Theta-join method for massive distributed data
A technology of distributed data and connection methods, applied in the field of value connection, can solve problems such as low efficiency, and achieve the effect of improving query efficiency, reducing workload, and speeding up query efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The specific steps of the non-equivalent connection method for massive distributed data in the present invention are as follows:
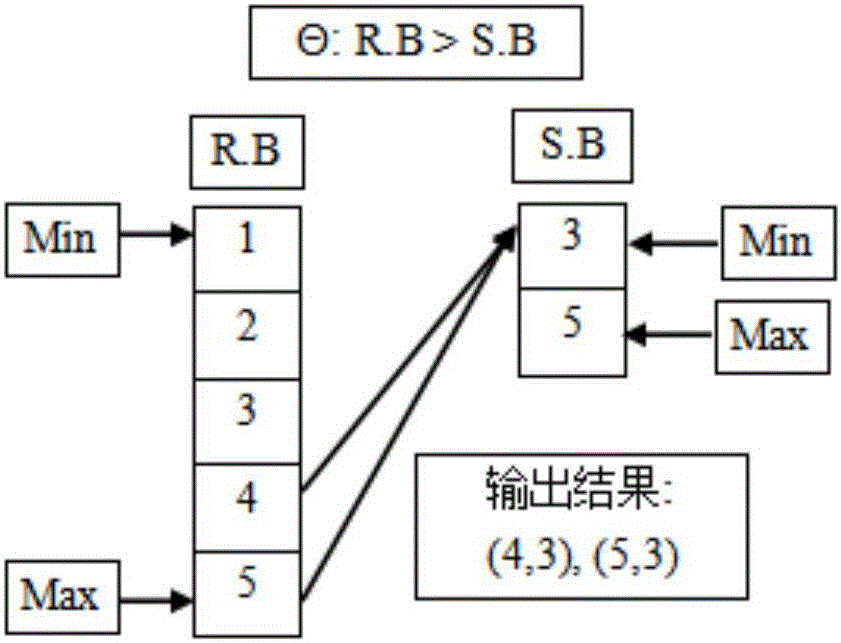
[0041] A. Theta-Join query definition:
[0042] Suppose there are two relational tables R(A,B) and S(B,C), the function θ belongs to {>,R.BθS.B S(B,C), then QB is called a non-equivalent join query between relational tables R and S connected by field B.
[0043] Explanation of symbols: R(A,B) represents relational table R, A, B are attributes of R, S(B,C) represents relational table S, and B, C are attributes of S. θ is the connection function of R and S. QB represents a query involving R and S, and "∞" represents a connection symbol. Since in a distributed environment, the calculation format of data is in the form of key-value, therefore, field B can be regarded as the key of R and S, and field A can be regarded as the combination of all fields in relational table R except B ( value), field C can be regarded as the combination (value) o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com