Near-infrared brain imager map collecting method based on cognitive tasks
A collection method and brain imaging technology, applied in the field of map collection, can solve problems such as the application of analysis results, difficult identification of maps, and inability to achieve quantitative statistics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The technical solution proposed by the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
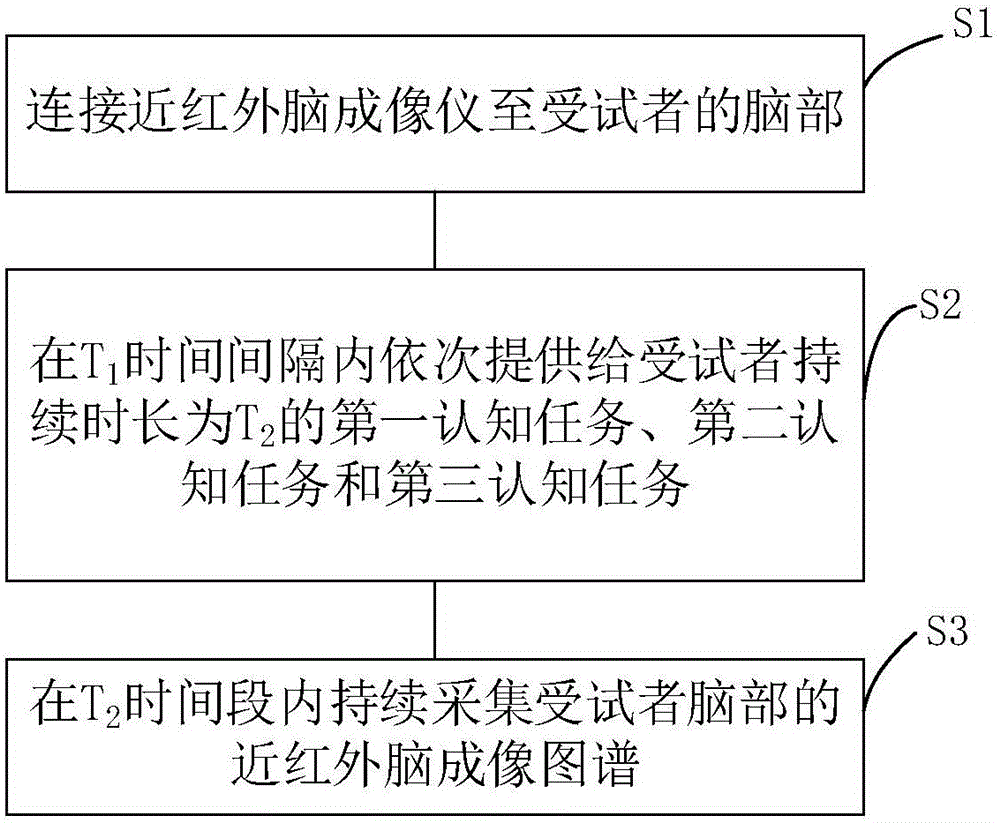
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, a near-infrared brain imaging atlas acquisition method based on cognitive tasks provided by the present invention includes:
[0021] The first step S1, connect the near-infrared brain imager to the subject's brain;
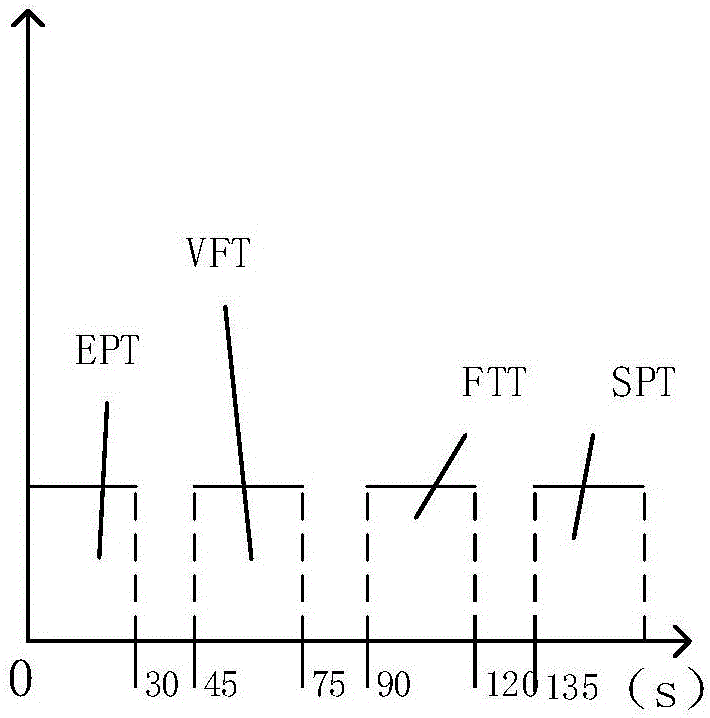
[0022] The second step S2, at T 1 Sequentially provided to subjects within the time interval for a duration of T 2 The first cognitive task, the second cognitive task, and the third cognitive task of, specifically, in the present invention, the first cognitive task, the second cognitive task, and the third cognitive task are selected from language One of the fluency task, the pointing motor task, and the symptom picture task. And, preferably, in the second step, before performing the first cognitive task, a fourth cognitive task is further included, and the fourth cognitive task is an e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com