Asymmetric operation control method for DC side single-pole ground fault in mmc‑hvdc system
An MMC-HVDC, single-pole grounding fault technology, applied in power transmission AC network, emergency treatment AC circuit layout, etc., can solve the problems of high construction cost, increase the difficulty of manufacturing transformers and related equipment in the connection area, etc., and achieve low construction cost. , The effect of improving active defense capability and fast system recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
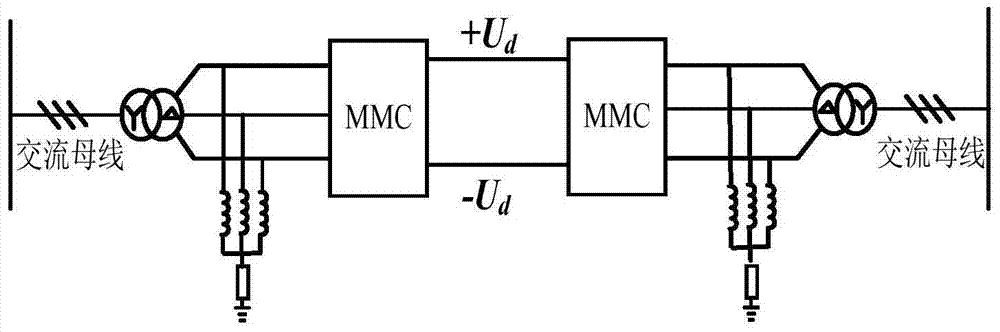
[0048] For the MMC-HVDC system with parallel reactance and resistance grounding on the AC side, after a unipolar ground fault occurs on the negative line, each bridge arm is equivalent to a controllable voltage source, then the AC side grounding electrode, sub-module capacitor and DC side fault are connected The location forms a fault circuit, such as Picture 10 Shown by the dotted line.
[0049] According to Kirchhoff's voltage law, the following relationship can be derived:
[0050]
[0051] According to Kirchhoff's current law, the following relationship can be derived:
[0052] I fault = I faultA +I faultB +I faultC
[0053] From the above formula, we can finally get:
[0054]
[0055] When the fault occurs to the steady state, the positive and negative bus voltages are:
[0056]
[0057] At this time, the three-phase outlet voltage of the AC side of the converter V a , V b , V c Expressed as:
[0058]
[0059] Where I fault Is the fault current at the fault point, I faultA , ...
Embodiment 2
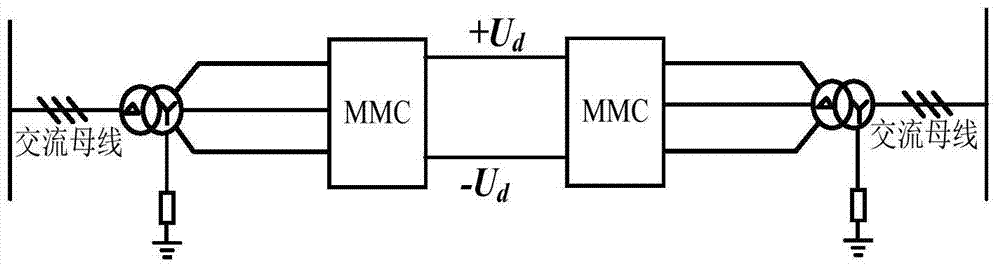
[0066] For the MMC-HVDC system where the Y winding of the AC side transformer is grounded with a resistance, after a unipolar ground fault occurs, the fault path is as Figure 14 Shown by the dotted line, and Picture 10 The grounding method of the external resistance of the parallel reactor on the AC side is similar. Also according to Kirchhoff's voltage and current law, it can be deduced that after a negative bus unipolar ground fault occurs, the positive and negative DC bus voltages at steady state are:
[0067]
[0068] Similarly, at this time, the three-phase outlet voltage V of the AC side of the converter a , V b , V c Expressed as:
[0069]
[0070] The relationship satisfied between the DC side positive and negative bus voltage and the AC side outlet voltage in the steady state is the same as that of the AC side shunt reactor in the first embodiment after the unipolar grounding fault occurs.
[0071] Suppose that at 1.0S, it is detected that a ground fault occurs on the nega...
Embodiment 3
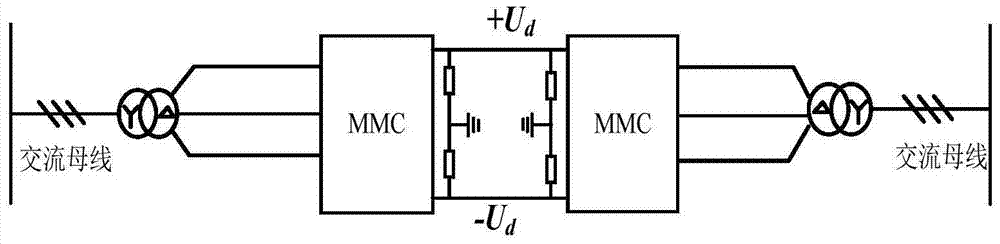
[0077] For the MMC-HVDC system with parallel clamping and large resistance grounding on the DC side, when a single-pole ground fault occurs, the equivalent circuit is simplified such as Figure 17 As shown, the grounding point changes from position ① to position ②. Because the resistance of the parallel resistor on the DC side is extremely large, which is almost open, each module capacitor does not have a discharge path with the fault grounding point, the capacitor voltage remains stable, and the capacitor current component remains the same as before the fault. Also due to the change of the grounding point, change The voltage on the AC side of the converter is equivalent to the voltage of the lower bridge arm, and a DC bias of half the rated DC voltage appears. The non-faulty pole DC line bears the entire DC voltage at this time, which is twice as high as before the fault. It can be seen that a unipolar ground fault on the DC side poses a serious insulation threat to the AC side...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com