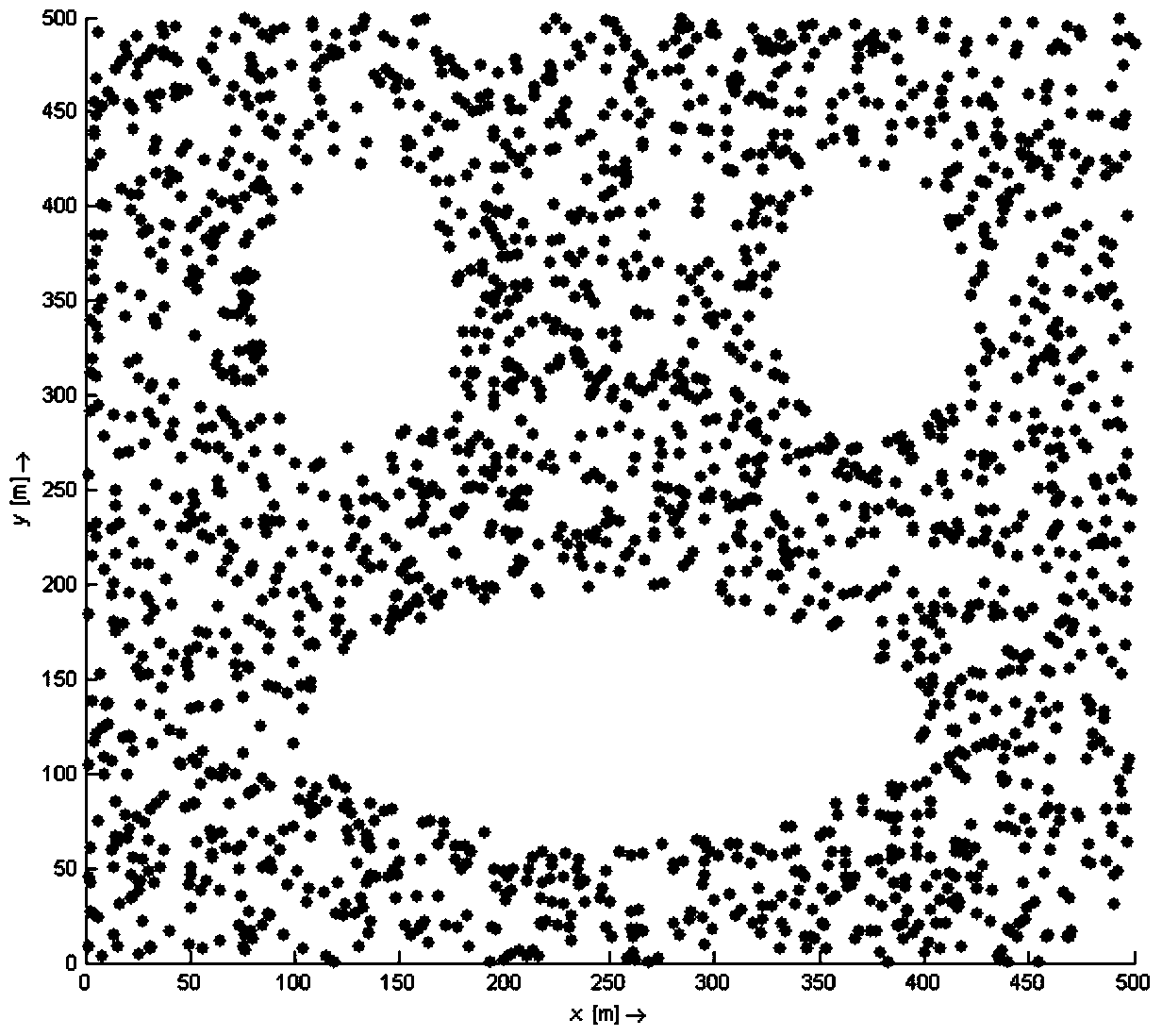
[0028] The invention provides a distributed wireless sensor network boundary node identification method, comprising the following steps:
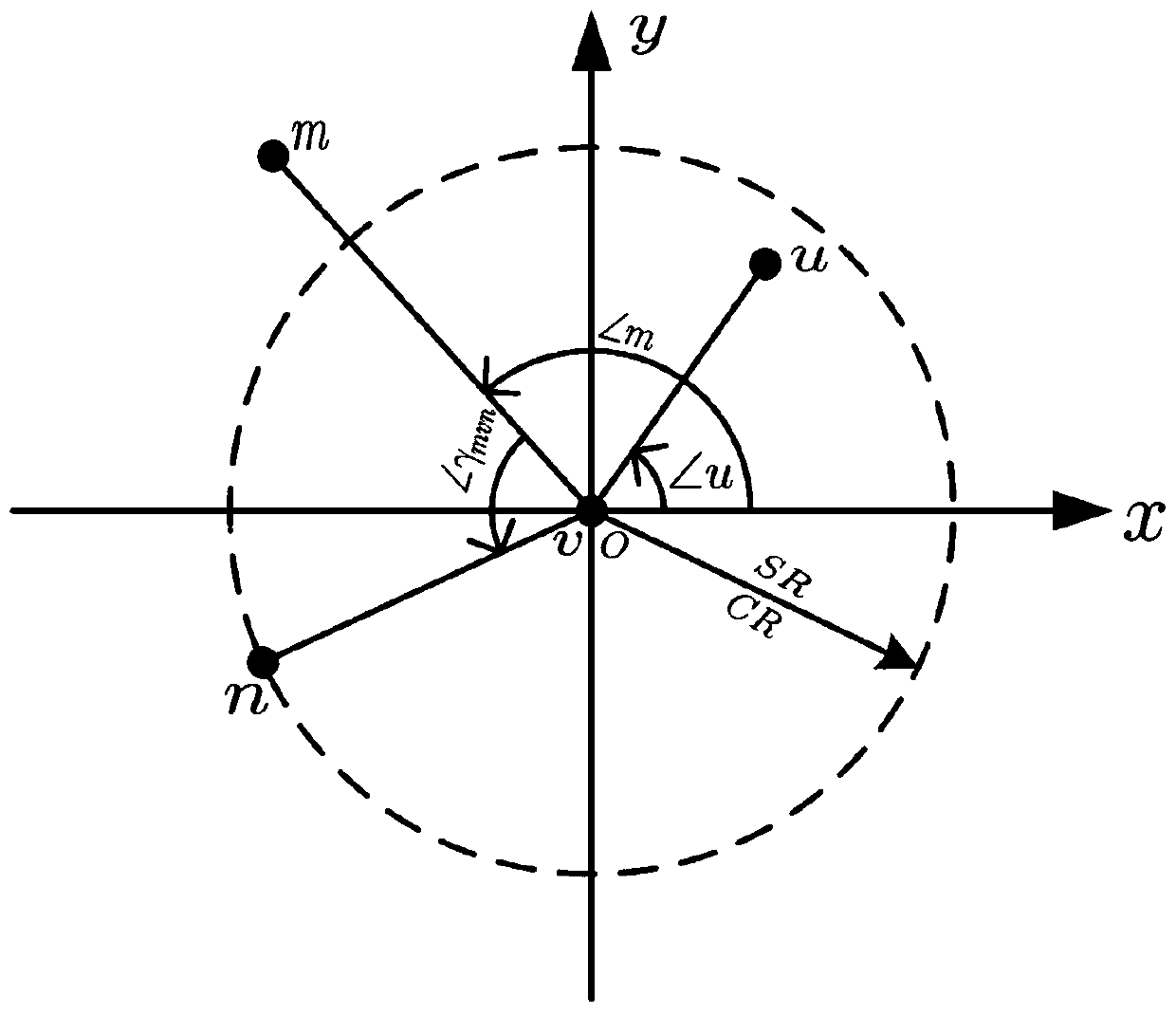
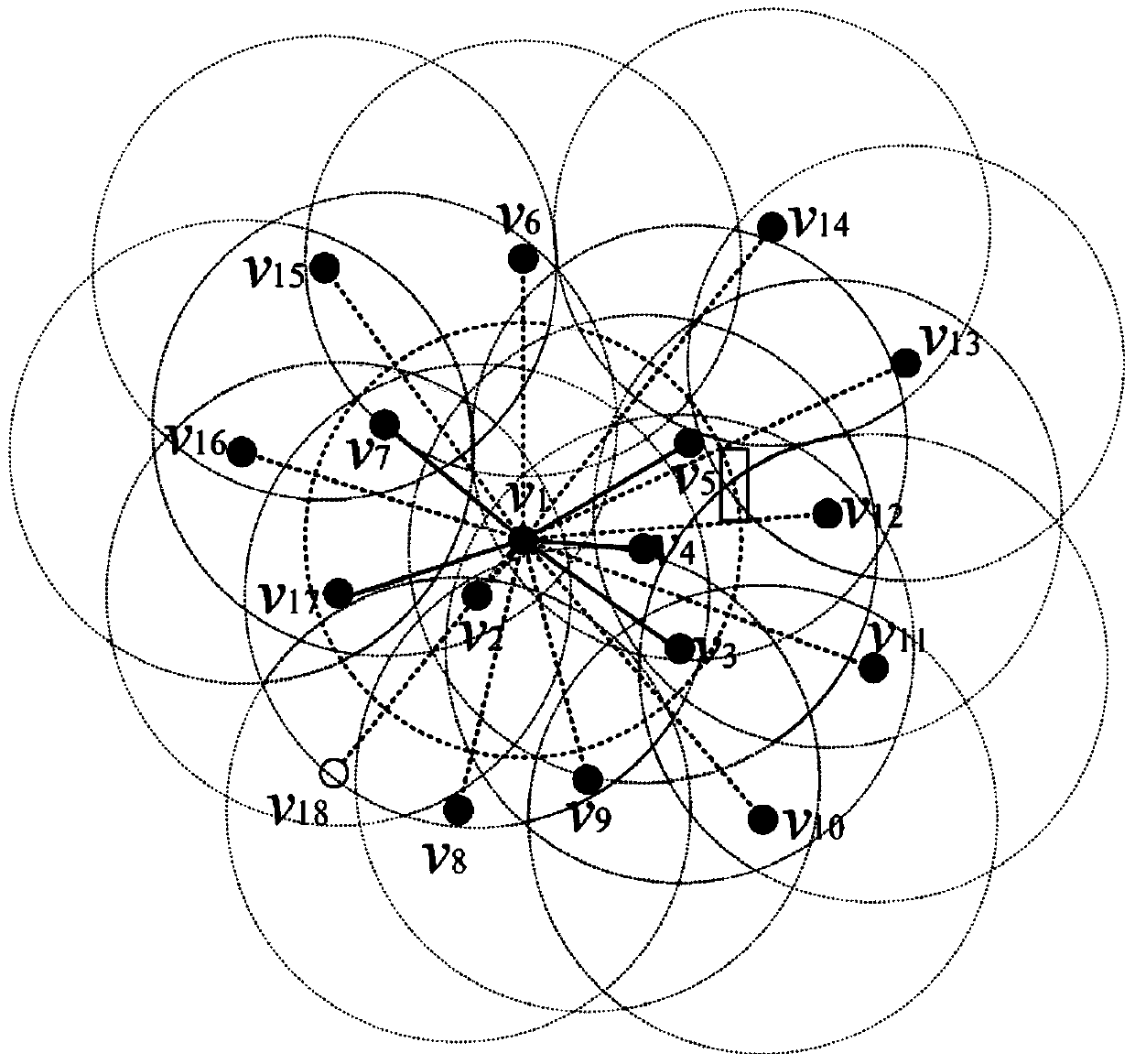
[0029] (1) Let the communication model of each node in the distributed wireless sensor network be a disc with the location of the node as the center and the communication coverage radius CR as the radius, and the node stores the information of the 1-hop neighbor nodes within its communication range Neighbor information: each node sends a request to its 1-hop neighbor node and exchanges 1-hop neighbor information to collect neighbor information of neighbor nodes within s hops, where s is 2 to 3; this embodiment collects neighbor nodes within 2 hops Neighborhood information is used as an example for illustration.
[0030] Each node calculates the neighbor information of its 2-hop neighbor nodes by the following formula:
[0031]
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com