Adaptive coding modulation and resource scheduling method based on sparse code multiple access system
A technology of sparse code multiple access and adaptive coding, which is applied in the fields of adaptive coding and modulation schemes and resource scheduling, and can solve problems such as the inability to achieve optimal allocation of system resources in the case of multiple users, the inability to select coding and modulation schemes in SCMA systems, and difficult system throughput. and transmission link quality trade-offs and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0038] Specific implementation mode 1: The adaptive coding and modulation scheme and resource scheduling method based on the sparse code multiple access system in this implementation mode are specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0039]Step 1. Establish a system model; establish a cellular network multi-cell system, select a cell in the cellular network multi-cell system, and use the sparse code multiple access SCMA method to access the users participating in the scheduling of the cell to the cellular network multi-cell system middle;
[0040] Among them, each cell in the multi-cell system is a regular hexagon with a radius of 500m; and each cell is adjacent to six cells, and the users participating in the scheduling are only randomly distributed in each cell; the users participating in the scheduling The simulated services are all real-time video streaming services; the guaranteed data transmission rate (GBR) required by real-time video streaming services ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
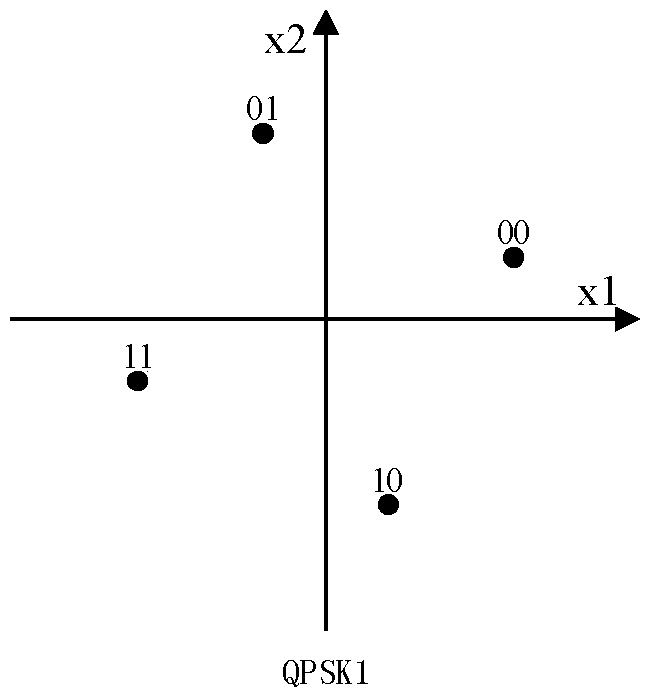
[0063] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of obtaining a pair of 16-point SCMA codebook according to the constellation diagram calculation in step 2 is:
[0064] Here we take the most complex 16-point SCMA codebook construction method as an example to introduce;
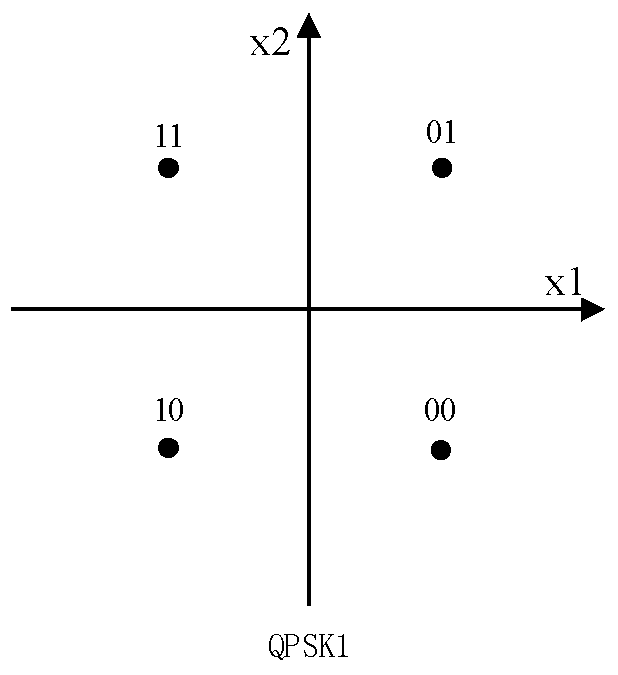
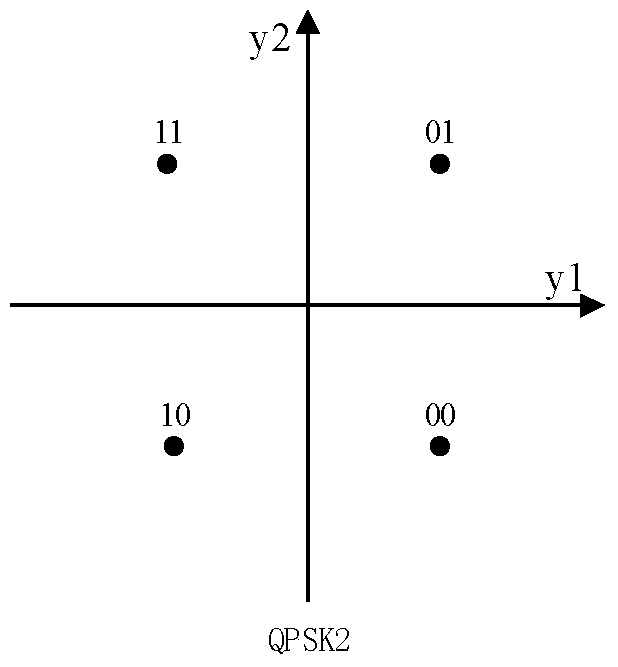
[0065] Step 21, draw two identical standard QPSK constellation diagrams, which are respectively QPSK1 as shown in Figure 1 (a) and QPSK2 as shown in Figure 1 (b); wherein, there are 4 constellation points in the QPSK constellation diagram, and 4 constellation points All on a circle, the angle between two adjacent constellation points and the origin of the four constellation points is 90°, the distance between the constellation point and the origin represents the amplitude of the modulated signal, and the connection between the constellation point and the origin The angle between the positive semi-axis and the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0079] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 3, according to the instantaneous downlink SINR value, the user reports the corresponding CQI value to the base station at each TTI, and the base station reports the CQI information in time according to the reported CQI information. Adjust and update the user's channel condition information specifically as follows:
[0080] When the channel condition is good, that is, SINR>10.3, high-order modulation and high channel rate are used, that is, according to a pair of 16-point SCMA codebook modulation to achieve high transmission rate and high throughput; When the difference SINR<4.606, the low-order modulation is used to modulate according to a pair of 4-point SCMA codebook to ensure the quality of the transmission link. When 4.606
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com