Data transmission delay and hop count-constrained Sink node movement path distributed selection method
A technology for data transmission and moving paths, applied in advanced technology, electrical components, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as large time complexity, low data collection volume, low node coverage, and large data discarding volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
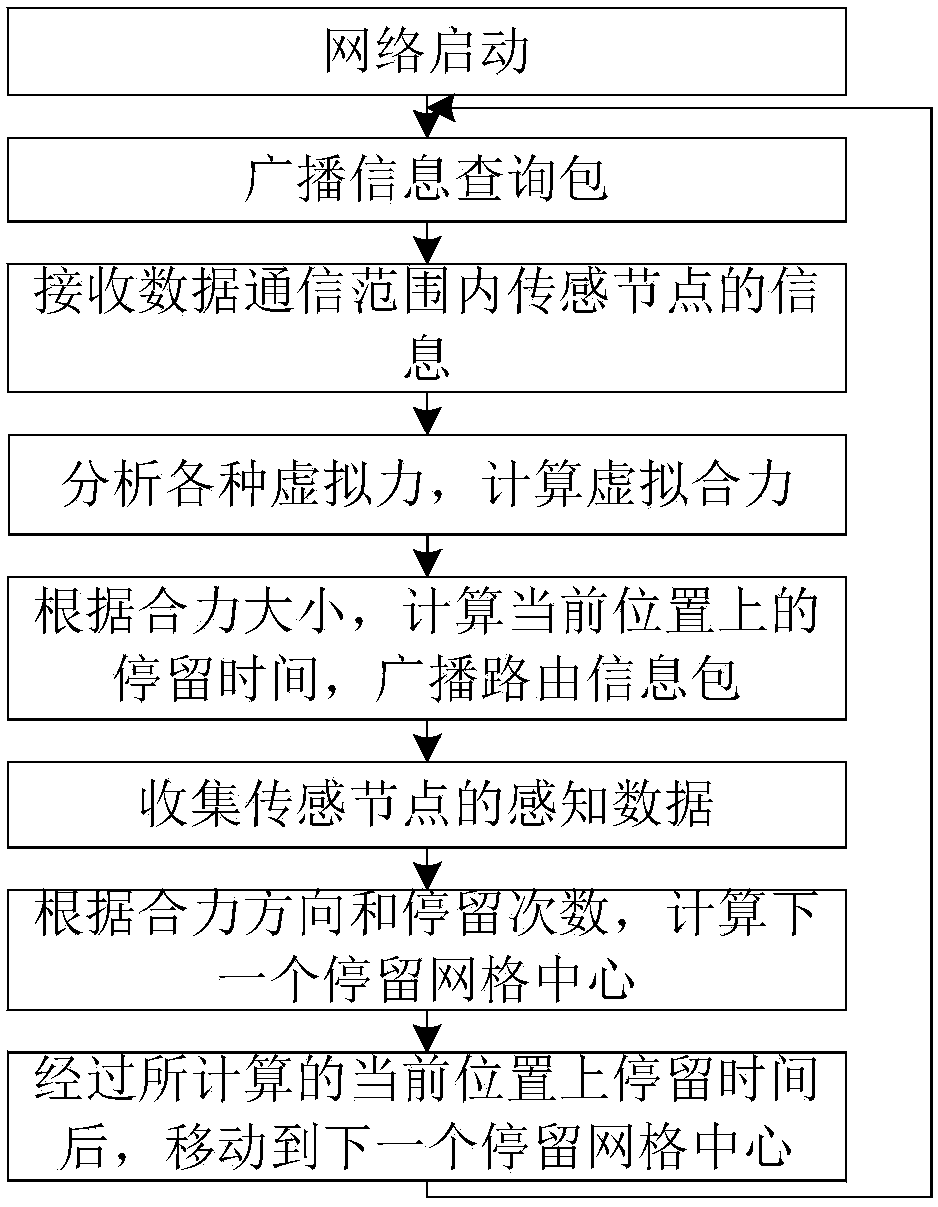
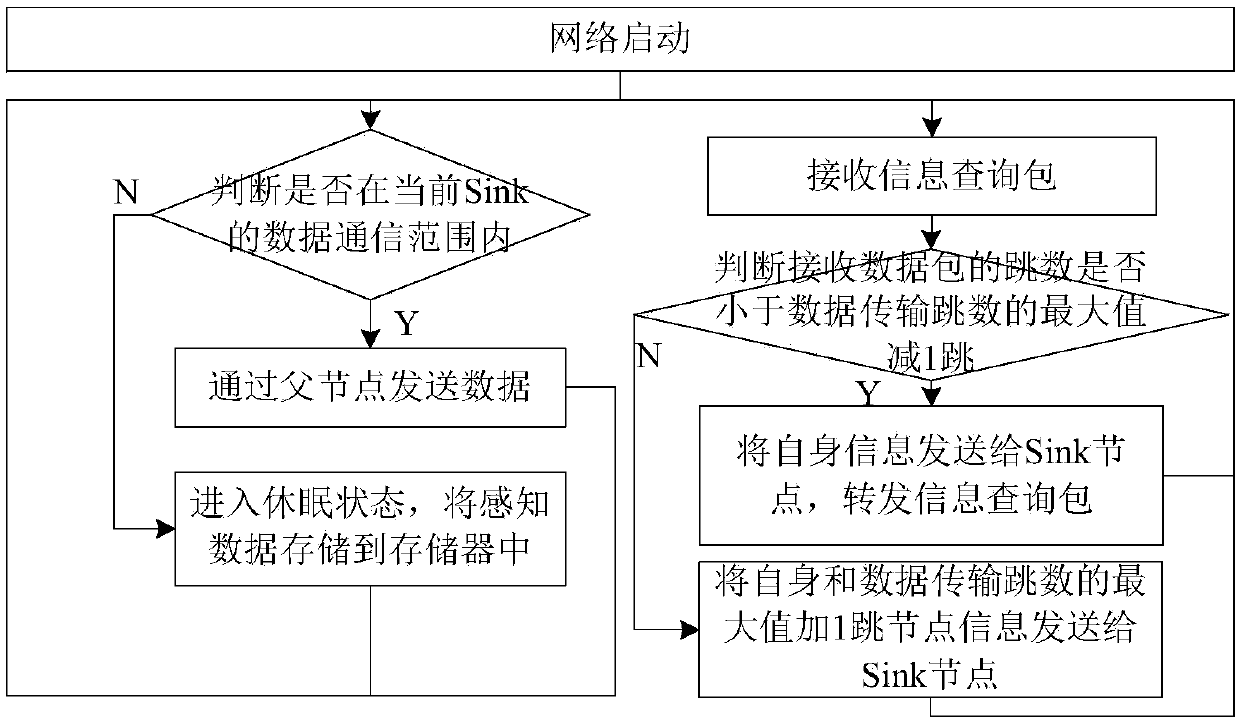
[0049] 1.2) The Sink node analyzes the boundaries, obstacles, and voids around the current location, and calculates the virtual repulsion of the boundary, the virtual repulsion of obstacles, the virtual repulsion of holes, and the virtual sensor node whose number of hops to the Sink node is the maximum number of data transmission hops plus 1. Gravity, calculates the resultant of virtual forces. The specific preferred implementation method of this step is as follows:
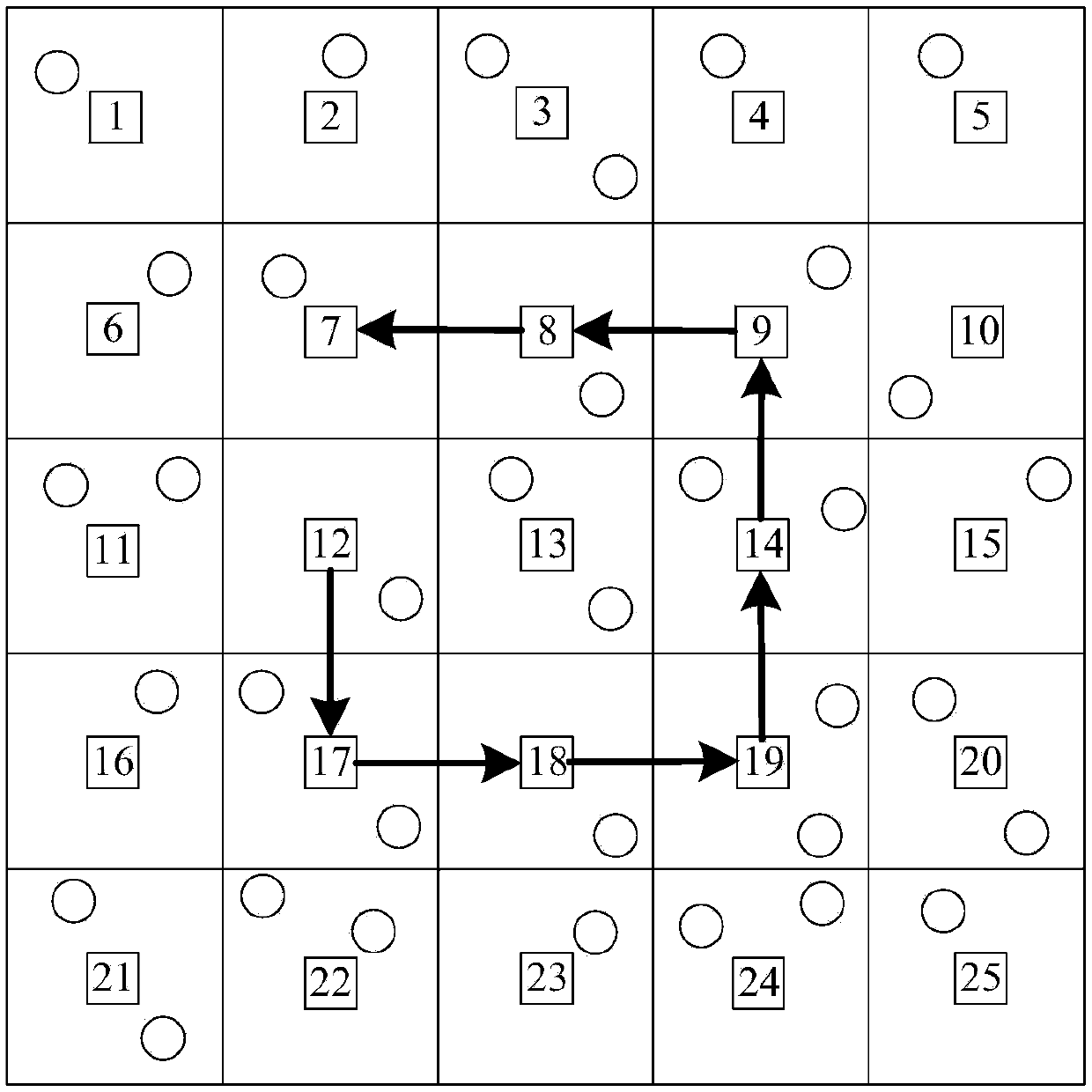
[0050] a1) The Sink node constructs a virtual grid with the current stay position as the center. If there are no sensor nodes in the grid, it is defined that the grid is not covered. refer to image 3 , divide the monitoring area of the wireless sensor network into n×n grids, and according to the principle of grid position from left to right, from top to bottom, all grids from 1 to n 2 Numbered separately. Among them, n represents the grid number of each row or each column. n can be determined according to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com