Method for identifying 3D model based on sparse coding
A sparse self-encoding and three-dimensional model technology, applied in the field of three-dimensional model recognition, can solve the problem of large redundancy between data and achieve the effect of improving the recognition effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example
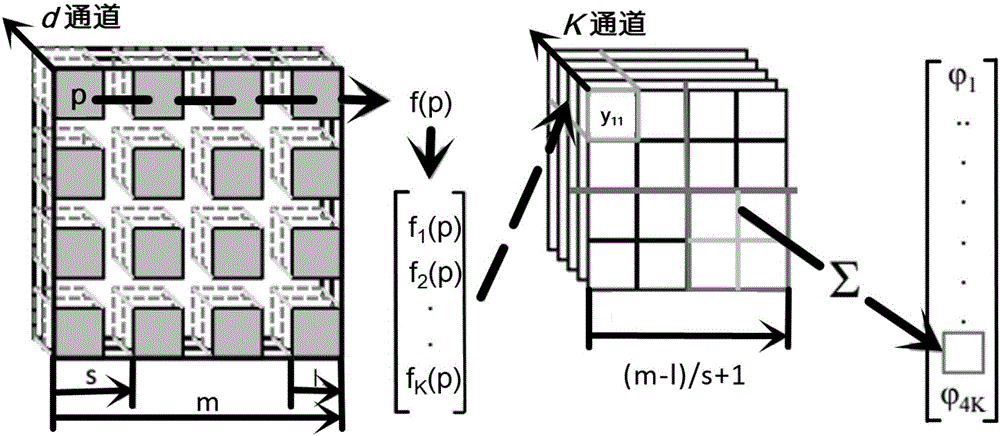
[0067] 1. Database
[0068] The database used in this experiment is the NTU (Nanyang Technological University) database published by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, which is well known in the art. The NTU database includes 549 different virtual 3D models in 47 categories, such as apples, water bottles, sailboats, seats, etc. We placed the virtual 3D model at the center of the sphere, and placed the virtual camera at each vertex of the C60 structure to capture 60 2D views.
[0069] 2. Parameter setting
[0070] In the embodiment of the present invention, specific parameter values are: l=8, d=3, s=1, m=240, K=128.
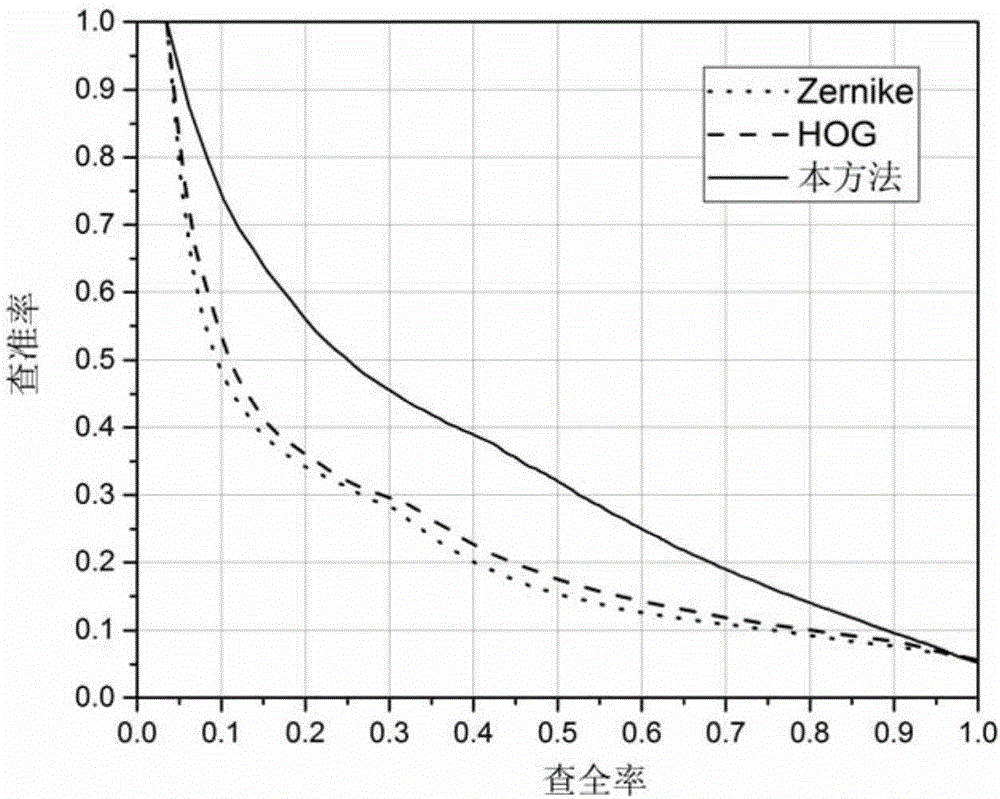
[0071] 3. Evaluation criteria
[0072] Precision-recall curve (PR, Precision-recall curve): It mainly describes the dynamic relationship between the recall rate and the precision rate based on the similarity list. A good PR curve should be as close to the upper right side of the coordinate axis as possible. The definitions of recall and precision ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com