Deadlock detection method suitable for generalized models
A deadlock detection and model technology, applied in the field of distributed systems, can solve problems such as deadlocks, achieve the effect of reducing computing pressure and solving common local deadlocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
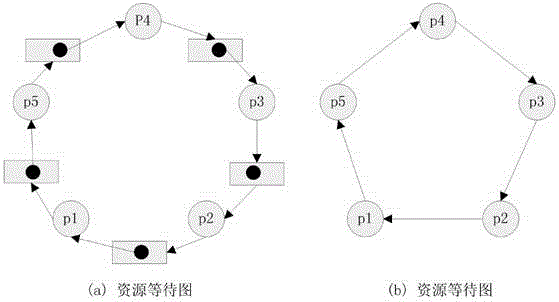
[0021] WFGWait-forGragh wait graph
[0022] RMResourceManager resource management node
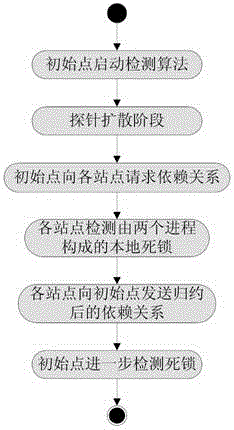
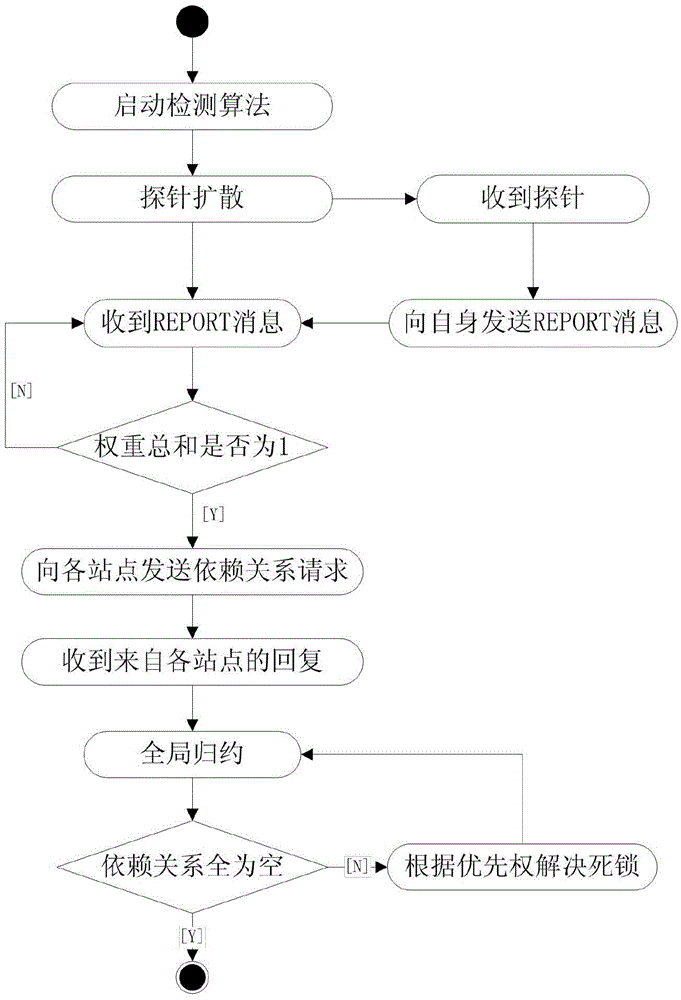
[0023] A deadlock detection method suitable for generalized models, including the following steps: (A) ordinary nodes save output edge information; (B) ordinary nodes detect and resolve local deadlocks and send reduction information to initial nodes; (C) initial Point-reduce detects global deadlocks.
[0024] The dependencies of the processes involved in an algorithm execution are saved on the common nodes.
[0025] In the step (B), the resource management node RM r When receiving a resource request, first put the process that sent the request into request_Q r Queue; if the resource management node assigns this resource to this process and sends a grant(r) message to the process, the process becomes a holder; if RM r After receiving the resource releas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com