Bionic vision transformation-based image RSTN (rotation, scaling, translation and noise) invariant attributive feature extraction and recognition method
An attribute feature and bionic technology, which is applied in the cross field of bioinformatics and machine vision technology, can solve the problems of noise sensitivity and insufficient robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
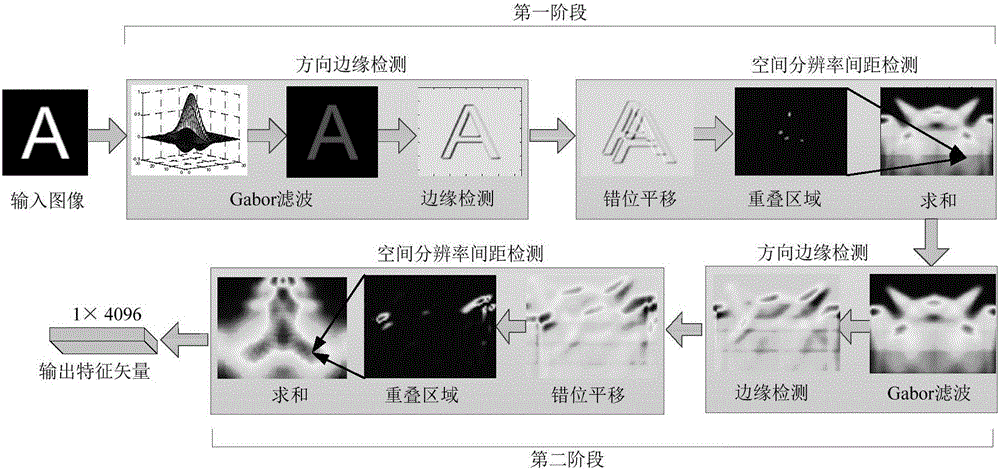
[0092] This embodiment is aimed at images with 26 letters and 10 numbers, such as figure 1 As shown, the invariant attribute feature extraction process is carried out in the following five steps:
[0093] Step 1: Perform grayscale processing on the original image, and normalize its grayscale value to [0,1]. And use the bilinear interpolation method to reset the image size to 128×128.
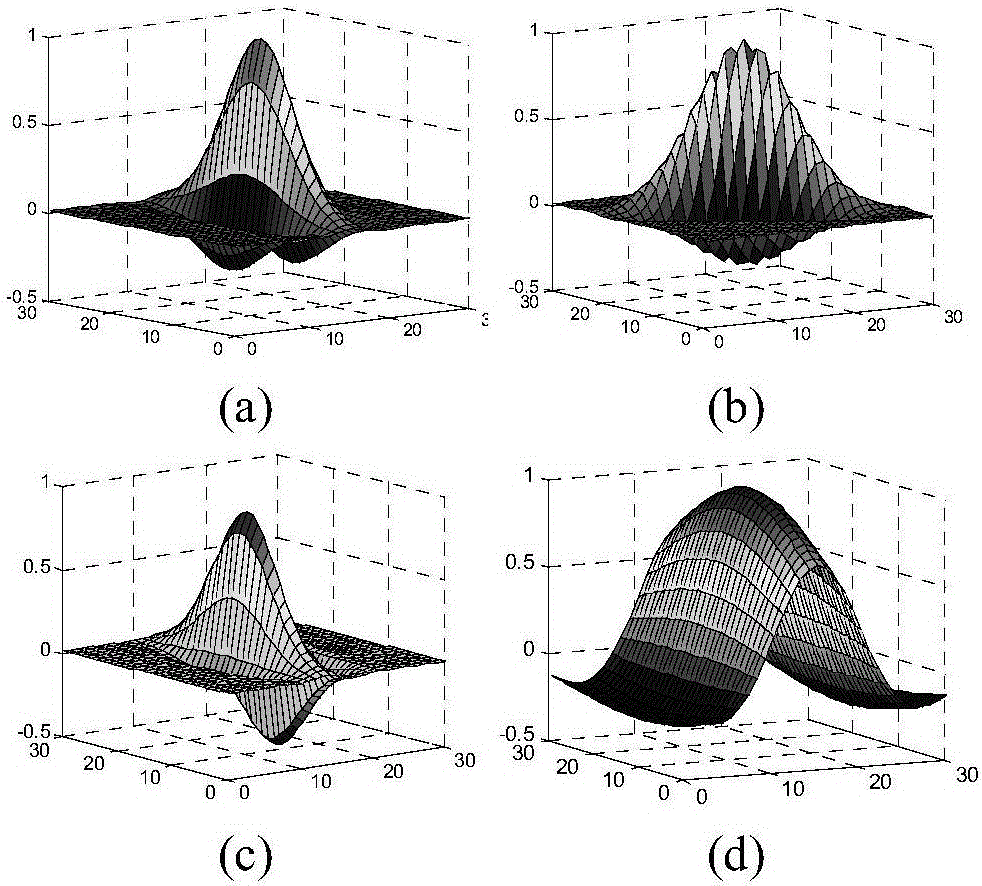
[0094] Step 2: Obtain the two-dimensional image M(x,y) after step 1 preprocessing, use Gabor filter to obtain the intermediate response G(x,y), and then use the horizontal-vertical bipolar filter F and G(x,y) Do the convolution. That is, the filter-filter filter based on Gabor and the bipolar filter F detects the direction edge of the target image and obtains the edge image E.
[0095] Step 3: For the edge image E, measure the spatial resolution of image lines with different edge directions θ and different distances I. First, carry out the dislocation processing with the distance I and the ...
Embodiment 2
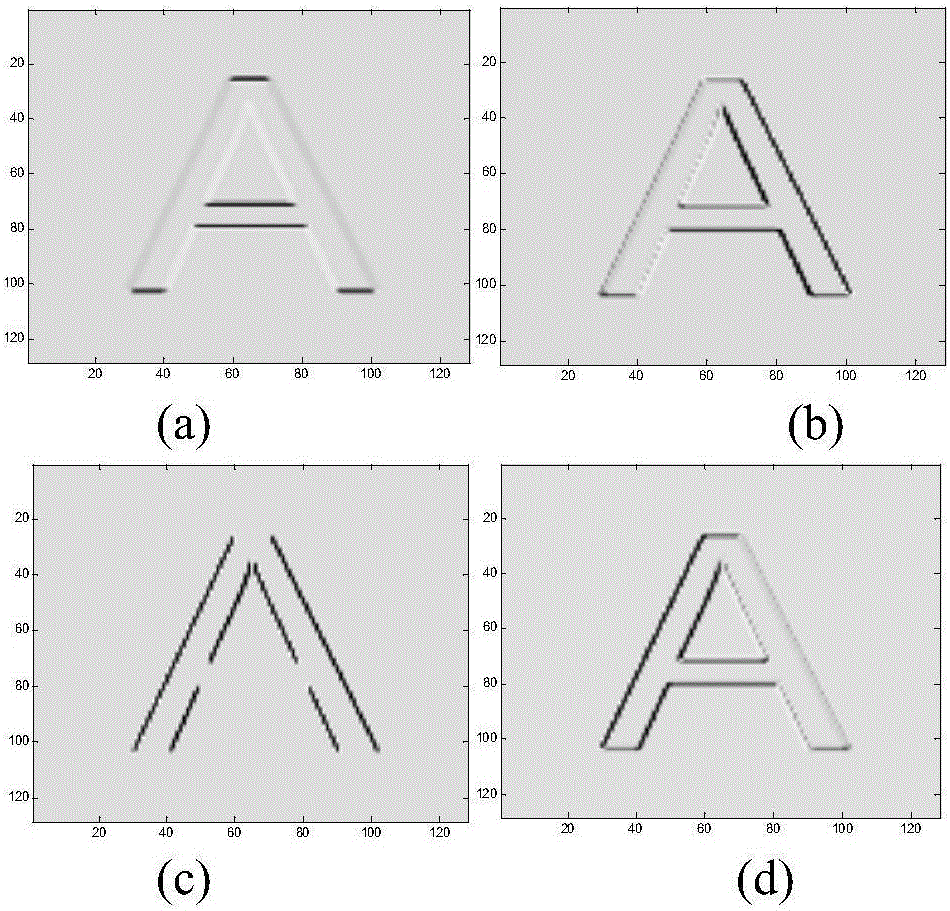
[0165] In order to verify the RSTN invariance of extracted image features, the original images of G and F letters are rotated, scaled, translated and noised to different degrees. For the visual comparison of the results, the output results of the first stage and the second stage are visualized in the form of images. Such as Figure 7 and Figure 8 (a) is the original image, where Figure 7 and Figure 8 (b) is the output result of (a) first-stage transformation, Figure 7 and Figure 8 (c) is the output feature map of the second stage of (a). Then, will Figure 7 and Figure 8 (a) is rotated 135° counterclockwise, such as Figure 7 and Figure 8 As shown in (d), the output of the first stage is obtained Figure 7 and Figure 8 (e). compare Figure 7 and Figure 8 In terms of (b), it is equivalent to a horizontal translation of 45° to the right. However, the second stage features Figure 7 and Figure 8 (f) of Figure 7 and Figure 8 As far as (c) is concerne...
Embodiment 3
[0171] In the process of traffic sign recognition in natural scenes, the image is easily disturbed by factors such as illumination, distance, and camera angle. Usually, the distance between the camera and the traffic sign cannot be obtained accurately, and the size of the traffic sign in the image is also difficult to uniformly determine. For this reason, the robustness of traffic sign feature extraction is insufficient, which constrains the performance of traffic sign recognition. Therefore, applying this method to the feature extraction of traffic sign recognition and extracting the invariant attribute features in the process of traffic sign recognition is of great significance for improving its recognition rate and robustness.
[0172] Figure 9 The first column shows 5 traffic signs with different sizes and rotation angles, which respectively indicate no left, straight or left. The rings and arrows in these two types of signs are in prominent positions. And it has conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com