Extremely toxic mushroom rapid detection method
A detection method and mushroom technology, which are applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by chemical reaction of materials, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome detection process, poor ease of use, dependence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
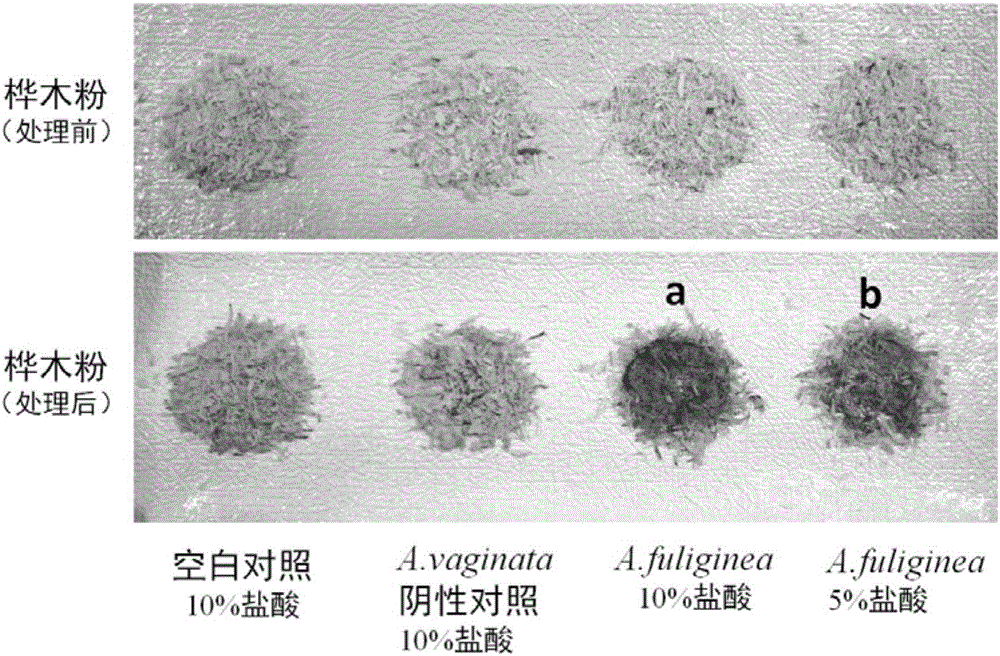
[0034] The present invention describes a color reaction-based rapid detection method for highly toxic mushrooms, aiming at the main deadly mushroom toxin - amanitin. The method of the invention is simple and quick to operate, and uses wood (birch, pine, etc.) or newsprint to identify the highly poisonous mushrooms containing amanitin through color reaction under the action of medium and low concentration hydrochloric acid. The following examples use birch wood and low-concentration hydrochloric acid (5% and 10%) as materials to describe this identification process in detail, and describe each step completely and accurately. The whole experimental process is roughly divided into two steps of material preparation and color development, the first step takes 5-8 minutes, the second step (color development) takes 2-5 minutes when heated, and 15-25 minutes at room temperature . The specific experimental conditions used in this example are heating at 55° C. for 5 minutes, material p...
Embodiment 2
[0056] 1. Materials and methods
[0057] This embodiment is completely consistent with embodiment 1 in materials and methods, and the only difference is that the selected highly poisonous mushroom objects are different, as follows:
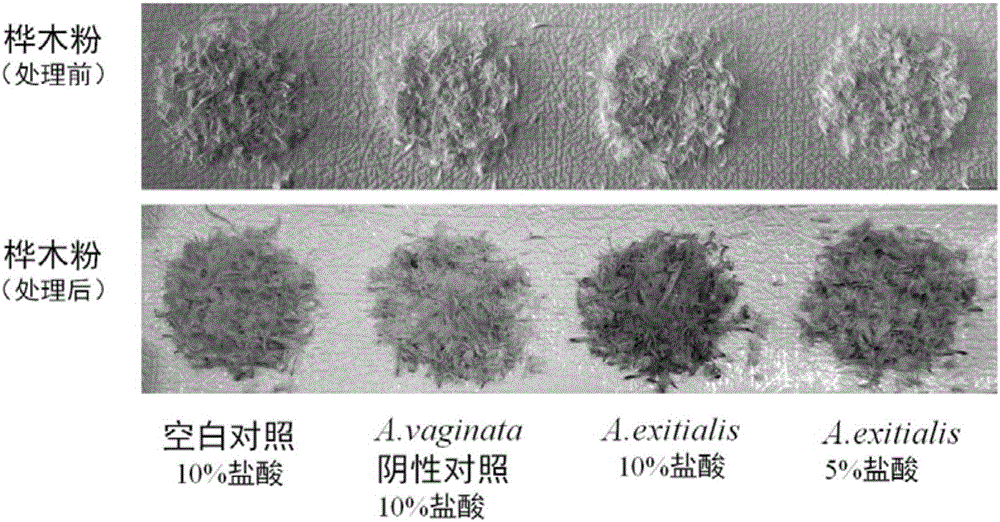
[0058] Select fresh Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota or other mushrooms containing Amanitin that are stored at -80°C. In this example, Amanita is specifically used. A representative highly poisonous species in Amanita, deadly Amanita (A.exitialis), has a large number of poisoning death cases reported in southern China, especially in Guangdong.
[0059] 2. Results and analysis
[0060] 2.1 Color reaction between highly poisonous amanita and birch powder
[0061] experiment result shows( figure 2 ), Amanita (Amanita) or genus Galerina (Galerina) or Lepiota (Lepiota) or other mushrooms containing Amanitin (Amanitin), specifically to the present embodiment is deadly Amanita (A.exitialis ), under the joint action of low-concentration hydrochloric acid a...
Embodiment 3
[0063] 1. Materials and methods
[0064] This embodiment is completely consistent with embodiment 1 in materials and methods, and the only difference is that the selected highly poisonous mushroom objects are different, as follows:
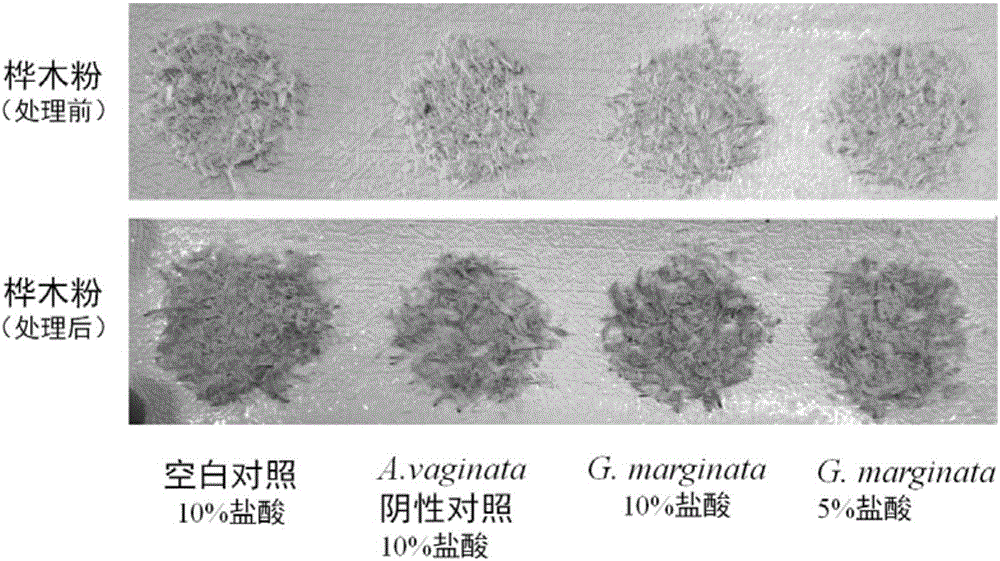
[0065] Select fresh Amanita (Amanita) or Galerina (Galerina) or Lepiota (Lepiota) or other mushrooms containing Amanitin (Amanitin) preserved at -80 ℃. A representative highly poisonous species, G. marginata, has been reported to be poisoned in the world and in China, but due to its small size and low toxin content, there are very few fatal cases. The highly poisonous mushroom selected in this example is based on the following considerations: the toxin content of the mushroom sample collected by the research group is low, about 1 / 5 of that of Amanita amanita, and the toxin content is the lowest among the mushrooms collected by the research group. This mushroom was used to test the sensitivity of the method of the present invention. If the detect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com