Ring knock-off protection structure for conical ring variable speed unit
A technology of continuously variable transmission and protective structure, which is applied to transmission parts, friction transmission devices, belts/chains/gears, etc., which can solve problems such as parts damage, and achieve the effect of avoiding shaft shoulder impact and component damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
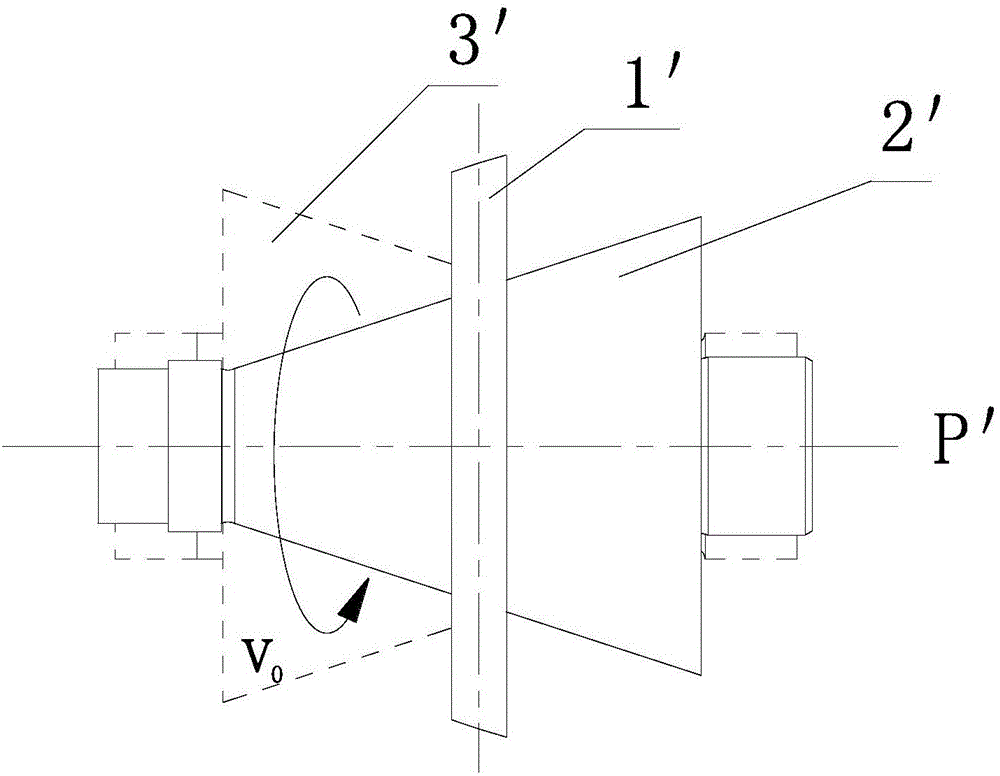
[0042] Refer to attached Figure 5a , 5c , 7, 8a, 8b, 8c, 11:
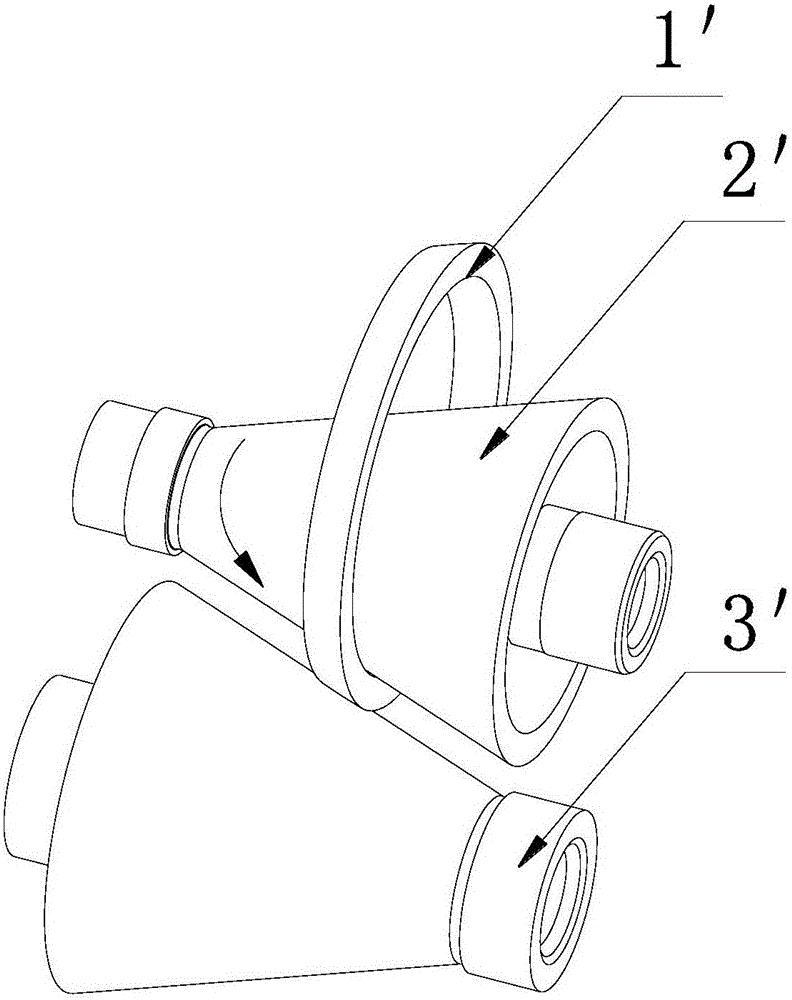
[0043] A ring crash protection structure for a cone-ring continuously variable transmission, including a first transmission cone 2 and a transmission ring 1, the surface of the first transmission cone 2 is in contact with one surface of the transmission ring 1, and the first transmission cone 2 The small end of the small end is provided with a shaft shoulder 21 opposite to the cone surface 22, and the shaft shoulder 21 has the shape of a revolving body; the transmission ring 1, the shaft shoulder 21, and the cone surface 22 have the following geometric fit: when the transmission ring 1 When contacting the shaft shoulder 21, there is a first contact point 211 between the transmission ring 1 and the shaft shoulder 21, and there is a second contact point 221 between the transmission ring 1 and the cone surface, the distance from the first contact point 211 to the cone axis P is the first contact radius r 1 , the d...
Embodiment 2
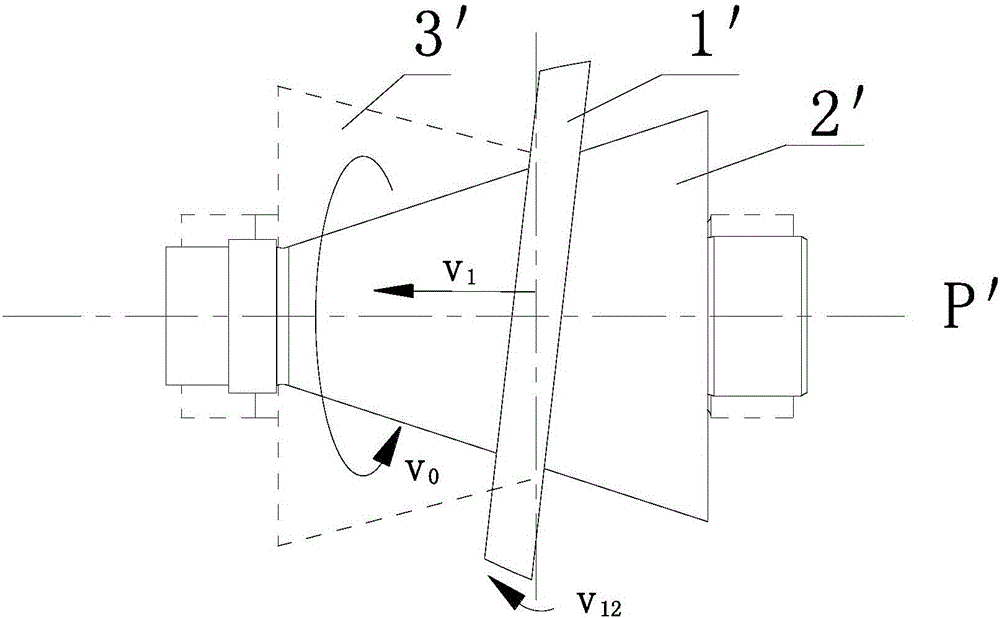
[0053] Refer to attached Figure 6a , 6c , 9, 10a, 10b, 10c, 12:
[0054] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the third transmission part is the second transmission cone 20, the second transmission cone 20 is the input cone, the transmission ring 1 is set on the second transmission cone 20, the second transmission cone 20 is A drive cone 30 is the output cone; the cone generatrix of the first drive cone 30 is parallel to the cone generatrix of the second drive cone 20 . The taper of the first transmission cone 30 and the second transmission cone 20 can be different, as Figure 6a Shown; when the taper of the two is the same, such as Figure 6c As shown, the cone axes P of the first transmission cone 30 and the second transmission cone 20 are parallel to each other, and the large end and the small end are oppositely arranged.
[0055] In an axial section through said cone axis P, a tangent 3111 of the generatrix 312 of said shoulder 31 at the first c...
Embodiment 3
[0063] refer to Figure 5b , 7 , 8a, 8b, 8c, 11, the difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is: the third transmission part is a cylinder, and the rest are the same.
[0064] In addition, the third transmission component may also be other rotary bodies except cylinders and cones.
[0065] Its work process is similar to the work process of embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com